Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set - 2015 MACRO
Uploaded by
Duge Galtsa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pages1. The document contains an advanced macroeconomics problem set with 14 multi-part questions covering topics such as the liquidity trap, monetary transmission mechanisms, rational expectations, IS-LM analysis, aggregate demand and supply frameworks, the Solow growth model, and open economy macroeconomics.
2. Students are asked to calculate equilibrium income, multipliers, and budget surpluses for economies with different consumption functions, investment levels, and tax rates.
3. Questions also address the shapes of the IS and LM curves under different assumptions, as well as the effects of fiscal and monetary policy in each case.
Original Description:
solved equation for linear programming
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document contains an advanced macroeconomics problem set with 14 multi-part questions covering topics such as the liquidity trap, monetary transmission mechanisms, rational expectations, IS-LM analysis, aggregate demand and supply frameworks, the Solow growth model, and open economy macroeconomics.
2. Students are asked to calculate equilibrium income, multipliers, and budget surpluses for economies with different consumption functions, investment levels, and tax rates.
3. Questions also address the shapes of the IS and LM curves under different assumptions, as well as the effects of fiscal and monetary policy in each case.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesProblem Set - 2015 MACRO
Uploaded by
Duge Galtsa1. The document contains an advanced macroeconomics problem set with 14 multi-part questions covering topics such as the liquidity trap, monetary transmission mechanisms, rational expectations, IS-LM analysis, aggregate demand and supply frameworks, the Solow growth model, and open economy macroeconomics.
2. Students are asked to calculate equilibrium income, multipliers, and budget surpluses for economies with different consumption functions, investment levels, and tax rates.
3. Questions also address the shapes of the IS and LM curves under different assumptions, as well as the effects of fiscal and monetary policy in each case.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Advanced Macroeconomics
Problem Set
Answer the following questions.
1. Write short note on the following.
a) Liquidity trap. E. The Marshall-Lerner condition h.
Crowding out
b) Monetary transmission mechanism f. Neutrality of money i. Possible causes of
inflation
c) Sterilization g. Devaluation j. Types of
unemployment
d) Rational expectation
2. Consider an economy with the following aggregates:
Consumption function: C = 50+0.8Yd, where Yd is disposable income
Autonomous investment: I =70
Government expenditure: G=200
Government transfer: TR=100
Tax rate: t=0.20
where r is interest rate.
a) Calculate the equilibrium level of income, the multiplier, and the budget surplus in this
model.
b) Suppose that the marginal propensity to consume increased permanently to 0.9. What is
the impact of this increase on the level of equilibrium income and the multiplier?
c) Suppose that the tax rate t increases to 0.25. Calculate the new equilibrium level of
income, the budget surplus, and the multiplier.
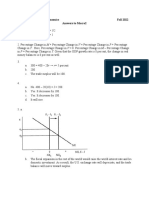
3. What would be the shape of:
a) The IS curve if investment does not depend on the interest rate?
b) The LM curve if the demand for money does not depend on interest rate?
c) The LM curve if the demand for money does not depend on income?
d) The LM curve if the demand for money is extremely sensitive to the interest
rate?
e) Discuss the effectiveness of fiscal and monetary policies in each of the above
cases.
4. Consider an economy with a different level of aggregates as follows:
Consumption function: C = 0.8 (1- t) Y
Tax rate: t = 0.25
Investment: I = 900 - 50r
Government expenditure: G=800
Demand for money: L = 0.25Y - 62.5r
Money supply: M = 1000
Price level: P = 2
a) Derive the IS and LM equations.
b) Determine the equilibrium levels of income and interest rate.
c) Calculate the government spending multiplier.
d) By how much income and interest change for a unit change in government spending?
e) How do you account for the difference between the value of the government spending
multiplier in (b) and the change in income in (d)? (Hint: What happens to investment?)
5. In question number 4 above, suppose that government spending increased to 900 from its
initial value of 800.
a) Calculate the new equilibrium levels of income and interest rate.
b) What would be the level of income at the initial equilibrium interest rate and how does
this compare to the full multiplier income?
c) Account for the difference between the full multiplier level of income and the actual
equilibrium level of income.
6. In question 5, suppose that, all other things being equal, the first round of policy measure
increased price level to 4.
a) Calculate the new equilibrium level of income and interest.
b) Derive the aggregate demand function.
7. Suppose that a government seeks an advice on how to achieve an increase in investment
without overheating the economy. Using your knowledge of the IS-LM framework, show
how you could advise the government on the policy mix.
8. Suppose the government of a typical developing country increased the salary of civil servants
at a time when there is bumper harvest due to timely rainfall. What will happen to prices?
Discuss using your knowledge of AD-AS framework.
9. Explain why trade off exists between inflation and unemployment.
10.
11. Consider the Solow model with technology. Suppose that saving rate increases from s to s’.
Demonstrate using graphs and quantitative methods how this shock affects
a) Level of per capita income.
b) Level of capital per effective worker.
c) Growth rate in per capita income.
12. The Solow exogenous growth model with augmented population growth and technological
progress is a dynamic model that allows us to see how our endogenous variables are being
affected and that describes how the economy moves toward a stable equilibrium position.
a) Assuming the Cobb-Douglas production function per effective labor is:
Calculate the Golden rule and the Steady state level of capital per effective labour and
interpret the result.
b) Mathematically prove that output per worker grows by the growth rate of technology (g),
and total output grows by the summation of the growth rates of population (n) and
technology (g).
13. Suppose that the economy is open to external trades, using the Mundell-Fleming model
evaluate the effectiveness of
a) Fiscal and monetary policies under fixed exchange rate regime.
b) Fiscal and monetary policies under flexible exchange rate regime when there is high
capital mobility.
14. Suppose that we have an overlapping generation model and the utility is
U t =ln C 1t +Bln C 2 t +1, and the production function is given as: F ( K t , Lt )= A K αt L1−α
t .
a) Find the appropriate first order conditions.
b) Solve the worker’s saving rate.
c) Find the Golden rule level of capital stock.
d) Compute the steady state saving that is required to maintain golden rule level of capital
stock.
e) Under what condition on the model parameters will the saving exceed the golden rule
level.
You might also like
- Bài tập ôn tậpDocument7 pagesBài tập ôn tậpLinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Qns Sec 222Document8 pagesQns Sec 222Haggai SimbayaNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University College of Business and Economics Department of Economics Macroeconomics I (Econ 2031) WorksheetDocument4 pagesAddis Ababa University College of Business and Economics Department of Economics Macroeconomics I (Econ 2031) WorksheetProveedor Iptv España100% (3)
- P T D Δ M P G X D T is real tax revenue, M is money supply, X is transfers. From this structureDocument7 pagesP T D Δ M P G X D T is real tax revenue, M is money supply, X is transfers. From this structureGökhan DüzüNo ratings yet
- Exam1 Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesExam1 Review QuestionsOpen ThedorNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper: EconomicsDocument3 pagesModel Question Paper: Economicssharathk916No ratings yet
- PQ 3Document3 pagesPQ 3tony345No ratings yet
- 2011 Spring - Econ 312 - Practice Problem Set 2Document16 pages2011 Spring - Econ 312 - Practice Problem Set 2hami619No ratings yet
- Exam1Answers 1Document6 pagesExam1Answers 1Ай МөлдирNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics 20181220 180426275Document4 pagesMacroeconomics 20181220 180426275Honelign ZenebeNo ratings yet
- Ficha de Trabalho III.1Document5 pagesFicha de Trabalho III.1yayaayoi27No ratings yet
- PS01Document4 pagesPS01Manooch GholmoradiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Sec 222 2020Document3 pagesAssignment 1 Sec 222 2020Haggai Simbaya100% (1)
- Macro Tutorial Set 2Document3 pagesMacro Tutorial Set 2Omari MaugaNo ratings yet
- Poly MacroMass N2Document10 pagesPoly MacroMass N2simao_sabrosa7794No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 For StudentsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 For Studentsdesada testNo ratings yet
- Economics Assignment QuestionsDocument5 pagesEconomics Assignment Questionsعبداللہ احمد جدرانNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Please Answer The Following QuestionsDocument7 pagesHomework 1 Please Answer The Following QuestionsAhmed Danaf100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 HoursDocument13 pagesSample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 Hourstheunsung taleNo ratings yet
- Class 5. The IS-LM Model and Aggregate Demand: Macroeconomics I. Antonio Zabalza. University of Valencia 1Document26 pagesClass 5. The IS-LM Model and Aggregate Demand: Macroeconomics I. Antonio Zabalza. University of Valencia 1Zenni Cr100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 HoursDocument4 pagesSample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Economics (030) Mm. 80 Time: 3 HoursGaurav VermaNo ratings yet
- Ecu-07412 Tutorial Qns 2Document3 pagesEcu-07412 Tutorial Qns 2Omari MaugaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Sec 222 2020Document2 pagesAssignment 3 Sec 222 2020Haggai SimbayaNo ratings yet
- ECON208 Main 20-21Document5 pagesECON208 Main 20-21dariusNo ratings yet
- MA Economics 2010Document19 pagesMA Economics 2010Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11-12 QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 11-12 QuestionsFreeBooksandMaterialNo ratings yet
- Macro TS1Document2 pagesMacro TS1Katunga MwiyaNo ratings yet
- MoE 2023Document28 pagesMoE 2023Teddy DerNo ratings yet
- Final Exam December 2020Document5 pagesFinal Exam December 2020Ikhwan RizkyNo ratings yet
- Exercises Chapter 1Document19 pagesExercises Chapter 1D LVNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 - MergedDocument43 pagesProblem Set 2 - MergedSamantha Marie RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Azərbaycan Dövlət İqtisad Universiteti Beynəlxalq İqtisadiyyat Məktəbi Beynəlxalq İqtisadiyyat (İngilis Dilli) KafedrasiDocument5 pagesAzərbaycan Dövlət İqtisad Universiteti Beynəlxalq İqtisadiyyat Məktəbi Beynəlxalq İqtisadiyyat (İngilis Dilli) KafedrasiNihad PashazadeNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Exam 1Document7 pagesSample Questions Exam 1Mindy Tweet NogNo ratings yet
- ECON 209 Midterm 2012WDocument2 pagesECON 209 Midterm 2012WexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Review Questions 3 For Advanced Macroeconomics-1Document4 pagesReview Questions 3 For Advanced Macroeconomics-1jared demissieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - Revision Questions Answers-1Document6 pagesChapter 18 - Revision Questions Answers-1Christiaan DiedericksNo ratings yet
- Econ 302 - Intermediate Macroeconomic AnalysisDocument3 pagesEcon 302 - Intermediate Macroeconomic AnalysisMangani IsaacNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Summer 2018Document4 pagesHomework 1 Summer 2018Amirhosein AbediniNo ratings yet
- Examen 5 MacroeconomíaDocument8 pagesExamen 5 MacroeconomíaluciaNo ratings yet
- Set A Intermediate Macro - 1 Sem 3 ST StephensDocument4 pagesSet A Intermediate Macro - 1 Sem 3 ST StephensJia KaurNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics Exercise 1Document2 pagesMacro Economics Exercise 1Daisy MistyNo ratings yet
- Exercise Sheet 11Document3 pagesExercise Sheet 11Jesse Maye SolaboNo ratings yet
- IOBM Question PaperDocument2 pagesIOBM Question PaperAtif AslamNo ratings yet
- Econ2123 Practice1 SolutionDocument9 pagesEcon2123 Practice1 SolutionNgsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document18 pagesChapter 9Karen ReasonNo ratings yet
- 2022 Midterm - SolutionDocument6 pages2022 Midterm - SolutionwannafadedNo ratings yet
- Ecn 101 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Summersession2 2007Document14 pagesEcn 101 - Intermediate Macroeconomics Summersession2 2007Kofi AsaaseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics: Exercise 8Document1 pageIntroduction To Economics: Exercise 8VrajNo ratings yet
- Mid TestDocument8 pagesMid Testseven_jason_guo0% (1)
- Problem Set 3: Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesProblem Set 3: Izmir University of Economics Department of Economics Econ 102 Principles of MacroeconomicsBahar SamiNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Macro Economics - Assignment 1 PDFDocument12 pagesIntermediate Macro Economics - Assignment 1 PDFTriple HNo ratings yet
- w10 112 v1Document22 pagesw10 112 v1Rusty ButlerNo ratings yet
- Model Test Paper For PHD Entrance in EconomicsDocument3 pagesModel Test Paper For PHD Entrance in EconomicsshardaharyaniNo ratings yet
- RB CAGMAT REVIEW Macroeconomics Reviewer - Yet Sample QuestionsDocument35 pagesRB CAGMAT REVIEW Macroeconomics Reviewer - Yet Sample QuestionsSylveth Novah Badal Denzo100% (1)
- AssigmentDocument4 pagesAssigmentYakubu AbassNo ratings yet
- PS4Document7 pagesPS4Steven Hyosup KimNo ratings yet
- To Scale. If It Causes Output To Increase by More Than 10 Percent, The ProductionDocument5 pagesTo Scale. If It Causes Output To Increase by More Than 10 Percent, The Production盧愷祥No ratings yet
- Final For Physics 1203Document8 pagesFinal For Physics 1203kmartdetectiveNo ratings yet
- The Process of Capitalist Production as a Whole (Capital Vol. III)From EverandThe Process of Capitalist Production as a Whole (Capital Vol. III)No ratings yet
- International Relations: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandInternational Relations: A Simple IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- BIOTECh Research Paper 2022Document28 pagesBIOTECh Research Paper 2022Duge Galtsa100% (1)
- Animal ManureDocument2 pagesAnimal ManureDuge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- Action ResearchDocument18 pagesAction ResearchDuge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- Answerstohomework 5 Summer 2012Document15 pagesAnswerstohomework 5 Summer 2012Duge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- T Calculated & Tabulated Value of ExeDocument1 pageT Calculated & Tabulated Value of ExeDuge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- IDM Term Paper 2023Document15 pagesIDM Term Paper 2023Duge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 SUMMARYDocument1 pageAssignment #2 SUMMARYDuge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- IDM Assignment#1Document3 pagesIDM Assignment#1Duge Galtsa100% (1)
- Answer For Assignment #2Document10 pagesAnswer For Assignment #2Duge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument8 pagesEconomicsDuge GaltsaNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave TheoryDocument29 pagesElliott Wave TheoryMikhael TinambunanNo ratings yet
- Consolidated CasesDocument91 pagesConsolidated CasesJames Jake ParkerNo ratings yet
- Downloads (1) PDFDocument17 pagesDownloads (1) PDFYarod Yisrael100% (1)
- Certificate in Accounting (IAS) Level 3/series 3-2009Document14 pagesCertificate in Accounting (IAS) Level 3/series 3-2009Hein Linn Kyaw75% (4)
- Major Project On Coca Cola For Marketing and Management StudentsDocument21 pagesMajor Project On Coca Cola For Marketing and Management Studentsfaizmkt94No ratings yet
- Termeni Contabili in Engleza PDFDocument11 pagesTermeni Contabili in Engleza PDFDo Minh DucNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Tuto c2Document1 pageMacroeconomics Tuto c2Nazri AnaszNo ratings yet
- Beda Pajak Dan RetribusiDocument6 pagesBeda Pajak Dan RetribusiimantaNo ratings yet
- Proforma Invoice For Solar LED Street Light From Zhongshan Alltop Lighting Co., LTD-20230215-C15.1878Document1 pageProforma Invoice For Solar LED Street Light From Zhongshan Alltop Lighting Co., LTD-20230215-C15.1878Reveco FermilioNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 102 - Share Based Payment - QuestionsDocument3 pagesInd AS 102 - Share Based Payment - QuestionsKashika AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Document-A Complete Guide To Volume Price AnalysisDocument8 pagesDocument-A Complete Guide To Volume Price AnalysisJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Banking Awareness PDF For All Banking Exams - 2141Document26 pagesBanking Awareness PDF For All Banking Exams - 2141AnuuNo ratings yet
- ID22 Financial PresentationDocument48 pagesID22 Financial PresentationRISHAV BAIDNo ratings yet
- Private Public and Global EnterprisesDocument23 pagesPrivate Public and Global EnterprisesusethNo ratings yet
- Salary Dost Credit Policy: Loan Limit and TenureDocument11 pagesSalary Dost Credit Policy: Loan Limit and TenureAlpesh KuleNo ratings yet
- 11A. GST VOL 1 - CA INTER NOV 2020 EXAM (6th EDITION) PDFDocument236 pages11A. GST VOL 1 - CA INTER NOV 2020 EXAM (6th EDITION) PDFHindutav aryaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting: Theory and Analysis: Text and CasesDocument69 pagesFinancial Accounting: Theory and Analysis: Text and CasesgabiNo ratings yet
- Banking Laws - DizonDocument26 pagesBanking Laws - DizonZsa-shimi FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Rebates Form: ASA Philippines Foundation IncDocument6 pagesRebates Form: ASA Philippines Foundation IncRichard Boy Terte FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Notice of Allodial Cost Schedule (Template) PDFDocument7 pagesNotice of Allodial Cost Schedule (Template) PDFAnonymous byf7jsz100% (3)
- Accounting For Business Combinations: Learning ObjectivesDocument41 pagesAccounting For Business Combinations: Learning Objectivesmohammad.mamdooh94720% (1)
- 49 2Document14 pages49 2Ali RaziNo ratings yet
- Flat Purchase by Way of Share Certificate MethodDocument4 pagesFlat Purchase by Way of Share Certificate MethodGuidance ValueNo ratings yet
- Bank Copy CandidateDocument1 pageBank Copy CandidateVijayBabuNo ratings yet
- Beiersdorf AG 2019 Annual Financial Statements PDFDocument40 pagesBeiersdorf AG 2019 Annual Financial Statements PDFPotato ChanNo ratings yet
- First Long Quiz COSMANDocument5 pagesFirst Long Quiz COSMANby ScribdNo ratings yet
- Corporate Credit Card AgreementDocument5 pagesCorporate Credit Card AgreementmanishNo ratings yet
- NPV Irr MCQDocument6 pagesNPV Irr MCQMM Fakhrul Islam0% (1)
- Income Tax Act, 2058 and Income Tax Regulation, 205921201613436 PMDocument248 pagesIncome Tax Act, 2058 and Income Tax Regulation, 205921201613436 PMSagun KatuwalNo ratings yet