Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary 14 March
Uploaded by
Dheeraj Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 page1) The document discusses strategies for new product demand forecasting and distribution network planning.
2) It outlines a process for predicting demand for new products using historical sales data, demand curve analysis, and machine learning techniques like clustering.
3) The distribution network planning section examines how to optimize factors like warehouse locations, sourcing, and transportation costs to balance service levels and expenses.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document discusses strategies for new product demand forecasting and distribution network planning.
2) It outlines a process for predicting demand for new products using historical sales data, demand curve analysis, and machine learning techniques like clustering.
3) The distribution network planning section examines how to optimize factors like warehouse locations, sourcing, and transportation costs to balance service levels and expenses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageSummary 14 March
Uploaded by
Dheeraj Kumar1) The document discusses strategies for new product demand forecasting and distribution network planning.
2) It outlines a process for predicting demand for new products using historical sales data, demand curve analysis, and machine learning techniques like clustering.
3) The distribution network planning section examines how to optimize factors like warehouse locations, sourcing, and transportation costs to balance service levels and expenses.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
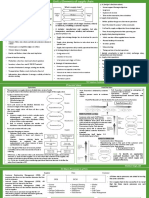
SUMMARY of DIGITAL SCM : Lecture 17&18
Air Vs Ocean Shipment Analysis New Product Introduction-Case Study
Data to be considered: • Footwear Manufacturer, Short Life Cycle & low demand accuracy
✓ Product Cost • Goal: Predict demand for new products twelve months prior to
✓ Mean Weekly Demand product in market.
✓ Review Period • Scope: About 2000 different SKUs
✓ Ocean & Air Lead times Step 1: Historical Data (Data from all the products sold)
✓ Ocean & Air Shipping Cost Step 2: Plotting the demand curve for the data
• At higher level it is the trade off between lead time and Step 3: Identifying number of curves which have same behavior of
cost demand curves and use machine learning techniques like clustering(K-
mean)
Base Stock Level Policy
Step 4: Use Classification tree and map the new product from the
Average Demand during an interval of r days, L being the lead
clustered data.
time: (r+L)*(AVG) (AVG: Average daily demand)
Using Forecast error to check the accuracy
Safety Stock: z* STD*SQRT(r+L)
Implementation Results: Decreased lost sales
Base Stock: (r+L)(AVG)+z*STD*SQRT(r+L)
Network Planning
• Key issues: Optimal number of location, size of warehouses, sourcing strategy, best distribution channels
• Objective is to balance service level against purchasing cost, inventory handling costs, facility costs, transportation costs
• Minimum annual cost configuration of the distribution network that satisfies product demand at specified customer service levels.
• Major tools: Mapping, Data, Engine
• Comparison between cost minimisation and service maximisation networks
• Cost differences observed on Aggregation of Customer as well as with Aggregation of Product Category
Impact of Aggregating Customers Strategy for Product Aggregation
• Customer zone balances the loss of accuracy due to over • Placing all SKUs in a source group
aggregation and needless complexity • Aggregating the SKUs by similar logistics characteristics (Weight,
• Efficiency of aggregation is affected by number of Volume, Holding Cost)
aggregated points and distribution of customers in each
zone
You might also like
- DigE HowGoDigital Workbook PDFDocument3 pagesDigE HowGoDigital Workbook PDFersgesheNo ratings yet
- Corey Wade - Hands-On Gradient Boosting With XGBoost and Scikit-Learn - Perform Accessible Python Machine Learning and Extreme Gradient Boosting With Python-PACKT Publishing LTD (2020)Document141 pagesCorey Wade - Hands-On Gradient Boosting With XGBoost and Scikit-Learn - Perform Accessible Python Machine Learning and Extreme Gradient Boosting With Python-PACKT Publishing LTD (2020)Dheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Capstone Project Final SubmissionDocument13 pagesCapstone Project Final SubmissionSavitaDarekarNo ratings yet
- Summary 14Document2 pagesSummary 14Dheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary 14 3Document9 pagesSummary 14 3Dheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary 14 4Document12 pagesSummary 14 4Dheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary 14 MahDocument4 pagesSummary 14 MahDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 SupplychaindriversametricsDocument24 pagesChapter3 SupplychaindriversametricsNoor Harlisa Irdina Mohd HasanNo ratings yet
- Inventory Optimization:: Better Inventory Management Through Forecasting and PlanningDocument31 pagesInventory Optimization:: Better Inventory Management Through Forecasting and Planningpatanahi1947No ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCheat Sheetonlysj134No ratings yet
- FiNO Inventory User Guide by Abhishek Nayar PDFDocument49 pagesFiNO Inventory User Guide by Abhishek Nayar PDFAbhishek KNo ratings yet
- MBA 502 Supply Chain Management Lesson 2Document44 pagesMBA 502 Supply Chain Management Lesson 2smsishaNo ratings yet
- Tema 4-1 - Techniques For Optimizing of Transportation Logistics NetworkDocument44 pagesTema 4-1 - Techniques For Optimizing of Transportation Logistics NetworkRaluca AndreeaNo ratings yet
- DSA II Notes UptoRegressionDocument38 pagesDSA II Notes UptoRegressionShakil Reddy BhimavarapuNo ratings yet
- Warehouse AutomationDocument4 pagesWarehouse Automationdeepakverma1981No ratings yet
- 9.log. Chapter 9Document71 pages9.log. Chapter 9Thuận TrầnNo ratings yet
- Sourcing Process ManagementDocument40 pagesSourcing Process ManagementAbhinandan DoleNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument52 pagesInventory Managementsatyamchoudhary2004No ratings yet
- Logistics Network LectureDocument44 pagesLogistics Network LectureDaniel RaharjaNo ratings yet
- Operations DoneDocument10 pagesOperations DoneAmbika Prasad ChandaNo ratings yet
- W3-Network OptimizationDocument21 pagesW3-Network OptimizationEva RosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Inventory ControlDocument18 pagesChapter 6: Inventory ControlRoshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Managing Logistical SystemsDocument33 pagesManaging Logistical SystemsJim OlesNo ratings yet
- SCM - CH3 Drivers and MetricsDocument45 pagesSCM - CH3 Drivers and MetricsMrunal ShethNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of OperationsDocument38 pagesBasic Concepts of Operationskarthik rampaNo ratings yet
- Lean Case StudyDocument9 pagesLean Case Studyiganu76No ratings yet
- INDE8900-30 Lecture 1 S23Document35 pagesINDE8900-30 Lecture 1 S23sohila reddyNo ratings yet
- w5 ABC ShortDocument26 pagesw5 ABC ShortEugene TeoNo ratings yet
- 6290 Lec 2 Inventory ManagementDocument61 pages6290 Lec 2 Inventory ManagementPayman SalimiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Inventory Analysis and ControlDocument57 pagesUnit 4. Inventory Analysis and Controlskannanmec100% (1)
- Data Driven Approaches For Optimal Order Quantity IE-797: Submitted ByDocument76 pagesData Driven Approaches For Optimal Order Quantity IE-797: Submitted BykrishnaNo ratings yet
- DMChapter 2 - ForclassDocument58 pagesDMChapter 2 - ForclassPrasanna Kumar pandaNo ratings yet
- Session 2 - Nsupply Chain Design and Linkage To Corporate StrategyDocument39 pagesSession 2 - Nsupply Chain Design and Linkage To Corporate Strategypulkit khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument25 pagesSupply Chain ManagementLino Gabriel100% (1)
- Cost Breakdown Analysisfinal v2 - 0Document13 pagesCost Breakdown Analysisfinal v2 - 0samerricNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology What Is Decision Support?Document4 pagesAn Overview of Data Warehousing and OLAP Technology What Is Decision Support?Rajani NainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7st - Multiple Items - Coordinated OrderingDocument33 pagesChapter 7st - Multiple Items - Coordinated OrderingVăn Ngọc Hoàng HảiNo ratings yet
- Ecom6008 24 L3Document84 pagesEcom6008 24 L3JLNo ratings yet
- Supply ChainDocument5 pagesSupply ChainCoralie GraslinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 SCMDocument25 pagesChapter 5 SCMFirzam AmirNo ratings yet
- System (Totals) M L L L: Product Quality Service QualityDocument1 pageSystem (Totals) M L L L: Product Quality Service QualityChad FreemanNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument87 pagesInventory ManagementMaruf AitizzoNo ratings yet
- Build An ODAG Qlik SolutionDocument18 pagesBuild An ODAG Qlik SolutionMarcos VargasNo ratings yet
- Distribution and 3PLDocument48 pagesDistribution and 3PLSamit Shandilya100% (1)
- SCM MBA 4thsemester SOC DAVVDocument31 pagesSCM MBA 4thsemester SOC DAVVKunal ShirsathNo ratings yet
- Madura Coats: Supply Chain Optimisation Through Order Frequency AnalysisDocument20 pagesMadura Coats: Supply Chain Optimisation Through Order Frequency Analysismohitegaurv87No ratings yet
- "Capital Decisions As Part of Strategic Scheduling Process": Eduardo Coloma - Maptek Christie Myburgh - AtomorphisDocument15 pages"Capital Decisions As Part of Strategic Scheduling Process": Eduardo Coloma - Maptek Christie Myburgh - AtomorphisLuis David RenteriaNo ratings yet
- Eis Inventory MGTDocument39 pagesEis Inventory MGTVawizyNo ratings yet
- SCM-Module 3B-PPT-01Document47 pagesSCM-Module 3B-PPT-01arkmaniNo ratings yet
- Procurement CH 5Document55 pagesProcurement CH 5KalkidanNo ratings yet
- Inventory ControlDocument24 pagesInventory ControlSudip KumarNo ratings yet
- Design For CostDocument18 pagesDesign For CostTejas ShindeNo ratings yet
- Johnson 16e Chapter08Document53 pagesJohnson 16e Chapter08Carmenn LouNo ratings yet
- SCM 0Document49 pagesSCM 0Jonathan EscamillanNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument33 pagesInventory Managementnottteeeerrrrr90% (10)
- Cloud-Based Data Warehouse Model Creation, Loading, and Performance Evaluation: A Comparative AnalysisDocument5 pagesCloud-Based Data Warehouse Model Creation, Loading, and Performance Evaluation: A Comparative AnalysisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 NotesDocument8 pagesQuiz 2 Notesaliaaaamer2003No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Elements of Supply Chain - NotesDocument3 pagesUnit 1 - Elements of Supply Chain - NotesAnuj VermaNo ratings yet
- EEAB-WP5 - Energy ModellingDocument33 pagesEEAB-WP5 - Energy ModellingAkshay RanadeNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - MISBIT30803 - AI210078 - SEC2Document3 pagesFinal Exam - MISBIT30803 - AI210078 - SEC2Noordamia Hazira Binti Ahmad DaudNo ratings yet
- Chap003 - Network PlanningDocument88 pagesChap003 - Network PlanningMukund KshirsagarNo ratings yet
- Paper Recycling ProblemDocument2 pagesPaper Recycling ProblemDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Operational ResearchDocument19 pagesEuropean Journal of Operational ResearchDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- PrintDocument32 pagesPrintDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Herbers JoergDocument275 pagesHerbers JoergDheeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- RRR DisserDocument69 pagesRRR Disserssrana26No ratings yet
- Job Description HR Business Partner October 2022Document5 pagesJob Description HR Business Partner October 2022Lalissa ZelalemNo ratings yet
- نظرية أصحاب المصالح - البحث عن التوازن بين المسؤولية الاجتماعية والمسؤولية الاقتصادية - حالة مجمع صيدال -Document14 pagesنظرية أصحاب المصالح - البحث عن التوازن بين المسؤولية الاجتماعية والمسؤولية الاقتصادية - حالة مجمع صيدال -La NoufNo ratings yet
- Sap GRC Process Control 1676376572Document82 pagesSap GRC Process Control 1676376572AMIT TIWARINo ratings yet
- uTTYU STR Pandey STR FileDocument67 pagesuTTYU STR Pandey STR FileSaurav ReyanshNo ratings yet
- TQM Implementation in ToyotaDocument15 pagesTQM Implementation in ToyotaSaikat GhoshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Corporate CommunicationDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Corporate CommunicationNicole Nishalynie A/P SaravananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document40 pagesChapter 1Andrea AtonducanNo ratings yet
- Alltel Pavilion Case Study Exhibit 1: Name Institution Course Professor DateDocument6 pagesAlltel Pavilion Case Study Exhibit 1: Name Institution Course Professor Datereigh paulusNo ratings yet
- Designing Enterprise Architecture Using TOGAF ArchDocument9 pagesDesigning Enterprise Architecture Using TOGAF ArchFIORELA HUARCAYA GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Ch-2 - Production PlanningDocument14 pagesCh-2 - Production PlanningRidwanNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Format EM 3 1Document4 pagesCASE ANALYSIS EXAMPLE Format EM 3 1Aianna Maryeth BeninsigNo ratings yet
- Soal DMP&Neg-2023-!7ADocument4 pagesSoal DMP&Neg-2023-!7AElmi SariNo ratings yet
- Mba Employment Report 2022Document7 pagesMba Employment Report 2022Min H. OONo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Project Quality Managemet Admas UniversityDocument48 pagesChapter 1 Project Quality Managemet Admas UniversityMingizem KassahunNo ratings yet
- Ihrm-CA 1 & 2-Sem 4Document14 pagesIhrm-CA 1 & 2-Sem 4PriyaNo ratings yet
- Resume 2023Document2 pagesResume 2023api-509849972No ratings yet
- Training Needs Assesment M3 TL1Document10 pagesTraining Needs Assesment M3 TL1pratimNo ratings yet
- CSM Framework - Varun Kaushal Oct 11 2021Document11 pagesCSM Framework - Varun Kaushal Oct 11 2021Varun KaushalNo ratings yet
- ARISH HUSSAIN BHATTI CVDocument5 pagesARISH HUSSAIN BHATTI CVMubeen ejazNo ratings yet
- Mis 2023Document62 pagesMis 2023Ana Mae MunsayacNo ratings yet
- Buchanan Et Al 2005 IJMR Sustainability of Organizational Change PDFDocument17 pagesBuchanan Et Al 2005 IJMR Sustainability of Organizational Change PDFShashi IsharaNo ratings yet
- 1.project Management - Course - Outline - 2022Document4 pages1.project Management - Course - Outline - 2022AISHWARYA SONINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. PRDocument15 pagesChapter 1. PRJunboy SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Business Structure For STIFFIESDocument7 pagesBusiness Structure For STIFFIESMichael Gabriel LopezNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Information System (FMIS)Document19 pagesFinancial Management Information System (FMIS)Purna Chandra MohantyNo ratings yet
- Business ModelDocument69 pagesBusiness ModelJeyryl Bartolome100% (1)
- Marketing Mind MapDocument3 pagesMarketing Mind MapsiyonaNo ratings yet
- Agunggeo,+6397 Article+Text 18228 1 2 20211224+ (52 60)Document9 pagesAgunggeo,+6397 Article+Text 18228 1 2 20211224+ (52 60)Momo chanNo ratings yet