Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechanics Review (NOV. 2018) : Engr. Karren May Simplina
Fluid Mechanics Review (NOV. 2018) : Engr. Karren May Simplina
Uploaded by
Leovhea AbuenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Mechanics Review (NOV. 2018) : Engr. Karren May Simplina
Fluid Mechanics Review (NOV. 2018) : Engr. Karren May Simplina
Uploaded by
Leovhea AbuenaCopyright:
Available Formats
FLUID MECHANICS
Review (NOV. 2018)
FLUID MECHANICS
INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following
Situation 4: A wooden storage vat full of oil (sg= 0.80) is in the
questions. Mark only one answer for each item by shading the box
shape of a frustum of a cone 2 m diameter at the top,
corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet provided.
4 m diameter at the bottom, and 3 m high. The vat is
STRICTLY NO ERASURES ALLOWED. Use pencil no. 1 only.
provided with two steel hoops, one at the top and
one at the bottom.
MULTIPLE CHOICE
13. Which of the following most nearly gives the hydrostatic force on
the side of the vat?
SET 1
a. 108.24 kN c. 70.63 kN
b. 117.72 kN d. 94.18 kN
Situation 1: An amount of carbon tetrachloride having a mass of
500 kg and a volume of 0.315 m 3 is placed in a
14. Which of the following most nearly gives the distance of the
container.
hydrostatic force from the bottom of the vat?
a. 0.90 m c. 1.00 m
1. Which of the following most nearly gives the weight of carbon
b. 0.80 m d. 0.75 m
tetrachloride?
a. 4.90 kN c. 5.16 kN
15. Which of the following most nearly gives the force in the bottom
b. 5.36 kN d. 3.86 kN
hoop?
a. 41.20 kN c. 35.16 kN
2. Which of the following most nearly gives the mass density of
c. 17.66 kN d. 44.58 kN
carbon tetrachloride?
a. 1785.30 kg/m3 c. 1758.30 kg/m3
Situation 5: A stone weighs 468 N in air. When submerged in
b. 1578.30 kg/m3 d. 1587.30 kg/m3
water it weighs 298 N.
3. Which of the following most nearly gives the unit weight of
16. Which of the following most nearly gives the volume of the
carbon tetrachloride?
stone?
a. 12.25 kN/m3 c. 17.02 kN/m3
a. 0.0015 m3 c. 0.0254 m3
b. 16.38 kN/m3 d. 15.57 kN/m3
b. 0.0173 m3 d. 0.0357 m3
4. Assuming specific weight of air to be constant at 12 N/m3, what
17. Which of the following most nearly gives the unit weight of the
is the approximate height of Mt. Banahaw if a mercury barometer
stone?
at the base of the mountain reads 654 mm and at the same time
a. 24.03 kN/m3 c. 25.00 kN/m3
another mercury barometer at the top of the mountain reads 480
b. 26.00 kN/m3 d. 27.05 kN/m3
mm?
a. 1835.62 m c. 1748.03 m
18. Which of the following most nearly gives the specific gravity of
b. 1602.19 m d. 1934.53 m
the stone?
a. 2.90 c. 2.25
5. A tank contains oil with specific gravity of 0.80, gasoline with
b. 2.45 d. 2.76
specific gravity of 0.90, and sea water with specific gravity of
1.05. What is the pressure at a depth of 1.20 m if the depths of
Situation 6: A cylindrical tank 1 m in diameter and 3 m tall weighs
the liquids are 0.50 m, 0.60 m, and 0.80 m, respectively?
3.86 kN.
a. 1812 kg/m2 c. 942 kg/m2
b. 1045 kg/m2 d. 1318 kg/m2
19. Which of the following most nearly gives the weight of the lead
(specific wt.= 110 kN/m3) that must be placed inside the tank to
6. A pressure gage at elevation 10 m at the side of a tank
make the tank float vertically with 2.50 m submerged in water?
containing a liquid reads 80 kPa. Another gage at elevation 4 m
a. 16.91 kN c. 19.25 kN
reads 120 kPa. Find the specific gravity of the liquid.
b. 21.14 kN d. 15.40 kN
a. 0.62 b. 0.65
b. 0.73 d. 0.68
20. Which of the following most nearly gives the weight of the lead
(specific wt.= 110 kN/m3) that must be fastened to the outside
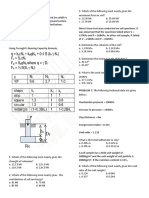
Situation 2: The tank is shown below.
bottom of the tank to make the tank float vertically with 2.50 m
submerged in water?
a. 21.14 kN c. 15.40 kN
b. 19.25 kN d. 16.91 kN
21. Which of the following most nearly gives the weight of the lead
3
(specific wt.= 110 kN/m ) that must be placed inside the tank to
make the top of the tank flushed with the water surface?
a. 19.25 kN c. 16.91 kN
b. 15.40 kN d. 21.14 kN
22. A wooden block is placed horizontally in the sea with oil spill as
7. Which of the following most nearly gives the hydrostatic force shown. What is the depth o f the block submerged?
acting in liquid 1?
a. 274.68 kN c. 247.86 kN
b. 472.68 kN d. 427.86 kN
8. Which of the following most nearly gives the hydrostatic force
acting in liquid 2?
a. 705.456 kN c. 750.465 kN
b. 349.78 kN d. 427.86 kN
9. Which of the following most nearly gives the hydrostatic force
acting in liquid 3?
a. 1758.24 kN c. 247.86 kN
b. 472.68 kN d. 1785.42 kN
10. Which of the following most nearly gives the location of the total a. 2.34 m c. 1.95 m
hydrostatic force from the bottom of the tank? b. 2.89 m d. 2.23 m
a. 4.56 m c. 3.36 m
b. 5.46 m d. 6.63 m Situation 7: A tall cylindrical tank 150 mm in diameter contains
water 200 mm deep and oil (sg=0.80) 30 mm deep. A
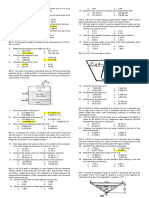
Situation 3: The parabolic plate is submerged in water as shown. cylindrical buoy 100 mm in diameter and 120 mm
high is placed vertically inside the tank. The buoy
weighs 5 N.
23. Which of the following most nearly gives the specific gravity of
the buoy?
a. 0.45 c. 0.54
b. 0.25 d. 0.35
11. Which of the following most nearly gives the hydrostatic force 24. Which of the following most nearly gives the depth of buoy
acting in the plate? submerged?
a. 2604.72 kN c. 2460.27 kN a. 79.65 mm c. 81.12 mm
b. 2640.27 kN d. 2406.72 kN b. 75.69 mm d. 45.07 mm
12. Which of the following most nearly gives the location of the 25. Which of the following most nearly gives the increase in height of
hydrostatic force from the top surface of the liquid? the contents?
a. 8.69 m c. 7.68 m a. 63.34 mm c. 41.12 mm
b. 9.68 m d. 6.81 m b. 23.45 mm d. 33.64 mm
Engr. Karren May Simplina
FLUID MECHANICS
Review (NOV. 2018)
2. Which of the following most nearly gives the kinematic viscosity
Situation 8: A pump draws water at 20 liters per second from of the liquid?
reservoir A and lifts it to reservoir B as shown. The a. 1.97x10-5 m2/s c. 3.19x10-5 m2/s
head loss from A to 1 is three times the velocity head b. 2.17x10-5 m2/s d. 2.49x10-5 m2/s
in the 150-mm diameter pipe and the head loss from
2 to B is fifteen times the velocity head in the 100- 3. Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow?
mm diameter pipe. a. 99.56 L/min c. 86.80 L/min
b. 78.71 L/min d. 127.89 L/min
26. Which of the following most nearly gives the power delivered by
the pump? Situation 2: Crude oil having a density of 856 kg/m3 and dynamic
a. 59.24 kW c. 52.49 kW viscosity of 0.0072 Pa-s flow through a 60 mm
b. 48.10 kW d. 41.80 kW diameter pipe at a rate of 0.24 m/s.
27. Which of the following most nearly gives the pressure head at 4. Which of the following most nearly gives the Reynolds number?
point 1? a. 1,217 c. 1,127
a. 19.74 m c. 17.49 m b. 1,271 d. 1,712
b. 24.97 m d. 14.97 m
5. Which of the following most nearly gives the friction factor?
28. Which of the following most nearly gives the pressure head at a. 0.0568 c. 0.0504
point 2? b. 0.0374 d. 0.0526
a. 259.86 m c. 269.86 m
b. 262.38 m d. 264.63 m 6. Which of the following most nearly gives the head lost if the pipe
is 1,500 m long?
Situation 9: Reservoirs A and B have elevations 250 m and 100 a. 4.17 m c. 3.86 m
m respectively, and are connected by a pipe having a b. 2.74 m d. 3.70 m
diameter of 250 mm and a length of 250 m. A turbine
is installed at a point in between reservoirs A and B. Situation 3: Three pipes 1, 2, and 3 from three reservoirs A, B,
The discharge in the pipeline is 140 L/s. Use C=120. and C, respectively, meet at a junction whose
elevation is 366 m. Water levels at reservoirs A and
29. Which of the following most nearly gives the head loss in the B are at elevations 825 m and 716 m, respectively.
pipe due to friction? Useful properties of the pipes are given in the
a. 9.17 m c. 6.15 m following table.
b. 7.35 m d. 8.55 m
7. If the pressure at the junction of the pipes is 2730 kPa, find the
30. Which of the following most nearly gives the head extracted by elevation of water at reservoir C.
the turbine? a. 480.33 m c. 462.07 m
a. 149.55 m c. 136.10 m b. 544.96 m d. 503.29 m
b. 141.45 m d. 160.75 m
8. Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow in
31. Which of the following most nearly gives the power generated by pipeline 2?
the turbine? a. 296.50 L/s c. 212.25 L/s
a. 215.65 kW c. 235.18 kW b. 316.17 L/s d. 192.34 L/s
b. 194.27 kW d. 180.50 kW
9. Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow in
Situation 10: A discharge of 750 L/s flows through a pipe having a pipeline 3?
diameter of 400 mm and a length of 65 m. a. 325.98 L/s c. 113.90 L/s
b. 235.98 L/s d. 261.18 L/s
32. Which of the following most nearly gives the head loss using
Manning’s equation with n= 0.013? Situation 4: A 600-mm diameter non-rigid pipe conveys water
a. 8.43 m c. 7.50 m from a reservoir with a velocity of 2.50 m/s. The flow
b. 8.96 m d. 7.18 m is suddenly stopped by the closure of a valve
situated 400 m from the reservoir. Assume that the
33. Which of the following most nearly gives the head loss using pressure increases at a uniform rate and that there is
Darcy-Weisbach formula with f= 0.012? no damping of the pressure wave. The pipe has a
a. 3.54 m c. 3.17 m thickness of 20 mm and a modulus of elasticity
b. 2.15 m d. 2.75 m 1.40x1011 Pa. The bulk modulus of elasticity of water
is 2.20x109 Pa.
34. Which of the following most nearly gives the head loss using
Hazen-Williams formula with C= 100? 10. Which of the following most nearly gives the celerity of the
a. 7.45 m c. 7.86 m pressure wave?
b. 6.12 m d. 7.05 m a. 1366.79 m/s c. 1483.24 m/s
b. 1222.76 m/s d. 1616.04 m/s
Situation 11: Water is pumped into a distribution reservoir at a rate
of 600 m3 every 4 hours. The estimated water 11. Which of the following most nearly gives the time for the
demands every 4 hours are shown below. pressure wave to travel round trip along the pipe?
a. 0.65 s c. 0.59 s
Time Demand (m3) b. 0.54 s d. 0.50 s
0400H 200
0800h 800 12. Which of the following most nearly gives the water hammer
1200H 1,100 pressure developed in the pipe due to instantaneous valve
1600H 700 closure?
2000H 500 a. 4040.11 kPa c. 3415.29 kPa
2400H 300 b. 3708.12 kpa d. 3056.90 kPa
Situation 5: The elasticity and dimension of the pile are such that
At 0800, the reservoir contains 700 m3 of water.
the celerity of the pressure wave is 970 m/s.
Suppose the pipe has a length of 1,600 m, and a
35. Which of the following most nearly gives the minimum reservoir
diameter of 1.20 m and initial flow of 0.85 m3/s.
capacity?
a. 800 m3 c. 900 m3
13. Find the water hammer pressure for instantaneous valve closure.
b. 700 m3 d. 600 m3
a. 650 kPa c. 810 kPa
b. 550.80 kPa d. 727.50 kPa
36. Which of the following most nearly gives the maximum
requirement from the reservoir?
14. How much time should be allowed for closing a valve to avoid
a. 400 m3 c. 600 m3
water hammer pressure.
b. 200 m3 d. 500 m3
a. 1.20 sec c. 3.30 sec
b. 5.10 sec d. 2.10 sec
37. Which of the following most nearly gives the water in the
reservoir at 2000H?
15. Find the appropriate water hammer pressure of the valve if it is
a. 100 m3 c. 500 m3
closed in 4 seconds?
b. 400 m3 d. 200 m3
a. 710 kPa c. 510 kPa
b. 600 kPa d. 555 kPa
SET 2
Situation 6: A trapezoidal canal with a base of 2 m has its sides
Situation 1: A liquid having a Reynolds number of 1700 flows
sloping at 45° with the horizontal. Water flows at a
through a 50-mm diameter pipe that is 1200 m long.
depth of 1m.
The head loss in the pipe due to friction is 25 m.
16. Which of the following most nearly gives the cross sectional area
1. Which of the following most nearly gives the friction factor?
of the water?
a. 0.0376 c. 0.0458
a. 3.00 m2 c. 5.66 m2
b. 0.0173 d. 0.0286
b. 2.83 m2 d. 6.00 m2
Engr. Karren May Simplina
FLUID MECHANICS
Review (NOV. 2018)
a. 0.1671 m3/s c. 0.3793 m3/s
17. Which of the following most nearly gives the wetted perimeter of b. 0.2844 m3/s d. 0.3136 m3/s
the canal?
a. 4.83 m c. 3.41 m 33. Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow in
b. 2.83 m d. 5.66 m pipeline 3?
a. 0.1671 m3/s c. 0.3793 m3/s
18. Which of the following most nearly gives the hydraulic radius? b. 0.2844 m3/s d. 0.3136 m3/s
a. 0.50 m c. 0.62 m
b. 1.00 m d. 0.68 m Situation 12: The flow rate for the pipe system shown is 0.050
m3/s with a total head loss of 12 m. Use C= 120 for
Situation 7: Water flows in a rectangular channel 10 m wide and all pipes.
1.20 m deep at a rate of 18.40 m3/s. The roughness
coefficient of the channel is 0.012.
19. Which of the following most nearly gives the slope of the
channel?
a. 0.000444 c. 0.000534
b. 0.000453 d. 0.000354
20. Which of the following most nearly gives the specific energy? Pipe Length Diameter
a. 1.22 m c. 1.86 m 1 400 m 200 mm
b. 1.32 m d. 1.59 m 2 500 m 180 mm
3 300 m
21. Which of the following most nearly gives the boundary shear 4 620 m 250 mm
stress?
a. 5.07 Pa c. 4.21 Pa
34. Which of the following most nearly gives the head loss in pipe 2?
b. 4.30 Pa d. 3.36 Pa
a. 5.56 m c. 2.81 m
b. 3.71 m d. 1.62 m
Situation 8: Water flows through an almost level channel 3 m
wide at a rate of 12 m3/s. The depth gradually
35. Which of the following most nearly gives the flow in pipe 3?
increases from 1 m to 1.10 m over a length of flow of
a. 0.0278 m3/s c. 0.0451 m3/s
5 m.
b. 0.0124 m3/s d. 0.0208 m3/s
22. Which of the following most nearly gives the head lost?
36. Which of the following most nearly gives the diameter of pipe 3?
a. 0.0249 m c. 0.0415 m
a. 129.73 mm c. 176.54 mm
b. 0.0829 m d. 0.0671 m
b. 158.12 mm d. 212.15 mm
23. Which of the following most nearly gives the slope of the energy
Situation 13: Water flows through a horizontal bend and a T
grade line?
section as shown below. AT section 1, the flow
a. 0.0083 c. 0.0050
enters with a velocity of 6 m/s, and the pressure is
c. 0.0134 d. 0.0166
4.80 kPa. At both sections 1 and 2, the flow exits the
device with a velocity of 3 m/s, and the pressures at
24. Which of the following most nearly gives the roughness
these sections are atmospheric. The cross sectional
coefficient?
areas at 1,2, and 3 are all the same at 0.20 m2.
a. 0.0134 c. 0.0173
b. 0.0245 d. 0.0220
Situation 9: A 90° triangular channel having a roughness
coefficient of 0.012 carries water at a rate of 6 m3/s.
25. Which of the following most nearly gives the critical depth?
a. 1.16 m c. 1.94 m
b. 1.49 m d. 1.61 m
26. Which of the following most nearly gives the critical velocity?
a. 2.07 m/s c. 2.46 m/s
b. 2.70 m/s d. 2.64 m/s
27. Which of the following most nearly gives the critical slope?
37. Which of the following most nearly gives the x component of the
a. 0.0025 c. 0.0037
force necessary to restrain the section?
b. 0.0073 d. 0.0052
a. 9.96 kN c. 4.44 kN
b. 6.36 kN d. 8.04 kN
Situation 10: A rectangular channel 5.50 m wide and 1.30 m deep
is laid on a uniform slope of 0.002. The roughness 38. Which of the following most nearly gives the y component of the
coefficient of the channel is 0.013.
force necessary to restrain the section?
a. 0.84 kN c. 0.96 kN
28. Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow in the
b. 2.76 kN d. 1.80 kN
channel?
a. 21.04 m3/s c. 22.63 m3/s
39. Which of the following most nearly gives the resultant force
b. 19.27 m3/s d. 16.28 m3/s
necessary to restrain the section?
a. 8.50 kN c. 10.12 kN
29. Which of the following most nearly gives the savings in lining per
b. 9.80 kN d. 10.34 kN
meter length of channel that could have been offered by using
the most efficient rectangular section but adhering to the same
flow capacity and slope?
a. 1.53 m2/m c. 0.87 m2/m
b. 1.10 m2/m d. 0.67 m2/m
30. Which of the following most nearly gives the savings in earth
excavation per meter length of channel that could have been
offered by using the most efficient rectangular section but
adhering to the same flow capacity and slope?
a. 0.61 m3/m c. 1.75 m3/m
b. 0.24 m3/m d. 1.03 m3/m
Situation 11: Pipelines 1, 2, and 3 are connected in parallel to
each other. The three pipes carry a combined
discharge of 0.86 m3/s.
Pipe Length Diameter Friction Factor
1 1800 m 400 mm 0.020
2 1500 m 350 mm 0.018
3 2000 m 300 mm 0.022
31. Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow in
pipeline 1?
a. 0.3136 m3/s c. 0.2844 m3/s
b. 0.1671 m3/s d. 0.3793 m3/s
32. Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow in
pipeline 2?
Engr. Karren May Simplina
You might also like
- Fluids Nov2021 Day2Document17 pagesFluids Nov2021 Day2Yedda M Ilagan100% (1)
- Irrigation Activity No. 1Document6 pagesIrrigation Activity No. 1Jeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- 123Document7 pages123Jennifer Damasco100% (2)
- Preboard Problems FinalDocument5 pagesPreboard Problems FinalAngel MarkNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics HandoutsDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics HandoutssadonNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech May 2021Document5 pagesFluid Mech May 2021Naigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- 16 Fluid Mechanics Review Notes 1 PDFDocument4 pages16 Fluid Mechanics Review Notes 1 PDFDoben CañebaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingFrancis Philippe CariñoNo ratings yet
- Fliuids MechanicsDocument8 pagesFliuids MechanicsCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- EERC Fluid Mechanics Refresher May 2021Document2 pagesEERC Fluid Mechanics Refresher May 2021Chum ElbaNo ratings yet
- 2003 Nov Prob OkDocument4 pages2003 Nov Prob OkreynaldmiasisNo ratings yet
- Structural 1Document3 pagesStructural 1eufemiorodolfoNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam StructDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Exam StructJejomar MotolNo ratings yet
- Sw3 Answer KeyDocument1 pageSw3 Answer KeyPati DukaNo ratings yet
- Quiz FEU-IT Correlation CourseDocument2 pagesQuiz FEU-IT Correlation CourseKayle Fajutagana FormillezaNo ratings yet
- Evals Fluids Answersheet Nov2021Document10 pagesEvals Fluids Answersheet Nov2021Yedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IiDocument3 pagesAssignment - IichritNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Review Exam 1 - 2014Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics Review Exam 1 - 2014The SixthNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 101820Document1 pageFluid Mechanics Lecture 101820John Dalton ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Problems 1Document2 pagesProblems 1Andoy Don M.No ratings yet
- Problems Worked in Class - All PDFDocument245 pagesProblems Worked in Class - All PDFGeva GarradoNo ratings yet
- Ce311 Villapando, Rs-Problem Set No. 3Document9 pagesCe311 Villapando, Rs-Problem Set No. 3Sky RomeoNo ratings yet
- File 1582710448 PDFDocument5 pagesFile 1582710448 PDFNatasha Marie MallareNo ratings yet
- Geo - 4Document2 pagesGeo - 4SamNo ratings yet
- Pretest in DesignDocument4 pagesPretest in DesignfrancessichNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 PDFDocument4 pagesHomework 1 PDFعلي علي صالح انقعNo ratings yet
- Situation 2. A 800 MM Ø Main Carrying 2.4 M 3/sDocument1 pageSituation 2. A 800 MM Ø Main Carrying 2.4 M 3/sFrancis VillacortaNo ratings yet
- TOS LectureDocument6 pagesTOS LectureAngelo Brian IlaganNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Examination - Geotech and HydraulicsDocument4 pagesPre Board Examination - Geotech and HydraulicsjefreyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Fluid Mech Fluid Mach IceDocument4 pagesProblem Set Fluid Mech Fluid Mach Icezyx xyzNo ratings yet
- Consolidation of SoilDocument8 pagesConsolidation of SoilRay JillNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument10 pagesHydraulicsAnonymous QinVShNo ratings yet
- GeoHydro Preboard 2Document8 pagesGeoHydro Preboard 2yajnad_10No ratings yet
- Policarpio 3 - Refresher GEODocument2 pagesPolicarpio 3 - Refresher GEOJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- DESIGNDocument9 pagesDESIGNRowena Remorosa GalayNo ratings yet
- Geo - 3Document2 pagesGeo - 3SamNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 22013 - 2014 Competency Exam StudentsDocument1 pagePhysics 2 22013 - 2014 Competency Exam StudentsAron BalinesNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 DesignDocument7 pagesPreboard 2 DesignApril Benosa100% (1)
- Seatwork 1 Mathematics: Specific WeightDocument5 pagesSeatwork 1 Mathematics: Specific WeightRenz PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Questionnaireanjago824No ratings yet
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDocument2 pagesFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- SurveyingDocument1 pageSurveyingrommel baldagoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 1 ProblemsDocument1 pageHydraulics 1 ProblemsJames NeoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 112720Document1 pageFluid Mechanics Lecture 112720John Dalton ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnic 2Document2 pagesGeotechnic 2Faez El-NinoNo ratings yet
- Correl1 Exam 2Document2 pagesCorrel1 Exam 2sunnyrezariNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 26 - Theory of Structures - Reinforced Concrete Design AnswerDocument2 pagesUnit Test 26 - Theory of Structures - Reinforced Concrete Design AnswerJustin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument12 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical EngineeringJamesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Sciences and Allied SubjectsDocument10 pagesEngineering Sciences and Allied SubjectsNathanael TayorNo ratings yet
- Rasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Document3 pagesRasco Civil Engineering Review Aloja Coffee Shop, Libas, Banga, Aklan CP: 09164618841 / Landline: (036) 267 - 7343 Fluid Mechanics - Evaluation 4Greg Rasco, REE, RMPNo ratings yet
- With Answers Fluid Mechanics Comprehensive ExamDocument3 pagesWith Answers Fluid Mechanics Comprehensive ExamMary Claire NevalgaNo ratings yet
- GEAS ExamDocument7 pagesGEAS ExamDenver MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechnaics and Fluid Machineries ReviewerDocument3 pagesFluid Mechnaics and Fluid Machineries ReviewerPaolo MontesinesNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (Statics) : A B A B A B BDocument2 pagesEngineering Mechanics (Statics) : A B A B A B BMallene EhurangoNo ratings yet
- Compre AS2 and AS3Document6 pagesCompre AS2 and AS3kimberlyjoyregaladoNo ratings yet
- DAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsDocument20 pagesDAY 1 - Statics, Dynamics, Strength of MaterialsJM De Guzman TuzonNo ratings yet
- Midterm Hge ProbsDocument2 pagesMidterm Hge ProbsIbo, Kim CaesarNo ratings yet
- Module in Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument5 pagesModule in Mechanics of Deformable BodiesPamela SanchezNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics, Geotechnical & Structural Engineering ReviewDocument1 pageHydraulics, Geotechnical & Structural Engineering ReviewJoy CleofeNo ratings yet
- Cacayan - Abuena May M.: Phone: 09158230983 Address: Pinaripad Norte Aglipay Quirino Birthday: May 03 1998Document2 pagesCacayan - Abuena May M.: Phone: 09158230983 Address: Pinaripad Norte Aglipay Quirino Birthday: May 03 1998Leovhea AbuenaNo ratings yet
- CV For VaDocument1 pageCV For VaLeovhea AbuenaNo ratings yet
- Application LetterDocument1 pageApplication LetterLeovhea AbuenaNo ratings yet
- Abuena May C. (Electrical Works)Document1 pageAbuena May C. (Electrical Works)Leovhea AbuenaNo ratings yet
- Abuena May C. (Steel Works)Document5 pagesAbuena May C. (Steel Works)Leovhea AbuenaNo ratings yet
- CE Licensure Exam CoverageDocument1 pageCE Licensure Exam CoverageLeovhea AbuenaNo ratings yet
- HGE Refresher QuestionsDocument8 pagesHGE Refresher QuestionsCj SuarezNo ratings yet
- Pipe and Pump Sizing For A NetworkDocument58 pagesPipe and Pump Sizing For A Networktt1242281984No ratings yet
- Version 5.10 CAESAR II Applications GuideDocument302 pagesVersion 5.10 CAESAR II Applications GuideBin XiangNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument2 pagesHydroelectric Power PlantMamta SinghNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer Pressure/ Surge Pressure Calculation : Developed by Engr. Abiodun AsadeDocument2 pagesWater Hammer Pressure/ Surge Pressure Calculation : Developed by Engr. Abiodun Asadecoolsummer1112143100% (1)
- Computer Modelling of Hydraulic Transients in Pipe NetworksDocument8 pagesComputer Modelling of Hydraulic Transients in Pipe Networkskhantiger100No ratings yet
- Acv Automatic Control Valves PDFDocument20 pagesAcv Automatic Control Valves PDFabdallah391No ratings yet
- Surge Control PDFDocument14 pagesSurge Control PDFMohamed Guezguez100% (1)
- Auxiliary Lesson - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAuxiliary Lesson - Water HammerEmmanuel MaalaNo ratings yet
- PIM300 Piping System Design PDFDocument66 pagesPIM300 Piping System Design PDFmika cabelloNo ratings yet
- 2014 PLTB Present Guide PDFDocument125 pages2014 PLTB Present Guide PDFPato Patiño MuñozNo ratings yet
- Computation Water Hammer With Finite ElementDocument6 pagesComputation Water Hammer With Finite ElementyousefNo ratings yet
- Hpge 2010 2022 Compilation of Terms EMTDocument57 pagesHpge 2010 2022 Compilation of Terms EMTjoshuaturai0312No ratings yet
- Bergant2003 Part 2Document11 pagesBergant2003 Part 2Fabio FolpiniNo ratings yet
- SMC 56 PA3110 F03 Datasheet PDFDocument37 pagesSMC 56 PA3110 F03 Datasheet PDFDaniela ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Asahi Wafer Check ValveDocument2 pagesAsahi Wafer Check ValveShaimaa BaataNo ratings yet
- PEX Installation Handbook 2006Document17 pagesPEX Installation Handbook 2006obNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)Document18 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Cenários Sobrepressão Conforme API RP 521Document3 pagesCenários Sobrepressão Conforme API RP 521Adilmar E. NatãnyNo ratings yet
- CH-13 Boiler SafetyDocument10 pagesCH-13 Boiler SafetyRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- NX VFCDocument24 pagesNX VFCtienNo ratings yet
- Water HammerDocument49 pagesWater HammerLakshmiprasad Kadari100% (2)
- Rainbid Landscape & Turf Irrigation Products 2018 PDFDocument196 pagesRainbid Landscape & Turf Irrigation Products 2018 PDFFöldi BélaNo ratings yet
- General Operating Manual For Valves: Version 02/2016Document17 pagesGeneral Operating Manual For Valves: Version 02/2016Harshil TejaniNo ratings yet
- Brochure 3Document12 pagesBrochure 3Gohilakrishnan ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Soil and Water Conservation EngineeringDocument266 pagesSoil and Water Conservation EngineeringUnodosNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of PVC PipeDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of PVC PipeWengineerNo ratings yet
- GD2Document14 pagesGD2youknows50% (2)
- Models For Analysis of Water Hammer in Piping With Entrapped Air - Chaiko - 2002 - PPL CorporationDocument11 pagesModels For Analysis of Water Hammer in Piping With Entrapped Air - Chaiko - 2002 - PPL CorporationElias TascaNo ratings yet