Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Momentum
Uploaded by
JunLi CaiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linear Momentum
Uploaded by
JunLi CaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Cracking the AP Physics C Exam
Chapter 8 Drill
The answers and explanations can be found in Chapter 17.
4. A ball of mass m traveling horizontally with velocity v
Section I: Multiple Choice strikes a massive vertical wall and rebounds back along
its original direction with no change in speed. What is
the magnitude of the impulse delivered by the wall to
1. An object of mass 2 kg has a linear momentum of mag-
the ball?
nitude 6 kg·m/s. What is this object’s kinetic energy?
(A) 0
(A) 3 J
(B) 12 mv
(B) 6 J
(C) mv
(C) 9 J
(D) 2mv
(D) 12 J
(E) 4mv
(E) 18 J
5. Two objects, one of mass 3 kg and moving with a speed
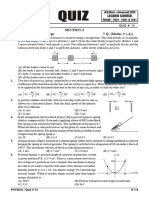
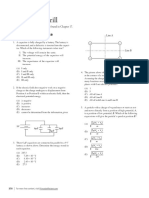
2. The graph below shows the force on an object over time.
of 2 m/s and the other of mass 5 kg and speed 2 m/s,
move toward each other and collide head-on. If the col-
20
lision is perfectly inelastic, find the speed of the objects
after the collision.
15 (A) 0.25 m/s
F(N)
(B) 0.5 m/s
10 (C) 0.75 m/s
(D) 1 m/s
5 (E) 2 m/s
2 4 6 8 6. A student is trying to balance a meter stick on its mid-
t(s) point. Given that m1 = 6 kg and m2 = 2 kg, how far from
the left edge should the student hang a third mass,
m3 = 10 kg, to balance the meter stick?
If the object has a mass of 8 kg and is moving in a
straight line, what is its change in speed?
(A) 16 m/s m2
(B) 14 m/s
(C) 12 m/s
(D) 10 m/s
(E) 8 m/s m1
3. A box with a mass of 2 kg accelerates in a straight line (A) 40 cm
from 4 m/s to 8 m/s due to the application of a force (B) 50 cm
whose duration is 0.5 s. Find the average strength of this (C) 60 cm
force. (D) 70 cm
(A) 2 N (E) 80 cm
(B) 4 N
(C) 8 N
(D) 12 N
(E) 16 N
8. Linear Momentum | 2 11
Cracking the AP Physics C Exam
7. Two objects move toward each other, collide, and 9. A car of mass 1,000 kg collides head-on with a truck of
separate. If there was no net external force acting on the mass 2,000 kg. Both vehicles are moving at a speed of
objects, but some kinetic energy was lost, then 21 m/s, and the collision is perfectly inelastic. After the
crash, the two vehicles skid to a halt. Assuming friction
(A) the collision was elastic and total linear momentum
is the only force acting on the vehicles after the colli-
was conserved
sion, how much work is done by friction after the crash?
(B) the collision was elastic and total linear momentum
was not conserved (A) 73,500 J
(C) the collision was not elastic and total linear (B) –73,500 J
momentum was conserved (C) 147,000 J
(D) the collision was not elastic and total linear (D) –147,000 J
momentum was not conserved (E) 220,500 J
(E) Cannot be determined
10. A block of mass m = 2 kg has an initial speed of 3 m/s
8. Three thin, uniform rods each of length L are arranged toward a second block. The second block, which starts 1
in the shape of an inverted U: m away from the first block, has a mass of 5 kg and an
initial speed of 2 m/s toward the first block. When the
blocks collide, they experience a perfectly inelastic col-
L lision. How long after the collision does it take for the
blocks to return to one of the starting positions?
2m (A) 0.55 s
(B) 0.75 s
(C) 0.95 s
(D) 1.05 s
(E) 1.25 s
L m m L
The two rods on the arms of the U each have mass m;
the third rod has mass 2m. How far below the midpoint
of the horizontal rod is the center of mass of this assem-
bly?
(A) L/8
(B) L/4
(C) 3L/8
(D) L/2
(E) 3L/4
2 1 2 | For more free content, visit PrincetonReview.com
Cracking the AP Physics C Exam
Section II: Free Response
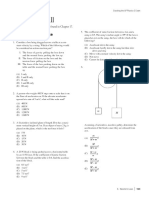
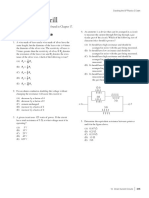
1. A steel ball of mass m is fastened to a light cord of length L and released when the cord is horizontal. At the bottom of its path,
the ball strikes a hard plastic block of mass M = 4m, initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic.
h
M
(a) Find the tension in the cord when the ball’s height above its lowest position is 12 L. Write your answer in terms of m and g.
(b) Find the speed of the block immediately after the collision.
(c) To what height h will the ball rebound after the collision?
2. A ballistic pendulum is a device that may be used to measure the muzzle speed of a bullet. It is composed of a wooden block
suspended from a horizontal support by cords attached at each end. A bullet is shot into the block, and as a result of the perfectly
inelastic impact, the block swings upward. Consider a bullet (mass m) with velocity v as it enters the block (mass M). The length
of the cords supporting the block each have length L. The maximum height to which the block swings upward after impact is
denoted by y, and the maximum horizontal displacement is denoted by x.
L L
m
v
M y
(a) In terms of m, M, g, and y, determine the speed v of the bullet.
(b) What fraction of the bullet’s original kinetic energy is lost as a result of the collision? What happens to the lost kinetic
energy?
(c) If y is very small (so that y2 can be neglected), determine the speed of the bullet in terms of m, M, g, x, and L.
(d) Once the block begins to swing, does the momentum of the block remain constant? Why or why not?
8. Linear Momentum | 2 1 3
Cracking the AP Physics C Exam
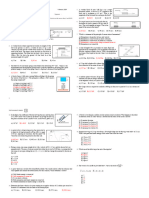
3. An object of mass m moves with velocity v toward a stationary object of the same mass. After their impact, the objects move off
in the directions shown in the following diagram:
v´1
1
m m
v =v θ1
1 1 2 θ2
v2 = 0
2
v´2
Before the collision After the collision
Assume that the collision is elastic.
(a) If K1 denotes the kinetic energy of Object 1 before the collision, what is the kinetic energy of this object after the colli-
sion? Write your answer in terms of K1 and θ1.
(b) What is the kinetic energy of Object 2 after the collision? Write your answer in terms of K1 and θ1.
(c) What is the relationship between θ1 and θ2?
2 1 4 | For more free content, visit PrincetonReview.com
You might also like
- Student's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Document2 pagesStudent's Name: Student ID:: A) MCQ Answer Sheet (5 M)Nam Anh Nguyễn HữuNo ratings yet
- Key Star MDCAT Crash Test # 1Document12 pagesKey Star MDCAT Crash Test # 1Ahmed Saud100% (1)
- WPE AssignmentDocument14 pagesWPE AssignmentSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- LAWS OF MOTION ASSIGNMENTDocument4 pagesLAWS OF MOTION ASSIGNMENTadv vsdvNo ratings yet
- Physics Bitsat 2010 Sample Test 2Document7 pagesPhysics Bitsat 2010 Sample Test 2Abhay Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Nso Class11 PDFDocument11 pagesNso Class11 PDFsanjayagrawal70-1No ratings yet
- Work Energy & PowerDocument7 pagesWork Energy & PowerMano PraveenNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS-IIT-JEE Advanced Revision PackageDocument220 pagesPHYSICS-IIT-JEE Advanced Revision PackageChaitanya Pandey100% (1)
- Work Power Energy QuestionsDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy QuestionsRakshit BiradarNo ratings yet
- Com and CollisionsDocument6 pagesCom and Collisionsarun2006No ratings yet
- 1718 WorkEnergy Practice Test KeyDocument4 pages1718 WorkEnergy Practice Test Keya jNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetDocument9 pagesAP Physics Chapter 9 Review SheetEAGLEFORCE06No ratings yet
- Tryout 1.0 IUP ITB - OctDocument7 pagesTryout 1.0 IUP ITB - Octsyafr.e.424No ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Assign - Physics PDFDocument26 pagesJEE Advanced Assign - Physics PDFaumoghNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam (90') Midterm Exam Model: A. B. C. D. EDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam (90') Midterm Exam Model: A. B. C. D. Eminh nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Physics Model 12Document10 pagesPhysics Model 12beabzkNo ratings yet
- NTSE Question Bank: ForceDocument4 pagesNTSE Question Bank: ForceAnonymous G5MnzqM2WvNo ratings yet
- BASARA GNANASARASWATHI CAMPUS MECHANICSDocument4 pagesBASARA GNANASARASWATHI CAMPUS MECHANICSNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Duration: 3Hrs: Hale Yearly Examination PhysicsDocument4 pagesDuration: 3Hrs: Hale Yearly Examination PhysicsVinodd.V 9eNo ratings yet
- 04 11 23 09 - 42 - 26 AmDocument4 pages04 11 23 09 - 42 - 26 Amjindalipad10No ratings yet
- JEE Mains 27 January Shift 1 Question Paper 2024 PDFDocument10 pagesJEE Mains 27 January Shift 1 Question Paper 2024 PDFamarjeet raiNo ratings yet
- Guided Revision: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 12 Q. (3 M (-1) )Document12 pagesGuided Revision: Section-I Single Correct Answer Type 12 Q. (3 M (-1) )Rahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Part 04 SET (320 - 323)Document2 pagesPart 04 SET (320 - 323)Baichitra MondalNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motions (Question Paper)Document6 pagesLaws of Motions (Question Paper)Vikas MeenaNo ratings yet
- Sucess Study Circle Monthly Test Sub-Physics (11) F.M-70 Tine 2hrsDocument4 pagesSucess Study Circle Monthly Test Sub-Physics (11) F.M-70 Tine 2hrsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument5 pagesNewton's LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Mu M+M Mu M+M Mu M M Mu M M: Topics Covered Physics: Kinemtics, Laws of Motion, Work Power EnergyDocument6 pagesMu M+M Mu M+M Mu M M Mu M M: Topics Covered Physics: Kinemtics, Laws of Motion, Work Power EnergyRohit DewanNo ratings yet
- Eamcet '13 PDFDocument44 pagesEamcet '13 PDFAmaan YousufNo ratings yet
- 1575286840Document12 pages1575286840Rloofy namiNo ratings yet
- Assignment & Previous Years' Questions: 2 3 4 X T T TDocument12 pagesAssignment & Previous Years' Questions: 2 3 4 X T T TAshi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- BAHUBALI Test - 01 QuestionsDocument18 pagesBAHUBALI Test - 01 QuestionsSiddhant RaiNo ratings yet
- IIT/AIIMS SCREENING TEST PHYSICS + CHEMISTRY + MATHEMATICSDocument8 pagesIIT/AIIMS SCREENING TEST PHYSICS + CHEMISTRY + MATHEMATICSb productiveNo ratings yet
- Booklet-A_cvplarDocument2 pagesBooklet-A_cvplarkral oyuncuNo ratings yet
- Jee Mains Level: PHYSICS - Work Energy and PowerDocument8 pagesJee Mains Level: PHYSICS - Work Energy and PowerAnju MohtaNo ratings yet
- BITSAT Solved Paper 2017 PDFDocument28 pagesBITSAT Solved Paper 2017 PDFAjkNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy Sindh Academy McqsAnusha HussainNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion - P-SSDocument2 pagesCircular Motion - P-SSniharika dadiNo ratings yet
- 05 - Laws of MotionDocument3 pages05 - Laws of MotionMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- ALPS 2310 Physics AssignmentDocument17 pagesALPS 2310 Physics AssignmentAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 12Document16 pagesWorksheet 12Ali MalikNo ratings yet
- Chapter (1) Revision QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter (1) Revision Questionssosoayman484No ratings yet
- Intso Stso Physics Class Viii Force & Pressure Worksheet - 2Document3 pagesIntso Stso Physics Class Viii Force & Pressure Worksheet - 2srisubhash03No ratings yet
- EXERCISE 81 AND 82 ON WORK AND ENERGYDocument44 pagesEXERCISE 81 AND 82 ON WORK AND ENERGYmynameis 1609No ratings yet
- Vibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedDocument3 pagesVibrant Academy: (India) Private LimitedShashaank JainNo ratings yet
- Advanced Revision Sheet: PhysicsDocument9 pagesAdvanced Revision Sheet: PhysicsPranav JoshiNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion Advanced Level Problems For IIT-JEEDocument5 pagesLaws of Motion Advanced Level Problems For IIT-JEEEr. Vineet Loomba (IIT Roorkee)89% (9)
- PHY231 Section 2, Form A March 22, 2012: S W S W TsDocument6 pagesPHY231 Section 2, Form A March 22, 2012: S W S W TsAbhirami Novel RajNo ratings yet
- Part Test 7 PCMDocument8 pagesPart Test 7 PCMpratikshaNo ratings yet
- KETS Topic-3 MDCAT Practice PDFDocument16 pagesKETS Topic-3 MDCAT Practice PDFzain ali100% (2)
- 3 Work-Energy PDFDocument9 pages3 Work-Energy PDFQwertyNo ratings yet
- Physics Model Examination For Grade 12Document9 pagesPhysics Model Examination For Grade 12biqilaadengNo ratings yet
- IIT (M+A) & JEE MAINS ONLY - Diwali Assignment - XIIDocument73 pagesIIT (M+A) & JEE MAINS ONLY - Diwali Assignment - XIIPremesh the greatNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocument7 pagesUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNo ratings yet
- LQuiz (TOV1) # 14 (Eng)Document4 pagesLQuiz (TOV1) # 14 (Eng)PkrNo ratings yet
- Physics 105 Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesPhysics 105 Exam ReviewjessieNo ratings yet
- DPYQ NEET Level Practice Test-1 for JEE Main & NEET AspirantsDocument6 pagesDPYQ NEET Level Practice Test-1 for JEE Main & NEET Aspirantsairs primeNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Question - Paper BitsatDocument15 pages2021 - Question - Paper BitsatNitisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics by Mista SirDocument5 pagesPhysics by Mista SirSatish PatelNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 11JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10Document3 pagesWorksheet 10JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 13Document4 pagesWorksheet 13JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- CH15 Oscillatory Motion and WavesDocument5 pagesCH15 Oscillatory Motion and WavesJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 14Document4 pagesWorksheet 14JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 15Document5 pagesWorksheet 15JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Laws of GravitationDocument3 pagesLaws of GravitationJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic InductionJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 16 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 16 PDFAlina Smagutta0% (1)
- The Velocity-Time Graphs Represent The Motion of Two Cars, Car A and Car B. Justify AllDocument5 pagesThe Velocity-Time Graphs Represent The Motion of Two Cars, Car A and Car B. Justify AllJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4-SolutionsDocument2 pagesQuiz 4-SolutionsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 17Document2 pagesWorksheet 17JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Cracking the AP Physics C ExamDocument5 pagesCracking the AP Physics C ExamJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Drill: Section I: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 13 Drill: Section I: Multiple ChoiceRadhika C.No ratings yet
- Direct Current CircuitsDocument4 pagesDirect Current CircuitsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument4 pagesKinematicsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Ch 8 Review: Circular Motion, Gravity, Work ProblemsDocument9 pagesCh 8 Review: Circular Motion, Gravity, Work ProblemsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument5 pagesNewton's LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Cracking the AP Physics C Exam Chapter 7 DrillDocument5 pagesCracking the AP Physics C Exam Chapter 7 DrillJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions VectorsDocument5 pagesChapter Questions VectorsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Work Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesChapter Questions Work Energy and PowerJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions OscillationsDocument8 pagesChapter Questions OscillationsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Newton S LawsDocument8 pagesChapter Questions Newton S LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Wave Review Questions and Doppler EffectDocument7 pagesChapter 10 Wave Review Questions and Doppler EffectJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions KinematicsDocument7 pagesChapter Questions KinematicsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Linear MomentumDocument6 pagesChapter Questions Linear MomentumJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- 2021 Book FibreReinforcedConcreteImproveDocument1,180 pages2021 Book FibreReinforcedConcreteImproveafmesamNo ratings yet
- VICAT TEST REPORTDocument7 pagesVICAT TEST REPORTKhalid MohammadNo ratings yet
- IB Physics 7e AnswersDocument171 pagesIB Physics 7e Answersღ꧁Lizzy X Roxiie꧂ღ100% (1)
- 1st Progress Report - Mert KarakaşDocument5 pages1st Progress Report - Mert KarakaşMNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Circuit Implementation of Demyelinated Human PDFDocument95 pagesEquivalent Circuit Implementation of Demyelinated Human PDFAndres PosadaNo ratings yet
- Astm A 322 - 07Document4 pagesAstm A 322 - 07Luis MendozaNo ratings yet
- Vernier CalipersDocument6 pagesVernier CalipersRani JahnaviNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelAshfaaq SkadamNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Analysis of Goalkeeper Punt Kicks Based on Effort LevelDocument8 pagesKinematic Analysis of Goalkeeper Punt Kicks Based on Effort Levelحسين جاموسNo ratings yet
- Engineering Experience - Example 1 - The P.Eng. ApplicantDocument26 pagesEngineering Experience - Example 1 - The P.Eng. Applicantgökhan keserNo ratings yet
- Engineering BooksDocument2 pagesEngineering BooksBen ChengNo ratings yet
- The 2020 Magnetism Roadmap: Journal of Physics D: Applied PhysicsDocument45 pagesThe 2020 Magnetism Roadmap: Journal of Physics D: Applied PhysicsFrancisco EstrellaNo ratings yet
- GIET UNIVERSITY PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS EXAMDocument2 pagesGIET UNIVERSITY PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS EXAMPritesh RayaguruNo ratings yet
- Ansaldo List of Cleaning AgentDocument2 pagesAnsaldo List of Cleaning AgentEDB100% (1)
- 6.hydraulic Structure Lab ManualDocument57 pages6.hydraulic Structure Lab ManualAmmar Ahmad EED100% (2)
- Sampling and QuantizationDocument7 pagesSampling and QuantizationShravani KodeNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Flow of Water Through SoilsDocument28 pages1.3 Flow of Water Through SoilsRegine DoronilaNo ratings yet
- Guide to Solving Differential EquationsDocument8 pagesGuide to Solving Differential Equationsسعد احمد حميديNo ratings yet
- Nippon Steel Technical ReportDocument8 pagesNippon Steel Technical ReportRumman Ul AhsanNo ratings yet
- Mud Logger # 10Document8 pagesMud Logger # 10Aiham AltayehNo ratings yet
- Setting Out ChapterDocument11 pagesSetting Out ChapterOusman JarjuNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Kamin Kain SiriwatwetchakulNo ratings yet
- 4.7.5 Walls: CK Yk CKDocument2 pages4.7.5 Walls: CK Yk CKBertin BakariNo ratings yet
- Stas 8600-79Document2 pagesStas 8600-79joseNo ratings yet
- Ugrd-Nsci6100-2016s Calculus-Based Physics 1 Midterm q2Document13 pagesUgrd-Nsci6100-2016s Calculus-Based Physics 1 Midterm q2Leo Jade AbiertasNo ratings yet
- n65619 Solutionsheet Opacimeter E WebDocument2 pagesn65619 Solutionsheet Opacimeter E WebRichardNo ratings yet
- Free Surface Modeling Methods - CFD-101 - FLOW-3DDocument7 pagesFree Surface Modeling Methods - CFD-101 - FLOW-3Dcopdeposu2071No ratings yet
- Revision - Ray and Wave OpticsDocument20 pagesRevision - Ray and Wave Opticsshailendrasinghbhadoria7389No ratings yet
- Test SessionDocument3 pagesTest SessionAMER MEHMOODNo ratings yet
- Bulk and Surface Acoustic Waves - Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications (Guigen Zhang) (Z-Library)Document361 pagesBulk and Surface Acoustic Waves - Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications (Guigen Zhang) (Z-Library)ostomaconsultingNo ratings yet