Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12sc Day178 GuidedNotes Ch29
Uploaded by
Dwayne Ashley DavidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12sc Day178 GuidedNotes Ch29
Uploaded by
Dwayne Ashley DavidCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics, 3rd ed.
Chapter 29 Guided Notes
Nuclear Physics
Fill in each blank with the correct word or phrase as you watch each video.
Radiation and Radioactivity
− Discovery of Radiation
• Roentgen
o Roentgen was studying electricity with a cathode-ray tube when he noticed that a nearby
screen was ___________________ (emitting visible light).
• Becquerel
o Becquerel reasoned that if x-rays ___________________ fluorescence, they may also be
___________________ in fluorescence.
• radiation—the ___________________ and ___________________ emitted by an
___________________ nucleus
• radioactivity—the ___________________ of rays and particles from an unstable nucleus
− Cause of Radioactivity
• Radiation
o Radiation is caused by an ___________________ nucleus.
o This instability is caused by too few or too many ___________________ in the neutron-to-
proton ratio.
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Kinds of Radiation
• Nuclear Decay
o There are three types of nuclear decay:
___________________ decay
___________________ decay
___________________ decay
− Alpha Decay
• Alpha Decay
o During alpha (α) decay, the atom’s nucleus ___________________ ___________________
protons and ___________________ neutrons (these four nucleons are collectively called an
___________________).
o Since an α-particle is the same as a ___________________ (_____) nucleus, we may
represent an α-particle as
4
2 He in an α-decay equation:
− Beta Decay
• Beta (β) decay occurs when an ___________________ leaves the nucleus and a neutron is
changed to a ___________________.
− Gamma Decay
• Gamma (γ) decay occurs when ___________________ ___________________ are emitted.
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Natural Fission
• fission––the ___________________ of a nucleus into two nuclei
− Detection of Radiation
• Ionizing Radiation
o Nuclear radiation is classified as ___________________ radiation to distinguish it from
nonionizing radiation, such as microwaves.
• Detectors
o ___________________ ___________________: a device that creates an electric current
o ___________________ ___________________: a chamber that contains a cold
___________________ near its condensation point
Nuclear particles cause a ___________________ near its vaporization point to condense
around ions.
o ___________________ ___________________: a chamber that contains a
___________________ near its vaporization point
Nuclear particles cause a ___________________ near its vaporization point to condense.
o ___________________ ___________________: a chamber that contains closely spaced
conducting plates maintained at a high potential difference with respect to one another
A spark easily jumps along a trail of ions such as those produced by nuclear particles.
o ___________________: a device that people can carry as they work to see how much
radiation they have been exposed to
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Units of Radiation and Radioactivity
• Radiation and Radioactivity Units
o ___________________ ___________________: the number of particles or rays produced per
unit time; the ___________________ (_____) of the sample
older unit: ___________________ (_____)
current SI unit: ___________________ (_____)
1 Bq = 1 disintegration per second
o ___________________ (_____): a unit for the amount of energy deposited in material exposed
to radiation; measures the ___________________ (_____) of radiation received by a material
_____________ _________________ is equal to _____________ _________________
of energy absorbed by _____________ _________________ of material.
o ___________________ (_____): a measurement of the ionizing effect of EM radiation on a
sample of air
o ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ (_____): a method
that accounts for the differences in damage caused by radiation
Different rays affect tissue differently.
o ___________________ ___________________ (_____): a measure of the comparative
amount of damage
measured in SI units called ___________________ (_____)
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
Radioactive Decay
− Radioactive Decay Law
• Radioactive Decay
o Figure 29-9 on ST p. 672
− Radioactive Dating
• radioactive dating––estimating the ___________________ of a material by comparing the
___________________ of a radioactive nuclide and its daughter products and then calculating
the amount of ___________________ necessary for the measured proportion to occur
• Radioactive Dating
o Radioactive dating involves estimating the age of a sample by comparing the
___________________ of parent and daughter nuclides (radionuclides).
o In calculating the original amount of a radionuclide in a sample, it is necessary to make several
assumptions:
The proportions of nuclides have remained ___________________ over time.
The sample has not been ___________________.
None of the nuclides have ___________________ from the sample.
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Problems with Radioactive Dating
• Carbon-14 Dating
o When an organism dies, it _____________ _________________ carbon with the atmosphere.
o Its own C-14 ___________________ to decay.
o Theoretically, it is possible to determine when an organism died by its ___________________
C-14 activity.
o To use C-14 dating, you must know the ___________________ C-14/C-12 ratio when the
organism died.
• Figure 29-11 on ST p. 675
Nuclear Reactions
− Nuclear Energy
• Nuclear Energy
o Where does nuclear energy (nuclear power plants and bombs) come from?
• mass defect—the ___________________ between the mass of a nucleus and the sum of the
masses of the individual particles from which it was formed
• Figure 29-14 on ST p. 679
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
Subatomic Particles
− Nuclear Building Blocks
• Subatomic Particles
o A zoo of several hundred ___________________ and ___________________
___________________ (particles smaller than atoms) may exist.
o Physicists use two basic rules when studying these particles:
Every reaction ___________________ ___________________ at some time unless it is
prohibited by a conservation law.
Every particle has an ___________________.
antiparticle—a particle of the ___________________ mass and spin but with the
___________________ charge
− Elementary Particle Zoo
• Subatomic Particles
o There are two major groups of subatomic particles: ___________________ (½ spin) and
__________________.
(spin of 0, 1, or 2).
fermions: ___________________ and ___________________
bosons: force carriers
combination of fermions and bosons: ___________________
___________________: composite fermions
___________________: composite bosons
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Exchange Particles
• Exchange Particles
o All forces are placed into four categories:
___________________ force
___________________ ___________________ interaction force
___________________ force
___________________ ___________________ interaction force
o Each kind of force can be understood in terms of an ___________________
___________________.
• exchange particle—a particle that when exchanged between two objects results in a
___________________ or ___________________ between the two objects
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- S1ExamSupplement KeyDocument4 pagesS1ExamSupplement KeyDwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day177 GuidedNotes Ch28Document8 pages12sc Day177 GuidedNotes Ch28Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day164 GuidedNotes Ch25Document21 pages12sc Day164 GuidedNotes Ch25Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day170 GuidedNotes Ch26Document14 pages12sc Day170 GuidedNotes Ch26Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day150 GuidedNotes Ch23Document27 pages12sc Day150 GuidedNotes Ch23Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
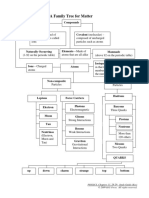
- 12SC 3 Day178 AFamilyTreeforMatterDocument1 page12SC 3 Day178 AFamilyTreeforMatterDwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Service Manual PWC215TDocument11 pagesService Manual PWC215TJovie GrohlNo ratings yet
- CPR 1 IR SpectraDocument2 pagesCPR 1 IR SpectrarunninkeysNo ratings yet
- Bouma, 2000Document7 pagesBouma, 2000Edilson Vagner SitoeNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Shut Off Operation 1682811247Document11 pagesFire Pump Shut Off Operation 1682811247Faisal AlotaibiNo ratings yet
- POGIL - ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - ThermodynamicsMar0% (1)
- EPRI Cycle Chemistry Guidelines For Fossil Plants All Volatile TreatmentDocument264 pagesEPRI Cycle Chemistry Guidelines For Fossil Plants All Volatile TreatmentCesardesidelia100% (2)
- CHEM 1040 General Chemistry I: Winter 2016 Student Course InformationDocument13 pagesCHEM 1040 General Chemistry I: Winter 2016 Student Course Informationjason12No ratings yet
- Separate Fine Solid Particles From Dusty Air With A Uniflow CycloneDocument4 pagesSeparate Fine Solid Particles From Dusty Air With A Uniflow CyclonechemengseliemNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentjosemonNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Full Book (Chem)Document7 pagesMcqs Full Book (Chem)Shiraz MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Aquapak Repulpability Assessment 25 April 2019 PDFDocument15 pagesAquapak Repulpability Assessment 25 April 2019 PDFchinchotarngNo ratings yet
- Macari Company Profile by SlidesgoDocument60 pagesMacari Company Profile by SlidesgoMajid KhanNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project (Thesis)Document197 pagesFinal Year Project (Thesis)Misgates100% (2)
- 0403041629-1302011-293-ExxonMobil CorporationDocument2 pages0403041629-1302011-293-ExxonMobil CorporationSoham TalwarNo ratings yet
- Beer Hazy Factor AffectDocument22 pagesBeer Hazy Factor AffectLanAnhNo ratings yet
- Static Analysis Report For Expansion BellowDocument15 pagesStatic Analysis Report For Expansion BellowJuan ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- CHEN 200 Homework Problems 1: Problem 1: (3 Marks)Document2 pagesCHEN 200 Homework Problems 1: Problem 1: (3 Marks)Amy MillerNo ratings yet
- Symmetry and Group TheoryDocument61 pagesSymmetry and Group TheoryAnonymous SVy8sOsvJD100% (1)
- Syllabus NTJP Jee (Main Advanced) AllenkotaDocument1 pageSyllabus NTJP Jee (Main Advanced) AllenkotaVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- BS 2874-1986 - (2021-05-03 - 09-38-52 Am)Document26 pagesBS 2874-1986 - (2021-05-03 - 09-38-52 Am)AkshayBhatkandeNo ratings yet
- 1501ENG Supplementary Material & Workbook For Statics 2019 (T3) - Pages-DeletedDocument14 pages1501ENG Supplementary Material & Workbook For Statics 2019 (T3) - Pages-DeletedMatthewNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Energy Work Power 2016 Ap WeeblyDocument34 pagesConservation of Energy Work Power 2016 Ap Weeblyapi-263675263No ratings yet
- NURS 1013 Lecture 1 - History and DefinitionDocument21 pagesNURS 1013 Lecture 1 - History and DefinitionMonique Christie100% (1)
- Tutorial 11 - MS3220 Rekayasa Termal (Mark Scheme)Document6 pagesTutorial 11 - MS3220 Rekayasa Termal (Mark Scheme)i need documentsNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Engineering: Engr. Joseph Benedict N. PrimDocument107 pagesMaterial Science and Engineering: Engr. Joseph Benedict N. PrimJOSEPH BENEDICT PRIMNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41hafizaqaiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Mrs Neha Srivastava Faculty of Pharmacy Punjab College of Technical Education LudhianaDocument22 pagesEnzymes: Mrs Neha Srivastava Faculty of Pharmacy Punjab College of Technical Education Ludhiananeha100% (1)
- AestheticDocument8 pagesAestheticLisa PuspitaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage - 2020 - Su - Electrical Tree Degradation in High Voltage Cable Insulation Progress and ChallengesDocument12 pagesHigh Voltage - 2020 - Su - Electrical Tree Degradation in High Voltage Cable Insulation Progress and ChallengesLuiz KowalskiNo ratings yet
- Environment International: Review ArticleDocument13 pagesEnvironment International: Review ArticlevacomanoNo ratings yet