Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12sc Day177 GuidedNotes Ch28
Uploaded by
Dwayne Ashley DavidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12sc Day177 GuidedNotes Ch28
Uploaded by
Dwayne Ashley DavidCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics, 3rd ed.
Chapter 28 Guided Notes
Quantum Physics
Fill in each blank with the correct word or phrase as you watch each video.
Quantum Theory
− Blackbody Radiation
• Blackbody Radiation
o ___________________: a perfect emitter of thermal radiation
Although perfect emitters do not exist, ___________________ are a close approximation.
o ___________________: voids in opaque materials that have small openings to the outside
o ___________________ ___________________: the energy emitted by a cavity
• Stefan’s Law
o The rate at which energy is emitted follows ___________________ ___________________.
− Wien’s Displacement Law
• Figure 28-2 on ST p. 642
• Wien’s Displacement Law
o This law states that the most intense radiant energy emitted by a cavity progresses to shorter
wavelengths as the cavity’s temperature rises.
In other words, ___________________ temperature shifts radiation to a
___________________ wavelength (___________________ energy).
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− The Rayleigh-Jeans Function
• Rayleigh and Jeans attempted to find the relationship between ___________________ and the
___________________ emitted at that frequency from a blackbody radiator at a given
temperature.
• Figure 28-3 on ST p. 642
− Plank and Quantized Energy
• Plank and Quantized Energy
o Max Planck proposed a nonclassical equation that agreed with experimentation:
___________________ ___________________ ___________________.
h: Planck’s constant, ___________________
o Planck assumed that energy is ___________________ (emitted as quanta—values
proportional to the frequency of the radiation).
These values are given by the equation ___________________, where n = 1, 2, 3, . . . .
o Since energy is quantized, it is _______ continuous but can take on only
___________________ values.
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Photons and the Photoelectric Effect
• photon—the smallest packet (quanta) of light energy
• photoelectric effect—the process of using energy to ___________________
___________________ electrons
o Light falling on a metal surface can ___________________ electrons from the metal.
The energy of the photon frequency must be ___________________ than hf (the
___________________ ___________________; the ___________________
___________________).
If the energy is ___________________ than hf, __________ electrons are emitted.
o The photoelectric effect shows that light has ___________________ properties.
Quantum Mechanics and the Atom
− Naming the New Physics
• Quantum
o Physicists use the word ___________________ (broken into increments or parcels) to
describe the physics of very small particles.
o Electrons and protons never have fractional charges—they are ___________________.
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− The Electrical Atom
• J. J. Thomson
o J. J. Thomson discovered that the charge carriers in different conductors have the same
___________________ -_________ -___________________ ratio.
o This evidence suggested that all atoms contain the ___________________ charge carriers,
now called ___________________.
o Thomson suggested that an atom is a ball of ___________________ charge containing
possibly thousands of ___________________ scattered evenly throughout.
This model is called the ___________________-___________________ model.
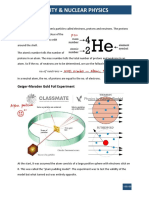
− The Nuclear Atom
• Rutherford
o ___________________ studied atoms by directing alpha particles at gold metal foils.
o He discovered that an atom is mostly ___________________ ___________________.
o The positive charge is concentrated in a small but massive ___________________.
− Isotopes
• Nucleus
o The nucleus is made up of two major kinds of particles (___________________ and
___________________), collectively called ___________________.
___________________ ___________________ (_____): the total number of nucleons in
a given nucleus
___________________ ___________________ (_____): the number of protons in a
nucleus
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
• Isotopes
o Atoms of the same element but with different mass numbers (different numbers of neutrons)
are called ___________________ of the element.
o ___________________ ___________________ displays the mass number and the atomic
number of an element.
Figure 28-7 on ST p. 647
− Energy Levels
• Bohr’s Model
o Bohr postulated that electrons are restricted to certain ___________________
___________________.
o The electron orbits are called ___________________ ___________________.
___________________ ___________________: All electrons in an atom are at their
___________________ energy states (applies to e− located nearest to the nucleus).
___________________ ___________________: The electrons have energies
___________________ than the ground state (applies to e− located farther away from the
nucleus).
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Evidence that Supports the Bohr’s Model
• Bohr’s Model
o Bohr’s model explained the line spectra of ________________-________________ gases.
There are several lines in a spectrum because several ___________________ are
possible.
Even hydrogen, the simplest element, has a ___________________ of lines.
− Particles as Waves
• Louis de Broglie
o If waves (like light) can be considered to be particles (like photons) under some circumstances,
why can’t particles act like waves at times?
o This question caused de Broglie to calculate what a ___________________
___________________ would be like.
o The wavelength of a matter wave would be
As m ___________________, λ ___________________.
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
− Schrödinger Wave Equation
• Schrödinger Wave Equation
o Waves are described by ___________________.
o Schrödinger developed an equation that uses the ___________________
___________________ (𝜓𝜓) of an electron’s wave.
o The function 𝜓𝜓 for an electron’s wave gives the probable ___________________ of the
particle.
The waveform is therefore called a ___________________ ___________________.
• ___________________––the probable location of an ___________________
− Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
• Heisenberg uncertainty principle––It is impossible to know the ___________________ and the
exact ___________________ of a quantum mechanical object at the same time.
• Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
o It is impossible to know where an electron ___________________ and where it is
___________________ at the same time.
o Measuring one property ___________________ the other, so the two properties
___________________ be known simultaneously.
− Wave-Particle Duality
• The uncertainty principle illustrates the principle of ___________________: the concepts of
waves and particles are both needed in order to describe reality.
o An electron is both a ___________________ and a ___________________.
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
Modern Atomic Models
− The Quantum Numbers
• Quantum Numbers
o There are four ___________________ ___________________ that uniquely specify each
electron’s energy in an atom.
___________________ quantum number (n): ___________________
___________________ quantum number (l): ___________________
___________________ quantum number (m): ___________________
___________________ quantum number (ms): ___________________
− Electron Ordering Using Quantum Numbers
• Pauli exclusion principle––No two electrons in the same atom can have
___________________ sets of quantum numbers.
• Spin-Paired
o Electrons can be in the same orbital only if they are ________________-________________
(the two electrons spin in opposite directions).
© 2019 BJU Press. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Gr3 Wk4 Waves and Currents PDFDocument2 pagesGr3 Wk4 Waves and Currents PDFAirah SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Classifying Matter and Chemical ChangesDocument31 pagesClassifying Matter and Chemical ChangesBhuwneesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect FactorsDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric Effect Factorsstudent Maximiliano Villanueva MorenoNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric Effect ExplainedDocument6 pagesPhotoelectric Effect ExplainedJoey MinogueNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Theoretical Minimum - Notes Part 2Document62 pagesQuantum Mechanics Theoretical Minimum - Notes Part 2dhpatton3222No ratings yet
- 12sc Day150 GuidedNotes Ch23Document27 pages12sc Day150 GuidedNotes Ch23Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory & Quantum Mechanics: WorksheetDocument4 pagesAtomic Theory & Quantum Mechanics: Worksheetapi-305003239No ratings yet
- 12sc Day164 GuidedNotes Ch25Document21 pages12sc Day164 GuidedNotes Ch25Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Booklet 1Document55 pagesModule 8 Booklet 1Maggie LeeNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms: Light and Quantized EnergyDocument9 pagesElectrons in Atoms: Light and Quantized EnergyRicki HanNo ratings yet
- BohrvswavemechanicalDocument5 pagesBohrvswavemechanicalapi-277220146No ratings yet
- OL Radioactivity and Nuclear PhysicsDocument24 pagesOL Radioactivity and Nuclear Physicssaifaly shaheenNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and PropertiesDocument53 pagesAtomic Structure and PropertiesYuvraj VermaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 1 - Atomic Model and Atomic Theory Frame NotesDocument7 pagesChemistry Notes 1 - Atomic Model and Atomic Theory Frame NotesErin KabezNo ratings yet
- Topic 12.2 Formative AHLDocument2 pagesTopic 12.2 Formative AHLpixelhoboNo ratings yet
- 11 Class Revision 01 AsDocument1 page11 Class Revision 01 AsNishali SamNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Ch. 11-13 NotesDocument8 pagesClass 5 - Ch. 11-13 Notesmark chenNo ratings yet
- Light and Quantized Energy Quantum Theory AtomDocument4 pagesLight and Quantized Energy Quantum Theory AtomKevin XavierNo ratings yet
- Particle Symbol Charge Relative Mass Location: The AtomDocument4 pagesParticle Symbol Charge Relative Mass Location: The AtomAngel SolivanNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY The Big DifferenceDocument2 pagesACTIVITY The Big DifferenceMonica Jane SaturninoNo ratings yet
- ENGR 1130 Module 6 Lecture OutlineDocument7 pagesENGR 1130 Module 6 Lecture Outlineskarpo 911No ratings yet
- 11th Class PhysicsDocument73 pages11th Class PhysicsRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 3.3a Atomic Math PPT Notes Slide 2: Definitions Atomic Number Is - Is An Atom of An - ThatDocument4 pagesChemistry 3.3a Atomic Math PPT Notes Slide 2: Definitions Atomic Number Is - Is An Atom of An - Thatanon-579447No ratings yet
- The Structure of the Atom DocumentDocument7 pagesThe Structure of the Atom DocumentAbdullah AlthaniNo ratings yet
- 2.3 The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory: ST ND RD THDocument4 pages2.3 The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory: ST ND RD THNelson HsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Fill in Blank Notes2009 - WorksheetDocument10 pagesChapter 11 Fill in Blank Notes2009 - WorksheetKiki EdsNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1-Science9-Quarter2Document1 pageQuiz 1-Science9-Quarter2Eden Rey ParoanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Unit 2 Guided NotesDocument9 pagesPhysical Science Unit 2 Guided NotesflyingmsNo ratings yet
- Study Sheet 2 Atoms and Subatomic ParticlesDocument8 pagesStudy Sheet 2 Atoms and Subatomic Particlesmihad osmanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic Structure Notes KeyDocument2 pages1.3 Atomic Structure Notes Keybunnyman zhangNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day170 GuidedNotes Ch26Document14 pages12sc Day170 GuidedNotes Ch26Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- Unit 2.2 - The Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesUnit 2.2 - The Atomic StructureNurdina JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of Matter ExplainedDocument8 pagesKinetic Theory of Matter ExplainedKwok Yee TherNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Electrons in Atoms NameDocument1 pageWorksheet: Electrons in Atoms Nameapi-295845150No ratings yet
- Electron Configuration Test ReviewDocument4 pagesElectron Configuration Test ReviewSri HartonoNo ratings yet
- C1.3 PhotosynthesisDocument24 pagesC1.3 PhotosynthesisteddyenNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic Structure Notes StudentDocument3 pages1.3 Atomic Structure Notes Studentbunnyman zhangNo ratings yet
- CH 5.1 Lecture Guide PDFDocument4 pagesCH 5.1 Lecture Guide PDFErica OhNo ratings yet
- Nuclear and Particle Physics: Vocabulary ReviewDocument8 pagesNuclear and Particle Physics: Vocabulary ReviewthamerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Introduction To Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument6 pagesChapter 7. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Introduction To Ionic and Covalent BondingLOVINGANGEL123No ratings yet
- NameDocument4 pagesNameromeyer810% (4)
- Chem f6 PDFDocument7 pagesChem f6 PDFCHONG YUNG FOO MoeNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Learning Guide Name: - : InstructionsDocument19 pagesUnit 7 Learning Guide Name: - : Instructionselina kimNo ratings yet
- October Half Term HomeworkDocument10 pagesOctober Half Term Homeworkzincbak warriorNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms: Reviewing VocabularyDocument6 pagesElectrons in Atoms: Reviewing VocabularyKDNGNo ratings yet
- BohrModelHydrogenSE 2Document5 pagesBohrModelHydrogenSE 2jadahkimberlyNo ratings yet
- Yanet Becerra - Molecular Polarity PhET LabDocument3 pagesYanet Becerra - Molecular Polarity PhET LabYanet BecerraNo ratings yet
- Element Builder FormDocument4 pagesElement Builder FormEven JorgensNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Element Builder: Samara VandeverDocument4 pagesStudent Exploration: Element Builder: Samara VandeverSamara VandeverNo ratings yet
- Chp4 AnswerDocument8 pagesChp4 Answeranon_608294229No ratings yet
- Isotopes and Atomic Mass Guided NotesDocument4 pagesIsotopes and Atomic Mass Guided Notesdivya raghavNo ratings yet
- 08 - Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pages08 - Intermolecular Forcesleafyfun100No ratings yet
- Spring 2009 Final Exam Review: Modified True/FalseDocument14 pagesSpring 2009 Final Exam Review: Modified True/FalsejkeelenNo ratings yet
- Maha Pay Attention!!:p: Electric Forces and Fields RevisionDocument25 pagesMaha Pay Attention!!:p: Electric Forces and Fields Revisionanna4463No ratings yet
- Physics ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesPhysics Electrostaticsebaieyong samuelNo ratings yet
- Physics 08-01 Static Electric Charge and ConductorsDocument2 pagesPhysics 08-01 Static Electric Charge and ConductorsMeahgan Renee FeudoNo ratings yet
- 1 6 Guided Notes SE Electron ConfigurationDocument9 pages1 6 Guided Notes SE Electron ConfigurationMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Atomic Radius vs. Atomic Number Graph InterpretationDocument3 pagesAtomic Radius vs. Atomic Number Graph InterpretationRaia The BerserkerNo ratings yet
- 2 - Atoms and Elements: South Pasadena - AP Chemistry Name - Period - DateDocument1 page2 - Atoms and Elements: South Pasadena - AP Chemistry Name - Period - DateLucas KazemNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day178 GuidedNotes Ch29Document8 pages12sc Day178 GuidedNotes Ch29Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- S1ExamSupplement KeyDocument4 pagesS1ExamSupplement KeyDwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day176 GuidedNotes Ch27Document6 pages12sc Day176 GuidedNotes Ch27Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day170 GuidedNotes Ch26Document14 pages12sc Day170 GuidedNotes Ch26Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day158 GuidedNotes Ch24Document23 pages12sc Day158 GuidedNotes Ch24Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- 12SC 3 Day178 AFamilyTreeforMatterDocument1 page12SC 3 Day178 AFamilyTreeforMatterDwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lecture Nuclear Stability and ModelsDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Lecture Nuclear Stability and ModelsSepamoNo ratings yet
- 5a Esoteric Theory of EverythingDocument6 pages5a Esoteric Theory of EverythingStephen J. RobertsNo ratings yet
- Contributions To The Development of Atomic ModelDocument12 pagesContributions To The Development of Atomic ModelHadif Darwish BadrulhishamNo ratings yet
- QED Chapter 11Document99 pagesQED Chapter 11Andrew HucekNo ratings yet
- 116news EntranceTest PHD Dec12Document37 pages116news EntranceTest PHD Dec12Jeremy HensleyNo ratings yet
- Wang Et Al (2013) Quantum Cognition PDFDocument17 pagesWang Et Al (2013) Quantum Cognition PDFloguitos123No ratings yet
- NucChem Week 1Document13 pagesNucChem Week 1Angel Akiko AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Quantum PhysicsDocument31 pagesLesson 3-Quantum Physicsabdulrahman alalawiNo ratings yet
- The Gravitational ForceDocument5 pagesThe Gravitational ForceGeorge RajnaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument17 pagesAtomic StructureVandana Khator100% (1)
- Atom StructureDocument2 pagesAtom StructureJel SuarezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - PH 301 & PH 401 - MODULE - 6 (Statistical Mechanics)Document31 pagesLecture Notes - PH 301 & PH 401 - MODULE - 6 (Statistical Mechanics)sad foxNo ratings yet
- The Joy of Quantum Physics - Appendices - OnlyDocument136 pagesThe Joy of Quantum Physics - Appendices - OnlyJonturk JonturkNo ratings yet
- Ising MCDocument18 pagesIsing MCFaizal abidNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Principles of Theoretical Physics (PDFDrive)Document518 pagesMathematical Principles of Theoretical Physics (PDFDrive)Fai Kuen Tang100% (1)
- Wave Properties and Particle DualityDocument37 pagesWave Properties and Particle DualityManoj Reddy33% (3)
- Rutherford ExperimentDocument3 pagesRutherford ExperimentShu MinNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom ExplainedDocument27 pagesStructure of Atom ExplainedEINSTEINNo ratings yet
- Stanley F. Grove - Quantum Theory and Aquina's Doctrine On MatterDocument329 pagesStanley F. Grove - Quantum Theory and Aquina's Doctrine On MatterIcaro100% (3)
- HW6Document4 pagesHW6callum174753No ratings yet
- Experimental Indications of Non-Classical Brain FunctionsDocument11 pagesExperimental Indications of Non-Classical Brain FunctionsJohnNo ratings yet
- Sciences An Integrated Approach 6th Edition Trefil Test BankDocument18 pagesSciences An Integrated Approach 6th Edition Trefil Test Bankaularianbruh7hq100% (23)
- Final SolutionsDocument8 pagesFinal SolutionsYenhao Philip ChenNo ratings yet
- David K. Ferry - An Introduction To Quantum Transport in Semiconductors (2018, Pan Stanford Publishing) PDFDocument539 pagesDavid K. Ferry - An Introduction To Quantum Transport in Semiconductors (2018, Pan Stanford Publishing) PDFpuceiroale100% (1)
- TFY4250 FY2045 Lecture Notes 14 Time DepDocument18 pagesTFY4250 FY2045 Lecture Notes 14 Time DepParitosh UpretiNo ratings yet
- MSU Baroda MSc Physics Quantum Mechanics & Statistical MechanicsDocument20 pagesMSU Baroda MSc Physics Quantum Mechanics & Statistical MechanicsrahulNo ratings yet
- Temporary Faculty Shortlisted Candidates III v2Document15 pagesTemporary Faculty Shortlisted Candidates III v2arunks4uNo ratings yet
- 2016 2017 6 7 Notes QuantumDocument85 pages2016 2017 6 7 Notes QuantumAlexander AdrogueNo ratings yet
- Direct Bell States Generation On A III-V Semiconductor Chip at Room TemperatureDocument5 pagesDirect Bell States Generation On A III-V Semiconductor Chip at Room TemperatureFrancisco Hernandez AlejandreNo ratings yet