Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardio Vascular System Nursing
Uploaded by
Gade BalajiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardio Vascular System Nursing
Uploaded by
Gade BalajiCopyright:
Available Formats
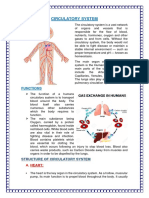
The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system, is a complex
network of blood vessels, heart, and blood that is responsible for delivering oxygen,
nutrients, and hormones to the cells of the body and removing waste products. The
following is a comprehensive set of notes on the cardiovascular system for nursing
students:
Structure of the Cardiovascular System:
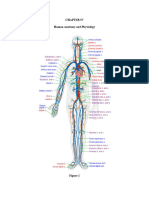
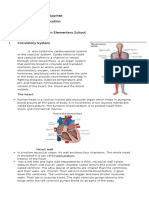
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
The Heart: The heart is a muscular organ that acts as a pump to circulate blood
throughout the body. It is located in the thorax and is divided into four chambers: the
right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle. The right atrium
and ventricle receive deoxygenated blood from the body and pump it to the lungs,
where it receives oxygen. The oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium and
ventricle, which pump it to the rest of the body.
Blood Vessels: Blood vessels are the pathways through which blood is transported
to and from the heart. There are three types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and
capillaries. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, veins carry oxygen-
poor blood back to the heart, and capillaries are the smallest blood vessels that
connect arteries and veins and provide a direct exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and
waste products between the blood and tissues.
Blood: Blood is a complex fluid that carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste
products to and from the cells of the body. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood
cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Functions of the Cardiovascular System:
1. Transportation: The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting
oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products to and from the cells of the
body. Blood carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and removes carbon
dioxide and waste products from the tissues.
2. Regulation of body temperature: Blood helps to regulate the body temperature
by carrying heat from the core of the body to the skin, where it can be lost to
the environment.
3. Defense against infections: White blood cells in the blood play a key role in
the defense against infections and help to prevent disease.
4. Blood clotting: Blood clotting is an important function of the cardiovascular
system that helps to prevent excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is
damaged. Platelets and proteins in the blood work together to form a clot and
stop bleeding.
5. Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance: The cardiovascular system
helps to regulate the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body by
transporting and distributing water, electrolytes, and hormones and
maintaining a balance between the amount of fluid inside and outside of the
cells.
6. Regulation of blood pressure: The cardiovascular system helps to regulate
blood pressure by controlling the amount of blood that is pumped from the
heart and the resistance of the blood vessels to blood flow.
Disorders of the Cardiovascular System:
There are several disorders of the cardiovascular system, including heart disease,
hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart failure. Heart disease is a general term used
to describe a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, such as
coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke. Hypertension, also known as high
blood pressure, is a condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is
persistently elevated. Atherosclerosis is a condition in which plaque builds up in the
arteries and restricts blood flow. Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is
unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body.
You might also like
- Improving Eyesight With Red Light TherapyDocument23 pagesImproving Eyesight With Red Light TherapyMark Sloan100% (8)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionFrom EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy - Lab-ManualDocument28 pagesPharmacognosy - Lab-ManualHarish KakraniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Jenkins and Continuous Integration: Jenkins Tutorial - Table of ContentDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Jenkins and Continuous Integration: Jenkins Tutorial - Table of ContentGade BalajiNo ratings yet
- Chinese Auricular Therapy, Bai XinghuaDocument243 pagesChinese Auricular Therapy, Bai Xinghuagamisemas100% (7)
- Hormones:: Signaling MoleculesDocument20 pagesHormones:: Signaling MoleculesSangeeta DwivediNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezNo ratings yet
- Function of The Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesFunction of The Circulatory SystemChristine SegundoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 67 Shock, SIRS, MODSDocument5 pagesChapter 67 Shock, SIRS, MODSMonica100% (1)
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Document13 pagesBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756No ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyDocument4 pagesBlood and Circulation, iGCSE BiologyMisterBlueSky89% (9)
- A Case Study On Typhoid FeverDocument42 pagesA Case Study On Typhoid FeverAna92% (13)
- B SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurDocument10 pagesB SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurMicaela Marcela Baldwin BarrigaNo ratings yet
- CirculatoryDocument9 pagesCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- The Cardivascular SystemDocument12 pagesThe Cardivascular SystemAbcNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio (Circulatory System)Document18 pagesGen Bio (Circulatory System)Kit KathNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular SytemDocument37 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular Sytemsophiapelayo326No ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument9 pagesHypertensionEdmr SlzarNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory System NotesDocument5 pagesHuman Circulatory System NotesAnurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Review of Related LiteratureDocument15 pagesCardiovascular System: Review of Related LiteratureCha AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Heart Structure and Blood Circulation Pathways in AnimalsDocument8 pagesHeart Structure and Blood Circulation Pathways in AnimalsKNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORTATIONDocument9 pagesTRANSPORTATIONAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Elvina CH 2Document2 pagesElvina CH 2Solomon Fallah Foa SandyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Summary - The Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesGrade 7 Science Summary - The Circulatory SystemNadine Salah El-DinNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemSaadNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument1 pageCardiovascularBea H DulatreNo ratings yet
- Biology PPT 11Document11 pagesBiology PPT 11agarwalabhinav050No ratings yet
- Organ System Amino Acids Electrolytes Blood Cells PH HomeostasisDocument25 pagesOrgan System Amino Acids Electrolytes Blood Cells PH HomeostasismilkosmalcolmNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument7 pagesCardiovascular System ExplainedRismala RANo ratings yet
- Circulatory System2Document9 pagesCirculatory System2Wajeeha AsifNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemDhea BugnaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Circulatory Systemolivia majcherNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System AssignmentDocument8 pagesCirculatory System AssignmentMonroe P ZosaNo ratings yet
- Mader Inquiry into Life Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System OutlineDocument3 pagesMader Inquiry into Life Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Outline117320No ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System The Lymphatic System The Immune SystemDocument18 pagesThe Circulatory System The Lymphatic System The Immune SystemSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- How Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemDocument8 pagesHow Long Fontanel Last For Babycirculatory SystemRoszana RafliaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Components and FunctionsDocument9 pagesCirculatory System Components and FunctionsHimanshu JindalNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument33 pagesCirculatory SystemMarco DadoNo ratings yet
- Biology Class NotesDocument1 pageBiology Class NotesSebastian RăileanuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemDrexel DalaygonNo ratings yet
- BookDocument8 pagesBookmohamed aweys abuukarNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartDocument6 pagesCirculatory System: Facts & Function: Top 10 Amazing Facts About Your HeartVance CeballosNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: FunctionsDocument12 pagesCirculatory System: FunctionsAngelica Raquel Diaz CorralesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesCardiovascular SystemErica RosislifeNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System: Parts of The Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesLymphatic System: Parts of The Circulatory Systemdownfree28No ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 3 - 2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesScience 6 - Week 3 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Transportation NotesDocument12 pagesTransportation NotesavanishNo ratings yet
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDocument31 pagesScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument22 pagesCardio Vascular SystemdeborahNo ratings yet
- Biology 3Document2 pagesBiology 3Shammy AbadNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio Chapter IVDocument3 pagesAnaphysio Chapter IVjannaelemento11No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-250543541No ratings yet
- Kami Export - Circulatory System Study Questions WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Circulatory System Study Questions WorksheetEshrat TushyNo ratings yet
- Año de la lucha contra la corrupción y la impunidad en el EcuadorDocument5 pagesAño de la lucha contra la corrupción y la impunidad en el EcuadorHelen Salazar SagasteguiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesCirculatory SystemRatiram LilhareNo ratings yet
- Transportation 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTransportation 1 PDFNakshatra PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Heart: Right Heart Left Heart. Fish in Contrast Have Two Chambers, An Atrium and A Ventricle, WhileDocument5 pagesHeart: Right Heart Left Heart. Fish in Contrast Have Two Chambers, An Atrium and A Ventricle, WhileMiguel PatrickNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42 Reading GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 42 Reading GuideCaleb SchantzNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VI Botong-Cabanbanan Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Region VI Botong-Cabanbanan Elementary SchoolRezzie Mae GelladulaNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument29 pagesTransport in HumansMadison SmithNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: By: Loricar Mae SagaDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System: By: Loricar Mae SagaI Need Some SleepNo ratings yet
- HCVD KoDocument10 pagesHCVD KoMarianne BaquilalaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument28 pagesCirculatory SystemMaria Theresa DemeterioNo ratings yet
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartFrom EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo ratings yet
- NewhashtagsDocument3 pagesNewhashtagsGade BalajiNo ratings yet
- How Can I Use The Push-Up To Improve My BreathingDocument1 pageHow Can I Use The Push-Up To Improve My BreathingGade BalajiNo ratings yet
- How Cortisol Contributes to Belly Fat and Weight GainDocument1 pageHow Cortisol Contributes to Belly Fat and Weight GainGade BalajiNo ratings yet
- Composition and Functions of BloodDocument2 pagesComposition and Functions of BloodGade BalajiNo ratings yet
- Early Stages of Embryogenesis of Tailless Amphibians - WikipediaDocument12 pagesEarly Stages of Embryogenesis of Tailless Amphibians - WikipediaGhulam MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Titration Curve of Amino Acids: Experiment No.Document7 pagesTitration Curve of Amino Acids: Experiment No.Lloyd CruzNo ratings yet
- The Link Between Schizophrenia and Substance Use DisorderDocument8 pagesThe Link Between Schizophrenia and Substance Use DisorderJHWNo ratings yet
- Kantor Cabang: BANJARMASIN - 1701 FKTP: Kertak Hanyar - 17040601Document6 pagesKantor Cabang: BANJARMASIN - 1701 FKTP: Kertak Hanyar - 17040601Ic-tika Siee ChuabbieNo ratings yet
- Materi OSC DamonDocument20 pagesMateri OSC Damonfika_khayanNo ratings yet
- Abasaglar Patient Information Leaflet Updated Dec 17Document2 pagesAbasaglar Patient Information Leaflet Updated Dec 17zafemarakiNo ratings yet
- TXII: Motor Learning and Specialized TechniquesDocument8 pagesTXII: Motor Learning and Specialized TechniquesLall JingerppangNo ratings yet
- Pengkajian Sistem PencernaanDocument44 pagesPengkajian Sistem Pencernaanmusa_nindaNo ratings yet
- Motivation, Emotion, and Stress and CopingDocument109 pagesMotivation, Emotion, and Stress and CopingeyobNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit Post AssessmentDocument15 pagesCell Unit Post Assessmentapi-282053052No ratings yet
- Use of English PDFDocument109 pagesUse of English PDFmuyi kunleNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle Events & PhasesDocument12 pagesCardiac Cycle Events & Phasesanupam manu100% (1)
- Somogyi Effect Case FileDocument2 pagesSomogyi Effect Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- CerebellumDocument62 pagesCerebellumadelina.jianu9991No ratings yet
- Pharma Nca1 Notes MidtermDocument8 pagesPharma Nca1 Notes MidtermAICEL A. ABILNo ratings yet
- The Cell A Molecular Approach 7th Edition Ebook PDFDocument41 pagesThe Cell A Molecular Approach 7th Edition Ebook PDFmathew.robertson818100% (32)
- Retina Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyDocument3 pagesRetina Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyjackNo ratings yet
- COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY KEY TERMSDocument8 pagesCOGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY KEY TERMSkringkytNo ratings yet
- Lacerated WoundDocument38 pagesLacerated Wounddomzlr18100% (2)
- Structuralism 2Document34 pagesStructuralism 2tiashukla08No ratings yet
- Embryology and Anatomy of the Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesEmbryology and Anatomy of the Nervous SystemLiza Elaine Ulep CawasNo ratings yet
- Liposic Clinical PaperDocument4 pagesLiposic Clinical Papernhutrang26No ratings yet
- Absorbable Suture IndicationDocument57 pagesAbsorbable Suture IndicationSariSyamerNo ratings yet
- Asta KarmasDocument11 pagesAsta KarmasAdriano BarbirNo ratings yet