Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Uploaded by
wally0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThis document discusses cell organelles and their functions. It begins by asking about which organelles would be abundant in skeletal muscle cells and palisade cells. It then lists functions of lysosomes and the Golgi apparatus. Later questions discuss the Golgi apparatus and ribosomes, as well as organelles involved in protein synthesis and transporting cell secretions. Diagrams of cells include labels for chloroplasts and vacuoles. The role of cristae in mitochondria and the function of the stroma in chloroplasts are provided. Formulas for calculating microscope magnification and reasons for specimen staining are given. Functions of the Golgi apparatus, structures in plant but not animal cells, and roles of microscope parts are listed. Definitions
Original Description:
the cell
Original Title
THE CELL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses cell organelles and their functions. It begins by asking about which organelles would be abundant in skeletal muscle cells and palisade cells. It then lists functions of lysosomes and the Golgi apparatus. Later questions discuss the Golgi apparatus and ribosomes, as well as organelles involved in protein synthesis and transporting cell secretions. Diagrams of cells include labels for chloroplasts and vacuoles. The role of cristae in mitochondria and the function of the stroma in chloroplasts are provided. Formulas for calculating microscope magnification and reasons for specimen staining are given. Functions of the Golgi apparatus, structures in plant but not animal cells, and roles of microscope parts are listed. Definitions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesThe Cell Organelles and Their Functions
Uploaded by
wallyThis document discusses cell organelles and their functions. It begins by asking about which organelles would be abundant in skeletal muscle cells and palisade cells. It then lists functions of lysosomes and the Golgi apparatus. Later questions discuss the Golgi apparatus and ribosomes, as well as organelles involved in protein synthesis and transporting cell secretions. Diagrams of cells include labels for chloroplasts and vacuoles. The role of cristae in mitochondria and the function of the stroma in chloroplasts are provided. Formulas for calculating microscope magnification and reasons for specimen staining are given. Functions of the Golgi apparatus, structures in plant but not animal cells, and roles of microscope parts are listed. Definitions
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
THE CELL
1. Which organelle would be abundant in?
Skeletal muscle cell __________________
Palisade cell __________________
2. State the functions of the following organelles.
Lysosomes __________________
Golgi apparatus __________________
3. State the functions of the following organelles;
Goigi apparatus _______________
Ribosomes cell _______________
4. Name the organelles that perform each of the following functions in a cell.
Protein synthesis __________________
Transport cell secretions __________________
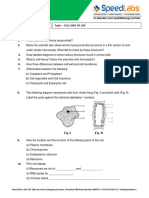
5. The diagram below represents a cell.
a) Name the parts labeled x and y
X _______________
Y _______________
b) Suggest why the structures labeled x would be more on one side than the other
side.
6. a) State the function of cristae in mitochondria
b) The diagram below represents a cell organelle
(i) Name the part labeled Y (1mk)
(ii) State the function of the part labeled X (2mks)
7. a) What is the formula for calculating linear magnification of a specimen when using
a hand lens? (1mk)
b) Give a reason why staining is necessary when preparing specimens for
observation under the microscope. (1mk)
8. State three functions of Golgi apparatus. (3mks)
9. Name two structures found in plant cell but are absent in animals cell.
10. Write the role of the following parts of a microscope
i) Nerve cell
ii) Palisade cell
iii) Root hair cell
iv) Red blood cell
11. The diameter field of view of a light microscopic is 3.5mm. Plant cells lying of the
diameter are 10. Determine the size of one cell microns (1mm = 1000µm)
12. Define the following
i) Tissue
ii) Organ
iii) Organ system
THE CELL ANSWERS
1. (a) - Secretion of useful substances
- Formation of secretory vesicles
2. (a) - Destroying old and worn out organelles
(b) - Secretion reticulum (rough)
- Formation of secretory vesicles
3. (a) - Mitochondrion
(b) - Chloroplast
4. - Ribosomes
- Endoplasmic reticulum (rough)
5. (a) - X- chloroplasts
- Y - Vacuole
(b) In dim light. They move to the upper part of the cell in order to receive
enough sunlight for photosynthesis
6. (a) - Increase surface area for attachment of respiratory enzymes hence
increasing rate of respiration.
(b) (i) Stroma
(ii) Absorb sunlight used for light stage of photosynthesis
7. (a) Drawing = Length of the drawing
Magnification Length of the object
(b) It is adding a dye to the specimen to make the features clearer and distinguishable
8. - Form vesicles that ransport materials to other parts of the cell e.g. proteins
-Transport secretions to the cell surface for secretion e.g. enzymes and mucus.
- They form lysosomes
9. - Cell wall
- Large vacuole
- Chloroplast
- Starch granules
10. (i) Reflect light from the source to the microscope/specimen
(ii) Regulate amount of light entering the microscope/reaching specimen.
(iii) Move body tube up and down in order to obtain a rough focus of the image of
specimen.
11. It is the ability to differentiate two structures or organelles lying close
12. (a) A cell is structurally and physiologically modified in order to perform a
particular function.
(b) (i) Presence of dendrites to receive impulses
(ii) Presence of chloroplasts to trap sunlight
(iii) Elongated and no cuticles in order to absorb water
(iv) Biconcave shape to increase surface area for diffusion of
oxygen/haemoglobin.
13. 1 mm = 1000μm
3.5 mm = 3500 μm
10 cells = 3500 μm
1 cell = 3500 μm
10
1 cell = 350 μm
14. (i) Made of several specialized cells grouped together and perform particular
function.
(ii) Made of a group of specialized tissues grouped together performing a particular
function
(iii) It is made of several organs that perform a particular function.
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- F1&2 BIOLOGYDocument93 pagesF1&2 BIOLOGYDylineNo ratings yet
- Form 1 the Cell a Teacher.co .KeDocument3 pagesForm 1 the Cell a Teacher.co .Kelydiaciru01No ratings yet
- Form 1 the Cell Questions Teacher.co .Ke (0)Document3 pagesForm 1 the Cell Questions Teacher.co .Ke (0)lydiaciru01No ratings yet
- Biology Made FamiliarDocument71 pagesBiology Made Familiarwaiswakeneth4No ratings yet
- Bio F2 MSDocument8 pagesBio F2 MSsolutiongrandtechNo ratings yet
- Attachment 2Document217 pagesAttachment 2Badmind JnrNo ratings yet
- GCSE Cell Structure & Transport Question BookletDocument14 pagesGCSE Cell Structure & Transport Question BookletMN NgọcNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument222 pagesBiologypNo ratings yet
- Cell the Unit of Life Important Qs Important Questions ICSE 3c1601ad Ede4 44cb 947c 45b6e70e0fd5Document2 pagesCell the Unit of Life Important Qs Important Questions ICSE 3c1601ad Ede4 44cb 947c 45b6e70e0fd5Shalu singhNo ratings yet
- Biology Class Test Date: Obtained Marks: Student's Name: Sec.Document3 pagesBiology Class Test Date: Obtained Marks: Student's Name: Sec.Ahmed HamimNo ratings yet
- Cells - 1 V2 (Euks, Proks & Viruses)Document9 pagesCells - 1 V2 (Euks, Proks & Viruses)mormerodNo ratings yet
- Biology MSC F1 Term 3 Exam 2021Document9 pagesBiology MSC F1 Term 3 Exam 2021milly khisaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Organization MCQsDocument13 pagesCell Structure & Organization MCQsMazzianty GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Magnification Cell Structure WorkbookDocument19 pagesMagnification Cell Structure WorkbookHaly786No ratings yet
- MB Biology MorningDocument7 pagesMB Biology MorningSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Panam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperDocument7 pagesPanam Academy End of Term Iii July 2021 Module Beginner Morning Biology PaperSamuel MainaNo ratings yet
- Nalanda Vidyalaya Science MCQ and Essay Questions on Living TissuesDocument5 pagesNalanda Vidyalaya Science MCQ and Essay Questions on Living TissuesRash PamithuNo ratings yet
- Biology AS Level exam paper with cell organellesDocument6 pagesBiology AS Level exam paper with cell organellesMohammad Izaz MahmudNo ratings yet
- 2015 f4 Bio Test1 Paper1 Question PaperDocument4 pages2015 f4 Bio Test1 Paper1 Question PaperPaconutNo ratings yet
- Assgt Biology-Form-1-End-Term-1-2020 PDFDocument8 pagesAssgt Biology-Form-1-End-Term-1-2020 PDFAnthonyNo ratings yet
- CL 10 Pre - Biology - 2020 - 21Document3 pagesCL 10 Pre - Biology - 2020 - 21Suvadip SanyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Figure 1 (I) Figure 1 (Ii)Document37 pagesChapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Figure 1 (I) Figure 1 (Ii)Jonathan LingNo ratings yet
- Biology f1 MsDocument8 pagesBiology f1 MswilliammakuuNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDocument7 pagesBiology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedoyooNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedDocument7 pagesBiology Form 1: Answer All The Questions in The Spaces ProvidedOchieng WilberforceNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument9 pagesAqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsDocument9 pagesAqa Gcse Cell Biology - Answers: A. Cell Structure Part 1 - Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes and Animal and Plant CellsJoeNo ratings yet
- Reminder b2Document11 pagesReminder b2Daniel thanh ducNo ratings yet
- Biology Quizs FNLDocument92 pagesBiology Quizs FNLAbdul WasayNo ratings yet
- PC 11437-NH: Section-CDocument1 pagePC 11437-NH: Section-Cjatin gargNo ratings yet
- Solved Worksheet-Cell and Specialized Cells4Document5 pagesSolved Worksheet-Cell and Specialized Cells4Everything EverythingNo ratings yet
- Biology worksheet on cell organellesDocument3 pagesBiology worksheet on cell organellesVedant SinghalNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Inte-Science Paper 2Document1 pageForm 2 Inte-Science Paper 2saajid hafizNo ratings yet
- Bio F2 QSDocument9 pagesBio F2 QSsolutiongrandtechNo ratings yet
- PT2 Revision Worksheet - Cell Structure and FuDocument2 pagesPT2 Revision Worksheet - Cell Structure and FuAarika SahaNo ratings yet
- Biology (2)Document2 pagesBiology (2)Swara BatheNo ratings yet
- TL Gonzalez Sala ValeriaDocument26 pagesTL Gonzalez Sala ValeriagloriaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesCell Structure and FunctionKanaga ValliNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsDocument87 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsMahimna SinghNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Solved Paper 2008 PDFDocument19 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Solved Paper 2008 PDFRakshak AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration and TransportDocument13 pagesCell Respiration and TransportDiva NoorzaiNo ratings yet
- F1 Endterm 2 AssignmentDocument75 pagesF1 Endterm 2 AssignmentDavid AdikaNo ratings yet
- 9th Bio Ques 1Document2 pages9th Bio Ques 1Yae KoNo ratings yet
- 12 BIOLOGY 2006 Set3Document2 pages12 BIOLOGY 2006 Set3anil.gelra5140No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-FORM-1 AbubaydaDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY-FORM-1 AbubaydaHaron HB WritersNo ratings yet
- Tissue Classification TestDocument5 pagesTissue Classification TestAnwesh NayakNo ratings yet
- f1 Set 3 All Subjects Champions-April 2020Document89 pagesf1 Set 3 All Subjects Champions-April 2020DennisNo ratings yet
- 1bio Assignment 1 Living Things DigitalDocument5 pages1bio Assignment 1 Living Things Digitalapi-632307358No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function - WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Structure and Function - WorksheetblackcatNo ratings yet
- Cell and transport -J.SDocument16 pagesCell and transport -J.Sjapeshshah30No ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument15 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 9 Biology Chapter 2 Cell The Unit of LifePrashun PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- مراجعة ساينس - 6 ب - أكتوبر - ذاكروليDocument257 pagesمراجعة ساينس - 6 ب - أكتوبر - ذاكروليNada MeselhyNo ratings yet
- ST - Catherines's SS, f5 Terminal Exam, Biology, Tuesday Nov 2023Document3 pagesST - Catherines's SS, f5 Terminal Exam, Biology, Tuesday Nov 2023jacklinegaudence247No ratings yet
- 2021 Test 1 Cell BiologyDocument7 pages2021 Test 1 Cell BiologyIzz IrfanNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Cells QuizDocument8 pagesIB Biology Cells QuizMatthew PettusNo ratings yet
- Cambridge School Noida Biology Practice PaperDocument4 pagesCambridge School Noida Biology Practice PaperDhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biology CELLS WorksheetDocument3 pagesBiology CELLS WorksheetDelisha BorichaNo ratings yet
- Biology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Document8 pagesBiology Ii: KARUNDURA TEST 2021 - 2022 District:Rwamagana Subject: Biology (Theory)Mutaganda Ami fideleNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument2 pagesLetterwallyNo ratings yet
- STD 7 Term 3 Maths 2021 Opener ExamDocument4 pagesSTD 7 Term 3 Maths 2021 Opener ExamwallyNo ratings yet
- Composition 7Document3 pagesComposition 7wallyNo ratings yet
- Grade 1 - Hygiene - Nutrition AssignmentDocument4 pagesGrade 1 - Hygiene - Nutrition AssignmentwallyNo ratings yet
- Cenre Monthly Report FormDocument2 pagesCenre Monthly Report FormwallyNo ratings yet
- Drug Evaluation Test Science STD7Term3 2021 Time: 1 hour 40 MinsDocument4 pagesDrug Evaluation Test Science STD7Term3 2021 Time: 1 hour 40 MinswallyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Activities PP1 Term 2Document9 pagesEnvironmental Activities PP1 Term 2wallyNo ratings yet
- PP1 Schemes of Work Religious ActivitiesDocument7 pagesPP1 Schemes of Work Religious ActivitieswallyNo ratings yet
- Classification IDocument2 pagesClassification IwallyNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 1 Notes ALLDocument84 pagesBiology Form 1 Notes ALLwallyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To BiologywallyNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Wk1 - Cell Organelles (S..Y. 22-23)Document13 pagesQ1 - Wk1 - Cell Organelles (S..Y. 22-23)Lian Gwyneth TomasNo ratings yet
- OCB Student Handbook v3.6Document321 pagesOCB Student Handbook v3.6barbosaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: A Comparison of Cell Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesProkaryotes vs Eukaryotes: A Comparison of Cell Structure and FunctionElla RelfNo ratings yet
- The Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument26 pagesThe Cell: The Basic Unit of Lifeحفيظو عبداللهNo ratings yet
- Cell Worksheet Class 11Document2 pagesCell Worksheet Class 11kaushikisrivastava95No ratings yet
- IX-5-The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument61 pagesIX-5-The Fundamental Unit of LifeAbhay AryaNo ratings yet
- Cbiescco 05Document7 pagesCbiescco 05Rishabh BhatiNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week 2 Stem G11 General Biology Las W2Document15 pagesQ3 Week 2 Stem G11 General Biology Las W2John Erniest Tabungar AustriaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Study GuideDocument1 pageChapter 1 Study GuideFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 First Periodical Test TosDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 First Periodical Test TosMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 1Document8 pagesChapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 1Arpan KaurNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Focusing Specimen Using The Compound MicroscopeDocument104 pagesLesson 2 - Focusing Specimen Using The Compound Microscopehakuna matataNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- 8 Science QaDocument233 pages8 Science QaAkanshaNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 Complete - BLANCHINGDocument12 pagesExp 4 Complete - BLANCHINGLiyana HalimNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell Theory Structure and Function of OrganellesDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell Theory Structure and Function of OrganellesYkhay ElfanteNo ratings yet
- Quipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellDocument17 pagesQuipper 1 - Earth and Life Science - CellPhil Christian MerinoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close ReadingDocument4 pagesProkaryoticandeukaryotic Cells Close Readingapi-165869000No ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3Document10 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3Akemi LeeNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Physiology An Integrated Approach 7th Edition Silverthorn Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Human Physiology An Integrated Approach 7th Edition Silverthorn Solutions Manual PDFbogoschollys100% (8)
- Rules and Parts of the MicroscopeDocument16 pagesRules and Parts of the MicroscopeDisgraceNo ratings yet
- DP1-SL - Unit Assessment AnswersDocument12 pagesDP1-SL - Unit Assessment AnswersAmeen amediNo ratings yet
- EarthandLifeSci 12 Q2 Mod9 Introduction To Lifescience v4Document23 pagesEarthandLifeSci 12 Q2 Mod9 Introduction To Lifescience v4Elvin Sajulla BulalongNo ratings yet
- General Biology (Biol. 1012) : Course Instructor: Kabeta LegeseDocument48 pagesGeneral Biology (Biol. 1012) : Course Instructor: Kabeta LegeseKena MegersaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Biology: Life ..Chapter 4 .Document15 pagesPrinciples of Biology: Life ..Chapter 4 .Mohammed ShehuNo ratings yet
- Science7 q2 Week 3 Refined FinalDocument10 pagesScience7 q2 Week 3 Refined FinalRonalynAlonsabeBernadasNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life NotesDocument12 pagesFundamental Unit of Life NoteshelloNo ratings yet
- Micro-Para-Lec Prelims ReviewerDocument22 pagesMicro-Para-Lec Prelims ReviewerEingel Mer Evangelista100% (1)