Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reference B - 8-Point Socioeconomic Agenda
Uploaded by
Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reference B - 8-Point Socioeconomic Agenda
Uploaded by
Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Annex A
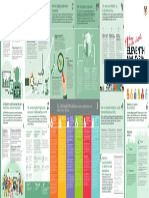
8-POINT SOCIOECONOMIC AGENDA
The overall goal is to reinvigorate job creation and poverty reduction by steering the economy
back to its high-growth path, and more importantly, through economic transformation for a
prosperous, inclusive and resilient society.
Although many uncertainties abound covering health, recovering learning losses from COVID-19,
environmental, and global trade and finance trends, the challenges are not insurmountable. The
reforms laid down by past administrations have paved pathways for the incoming administration
to pursue opportunities for accelerating economic transformation. Such reforms can be
deepened to build stronger foundations for a more robust, more inclusive, and more resilient
Philippine society.
The Philippine Development Plan 2023-2028 will focus on an 8-point agenda, where a number of
strategies are intended to address the immediate issues of inflation, socioeconomic scarring and
low income.
Amid continuing inflationary pressures from both global and domestic sources, prices of basic
goods and services must be kept within the ordinary Filipino’s reach. To arrest inflation,
constraints in food, energy, and transportation and logistics sectors must be holistically
addressed to ensure that there is enough supply of basic goods and services that is affordable
and accessible to all. Medium- and longer-term strategies to ensure food and energy security will
also be implemented.
To reduce vulnerability and remedy the scars from COVID-19, the government will continue to
implement risk-managed interventions to fully reopen the economy and ensure the unimpeded
and adequate delivery of social services, such as health, education, and social protection.
Over the medium term, the agenda will focus on creating more JOBS, quality JOBS, and green
JOBS. There will be more job opportunities for Filipinos. Productivity-enhancing investments will
be promoted while exercising prudence in fiscal management. Government will implement a
more holistic Build, Build, Build program, including strategic utilization of public private
partnerships (PPPs), supporting LGUs to increase infrastructure spending more effectively, and
upgrading of the country’s internet infrastructure. There will be avenues for re-tooling and re-
skilling, and effective job facilitation processes to increase the employability of jobseekers.
Finally, special attention will be given to the development of sustainable technologies to create
green jobs and establish livable communities.
Draft Planning Guidelines for the formulation of PDP 2023-2028 as of Sept 16
Page 12 of 30
Economic Transformation for a Prosperous, Inclusive and Resilient Society
In our continuing pursuit of AmBisyon Natin 2040 of a matatag, maginhawa at panatag na
buhay para sa lahat, the government will work with all of society to realize economic
transformation for a prosperous, inclusive and resilient society. The economy is targeted to grow
by 6.5 to 8 percent through 2028. Unemployment rate will be reduced from about 8 percent in
2021 to a range of 4 to 5 percent in 2028. To reflect the increase in quality jobs, the percentage
of wage and salaried workers in private establishments to total employed workers will increase
from 48 percent in 2021 to a range of 53 to 55 percent in 2028. Poverty is targeted to decline to
9 percent of population by 2028.
8-point agenda
1. Protect purchasing power and mitigate socioeconomic scarring
▪ Ensure Food Security. Ensure availability, affordability, accessibility of food in the
country amid the looming global food shortages. Prioritize spending on productivity-
enhancing measures, research and development, and efficient marketing and
distribution of the produce. Rationalize subsidies and provide targeted nutritional
support to pregnant women and children under three years old.
▪ Reduce Transport and Logistics Cost. Streamline regulatory processes to facilitate
seamless international trade and domestic transactions, and hasten the movement of
goods from ports and warehouses to wet markets and end consumers. Implement a
program to bring down the cost of transporting food produce from the farm to the
market.
Draft Planning Guidelines for the formulation of PDP 2023-2028 as of Sept 16
Page 13 of 30
▪ Reduce Energy Cost to Families. To conserve energy, implement alternative/ flexible
work arrangements that reduce the need to travel where these have been proven to be
effective and productivity-enhancing. Encourage the use of active transport and other
alternative modes of transportation by improving and creating structures and
regulations for safety, convenience and mobility for pedestrians and bicyclists.
2. Reduce vulnerability and mitigate scarring from the COVID-19 pandemic
▪ Tackle Health. Ramp up vaccination and uptake of boosters for the elderly and
vulnerable populations. Maintain compliance with minimum public health standards to
enable safe reopening of the economy and schools. Strengthen surveillance and
laboratory capacity to enable the prompt identification and response to outbreaks.
Resume implementation of reforms and investments enshrined in the Universal Health
Act.
▪ Strengthen Social Protection. Strengthen the core functions of poverty reduction and
human capital investment of the Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program (4Ps). Expedite
the adoption of the National ID system (PhilSys) and facilitate digital transformation of
social protection systems to allow for a more efficient, targeted, and equitable delivery
of social programs. Strengthen social protection delivery to be more adaptive and
responsive to needs, by streamlining contingency financing mechanisms, establishing a
dynamic social registry, and defining business process for national and local
governments with emergency cash transfers. Rationalize the existing programs to
ensure that the objectives of promotion, transformation, prevention and protection of
well-being are achieved.
▪ Address Learning Losses. Quickly and safely reopen classes at all levels. Improve
curriculum to focus on foundational skills, and provide tutorial and remedial classes to
address learning gaps arising from the pandemic. Expand the Alternative Learning
System to support dropouts. Support teachers to improve pedagogical competences,
including the use of digital learning platforms, and subject knowledge. Through the
Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA), promote reskilling and
upskilling programs for displaced workers and out-of-school youth. Improve school
governance at all levels. Enhance and modify the Government Internship Program to
provide opportunities for new graduates to gain shop, laboratory or internship
experiences.
3. Ensure sound macroeconomic fundamentals
▪ Enhance Bureaucratic Efficiency and sound fiscal management. Facilitate the
transformation and digitalization of government processes, records and databases, and
ensure full functionality with the PhilSys. Implement a right-sizing program for the
bureaucracy particularly on functions that have been devolved following the Mandanas-
Garcia ruling. Implement tax administration reforms to increase revenue collection.
Realign expenditure priorities and improve spending efficiency to immediately address
Draft Planning Guidelines for the formulation of PDP 2023-2028 as of Sept 16
Page 14 of 30
the economic scarring arising from the effects of Covid-19 and be prepared for future
shocks. Adjust taxes on non-essential and luxury goods and services. Focus government
resources on health, education, infrastructure, and social protection.
▪ Ensure a resilient and innovative financial sector. Adopt regulatory frameworks and
platforms for digital finance to enhance the scope, scale and reach of digital financial
services. Pursue compelling use cases for digital payments, alongside expanded digital
financial literacy programs, more robust consumer protection policies, and enhanced
ability of microfinance institutions to provide digital financial services. Support reforms
in the domestic financial market through innovative solutions such as the establishment
of digital supply chain financing, credit risk database, and online collateral registry.
4. Create more jobs
▪ Promote trade and investments. Aggressively promote the country as an investment
destination, capitalizing on the Corporate Recovery and Tax Incentives for Enterprise
(CREATE) Law and amended economic liberalization laws (i.e., Public Service Act, Retail
Trade Liberalization Act, Foreign Investment Act). Reinvigorate manufacturing,
including agri-food processing, for more and high-quality jobs. Utilize and fully support
ecozones as an agglomeration strategy, especially to bring in strategic industries (high-
tech manufacturing, health and medical care, emerging tech, among others) and
promote growth outside NCR. Continue to improve government regulatory processes,
in both national and local government units.
▪ Improve Infrastructure. Continue implementation of Build, Build, Build projects that are
near completion and those with firm funding commitments. Refocus Build, Build, Build
towards infrastructure projects that strengthen industry linkages, expand physical and
digital connectivity, improve access of the poor to basic services including water supply
and sanitation, public transportation, affordable energy and flood protection
infrastructure, and improve climate resilience. In recognition of the tighter fiscal space,
encourage solicited PPPs. Invest in smart social and economic infrastructure. Expand
equitable internet connectivity for education institutions at all levels.
▪ Achieve Energy Security. Pursue an energy transition and development program aimed
at achieving a clean, reliable, cost-effective, and secure mix of energy sources.
Encourage continued innovation and investment in the energy sector.
5. Create quality jobs
▪ Increase Employability. Improve the quality and relevance of education and provide
opportunities for life-long learning and options to obtain micro-credentials. Enhance
skills development to ensure that there is a critical mass of skilled workforce, especially
for strategic industries. Improve job facilitation programs. Strengthen linkages between
industry, business and training institutions for a more efficient labor market. Ensure
Draft Planning Guidelines for the formulation of PDP 2023-2028 as of Sept 16
Page 15 of 30
access to social insurance and worker protection (cum labor regulation) as well as safe
and productive overseas migration.
▪ Encourage R&D and Innovation. Encourage R&D and innovation especially in products
and processes that promote linkages between and among agriculture, industry and
services. Create and expand a research network that will enable collaboration among
higher education institutions, research institutions, and local industries particularly for
enhancing productivity. Encourage greater innovation in the food sector to produce
higher value, but affordable products – high-nutrition, immune-boosting, even
therapeutic food products that can serve the domestic and international markets.
Sustain improvement of business environment, financial inclusion, competition, to
encourage entrepreneurship and innovation. Develop technologies that contribute to
climate action, and those that mitigate and adapt to climate change impact.
▪ Enhance the Digital Economy. Implement policies that enable greater private-sector
investment in the country’s internet infrastructure. Level the playing field in
telecommunications and prohibit exclusivity dealings for internet services to promote
competition in the sector. Facilitate digital payments, promote digital financial services,
adoption of PhilSys by service providers, enable market regulations for building trust
and data transfers to provide greater opportunities for individuals and MSMEs.
6. Create green jobs
▪ Purse a Green and Blue Economy. Introduce risk-based budgeting and fiscal risk
monitoring; strengthen market for insurance against catastrophe; protect farmers
against climate extremes by reforming agricultural insurance; and implement public
asset insurance. Expand green (and blue) financing to a broader set of businesses.
Introduce carbon pricing mechanisms in the medium term. Expedite the
operationalization of the Green Jobs Act and its IRR by establishing the green jobs
certification system and incentive schemes and developing the green work force with
skills accreditation. Implement the Philippine Action Plan for Sustainable Consumption
and Production.
▪ Establish Livable and Sustainable Communities. Develop sustainable livable and
affordable cities and townships where residents enjoy a comfortable and secure life,
resilient to climate change and disasters. Promote green public works and include a
green score as part of LGU performance indicators. Given the limited resources,
incentivize LGUs to focus more on climate-friendly projects in: i) electric vehicles and
public transport and active transport development; (ii) sustainable tourism, (iii) nature-
based solutions (coastal habitat restoration and biodiversity protection); (iv) energy
efficiency (street lighting, public building retrofits, green buildings); and (v) water
security.
Draft Planning Guidelines for the formulation of PDP 2023-2028 as of Sept 16
Page 16 of 30
7. Uphold public order and safety, peace and security. Develop and pursue an integrated,
transparent, and human rights-based peace and security strategy to ensure that
socioeconomic efforts are implemented without disruptions. Address and respond to all
forms of internal (e.g., criminality, local communist armed conflict, other threats to public
safety), external (e.g., threats to territorial integrity and sovereignty, transnational crimes),
and non-traditional threats (e.g., cybercrime, health emergencies). Strengthen national and
local institutions and empower communities to address these threats to security and public
safety. Strengthen intergovernmental relations with the Bangsamoro government and
ensure smooth transition towards a fully functioning autonomous government. Expedite the
modernization and capability enhancement of the armed forces and other security sector
agencies to uphold our sovereignty and territorial integrity, ensure the safety of the public,
and protect critical assets including digital infrastructures. Strengthen international
engagements and pursue diplomatic measures to advance the country’s interests and
support international development objectives particularly in the areas of regional peace and
stability, maritime cooperation, humanitarian response, border control and management,
and transnational crime, among others.
8. Ensure a level playing field.
▪ Strengthen market competition. Enhance whole-of-government effort to implement the
National Competition Policy, specifically to address abuse of dominant position, prevent
anti-competitive mergers and acquisitions, and penalize other anti-competitive practices.
Review mandates of GOCCs to ensure competitive neutrality between state-owned and
private businesses. Sustain research and development efforts to identify competition-
related issues in priority sectors such as telecommunications, energy, food, and
agriculture.
▪ Reduce barriers to entry and limits to entrepreneurship. Expedite efforts to automate
and streamline regulatory and licensing processes, and establish the Philippine Ease of
Doing Business Reporting System. Issue and implement the National Policy on Regulatory
Management System to improve the quality of regulations and to foster an environment
that would allow enterprises of any form and size to easily and fairly participate and
compete in the market. Expedite the operationalization of recently-enacted economic
liberalization laws (i.e., Public Service Act, Retail Trade Liberalization Act, and Foreign
Investment Act).
Draft Planning Guidelines for the formulation of PDP 2023-2028 as of Sept 16
Page 17 of 30
You might also like
- Programs - Projects For Philippine Socio - Economic DevelopmentDocument7 pagesPrograms - Projects For Philippine Socio - Economic Developmentdjm070376No ratings yet
- Supporting Post-COVID-19 Economic Recovery in Southeast AsiaFrom EverandSupporting Post-COVID-19 Economic Recovery in Southeast AsiaNo ratings yet
- Updated Philippine Housing Socio - Economic Goals.Document8 pagesUpdated Philippine Housing Socio - Economic Goals.Christian VinluanNo ratings yet
- Harnessing the Potential of Big Data in Post-Pandemic Southeast AsiaFrom EverandHarnessing the Potential of Big Data in Post-Pandemic Southeast AsiaNo ratings yet
- Tingnan Mo Nagbabago Na Ang LahatDocument6 pagesTingnan Mo Nagbabago Na Ang LahatpjmrtnzNo ratings yet
- PDP 2023 2028 Briefer 1Document13 pagesPDP 2023 2028 Briefer 1Joshua Gonzales CorpuzNo ratings yet
- National PlanningDocument13 pagesNational PlanningppayonggNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Domestic Resource Mobilization in Southeast AsiaFrom EverandStrengthening Domestic Resource Mobilization in Southeast AsiaNo ratings yet
- Report On PDPDocument23 pagesReport On PDPfroilan copilingNo ratings yet
- PDP 2023 2028 BrieferDocument10 pagesPDP 2023 2028 BrieferKanra Mendoza100% (1)
- Transforming Towards a High-Income People's Republic of China: Challenges and RecommendationsFrom EverandTransforming Towards a High-Income People's Republic of China: Challenges and RecommendationsNo ratings yet
- 9 1Document9 pages9 1Xhyrich IsletaNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY of The Article A Reform Agenda by Miftah IsmailDocument15 pagesSUMMARY of The Article A Reform Agenda by Miftah IsmailPalwasha SheikhNo ratings yet
- Philippine Administrative ReformsDocument58 pagesPhilippine Administrative ReformsMarvin Cabantac100% (2)
- ETC Document FINAL 8 July 2020Document31 pagesETC Document FINAL 8 July 2020janet71% (7)
- 10-Point Socioeconomic Agenda of The Duterte Administration: UsualDocument2 pages10-Point Socioeconomic Agenda of The Duterte Administration: UsualchenlyNo ratings yet
- ADS514Document4 pagesADS514diyanah khalidNo ratings yet
- DBM Citizens Charter As of March 31 2021Document204 pagesDBM Citizens Charter As of March 31 2021Michael LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Buenos Aires Leaders DeclarationDocument40 pagesBuenos Aires Leaders DeclarationMelina RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Documento G20Document8 pagesDocumento G20EL DESTAPENo ratings yet
- Programs-Projects For Philippine Socio Economic DevelopmentDocument27 pagesPrograms-Projects For Philippine Socio Economic Developmentdjm070376100% (1)
- PDP 2023 2028 PrimerDocument9 pagesPDP 2023 2028 Primerlynda_christineNo ratings yet
- Dayalo Workshop #2Document7 pagesDayalo Workshop #2Jonathan OcheNo ratings yet
- Socioeconomic AgendaDocument3 pagesSocioeconomic AgendappayonggNo ratings yet
- PDP 2017-2022 PDFDocument62 pagesPDP 2017-2022 PDFGeorgie IbabaoNo ratings yet
- Apec 2022 MsmesDocument18 pagesApec 2022 MsmesMichelle PalNo ratings yet
- 10+0 Point Agenda of President Rodrigo DuterteDocument20 pages10+0 Point Agenda of President Rodrigo DuterteYkskciv Ced Prince100% (1)
- Regional Development Plan CAR 2017-2022 Chapter 1Document6 pagesRegional Development Plan CAR 2017-2022 Chapter 1Andrew EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - PRRD GDP PerformanceDocument6 pagesCase Study - PRRD GDP Performancekasugabarangay700No ratings yet
- City Development StrategyDocument2 pagesCity Development StrategyPlinky AgumNo ratings yet
- Power of Econimics and Financing of Education in PakistanDocument30 pagesPower of Econimics and Financing of Education in PakistanAli JadoonNo ratings yet
- Transforming Pakistan's Economic Landscape A Comprehensive ODocument8 pagesTransforming Pakistan's Economic Landscape A Comprehensive Oarbelsb3No ratings yet
- 10+0 Point Socio-Economic Agenda of President DuterteDocument4 pages10+0 Point Socio-Economic Agenda of President DuterteYkskciv Ced PrinceNo ratings yet
- Formulating and Implementing A Successful Plan For KenyaDocument8 pagesFormulating and Implementing A Successful Plan For KenyaMARVIN GROUPNo ratings yet
- PWC Restart MalaysiaDocument35 pagesPWC Restart MalaysiaMohamad Hassaidi Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- 04 Overview 5 Year Plan2Document18 pages04 Overview 5 Year Plan2Zuhair A. RehmanNo ratings yet
- Econ 225Document4 pagesEcon 225emmalyn melgoNo ratings yet
- Guiding Principles of Sound Management Fiscal SystemsDocument32 pagesGuiding Principles of Sound Management Fiscal SystemsMark Jayson Yamson PinedaNo ratings yet
- Public Finance Free EnterpriseDocument2 pagesPublic Finance Free EnterpriseJennifer RomaNo ratings yet
- National Colloquium Pre-Budget Expectation 2023 (10 Jan)Document2 pagesNational Colloquium Pre-Budget Expectation 2023 (10 Jan)Harshit SinglaNo ratings yet
- The South African Economic Reconstruction and Recovery Plan EISEID Cluster October 7, 2020Document48 pagesThe South African Economic Reconstruction and Recovery Plan EISEID Cluster October 7, 2020CityPressNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Development Programs For MSMEs by NEDADocument11 pagesUnit 5 Development Programs For MSMEs by NEDARena Mae BalmesNo ratings yet
- Economics AssignmentDocument4 pagesEconomics Assignment768balochNo ratings yet
- Overview of Botswana'S Development Strategy/Plan: National Workshop On The Vienna Programme of ActionDocument26 pagesOverview of Botswana'S Development Strategy/Plan: National Workshop On The Vienna Programme of ActionDidier D. Boko-hayaNo ratings yet
- Budget Speech enDocument55 pagesBudget Speech enBrant XuNo ratings yet
- Economic DevelopmentDocument26 pagesEconomic DevelopmentClarissa Leilany ColomaNo ratings yet
- SER 2021 Chapter 01Document16 pagesSER 2021 Chapter 01TV BOX MXQ PRONo ratings yet
- Tutorials Guiding AnswersDocument7 pagesTutorials Guiding AnswersHitesh MaharajNo ratings yet
- Rmk11 11mp Brochure BiDocument2 pagesRmk11 11mp Brochure BiZulkifli Zainal RampakNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Temario, Ray CrisDocument5 pagesActivity 1 - Temario, Ray CrisRay Cris TemarioNo ratings yet
- Economic DevelopmentDocument12 pagesEconomic Developmentemmalyn melgoNo ratings yet
- 2002 Samson Van NiekerkDocument27 pages2002 Samson Van NiekerklecaracalNo ratings yet
- Development: Small-Scale AgricultureDocument18 pagesDevelopment: Small-Scale AgricultureSafrian Adam FariziNo ratings yet
- National Development PolicyDocument4 pagesNational Development PolicyHafiz NasriNo ratings yet
- Phil Devt Plan 2017 - 2022Document29 pagesPhil Devt Plan 2017 - 2022Zheerica Ella Del CarmenNo ratings yet
- Economic and Monetary ReviewDocument133 pagesEconomic and Monetary ReviewAravindAgueroNo ratings yet
- Environmental Awareness Through Forum THDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Awareness Through Forum THLimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- 300 AI Tools For Digital SpartansDocument40 pages300 AI Tools For Digital SpartansLimuel Richa Paghubasan Trangia100% (2)
- 02B Design of Bridges FE Training 101718Document88 pages02B Design of Bridges FE Training 101718Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Rdip-2023-2028-Launionif 2022Document39 pagesRdip-2023-2028-Launionif 2022Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- PNB PROPERTIES READY FOR SALE As of OCTOBER 25 2022Document34 pagesPNB PROPERTIES READY FOR SALE As of OCTOBER 25 2022Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- COE 1st Sem Subjects 2021-2022Document10 pagesCOE 1st Sem Subjects 2021-2022Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Descriptive Words 1Document1 pageGrammar Descriptive Words 1Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Compressive Strengths of Concrete Hollow Blocks Using Rice Husk AshDocument12 pagesCompressive Strengths of Concrete Hollow Blocks Using Rice Husk AshLimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Department of Public Works and Highways: Office of The Regional DirectorDocument1 pageDepartment of Public Works and Highways: Office of The Regional DirectorLimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Basics of PlanningDocument23 pages1 Basics of PlanningLimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- SurveyNoteReduction05Feb14 PIADocument35 pagesSurveyNoteReduction05Feb14 PIALimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Speaker: Engr. Merlito Castor Catolico: PRC Accredited Speaker No. 071 Real Estate Broker/Appraiser /consultantDocument58 pagesSpeaker: Engr. Merlito Castor Catolico: PRC Accredited Speaker No. 071 Real Estate Broker/Appraiser /consultantLimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- LE Traverse Calculation Release 4 v0719Document280 pagesLE Traverse Calculation Release 4 v0719Limuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Enter Co-Ordinates To Get Bearing of Lines Co-Ordinate To Bearing Calculation FormulaDocument5 pagesEnter Co-Ordinates To Get Bearing of Lines Co-Ordinate To Bearing Calculation FormulaLimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- MSE Policy Review in Nepal Current Reform ProcessDocument20 pagesMSE Policy Review in Nepal Current Reform ProcessRaj K AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Le Nouveau Systeme Francais de Protectio PDFDocument5 pagesLe Nouveau Systeme Francais de Protectio PDFAmelNesrineNo ratings yet
- RA 9994 Numbering 1st Page Revised1 Last RevisedDocument12 pagesRA 9994 Numbering 1st Page Revised1 Last RevisedKaren Hazel ArcigaNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia National Social ProtectionDocument31 pagesEthiopia National Social ProtectionMelatNo ratings yet
- Global Study On Child Poverty and Disparities: The Case of The PhilippinesDocument255 pagesGlobal Study On Child Poverty and Disparities: The Case of The PhilippinesPauline Sanchez100% (1)
- ShengDocument47 pagesShengJanice LopecilloNo ratings yet
- PDF Social NigeriaDocument80 pagesPDF Social NigeriaKhadija RvNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and PovertyDocument49 pagesClimate Change and Povertykshahyd05No ratings yet
- Boys and Girls in EthiopiaDocument130 pagesBoys and Girls in EthiopiaMark Ebrahim100% (1)
- Learning Task-No. 2-Documentary Film - Stories From The Hidden Worlds-PhilippinesDocument2 pagesLearning Task-No. 2-Documentary Film - Stories From The Hidden Worlds-PhilippinesGarhole MLNo ratings yet
- Welfare Regimes and Social Policy: A Review of The Role of Labour and Employment by James Heintz and Francie LundDocument40 pagesWelfare Regimes and Social Policy: A Review of The Role of Labour and Employment by James Heintz and Francie LundUnited Nations Research Institute for Social DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- ILO-Unicef: Child Labor in PH Prevalent, Reaches 3.2 MDocument3 pagesILO-Unicef: Child Labor in PH Prevalent, Reaches 3.2 Mnut_crackreNo ratings yet
- Europe 2020 Book Social EUDocument282 pagesEurope 2020 Book Social EUCristina MelnicNo ratings yet
- Better Cities After COVID-19: Transformative Urban Recovery in The Global SouthDocument28 pagesBetter Cities After COVID-19: Transformative Urban Recovery in The Global SouthAliya RahmanNo ratings yet
- PCW Neda DBM JC 2012 01Document49 pagesPCW Neda DBM JC 2012 01Mark Emann Baliza Magas100% (1)
- 3 NEDA Alignment of Plan and Investment Program Within The Context of EO 138Document34 pages3 NEDA Alignment of Plan and Investment Program Within The Context of EO 138Alicia GraciadasNo ratings yet
- President Michael Sata's Speech To The Second Session of The Eleventh National AssemblyDocument76 pagesPresident Michael Sata's Speech To The Second Session of The Eleventh National AssemblyPMRCZAMBIANo ratings yet
- Poverty: Poverty Is Not A Consequence of Limited Global Resources, But Political and EconomicDocument10 pagesPoverty: Poverty Is Not A Consequence of Limited Global Resources, But Political and EconomicSidra ShehzadiNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of "Social Safety Nets": Journal of Asian Economics November 2008Document9 pagesThe Meaning of "Social Safety Nets": Journal of Asian Economics November 2008yunus alfiansahNo ratings yet
- Philippines Social Protection Review and AssessmentDocument97 pagesPhilippines Social Protection Review and AssessmentBernice MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assessment MultisectorDocument92 pagesAssessment MultisectorEngkhalid AlghaziNo ratings yet
- Combating Trafficking of Women and Children in South Asia: Regional Synthesis Paper For Bangladesh, India, and NepalDocument306 pagesCombating Trafficking of Women and Children in South Asia: Regional Synthesis Paper For Bangladesh, India, and NepalAsian Development BankNo ratings yet
- NCDDP-AF Operations ManualDocument79 pagesNCDDP-AF Operations ManualMichelle Valledor80% (5)
- GNDDocument16 pagesGNDDEAN TENDEKAI CHIKOWONo ratings yet
- Magna Carta For Women - Republic Act No. 9710Document27 pagesMagna Carta For Women - Republic Act No. 9710libralanxaustralisNo ratings yet
- Undesa PD 2023 Wsr-FullreportDocument161 pagesUndesa PD 2023 Wsr-FullreportСофія ЯремчукNo ratings yet
- Report by Jamshid Sharipov and Muhammad DavronovDocument21 pagesReport by Jamshid Sharipov and Muhammad DavronovМухаммад БобоNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health and Safety PhilippinesDocument6 pagesOccupational Health and Safety PhilippinesIan CutinNo ratings yet
- The Atlas of Rural Marginalized Areas An PDFDocument368 pagesThe Atlas of Rural Marginalized Areas An PDFCristina MaruntuNo ratings yet
- Overcoming Social SegregationDocument13 pagesOvercoming Social SegregationmnardeyNo ratings yet
- The Black Girl's Guide to Financial Freedom: Build Wealth, Retire Early, and Live the Life of Your DreamsFrom EverandThe Black Girl's Guide to Financial Freedom: Build Wealth, Retire Early, and Live the Life of Your DreamsNo ratings yet
- Basic Python in Finance: How to Implement Financial Trading Strategies and Analysis using PythonFrom EverandBasic Python in Finance: How to Implement Financial Trading Strategies and Analysis using PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- How to Save Money: 100 Ways to Live a Frugal LifeFrom EverandHow to Save Money: 100 Ways to Live a Frugal LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Budget Management for Beginners: Proven Strategies to Revamp Business & Personal Finance Habits. Stop Living Paycheck to Paycheck, Get Out of Debt, and Save Money for Financial Freedom.From EverandBudget Management for Beginners: Proven Strategies to Revamp Business & Personal Finance Habits. Stop Living Paycheck to Paycheck, Get Out of Debt, and Save Money for Financial Freedom.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (91)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNo ratings yet
- You Need a Budget: The Proven System for Breaking the Paycheck-to-Paycheck Cycle, Getting Out of Debt, and Living the Life You WantFrom EverandYou Need a Budget: The Proven System for Breaking the Paycheck-to-Paycheck Cycle, Getting Out of Debt, and Living the Life You WantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (104)
- Swot analysis in 4 steps: How to use the SWOT matrix to make a difference in career and businessFrom EverandSwot analysis in 4 steps: How to use the SWOT matrix to make a difference in career and businessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Radically Simple Accounting: A Way Out of the Dark and Into the ProfitFrom EverandRadically Simple Accounting: A Way Out of the Dark and Into the ProfitRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Heart and Hustle: Use your passion. Build your brand. Achieve your dreams.From EverandHeart and Hustle: Use your passion. Build your brand. Achieve your dreams.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- CAPITAL: Vol. 1-3: Complete Edition - Including The Communist Manifesto, Wage-Labour and Capital, & Wages, Price and ProfitFrom EverandCAPITAL: Vol. 1-3: Complete Edition - Including The Communist Manifesto, Wage-Labour and Capital, & Wages, Price and ProfitRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- CDL Study Guide 2022-2023: Everything You Need to Pass Your Exam with Flying Colors on the First Try. Theory, Q&A, Explanations + 13 Interactive TestsFrom EverandCDL Study Guide 2022-2023: Everything You Need to Pass Your Exam with Flying Colors on the First Try. Theory, Q&A, Explanations + 13 Interactive TestsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Complete Strategy Guide to Day Trading for a Living in 2019: Revealing the Best Up-to-Date Forex, Options, Stock and Swing Trading Strategies of 2019 (Beginners Guide)From EverandThe Complete Strategy Guide to Day Trading for a Living in 2019: Revealing the Best Up-to-Date Forex, Options, Stock and Swing Trading Strategies of 2019 (Beginners Guide)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (34)
- Money Made Easy: How to Budget, Pay Off Debt, and Save MoneyFrom EverandMoney Made Easy: How to Budget, Pay Off Debt, and Save MoneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Money Mentor: How to Pay Off Your Mortgage in as Little as 7 Years Without Becoming a HermitFrom EverandThe Money Mentor: How to Pay Off Your Mortgage in as Little as 7 Years Without Becoming a HermitNo ratings yet
- Minding Your Own Business: A Common Sense Guide to Home Management and IndustryFrom EverandMinding Your Own Business: A Common Sense Guide to Home Management and IndustryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How To Budget And Manage Your Money In 7 Simple StepsFrom EverandHow To Budget And Manage Your Money In 7 Simple StepsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Personal Finance for Beginners - A Simple Guide to Take Control of Your Financial SituationFrom EverandPersonal Finance for Beginners - A Simple Guide to Take Control of Your Financial SituationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Money Management: An Essential Guide on How to Get out of Debt and Start Building Financial Wealth, Including Budgeting and Investing Tips, Ways to Save and Frugal Living IdeasFrom EverandMoney Management: An Essential Guide on How to Get out of Debt and Start Building Financial Wealth, Including Budgeting and Investing Tips, Ways to Save and Frugal Living IdeasRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Best Team Wins: The New Science of High PerformanceFrom EverandThe Best Team Wins: The New Science of High PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (31)
- Bookkeeping: An Essential Guide to Bookkeeping for Beginners along with Basic Accounting PrinciplesFrom EverandBookkeeping: An Essential Guide to Bookkeeping for Beginners along with Basic Accounting PrinciplesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- Debt Freedom: A Realistic Guide On How To Eliminate Debt, Including Credit Card Debt ForeverFrom EverandDebt Freedom: A Realistic Guide On How To Eliminate Debt, Including Credit Card Debt ForeverRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Official Guide to Financial Accounting using TallyPrime: Managing your Business Just Got SimplerFrom EverandOfficial Guide to Financial Accounting using TallyPrime: Managing your Business Just Got SimplerNo ratings yet
- An easy approach to common investment funds: The introductory guide to mutual funds and the most effective investment strategies in the field of asset managementFrom EverandAn easy approach to common investment funds: The introductory guide to mutual funds and the most effective investment strategies in the field of asset managementNo ratings yet