Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microcontroller Basics Explained
Uploaded by
JK CreationOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microcontroller Basics Explained
Uploaded by
JK CreationCopyright:
Available Formats
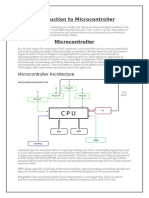
Microcontroller
A microcontroller (μC or uC) is a solitary chip microcomputer
fabricated from VLSI fabrication. A micro controller is also known
as embedded controller. Today various types of microcontrollers are
available in market with different word lengths such as 4bit,
8bit, 64bit and 128bit microcontrollers. Microcontroller is a
compressed micro computer manufactured to control the functions of
embedded systems in office machines, robots, home appliances,
motor vehicles, and a number of other gadgets. A microcontroller
is comprises components like - memory, peripherals and most
importantly a processor. Microcontrollers are basically employed in
devices that need a degree of control to be ap plied by the user of the
device.
Microcontroller Basics:
Any electric appliance that stores, measures, displays
information or calculates comprise of a
microcontroller chip inside it. The basic structure of a microcontroller
comprise of: -
1. CPU- Microcontrol lers brain is named as CPU. CPU is the device
which is employed to fetch data, decode it and at the end complete the
assigned task successfully. With the help of CPU all the components
of microcontroller is connected into a single system. Instruction fetch
ed by the programmable memory is decoded by the CPU.
2. Memory– In a microcontroller memory chip works same as
microprocessor. Memory chip stores all programs & data.
Microcontrollers are built with certain amount of ROM or RAM
(EPROM, EEPROM, etc) or flash memory for the storage of program
source codes.
3. Input/output ports– I/O ports are basically employed to interface
or drive different appliances such as - printers, LCD’s, LED’s, etc.
4.Serial Ports– These ports give serial interfaces amid
microcontroller & various other peripherals such as parallel port.
5.Timers– A microcontroller may be in-built with one or more
timer or counters. The timers & counters control all counting &
timing operations within a microcontroller. Timers are employed to
count external pulses. The main operations performed by timers’
are-pulse generations, clock functions, frequency measuring,
modulations, making oscillations, etc.
6.ADC (Analog to digital converter)–ADC is employed to convert
analog signals to digital ones. The input signals need to be analog for
ADC. The digital signal production can be employed for different
digital applications (such as measurement gadgets).
7.DAC (digital to analog converter)–this converter executes
opposite functions that ADC perform. This device is generally
employed to supervise analog appliances like-DC motors, etc.
8.Interpret Control- This controller is employed for giving delayed
control for a working program. The interpret can be internal or
external.
9. Special Functioning Block– Some special microcontrollers
manufactured for special appliances like - space systems, robots,
etc, comprise of this special function block. This special block
has additional ports so as to carry out some special operations.
You might also like
- Microcontrollers - Types & Applications What Is A Microcontroller?Document5 pagesMicrocontrollers - Types & Applications What Is A Microcontroller?nazmulNo ratings yet
- MICROCONTROLLER GUIDEDocument28 pagesMICROCONTROLLER GUIDERynefel ElopreNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller:: Chapter-8: MicrocontrollersDocument20 pagesMicrocontroller:: Chapter-8: MicrocontrollersMd Raton AliNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller ApplicationsDocument19 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller ApplicationsabdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Basics of MicroprocessorsDocument38 pagesCH-6 Basics of MicroprocessorsbelaynehNo ratings yet
- Types of MicrocontrollerDocument3 pagesTypes of MicrocontrollerHoney Joy LacunaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-Intro To Es - Part 1Document39 pagesTopic 1-Intro To Es - Part 1hadimustaffa00No ratings yet
- Module 1: Overview of Mechatronics: Lesson 1: Microcontrollers, Microprocessors, and Embedded ComputersDocument18 pagesModule 1: Overview of Mechatronics: Lesson 1: Microcontrollers, Microprocessors, and Embedded ComputersCerealNo ratings yet
- Embedded System NotesDocument66 pagesEmbedded System NotesChetnaNo ratings yet
- Types and Applications of MicrocontrollersDocument6 pagesTypes and Applications of MicrocontrollersAndré TelesNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: DEVICE MANEGMENT SYSTEM" Has Given Us Immense PleasureDocument20 pagesAcknowledgement: DEVICE MANEGMENT SYSTEM" Has Given Us Immense PleasuresonalsrsNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Overview of Embedded Systems Characteristics of Embedded SystemsDocument51 pagesUnit - I Overview of Embedded Systems Characteristics of Embedded SystemsKushal RajvanshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document29 pagesUnit 1Omkar VanjariNo ratings yet
- What is a MicrocontrollerDocument3 pagesWhat is a MicrocontrollerPotato BitsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Learning MaterailDocument52 pagesUnit 2 - Learning MaterailPILLARISETTY KARTHIK 2021-CSE UGNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 (Introduction, Hardwired Logic) : MPI Unit 1Document34 pagesLecture-1 (Introduction, Hardwired Logic) : MPI Unit 1Tushar VermaNo ratings yet
- 5-Microcontrollers 8051Document8 pages5-Microcontrollers 8051Dhiraj ShahNo ratings yet
- BATCH-9Document78 pagesBATCH-9kota naikNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document18 pagesModule 1Rohit AnejaNo ratings yet
- Micro-Controller: Embedded: Designing & Programming Using ArduinoDocument18 pagesMicro-Controller: Embedded: Designing & Programming Using ArduinoSatyjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Architecture and ApplicationsDocument13 pagesMicrocontroller Architecture and ApplicationsShabeebaNawabNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument22 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers6012 ANILNo ratings yet
- 1.Dr - Mohamed Abdel Motelb - Introduction To ComputerDocument12 pages1.Dr - Mohamed Abdel Motelb - Introduction To ComputerKhaled AhmedNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller - LectureDocument29 pagesMicrocontroller - LectureChouaibou MouminiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction & Evolution of MicroprocessorDocument68 pagesChapter One Introduction & Evolution of Microprocessorabel bahiru100% (1)
- Esd 1Document40 pagesEsd 1154Soyal LonareNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of MicrocontrollerDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Microcontrollerashley panganNo ratings yet
- MicroprocessorDocument16 pagesMicroprocessorReenaNo ratings yet
- EmbeddedDocument20 pagesEmbeddedSrilekha RajakumaranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocument5 pagesIntroduction To MicrocontrollerSongNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems - Quick GuideDocument56 pagesEmbedded Systems - Quick Guideasdfg ghjklNo ratings yet
- 1.0 PIC Programming in CDocument18 pages1.0 PIC Programming in CMohd HafizNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocument53 pagesUnit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerAKSHANSH MATHUR100% (1)
- Microprocessor Systems Chapter 1 1Document39 pagesMicroprocessor Systems Chapter 1 1Johnbob ToveraNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemDocument19 pagesEmbedded SystemMohammed GomaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Microcomputer System - Peripheral DesignDocument70 pagesChapter 1 Microcomputer System - Peripheral DesignJevithaNo ratings yet
- Microcomputer SystemDocument6 pagesMicrocomputer SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument27 pagesEmbedded Systemsnavneet100% (1)
- PDR - Unit IDocument16 pagesPDR - Unit IMUKILANNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7 Introduction To MicroprocessorsDocument5 pagesChapter-7 Introduction To MicroprocessorsMeet ThakkerNo ratings yet
- Unit 1B Typical Emb SysDocument52 pagesUnit 1B Typical Emb SysNandan BallaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NewDocument59 pagesUnit 1 NewHari PrasathNo ratings yet
- 4. IOT BASED COAL MINE SAFETY SYSTEMDocument79 pages4. IOT BASED COAL MINE SAFETY SYSTEMkota naikNo ratings yet
- ControllerDocument10 pagesControllerKashif SharifNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller AssignmentDocument16 pagesMicrocontroller AssignmentMusa MwasemboNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems - Quick GuideDocument55 pagesEmbedded Systems - Quick GuideOdunayo AkinladeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Micro ProcessorsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Micro ProcessorsJapheth NgugiNo ratings yet
- BATCH-8Document9 pagesBATCH-8kota naikNo ratings yet
- Temperature Controlled Fan ReportDocument85 pagesTemperature Controlled Fan ReportyrikkiNo ratings yet
- Types of MicrocontrollersDocument3 pagesTypes of MicrocontrollersJMNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollerpresentation 141213101338 Conversion Gate01Document41 pagesMicrocontrollerpresentation 141213101338 Conversion Gate01priyalNo ratings yet
- New Chapter 1Document18 pagesNew Chapter 1Amzar ShukriNo ratings yet
- Automatic Temperature & Brightness ControllerDocument67 pagesAutomatic Temperature & Brightness ControlleryrikkiNo ratings yet
- Lab01 MP PDFDocument11 pagesLab01 MP PDFAlicia KohNo ratings yet
- 1 Course Material - All Chapter 04-01-2024Document148 pages1 Course Material - All Chapter 04-01-2024RU MATH GamerNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor ComponentsDocument2 pagesMicroprocessor ComponentsBryan YaranonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Microcontroller Fundamental and ProgrammingDocument77 pagesChapter 2 Microcontroller Fundamental and ProgrammingsrjaswarNo ratings yet
- Embedded (Practical)Document18 pagesEmbedded (Practical)Devika KachhawahaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- BadmintonDocument1 pageBadmintonJK CreationNo ratings yet
- FootballDocument1 pageFootballJK CreationNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Archery From Its Origins Over 70,000 Years AgoDocument1 pageA Brief History of Archery From Its Origins Over 70,000 Years AgoJK CreationNo ratings yet
- GolfDocument1 pageGolfJK CreationNo ratings yet
- CarromDocument1 pageCarromJK CreationNo ratings yet
- Basketball's Origins in 1891 by Canadian Instructor James NaismithDocument1 pageBasketball's Origins in 1891 by Canadian Instructor James NaismithJK CreationNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument1 pageWaterJK CreationNo ratings yet
- Sports IndiaDocument6 pagesSports IndiaJK CreationNo ratings yet
- ShushrutDocument1 pageShushrutJK CreationNo ratings yet
- Cultural HeritageDocument1 pageCultural HeritageJK CreationNo ratings yet
- DiversityDocument1 pageDiversityJK CreationNo ratings yet
- India's Tax Structure Explained: Direct, Indirect Taxes and ReformsDocument1 pageIndia's Tax Structure Explained: Direct, Indirect Taxes and ReformsJK CreationNo ratings yet
- Asignment 1Document3 pagesAsignment 1Nguyen Quy Duong (K17 HL)No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - MCQDocument5 pagesChapter 14 - MCQSimer FibersNo ratings yet
- Volvo Ew 140 VaDocument66 pagesVolvo Ew 140 VaApexiNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Tieng Anh Lop 4 Chuong Trinh Moi Unit 18 What S Your Phone NumberDocument5 pagesBai Tap Tieng Anh Lop 4 Chuong Trinh Moi Unit 18 What S Your Phone NumberDevil -.-No ratings yet
- Removing the UEPP Display and Input DevicesDocument10 pagesRemoving the UEPP Display and Input Devicesرانا راشدNo ratings yet
- C++ function pointers guide: How to declare, define and call functions using pointersDocument146 pagesC++ function pointers guide: How to declare, define and call functions using pointersPrasad MahajanNo ratings yet
- Revolutionary Creative Thinking Method Unlocks Breakthrough IdeasDocument12 pagesRevolutionary Creative Thinking Method Unlocks Breakthrough IdeasDhanesh Kumar KasinathanNo ratings yet
- Manual Compl Parte1de5 U5n404 Osn9800Document27 pagesManual Compl Parte1de5 U5n404 Osn9800Liu BruceNo ratings yet
- The Complete Nodejs Developer CourseDocument31 pagesThe Complete Nodejs Developer CourseAkashNo ratings yet
- W1 - Lecture 1Document22 pagesW1 - Lecture 1Mariam El-shabraweNo ratings yet
- 421-4-5 GS 20121214Document3 pages421-4-5 GS 20121214sparkCENo ratings yet
- Lampiran 42 Block Sequence Codes - Kode Produk: CameraDocument23 pagesLampiran 42 Block Sequence Codes - Kode Produk: CameraAndry OnixNo ratings yet
- Phonic Summit 1383126546Document2 pagesPhonic Summit 1383126546K SNo ratings yet
- Sap Learning Hub - Course List: G-Tec EducationDocument50 pagesSap Learning Hub - Course List: G-Tec EducationCiril100% (1)
- OpenLDAP Admin GuideDocument267 pagesOpenLDAP Admin Guidejonas leonel da silvaNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications and Compliance of Goods and Related ServicesDocument5 pagesTechnical Specifications and Compliance of Goods and Related ServicesvskNo ratings yet
- Gigabyte X570 AORUS ELITE Schematic DiagramDocument55 pagesGigabyte X570 AORUS ELITE Schematic Diagrammm aaNo ratings yet
- Module 07a SEHDocument21 pagesModule 07a SEHoscar tebarNo ratings yet
- Rob Conery - Using Entity Framework 6 With PostgreSQLDocument11 pagesRob Conery - Using Entity Framework 6 With PostgreSQLAlexandre CustodioNo ratings yet
- Snx5176B Differential Bus Transceivers: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument28 pagesSnx5176B Differential Bus Transceivers: 1 Features 3 Descriptionmerdas merdasNo ratings yet
- Reviews Scam, Legit or Safe Check Scamadviser PDFDocument1 pageReviews Scam, Legit or Safe Check Scamadviser PDFOghenetega udiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Inheritance and PolymorphismDocument51 pagesChapter - 3 Inheritance and PolymorphismYididya Melaku100% (1)
- Manual System QBiX Plus EHLA6412 A1 - 20221213Document64 pagesManual System QBiX Plus EHLA6412 A1 - 20221213Nestor MartinezNo ratings yet
- Hua Hua Hua WDocument5 pagesHua Hua Hua WbiedhafiNo ratings yet
- Dual OptDocument11 pagesDual OptShahzad AshrafNo ratings yet
- MALAYSIA'S NATIONAL EDUCATION CODE 2020Document122 pagesMALAYSIA'S NATIONAL EDUCATION CODE 2020NORASIKIN ALIMOMNo ratings yet
- The Relational ModelDocument34 pagesThe Relational Modellouarianedlr17No ratings yet
- Types of Data TransmissionDocument11 pagesTypes of Data TransmissionsunriseformoneNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis of An Airfoil With Arbitrary Dimensions, Material and Number of Spars, Using ANSYS® and SolidWorks®.Document5 pagesComputer Aided Design and Finite Element Analysis of An Airfoil With Arbitrary Dimensions, Material and Number of Spars, Using ANSYS® and SolidWorks®.YussefRikliNo ratings yet
- GIS Fundamentals 7e ContentsDocument9 pagesGIS Fundamentals 7e ContentsJose AraujoNo ratings yet