Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sci Notes
Sci Notes
Uploaded by
학년Ju0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe document discusses how convex lenses are used to form magnified and inverted images. It explains that when an object is placed between the focal point F and the lens, three light rays from the object cross at the focal point behind the lens to form a real, inverted and magnified image. When an object is less than one focal length from the lens, two light rays form an upright, magnified but virtual image that cannot be projected onto a screen. Film in a projector is loaded upside down so the projected image appears right-side up. A magnifying glass uses this same principle to make objects appear larger.
Original Description:
Original Title
sci notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses how convex lenses are used to form magnified and inverted images. It explains that when an object is placed between the focal point F and the lens, three light rays from the object cross at the focal point behind the lens to form a real, inverted and magnified image. When an object is less than one focal length from the lens, two light rays form an upright, magnified but virtual image that cannot be projected onto a screen. Film in a projector is loaded upside down so the projected image appears right-side up. A magnifying glass uses this same principle to make objects appear larger.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageSci Notes
Sci Notes
Uploaded by
학년JuThe document discusses how convex lenses are used to form magnified and inverted images. It explains that when an object is placed between the focal point F and the lens, three light rays from the object cross at the focal point behind the lens to form a real, inverted and magnified image. When an object is less than one focal length from the lens, two light rays form an upright, magnified but virtual image that cannot be projected onto a screen. Film in a projector is loaded upside down so the projected image appears right-side up. A magnifying glass uses this same principle to make objects appear larger.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
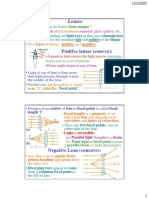
*inverted (upside down)
*magnified (larger than the object)
*real (can be produced on a screen)
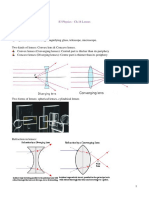
-Three light rays extend out from the object arrows and cross the lens. These
cross on the other side of the lens under a larger green arrow that is labelled
'image'.
-Ray diagram for an object placed between 2F and F from a convex lens
In a film or data projector, this image is formed on a screen. Film must be
loaded into the projector upside down so the projected image is the right way
up.
Magnifying Glass-Beyond 2F'
-A magnifying glass is a convex lens used to make an object appear much
larger than it actually is. This works when the object is placed at a distance
less than the focal length from the lens.
*upright (the right way up)
*magnified (larger than the object)
*virtual (cannot be produced on a screen)
-Two light rays extend out from the object which is shown by a small green
arrow that sits between F and the lens. The rays that extend to the image are
in a lighter shade.
-Ray diagram for an object placed less than one focal length from a convex
lens
Only the person using the magnifying glass can see the image. The image
cannot be projected onto a screen because it is a virtual image.
You might also like
- Exposure Mastery: Aperture, Shutter Speed & ISO: The Difference Between Good and Breathtaking PhotographsFrom EverandExposure Mastery: Aperture, Shutter Speed & ISO: The Difference Between Good and Breathtaking PhotographsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Principal of Optical InstrumentsDocument24 pagesThe Principal of Optical InstrumentsRabieRusdiNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide to 3D photos and 3D videos: Now everybody can make themFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide to 3D photos and 3D videos: Now everybody can make themNo ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentsDocument16 pagesOptical Instrumentsanand01191% (11)
- LensesDocument23 pagesLensessmartamjad100% (2)
- Convex LensesDocument32 pagesConvex LensesCrisanta LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Lenses: - Lenses Are Made of A Material: Glass, Quartz, EtcDocument5 pagesLenses: - Lenses Are Made of A Material: Glass, Quartz, EtcADimas Cahyaning FurqonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightDocument9 pagesChapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightHHK88893% (15)
- Vansh Srivastava Physics Class 12 ProjectDocument36 pagesVansh Srivastava Physics Class 12 ProjectOm Tiwari PandeyNo ratings yet
- L10. 13.5 Lens ApplicationsDocument8 pagesL10. 13.5 Lens Applicationszhuhu2002No ratings yet
- 3.2.4 Thin Converging LensDocument5 pages3.2.4 Thin Converging LensPeterMwagweNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled Documentaaisp015013No ratings yet
- Applications of Optical InstrumentsDocument2 pagesApplications of Optical Instrumentsujjawal kumarNo ratings yet
- Images by Optical InstrumentsDocument1 pageImages by Optical InstrumentsMaslen DadeeNo ratings yet
- Useful Magnification OlympusDocument6 pagesUseful Magnification OlympusLilian RoseNo ratings yet
- Sign Conventions:: Lesson 8: Title: Thin Lens EquationDocument3 pagesSign Conventions:: Lesson 8: Title: Thin Lens EquationJatmiko RosindahNo ratings yet
- BuildatelescopeDocument4 pagesBuildatelescopeapi-266460688No ratings yet
- Compound MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCompound Microscopeaman100% (1)
- Form 4 - Chapter 7 - Formation of Images by Plane Mirrors and Lenses Images Formed by Plane Mirror Convex Lens Concave LensDocument3 pagesForm 4 - Chapter 7 - Formation of Images by Plane Mirrors and Lenses Images Formed by Plane Mirror Convex Lens Concave LensleosakmaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Term 2 Physics ActivityDocument8 pagesClass 12 Term 2 Physics Activitysuvodeep715No ratings yet
- Ray DiagramsDocument3 pagesRay DiagramsAqila MumtazNo ratings yet
- LENSESDocument8 pagesLENSESspammy fammyNo ratings yet
- Uri AttaacksDocument7 pagesUri AttaacksArJitYaDavNo ratings yet
- Simplify: - Input (Light) - Image Formation - Image DetectionDocument29 pagesSimplify: - Input (Light) - Image Formation - Image DetectionVibhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Pinhole Camera InformationDocument4 pagesPinhole Camera InformationD'ferti AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Optics NotesDocument6 pagesSupplementary Optics NotesEva Maria LouisNo ratings yet
- Mirror and Lenses 10Document59 pagesMirror and Lenses 10Mesheil TaladroNo ratings yet
- Physic - LensesDocument33 pagesPhysic - Lensesfelitrochristopher924No ratings yet
- 8.1 Uses of LightDocument26 pages8.1 Uses of LightEmily Ti Er ChiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OpticsDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Opticsapi-286207993No ratings yet
- 0708 Optics Mirrors and LensesDocument21 pages0708 Optics Mirrors and LensesJEssa TrixiaNo ratings yet
- Single Slide ProjectorDocument3 pagesSingle Slide ProjectorRehan SadiqNo ratings yet
- Vansh Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesVansh Physics ProjectOm Tiwari PandeyNo ratings yet
- Section 13.3 Telescopes and Microscopes: Questions To Think AboutDocument10 pagesSection 13.3 Telescopes and Microscopes: Questions To Think Aboutsamyak jainNo ratings yet
- Pinhole Camera (Word)Document8 pagesPinhole Camera (Word)DanaNo ratings yet
- Optical InstrumentalDocument23 pagesOptical Instrumentalsaroj.bagga02No ratings yet
- The Incident Ray, Reflected Ray and Normal To Surface at The Point of Incidence All Lie in The Same PlaneDocument4 pagesThe Incident Ray, Reflected Ray and Normal To Surface at The Point of Incidence All Lie in The Same PlaneBemgbaNo ratings yet
- ConcaveDocument2 pagesConcavenickayesstudyyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourDocument43 pagesCHAPTER 7 Light, Sight and ColourAkmar MataliNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and LensesDocument18 pagesMirrors and LensesJohn Rymar LameraNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document25 pagesScience 10rosellmariateresaNo ratings yet
- Real and Virtual ImagesDocument11 pagesReal and Virtual Imagesapi-263850753No ratings yet
- Light, Colour and SightDocument61 pagesLight, Colour and SightDayah D DebabNo ratings yet
- The Telescope: 7.1 PurposeDocument10 pagesThe Telescope: 7.1 PurposeAlice Mengyao HeNo ratings yet
- Concave MirrorsDocument16 pagesConcave MirrorsJian Christian FerminNo ratings yet
- S3 Physics - Ch.18 LensesDocument6 pagesS3 Physics - Ch.18 LensesJoseph LeeNo ratings yet
- Physics ExperimentDocument11 pagesPhysics ExperimentrashbasheerNo ratings yet
- LightsDocument2 pagesLightsnatalie28kiuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document9 pagesUnit 2Mohamed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- PPT-3 Chapter 2.2 Concave MirrorsDocument20 pagesPPT-3 Chapter 2.2 Concave MirrorsAreen Alhazaymeh100% (1)
- The Formation of Images by Optical InstrumentDocument30 pagesThe Formation of Images by Optical InstrumentNg Yi XiangNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscopes:: Parts of A Compound MicroscopeDocument2 pagesCompound Microscopes:: Parts of A Compound MicroscopeJade SamonteNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Questions-AnsweredDocument7 pagesModule 3 Questions-AnsweredVincee SamsonNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6ArpitNo ratings yet
- Light ShikshaDocument13 pagesLight Shikshabratajeet.ghosh.14No ratings yet
- Asm 8579Document2 pagesAsm 8579Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Topic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesDocument14 pagesTopic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics UsesNorhisham Mohamed SobriNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Class NotesDocument5 pagesRay Optics Class NotescutebeneNo ratings yet
- Optical Instruments Class 12 Investigatory ReportDocument21 pagesOptical Instruments Class 12 Investigatory Reportsakshamjainking5No ratings yet
- Mirrorslenses 1Document46 pagesMirrorslenses 1Katelene Lyle D. DayagNo ratings yet
- Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesPractice Questions학년JuNo ratings yet
- Sci Reviewer 1Document1 pageSci Reviewer 1학년JuNo ratings yet
- Science For TheDocument2 pagesScience For The학년JuNo ratings yet
- It Is AgreedDocument2 pagesIt Is Agreed학년JuNo ratings yet
- Body Shaming ScriptDocument3 pagesBody Shaming Script학년JuNo ratings yet