Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal - 20
Analisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal - 20
Uploaded by
Jorge Luis Huahuachampi Cayllahua0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views20 pagesOriginal Title
Analisis del Estado Estacionario sinusoidal -20
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views20 pagesAnalisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal - 20
Analisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal - 20
Uploaded by
Jorge Luis Huahuachampi CayllahuaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
CHAPTER 9
Sinusoidal
Steady-State Analysis
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
CHAPTER CONTENTS
• 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source
• 9.2 The Sinusoidal Response
• 9.3 The Phasor
• 9.4 The Passive Circuit Elements in the Frequency Domain
• 9.5 Kirchhoff’s Laws in the Frequency Domain
• 9.6 Series, Parallel, and Delta-to-Wye Simplifications
• 9.7 Source Transformations and Thévenin-Norton Equivalent
Circuits
• 9.8 The Node-Voltage Method
• 9.9 The Mesh-Current Method
• 9.10 The Transformer
• 9.11 The Ideal Transformer
• 9.12 Phasor Diagrams
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
CHAPTER OBJECTIVES
1. Understand phasor concepts and be able to perform a phasor
transform and an inverse phasor transform.
2. Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the
frequency domain using phasor concepts.
3. Know how to use the following circuit analysis techniques to solve
a circuit in the frequency domain:
▪ Kirchhoff’s laws;
▪ Series, parallel, and delta-to-wye simplifications;
▪ Voltage and current division;
▪ Thévenin and Norton equivalents;
▪ Node-voltage method; and
▪ Mesh-current method.
4. Be. able to analyze circuits containing linear transformers using
phasor methods
5. Understand the ideal transformer constraints and be able to analyze
circuits containing ideal transformers using phasor methods.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
9.1 The Sinusoidal Source
• A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or
dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally
with time.
• A sinusoidal current source (independent or
dependent) produces a current that varies sinusoidally
with time.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Figure 9.1 A sinusoidal voltage.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
• The sinusoidal function repeats at regular intervals is
called periodic.
• The length of time is referred to as the period of the
function and is denoted T.
• The angular frequency of the sinusoidal function
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
• The angle f is know as the phase angle of the
sinusoidal voltage.
Figure 9.2 The sinusoidal voltage from Fig.
9.1 shifted to the right when ϕ = 0.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Root mean square (rms)
• The rms value of a periodic function is defined as the
square root of the mean value of the squared function.
• rms value of a sinusoidal voltage source
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.1
• A sinusoidal current has a maximum amplitude of 20
A.The current passes through one complete cycle in 1
ms. The magnitude of the current at zero time is 10 A.
a) What is the frequency of the current in hertz?
b) What is the frequency in radians per second?
c) Write the expression for i(t) using the cosine function.
Express f in degrees.
d) What is the rms value of the current?
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.1
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.2
• A sinusoidal voltage is given by the expression v =
300 cos (120pt + 30°).
a) What is the period of the voltage in milliseconds?
b) What is the frequency in hertz?
c) What is the magnitude of at t = 2.778 ms?
d) What is the rms value of v?
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.2
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.3
• We can translate the sine function to the cosine
function by subtracting 90° (p/2 rad) from the
argument of the sine function.
a) Verify this translation by showing that
sin (ωt + θ) = cos (ωt + θ – 90°).
b) Use the result in (a) to express sin (ωt + 30°) as a
cosine function.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.3
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.4
• Calculate the rms value of the periodic triangular
current shown in Fig. 9.3. Express your answer in
terms of the peak current Ip.
Figure 9.3 Periodic triangular current.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.4
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.4
Figure 9.4 i2 versus t.
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
Example 9.4
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
9.2 The Sinusoidal Response
Figure 9.5 An RL circuit
excited by a sinusoidal
voltage source.
• Kirchhoff’s voltage law
transient component steady-state component
Electronic Circuits, Tenth Edition Copyright ©2015 by Pearson Higher Education.
James W. Nilsson | Susan A. Riedel All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Introduction - Protagonist Personality (ENFJ-A: ENFJ-T) - 16personalitiesDocument1 pageIntroduction - Protagonist Personality (ENFJ-A: ENFJ-T) - 16personalitiesIrina MarinaşNo ratings yet
- Kaiser - Electromagnetic Compatibility Handbook - ToCDocument18 pagesKaiser - Electromagnetic Compatibility Handbook - ToCbodymorph20% (5)
- Worksheet 09 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 09 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- The Asterisk War, Vol. 10Document158 pagesThe Asterisk War, Vol. 10putroaji aureliusNo ratings yet
- TDW and WP May 2022 Editorial InterventionIsolation TM2460 3XL David SDocument4 pagesTDW and WP May 2022 Editorial InterventionIsolation TM2460 3XL David SMauricio CarestiaNo ratings yet
- HSE-04 - Hot Work PermitDocument3 pagesHSE-04 - Hot Work PermitMaheshwor Man Joshi100% (1)
- Analisis Del Estado Estacionario SinusoidalDocument33 pagesAnalisis Del Estado Estacionario SinusoidalJorge Luis Huahuachampi CayllahuaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal (1222Document84 pagesAnalisis Del Estado Estacionario Sinusoidal (1222Jorge Luis Huahuachampi CayllahuaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document10 pagesLecture 6Mohammed ZaitounNo ratings yet
- LC and Sinusoidal VoltagesDocument8 pagesLC and Sinusoidal VoltagesEly DalimanNo ratings yet
- Circuits II 1.01 (Autosaved)Document98 pagesCircuits II 1.01 (Autosaved)Patricia DatinguinooNo ratings yet
- Regulators PDFDocument24 pagesRegulators PDFH Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Edition Boylestad Louis Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsDocument26 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Edition Boylestad Louis Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsengitalomedeirosNo ratings yet
- Sinusoids and PhasorsDocument17 pagesSinusoids and PhasorsJenny A. BermudezNo ratings yet
- CHAP2 ADocument26 pagesCHAP2 AKyte Valerie SamonteNo ratings yet
- Transformers: Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesTransformers: Physics Investigatory ProjectA. S AhmedNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicspratikayadav263No ratings yet
- Diffusion: Which Is The Flow Caused by Variations in The Concentration I.E. Drift: It Is The Movement Caused by Electric FieldsDocument22 pagesDiffusion: Which Is The Flow Caused by Variations in The Concentration I.E. Drift: It Is The Movement Caused by Electric FieldsnagarajudbpNo ratings yet
- Basic AC Theory Handout 01-Mec. EngDocument10 pagesBasic AC Theory Handout 01-Mec. EngParamananda_SurangaNo ratings yet
- Linear TransformerDocument44 pagesLinear TransformerRonmark AbinoNo ratings yet
- ES7 - AC I V Plus DC Power Suppply Intro - 09may21Document13 pagesES7 - AC I V Plus DC Power Suppply Intro - 09may21Sri RamanNo ratings yet
- Surendranath Centenary School - 1Document16 pagesSurendranath Centenary School - 1priyamdattaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Module 1Document28 pagesAC Circuits Module 1YoNo ratings yet
- A Full Wave RectifierDocument17 pagesA Full Wave RectifierAnonymous xoQWeF4No ratings yet
- Physics Investagatory ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Investagatory ProjecttotallynotparthdubeyNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Cont..Document50 pagesUnit-1 Cont..mitparikh1046No ratings yet
- Alternating Voltages and Currents and AC ValuesDocument35 pagesAlternating Voltages and Currents and AC ValuesUtkarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 1.overview of Electronic ComponentsDocument13 pages1.overview of Electronic ComponentsArpita 18No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Transformer 1 23Document23 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Transformer 1 23Swayam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Transformers: ProjectDocument21 pagesTransformers: ProjectHimanshu Rawat100% (1)
- AC FundamentalsDocument16 pagesAC FundamentalsQiyanaNo ratings yet
- AC FundamentalsDocument16 pagesAC FundamentalsJayson Bryan MutucNo ratings yet
- Transformers Project FileDocument14 pagesTransformers Project FiledikshaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Singlephase 21Document41 pagesAC Circuits Singlephase 21Anant UpadhiyayNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byDocument23 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byAsh wanth100% (1)
- Module 1 - Foundation of DC Concepts, Ohm's Law, Power and EnergyDocument51 pagesModule 1 - Foundation of DC Concepts, Ohm's Law, Power and EnergyUsername88plooNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Prelim)Document21 pagesLesson 1 (Prelim)Ruth Abegail de VeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 p2 NITHDocument21 pagesChapter2 p2 NITHPriyanshu GargNo ratings yet
- LEC 1 Rev1Document35 pagesLEC 1 Rev1Ovie MacatiagNo ratings yet
- Basic Harmonics TrainingDocument74 pagesBasic Harmonics Trainingmaruf048100% (2)
- Diode Applications: Dr. Talal SkaikDocument21 pagesDiode Applications: Dr. Talal Skaikmessage4guruNo ratings yet
- Schaum's Outline of ElectromagneticsDocument22 pagesSchaum's Outline of Electromagneticslionelplay774725% (4)
- A Full Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesA Full Wave RectifierPawan Kumar Singh100% (2)
- Unit-Ii: Fundamental of Ac CircuitsDocument30 pagesUnit-Ii: Fundamental of Ac CircuitsYashNo ratings yet
- Actavis Notes - Session6 - Elex (Compatibility Mode)Document14 pagesActavis Notes - Session6 - Elex (Compatibility Mode)Alfred GaleaNo ratings yet
- Ac Fundamentals Mod 2Document23 pagesAc Fundamentals Mod 2NINAN JOHNNo ratings yet
- EECKT230 - Course Material 1Document35 pagesEECKT230 - Course Material 1reasjames0No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument28 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectHET PatelNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge Oscillator DesignDocument16 pagesWien Bridge Oscillator DesignReece RevosaNo ratings yet
- CH-7 Alternating CurrentDocument90 pagesCH-7 Alternating CurrentAviralTNo ratings yet
- Ece131 Unit 2Document189 pagesEce131 Unit 2rahtdf47No ratings yet
- AC Sinusoidal Analysis: Course Number and NameDocument7 pagesAC Sinusoidal Analysis: Course Number and NameahmedNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Evaluation BookDocument6 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Evaluation BookAdel KhamisNo ratings yet
- 01D Basic ConceptsDocument64 pages01D Basic ConceptsRA MemijeNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document38 pagesModule 2Govind SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuit: Ee1CpeDocument106 pagesFundamentals of Electric Circuit: Ee1CpeDark AngelNo ratings yet
- ACDocument16 pagesACNelson SalvadorNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument55 pagesNotesKhushi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Full Wave RectifierDocument19 pagesPhysics Project On Full Wave RectifierSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document11 pagesActivity 3Ultima_SarinNo ratings yet
- New Revised IEEE Unit 2 Alternating Voltage and CurrentDocument81 pagesNew Revised IEEE Unit 2 Alternating Voltage and CurrentNUTS GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Physics Investagatory ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics Investagatory ProjecttotallynotparthdubeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment3 LastName 1Document8 pagesAssignment3 LastName 1Kabir WestNo ratings yet
- 07a10101 Applied MechanicsDocument11 pages07a10101 Applied MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Foliar Diseases of Hydrangea FBG 022916 G1Document7 pagesFoliar Diseases of Hydrangea FBG 022916 G1Codrean VladNo ratings yet
- tpa3110d2两种接法Document2 pagestpa3110d2两种接法57184522No ratings yet
- Aviation: " Weath ErDocument237 pagesAviation: " Weath ErLOUIS MOONNo ratings yet
- Complete Notes Koe062 FinalDocument152 pagesComplete Notes Koe062 FinalAnsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- DuraDeck Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesDuraDeck Brochure PDFSignatureFencingNo ratings yet
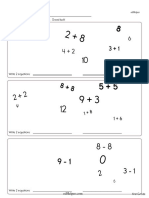
- Kindergarten Math and Critical Thinking WorksheetsDocument21 pagesKindergarten Math and Critical Thinking WorksheetsLisaNo ratings yet
- CHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Document83 pagesCHP 12 - Oral Mucosa-1Areej Fatima100% (2)
- Wa420-1 S - N 10001-Up - Steering Demand Valve (#20001-)Document2 pagesWa420-1 S - N 10001-Up - Steering Demand Valve (#20001-)Lenin GullapalliNo ratings yet
- Laporan Igd Mei 2021Document12 pagesLaporan Igd Mei 2021Aris Eka KristiantoNo ratings yet
- Importance of A Proper Sleep RoutineDocument2 pagesImportance of A Proper Sleep Routinesakshi sarojNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Medicinal PlantsDocument69 pagesKarnataka Medicinal PlantsRavindra BabuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- How To Perform Lakshmi Maata Puja For DivaliDocument7 pagesHow To Perform Lakshmi Maata Puja For Divalirajanp_k393No ratings yet
- Report Numerical Analyses of The Behaviour of The Sheet Pile WallDocument262 pagesReport Numerical Analyses of The Behaviour of The Sheet Pile WallsalmanNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage: General Performance Cast Iron Motors 400 V 50 HZDocument36 pagesLow Voltage: General Performance Cast Iron Motors 400 V 50 HZLance AyoubNo ratings yet
- Resume Khairul AfizanDocument7 pagesResume Khairul AfizanKhairul AfizanNo ratings yet
- C ProgramData Caterpillar Electronic Technician TempDocument32 pagesC ProgramData Caterpillar Electronic Technician TempIMAM MAHFUDNo ratings yet
- Name: - Lab Team: - Date: - Per: - Adaptations LabDocument3 pagesName: - Lab Team: - Date: - Per: - Adaptations LabHenry PriceNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom QuestionsDocument5 pagesStructure of Atom QuestionssingamroopaNo ratings yet
- Waste Disposal Systems: "Regulated Medical Waste" "Unregulated Medical Waste (UMW) "Document5 pagesWaste Disposal Systems: "Regulated Medical Waste" "Unregulated Medical Waste (UMW) "lakshma reddyNo ratings yet
- Trucos Gta 5Document2 pagesTrucos Gta 5Beto CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Carpet Green Label InfoDocument2 pagesCarpet Green Label InfoTariq KhurshaidiNo ratings yet
- Do's Don'Ts - Final - TeluguDocument1 pageDo's Don'Ts - Final - TelugufelixprabuNo ratings yet