Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 13
Uploaded by
April Rose Elopre0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views5 pagesABNORMAL PSYCH CHAPTER 13 NOTES
Original Title
CHAPTER 13.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentABNORMAL PSYCH CHAPTER 13 NOTES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views5 pagesChapter 13
Uploaded by
April Rose ElopreABNORMAL PSYCH CHAPTER 13 NOTES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
CHAPTER 13: SCHIZOPHRENIA
SPECTRUM AND OTHER
Identifying Symptoms
PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS
- Schizophrenia is a number of
behaviors or symptoms that aren’t
Psychosis – gross departure from reality, necessarily shared by all people who
which includes hallucinations and are given the diagnosis
delusions
Clinical Description, Symptoms, and
Schizophrenia Subtypes
- Pervasive type of psychosis Psychotic behavior – Used to characterize
characterized by disturbed thought, many unusual behaviors, although in tis
emotion, behavior strictest sense it usually involves delusions
- Comes from the combination of the (irrational beliefs) and/or hallucinations
Greek words for split (skhizein) and (sensory experiences in the absence of
mind (phren) external events)
- A startling disorder characterized by
- May refer to only hallucinations or
a broad spectrum of cognitive and
delusions or the unusual behavior
emotional dysfunctions, including
delusions and hallucinations, Schizophrenia – involves psychotic behavior
disorganized speech and behavior,
and inappropriate emotions Positive symptoms – symptoms
- Disrupts a person’s perception, around distorted reality; disturbing
thought, speech, and movement experiences of delusions and
- Onset: adolescence hallucinations (50-70% of
- Demence (loss of mind) schizophrenic individual have
- Precoce (early premature) hallucinations, delusions or both)
- Catatonia – alternating immobility Active manifestations of abnormal
and excited agitation behavior
- Hebephrenia – silly and immature Distortion or exaggerations of
emotionality normal behavior
- Paranoia – delusions of grandeur ● Delusions
or persecution - Gross misrepresentations of reality
- Disorder of thought content
Historical Background - Basic characteristics of madness
- Common delusions
● Emil Kraeplin – used the term
⮚ others are out to get them
dementia praecox to describe
(delusions of persecution)
schizophrenic syndrome
⮚ belief of having to end something
● Early subtypes – catatonia,
for the sake of everybody;
herniarenia and paranoia
mistaken belief that the person is
● Eugen Bleuler – introduced the term
famous or powerful (delusions of
schizophrenia – splitting of the mind
grandeur)
⮚ when a person believes that ⮚ Affective flattening – little
he/she knows has been replaced expressed emotion
by a double (Capgras syndrome) ⮚ Asociality – lack of interest in
⮚ when a person believe he is dead social interactions; social
(cotard’s syndrome) withdrawal
● Theories -
⮚ Motivational view of delusions
Disorganized motivation – includes
– beliefs as attempts to deal with
rambling speech, erratic behavior, and
and relive anxiety and stress such
inappropriate affect (ex. Smiling when
as developing stories around
you are upset)
some issues to make sense out of
uncontrollable anxieties in the - Confused or abnormal speech,
world behavior, and emotion
⮚ Deficit view of delusion - Nature of disorganized speech
- Beliefs as resulting from brain ⮚ Cognitive slippage – illogical
dysfunction that creates these and incoherent speech
disordered cognitions or perceptions ⮚ Tangentiality – going off on a
● s tangent
- Experience of a sensory events ⮚ Loose associations – conversion
without any input form the in unrelated directions
surrounding environment - Nature of disorganized affect –
- Can involve all senses inappropriate emotional behavior
- Most common: auditory - Nature of disorganized behavior –
● Findings from SPECT includes variety of unusual behaviors
Studies - Catatonia – a psychotic spectrum
- Neuroimaging shows that the part of disorder in its own right, or when
the brain most active during auditory occurring in the presence of
hallucinations is Broca’s area schizophrenia
(involved in speech production not Note: diagnosis of schizophrenia
comprehension) requires that 2 or more positive,
negative, and/or disorganized
Negative symptoms – deficits in normal
symptoms be present for at least 1
behavior in such areas as speech, blunted
month, with at least one of these
affect (lack of emotional reactivity) and
symptoms including delusions,
motivation
hallucinations, or disorganized
- Absence of normal behavior speech
⮚ Avolition/apathy – inability to SEVERITY SCALE
initiate and persist in 0 – symptoms not present
activities/apathy 1 – indicating equivocal evidence
⮚ Alogia – relative absence of (not sure)
speech 2 – present but mild symptoms
⮚ Anhedonia – presumed lack of 3 – present and moderate
pleasure; indifference symptoms
4 – present and severe psychotic features have been ruled out
because 1. No major depressive or manic
episodes have occurred concurrently
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA
with the active-phase symptoms; 2. If
A. 2 or more of the following, each mood episodes have occurred during
present for at least 1 month active-phase symptoms they have been
1. Delusions present for a minority of the total
2. Hallucinations duration of the active and residual
3. Disorganized speech (frequent periods of the illness
derailment or incoherence)
E. The disturbance is not attributable to
4. Grossly disorganized or catatonic
the physiological effects of a
behavior
substance (drug abuse, medication)
5. Negative symptoms (diminished
or another medical condition
emotional expression or
F. If there is a history of autistic
avolition)
spectrum disorder or a
B. For a significant portion of the time
communication disorder of
since the onset of the disturbance,
childhood onset, the additional
level of functioning in one or more
diagnosis of schizophrenia is made
major relations, or self-care, is
only if prominent delusions or
markedly below the level achieved
hallucinations, in addition to the
prior to the onset (or when the
other required symptoms of
onset is in childhood or adolescence,
schizophrenia, are also present for at
there is failure to achieve expected
least 1-month 9or less if successfully
level of interpersonal, academic, or
treated)
occupational functioning
C. Continuous signs of the Other Psychotic Disorders
disturbarnace persist for at least 6
● Schizophreniform disorder
months. This 6-month period must
- Psychotic symptoms lasting between
include at least 1 month of symptoms
-6 months (6 months =
( or less if successfully treated) that
schizophrenia)
meet Criterion A (active-phase
- Associated with relatively good
symptoms) and may include periods
functioning
of prodromal or residual symptoms.
- Most patients resume normal lives
During these prodromal or residual
- Lifetime prevalence: approximately
periods, the signs of the disturbance
0.2 %
may be manifested by only negative
● Schizoaffective disorder
symptoms or by two or more
- Symptoms of schizophrenia +
symptoms listed in Criterion A
additional experience of a major
present in an attenuated form (odd
manic episode
beliefs, unusual perceptual
- Psychotic symptoms must also occur
experience)
outside the mood disturbance
D. Schizoaffective disorder and
depressive or bipolar disorder with
- Prognosis is similar for people with having difficulty understanding what
schizophrenia she says. Disorganized
- Do not tend to get worried on their 2. Drew has experienced hallucinations
own and bizarre delusions for the past
● Delusional Disorder four months. Schizophreniform
- Delusions – contrary to reality disorder
⮚ Lack of other positive and 3. Greg’s cognitive skills and affect are
negative symptoms relatively intact. He, however, often
⮚ Types of delusions includes: has delusions and hallucinations that
erotomanic – irrational belief convince him enemies are out to
that one is loved by another persecute him. Delusional disorder
person, usually of higher status; 4. Alice usually holds an unusual
grandiose – involves believing posture and is sometimes seen
in one’s inflated worth, power, grimacing. catatonic
knowledge, etc.; jealous – 5. Cameron has started to hear voices,
believes the sexual partner is and this is very disturbing to him. He
unfaithful; persecutory – told his parents and recognized that
involves believing oneself is he needs to see a mental health
being malevolently treated in professional for help. Attenuated
some way; somatic – person psychosis syndrome
feels afflicted by physical defect
6. Lately Dom has become more isolated
or general medical condition
because he believes his coworkers are
⮚ Delusional
conspiring to get him fired. He becomes
- Rarel affects 20-60 individual per
agitated whenever he sees a group of
100,000
employees talking and laughing, because he
- Later age of onset, between ages
believes that they are plotting against him.
35-55
Delusional disorder
- Somewhat common in women
- 55% if patients with this hisorder are 7. Natalie reveals to her therapist that she
female hears numerous voices talking to her and
giving her orders. Her doctor has just sent
her to this therapist for what he believes to
be a major depressive episode. She had
begun to sleep all the time and contemplated
suicide often. Schizoaffective disorder
CONCEPT CHECKS
8. Shawn’s schizophrenic symptoms
13.1 disappeared afer about 4 months and he
returned to his normal life, what diagnosis
1. Jane has spent the past half hour might he have received? Schizophreniform
staring in the mirror. As you disorder
approach her, she turns away and
giggles. When you ask what she’s 9. Elias believes the government is out to get
laughing at, she answers, but you’re him. He thinks agents follow him daily,
monitor his calls, and read his mail. His 2. In _________, clinicians attempt to
roommate Cedric tried to convince him reteach such behaviors as basic
otherwise. Afer a year of this, however, conversation, assertiveness, and relationship
Cedric began to believe Elias was correct building to people with schizophrenia social
and the government was out to get him, too. skills training
Shared psychotic disorder
3. Aside from social skills training, two
13. 2 psychosocial treatments for schizophrenia,
_________ (teaching family members to be
1. The greatest risk of having
supportive) and _________ (teaching
schizophrenia is in those who have
meaningful jobs), may be helpful. Family
a(n) __________ or __________
intervention; vocational rehabilitation
with schizophrenia. Any relative
with schizophrenia will make your 4. Recent studies sometimes indicate that
chances of developing the disorder the relationship of the neurotransmitters
__________ than those of the _________ and _________ may explain
general population. Severity; dopamine; serotoninsome positive
general symptoms of schizophrenia.
2. Raised in a home other than that of
5. Because antipsychotic medications may
their biological parents, adopted
cause serious side effects, some patients stop
children of parents with
taking them. One serious side effect is called
schizophrenia have a(n) __________
_________, which may include
chance of having the disorder
Parkinsonian symptoms. Extrapyramidal
themselves. Children of people with
symptoms
schizophrenia adopted into families
without schizophrenia have a 6. Difficult cases of schizophrenia seem to
__________ than-average chance of improve with a serotonin and dopamine
having schizophrenia. Higher and antagonist called olanzapine
lower
3. the likelihood of a child’s having
schizophrenia is influenced by the
__________ of the parent’s disorder.
One may inherit a predisposition for
__________ schizophrenia that is the
same or different from that of the
parent. Severity, general
Concept Check 13.3
1. Setting up an elaborate _________ in
which patients are fined for disruptive or
inappropriate behavior and rewarded for
appropriate behavior is beneficial in
hospitals. Token economy
You might also like
- Schizophrenia Unmasked: Personal Stories and Proven Techniques to Reclaim Your LifeFrom EverandSchizophrenia Unmasked: Personal Stories and Proven Techniques to Reclaim Your LifeNo ratings yet
- PSY322 Chap 12 - Schizophrenia Spectrum and Psychotic DisordersDocument14 pagesPSY322 Chap 12 - Schizophrenia Spectrum and Psychotic DisordersGabrielle ParlaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia pdf-1Document10 pagesSchizophrenia pdf-1Jayanth MamundiNo ratings yet
- FHHBBCFDocument53 pagesFHHBBCFAayush AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and Mental Status ExamDocument14 pagesSchizophrenia and Mental Status ExamGeraldine TeneclanNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia, Neurodevelopmental & Neurocognitive DisordersDocument11 pagesSchizophrenia, Neurodevelopmental & Neurocognitive DisordersSyndell PalleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16: Schizophrenia: Tomorrow: Chapter 17: Mood Disorders and SuicideDocument65 pagesChapter 16: Schizophrenia: Tomorrow: Chapter 17: Mood Disorders and SuicideRainier Moreno-LacalleNo ratings yet
- Sudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheDocument2 pagesSudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheNeicole BandalaNo ratings yet
- NOTES SCHIZOPHRENIA and EATING DISORDERSDocument10 pagesNOTES SCHIZOPHRENIA and EATING DISORDERSshaimb.portuguezNo ratings yet
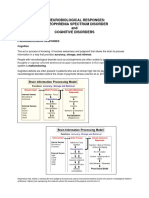
- D. Neurobiological Responses: Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder and Cognitive DisordersDocument12 pagesD. Neurobiological Responses: Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorder and Cognitive DisordersAnna Sofia Reyes100% (1)
- Notes On SchizophreniaDocument6 pagesNotes On SchizophreniaUnkown IndividualNo ratings yet
- Ap 7Document3 pagesAp 7Andrea LuraNo ratings yet
- Ab PsychDocument8 pagesAb PsychKristine ManaloNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderDocument89 pagesSchizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorderethiomoney15No ratings yet
- ShizopreniaDocument5 pagesShizopreniaFarmisa MannanNo ratings yet
- Summarized Abnormal PsychologyDocument13 pagesSummarized Abnormal PsychologyMa.Janine Torres100% (1)
- SchizopheniaDocument2 pagesSchizopheniaChamara MudalinayakaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesSchizophrenia Lecture NotesDale BuckmanNo ratings yet
- Treating Delusional Disorder and SchizophreniaDocument68 pagesTreating Delusional Disorder and SchizophreniaLana LocoNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument17 pagesSchizophreniaLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
- PSY 8 Finals NotesDocument24 pagesPSY 8 Finals Noteskoyaaniqatsi0206No ratings yet
- SCHIZOPHRENIA ReviewerDocument4 pagesSCHIZOPHRENIA ReviewerEvieNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and Related DisordersDocument11 pagesSchizophrenia and Related DisordersOana Maria PopaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Cognitive DisorderDocument13 pagesSchizophrenia Spectrum Disorders Cognitive DisorderRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument20 pagesSchizophreniavoiceman1106No ratings yet
- Lesson1 SchizophreniaDocument4 pagesLesson1 SchizophreniaAngelica PabelloNo ratings yet
- Got Me Feelin Like A PsychoDocument5 pagesGot Me Feelin Like A PsychoChan's RoomNo ratings yet
- Delirium (Disturbance in Mental Abilities That Result in Confused Thinking and Reduce AwarenessDocument8 pagesDelirium (Disturbance in Mental Abilities That Result in Confused Thinking and Reduce Awarenessmed sofNo ratings yet
- Psychosis and Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersDocument5 pagesPsychosis and Schizophrenia Spectrum DisordersMegan ClearyNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument64 pagesSchizophreniaALMAZ SAHANANo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Types of SchizophreniaDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To The Types of Schizophreniasarzlasco09No ratings yet
- Women and Schizophrenia ComplianceDocument7 pagesWomen and Schizophrenia ComplianceDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Schizophrenia and Other PsychosisDocument7 pages1.1 Schizophrenia and Other PsychosisMark Christian CuiNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 1.1A Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderDocument28 pagesPSYCH 1.1A Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderZaza100% (1)
- SCHIZOPHRENIA: A Clinical Syndrome of Variable PsychopathologyDocument7 pagesSCHIZOPHRENIA: A Clinical Syndrome of Variable PsychopathologyNica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Consider The Effect of Nature & Nurture Predisposing & Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesConsider The Effect of Nature & Nurture Predisposing & Precipitating FactorMarichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia (Draft)Document8 pagesSchizophrenia (Draft)ag.carismaaNo ratings yet
- Tugas UNtar 3Document28 pagesTugas UNtar 3Daniel Filemon PosoNo ratings yet
- Tugas UNtar 3Document40 pagesTugas UNtar 3Daniel Filemon PosoNo ratings yet
- Psychology ReviewerDocument103 pagesPsychology ReviewerRachel AlmiaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and TreatmentDocument62 pagesSchizophrenia: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and TreatmentMA 09No ratings yet
- Understanding Abnormal Behavior and Classification of PsychosisDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Abnormal Behavior and Classification of PsychosisWATI KAKINo ratings yet
- This Person Is Not Manifesting To Reality Perception (Ego)Document4 pagesThis Person Is Not Manifesting To Reality Perception (Ego)Nica VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Psychopathology concepts and phenomenaDocument12 pagesPsychopathology concepts and phenomenaskNo ratings yet
- 1: Schizoprhenia Spectrum Disorder: Sazon, Marva Therysse A. Psych 136 - Abnormal Psychology Bs Psychology FinalsDocument37 pages1: Schizoprhenia Spectrum Disorder: Sazon, Marva Therysse A. Psych 136 - Abnormal Psychology Bs Psychology FinalsMARIE ROSE L. FUNTANARNo ratings yet
- Psychotic DisordersDocument67 pagesPsychotic DisordersHappy chifundaNo ratings yet
- Psychotic Disorder: HallucinationDocument12 pagesPsychotic Disorder: HallucinationDr-Laila YousafzaiNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument21 pagesSchizophreniaDjordje AndonovNo ratings yet
- Paranoid Schizophrenia: OlehDocument52 pagesParanoid Schizophrenia: Olehbunga julia100% (1)
- Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisorderDocument14 pagesSchizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disordereyesheild100% (1)
- SchizophreniaDocument58 pagesSchizophreniaArpit AroraNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Symptoms and TreatmentDocument12 pagesSchizophrenia Symptoms and TreatmentWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Schizophrenia - Students Copy (2023)Document72 pagesUnit 4 - Schizophrenia - Students Copy (2023)jihanrajabNo ratings yet
- Positive Symptoms: Thought WithdrawalDocument4 pagesPositive Symptoms: Thought WithdrawallindiNo ratings yet
- Pages From First Aid For The Psychiatry Boards (2010)Document7 pagesPages From First Aid For The Psychiatry Boards (2010)Julio DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: DR Rachel Kang'Ethe Department of PsychiatryDocument76 pagesSchizophrenia and Other Psychotic Disorders: DR Rachel Kang'Ethe Department of PsychiatryRahul Kumar Diwakar100% (1)
- SCHIZOPHRENIA AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS LECTUREDocument69 pagesSCHIZOPHRENIA AND OTHER PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS LECTURERahul Kumar DiwakarNo ratings yet
- 03 SignsSymptomsPsychopathologyDocument10 pages03 SignsSymptomsPsychopathologyava1234567890100% (1)
- Nursing Care of The Patient With Schizophrenia & Psychosis F20Document47 pagesNursing Care of The Patient With Schizophrenia & Psychosis F20nidhi PatelNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Chapter EditedDocument15 pagesSchizophrenia Chapter EditedamarnehNo ratings yet
- UtilitarianismDocument2 pagesUtilitarianismApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- Aretaic VirtueDocument1 pageAretaic VirtueApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- Aretaic VirtueDocument1 pageAretaic VirtueApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- HylemorphismDocument3 pagesHylemorphismApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- CONFUCIUSDocument2 pagesCONFUCIUSApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- MendalianDocument3 pagesMendalianApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- British and American Vocabulary DifferencesDocument1 pageBritish and American Vocabulary DifferencesApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- Institutional Mechanisms and Human Rights of WomenDocument4 pagesInstitutional Mechanisms and Human Rights of WomenApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Organization and DNA ReplicationDocument10 pagesChromosome Organization and DNA ReplicationApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Neurocognitive DisordersDocument49 pagesChapter 15 Neurocognitive DisordersApril Rose ElopreNo ratings yet
- Health Statistics and EpidemiologyDocument15 pagesHealth Statistics and EpidemiologyDaniela Nicole Manibog ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Tests for Liver Function: Serum BilirubinDocument4 pagesTests for Liver Function: Serum BilirubinHiba EmadNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Medicne: Prof. Gilbert EzengigeDocument33 pagesNutritional Medicne: Prof. Gilbert EzengigeGilbert EzengigeNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Facial Fat Grafting PDFDocument7 pagesTechniques in Facial Fat Grafting PDFshininghmNo ratings yet
- Mal de Ojo (English)Document2 pagesMal de Ojo (English)Tim OrtizNo ratings yet
- Safety and Efficacy of Vinyl Bags in Prevention of Hypothermia of Preterm Neonates at BirthDocument3 pagesSafety and Efficacy of Vinyl Bags in Prevention of Hypothermia of Preterm Neonates at BirthArgadia YuniriyadiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument56 pagesUntitledkelvin kyandoNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Activities LGCDD LGMEDDocument8 pagesConsolidated Activities LGCDD LGMEDRegion PersonnelNo ratings yet
- Tumour Markers PPT by DR VijayDocument31 pagesTumour Markers PPT by DR Vijaydr vijay60% (5)
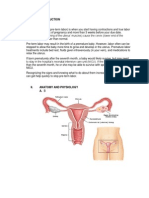
- AnatomyDocument93 pagesAnatomyHiba V.ANo ratings yet
- Health, Safety & Nutrition for Young ChildrenDocument50 pagesHealth, Safety & Nutrition for Young ChildrenChen Lee WanNo ratings yet
- Ortho ExamDocument9 pagesOrtho ExamPrince Rener Velasco Pera100% (2)
- Mechanism of BreathingDocument1 pageMechanism of BreathingjaysraelNo ratings yet
- Exploring Nurses ' Experiences of Psychological Distress During Care of Patients With COVID-19: A Qualitative StudyDocument9 pagesExploring Nurses ' Experiences of Psychological Distress During Care of Patients With COVID-19: A Qualitative StudyPinj BlueNo ratings yet
- Probiotics For Preventing Urinary Tract Infections in Adults and Children - Schwenger, EM - 2015 - Cochrane LibraryDocument21 pagesProbiotics For Preventing Urinary Tract Infections in Adults and Children - Schwenger, EM - 2015 - Cochrane LibraryMixcy MabatidNo ratings yet
- Salicylates Tca ToxicityDocument54 pagesSalicylates Tca Toxicityapi-298936498No ratings yet
- Ritickoval Professional Latin For PharmacistsDocument143 pagesRitickoval Professional Latin For PharmacistsÁnh Ngọc PhanNo ratings yet
- Pathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersDocument5 pagesPathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersAmna Baig0% (1)
- Killer Inside: Aaron Hernandez's Brain DamageDocument3 pagesKiller Inside: Aaron Hernandez's Brain DamageshevarkNo ratings yet
- CSIR Life Sciences Official Model PaperDocument34 pagesCSIR Life Sciences Official Model PaperSoftqGunturNo ratings yet
- DepEd LCP July3Document49 pagesDepEd LCP July3Jelai ApallaNo ratings yet
- Pre Term Case OlieDocument10 pagesPre Term Case OlieKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- NLE 2015 Questions SampleDocument8 pagesNLE 2015 Questions SampleJona Suarez100% (4)
- (Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences) A Toxic Hepatitis Caused The Kombucha Tea Case ReportDocument4 pages(Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences) A Toxic Hepatitis Caused The Kombucha Tea Case ReportNguyễn ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Adverse Event Tracking Log: Subject Initials Subject ID# Page ofDocument1 pageAdverse Event Tracking Log: Subject Initials Subject ID# Page ofPratyNo ratings yet
- Master Plan to Achieve Zero Workplace AccidentsDocument38 pagesMaster Plan to Achieve Zero Workplace AccidentsgilbertwildNo ratings yet
- Sop-1-Hand-Hygiene NOSIDocument7 pagesSop-1-Hand-Hygiene NOSINosi Aprilia RinaldiNo ratings yet
- YouTube Promotes BrandsDocument6 pagesYouTube Promotes BrandsSilpi YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Nicotinic Acid LPDocument10 pagesNicotinic Acid LPRUEDAS JennyNo ratings yet
- Farnsworth D15 Color Test KitDocument4 pagesFarnsworth D15 Color Test Kitdian eka saputraNo ratings yet