Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic Code
Uploaded by
ALMAR Harrison0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesGenetic Code
Uploaded by
ALMAR HarrisonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
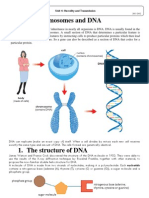
Every organism inherited certain traits from their parents
which are genes. Genes are pieces of hereditary material
that pass from the parents to offspring. Genes affect the its
inherited traits. For an example of eye color is an inherited
trait from the parents.
Alleles are the form or position of DNA or gene in
chromosomes.
There are 2 types which determines an organism’s traits:
Genotype and Phenotype
Genotype is the unique DNA sequence which combined
with two alleles from each parent or it’s the genetic code in
gene which isn’t observed by naked eye or from certain
traits. For example, allergic to certain foods or medication
and the causes of diseases are the genotype which is 2
alleles that form inherited traits in DNA from each parents.
For example, If one of the parents is allergic to peanut but
one doesn’t, the offspring can have both of the alleles from
its parents, on the other hand, the offspring might allergic
to peanut if the one allele is dominant like Ff.
Phenotype is the observable inherited traits which depends
on both genotype and environment factors such as eye
color or height. If an offspring has brown eye or brown hair,
one of or both parents have brown eye such as FF_ both
are dominant alleles, Ff_ uppercase is dominant allele, if
both parents don’t have brown eyes, ff_ recessive alleles.
Environment factors are the way that we see or observe
those eye color or height.
An individual inherits two alleles, one from each parent, for
any given genomic location where such variation exists.
Alleles are variants in gene which carry the inherited traits
in DNA position or genomic location. Alleles are variants
form of gene but locus is the position of an allele in
chromosome for example, in a locus, there are 2 alleles.
Some genes have a variety of different forms, which are
located at the same position, or genetic locus, on a
chromosome. Humans are called diploid organisms
because they have two alleles at each genetic locus, with
one allele inherited from each parent. Each pair of alleles
represents the genotype of a specific gene.
Genotypes are described as homozygous if there are two
identical alleles at a particular locus such as FF or AA and
as heterozygous if the two alleles differ such as Ff. Alleles
contribute to the organism's phenotype, which is the
outward appearance of the organism (observable traits).
Some alleles are dominant or recessive. When an organism
is heterozygous at a specific locus and carries one
dominant and one recessive allele such as Ff, the organism
will express the dominant phenotype.
Uppercase are dominant if one of the uppercase contains in
alleles, so the phenotype is dominant. Ff or FF
Lowercase are recessive if both alleles containing both
lowercase such as aa or ff, the phenotype is recessive.
Facts: alleles are one or two forms or versions of DNA or
gene sequence but many of the organisms have more than
two alleles which are inherited from each parent such as
frog which has 8 alleles in gene, 4 alleles are from each
parent.
DNA molecules are made up of smaller parts called
nucleotides. Each chromosome contains one long molecule
of DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid. Each gene is a specific
section of the long DNA molecule. A gene is a specific
section of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. The order of the
nucleotides in a gene is the gene sequence, which can be
written as a series of Cs, Gs, As, and Ts. A gene is the
specific order of nucleotides. Each nucleotide represents by
a single letter but gene sequence represents as a series of
letters.
Fact: The longest gene is over 2 million nucleotides long
which found in muscle fibers, made of dystrophin( a
protein). The shortest gene are around a few hundred
nucleotides.
The nucleotides that make up a gene are in a specific
order, or sequence. The gene sequence are determined by
the order of nucleotides sequence in a gene. The cell uses
gene sequence as a instruction to make molecule called
protein. _Protein gives shape to certain cells or tissues or
organs and control how an organism grow or develop and
control certain chemical reaction in cells. Protein affects
the organism’s traits.
Proteins are made up of parts called amino acids. Many
different amino acids are used to build proteins.
When a protein is made in cell, the amino acid first linked
to the chain to form the amino acid sequence in a gene
sequence. As amino acid builds, it folds to 3D shape and a
protein final shape depends on the amino acid sequence.
The protein structure depends on the order or sequence of
amino acid and the different protein structure function
differently which means the function of the protein in a cell
depends on the protein structure.
A protein's three-dimensional shape and the way its
different in amino acids are positioned within that shape
make up its structure. A protein's structure depends on the
order of amino acids in its chain. This is because as a
protein folds, the amino acids interact with each other and
with nearby molecules in the cell. Each type of amino acid
has unique properties and interacts with molecules in a
different way. These interactions determine the final shape
of the protein.
As genes contain structure for building amino acids, gene
sequence use as a code and tell the cell to add certain
amino acids or to link to its chain.
Each set of three nucleotides in a row is called codon, each
codon in gene sequence tells the cell to build or add amino
acids to its chain. The order of codons in a gene sequence
determines the order or sequence of amino acids because
there are different codons that correspond to each of the
different amino acids used to build proteins. For example,
the codon ATG corresponds to the amino acid methionine.
When a gene sequence contains the codon ATG, the protein
encoded by that gene will contain methionine.
Gene encodes proteins and protein affects the traits
because the protein carry out many function in a cell or
body to grow and develop.
A set of rules of how codons in gene sequence encode or
convert amino acid is called_ genetic code. The cells uses
as a code or a set of rules to determine the order or
sequence of amino acids(serine, methionine) in a protein
from a gene sequence(codons like ATG,TAA,UAA) is called
genetic code.
Most codons encode amino acids, but some do not. The
codons TGA, TAG, and TAA mark the end of a protein's
amino acid chain, so they are called stop codons. When a
cell builds a protein, it stops adding amino acids to the
protein when it reaches a stop codon. Many of the genes
don’t contain code for making protein but some do.
You might also like
- Beyond DNA: From Cellular Mechanisms to Environmental Factors: How Epigenetics Shapes Our Biological Destiny and its Implications for Health, Behavior, and the Future of ResearchFrom EverandBeyond DNA: From Cellular Mechanisms to Environmental Factors: How Epigenetics Shapes Our Biological Destiny and its Implications for Health, Behavior, and the Future of ResearchNo ratings yet
- DNA Provides The Set of Coded Instructions Required by Every Organism ForDocument8 pagesDNA Provides The Set of Coded Instructions Required by Every Organism ForDanaNo ratings yet
- 3.4 The Effect of The Interaction of Genotype and The Environment On PhenotypeDocument13 pages3.4 The Effect of The Interaction of Genotype and The Environment On PhenotypeOmar ZraikatNo ratings yet
- 2 - Modes of InheritanceDocument42 pages2 - Modes of InheritanceSimon Grant100% (1)
- Mendelian Non Mendelian Lethal GenesDocument22 pagesMendelian Non Mendelian Lethal GenesRochelle BambaNo ratings yet
- Intro To GeneticsDocument37 pagesIntro To GeneticsCess Abad AgcongNo ratings yet
- Genes and ChromosomeDocument8 pagesGenes and ChromosomeAuricio, Kent Margarrette B.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Science - 1Document14 pagesIntroduction To Animal Science - 1Jesus Gomez Cortizzo100% (1)
- Introduction To Genetics: Genetics Is The Study ofDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Genetics: Genetics Is The Study ofThe Epic XerneasNo ratings yet
- The Gene:: Eye Color BloodDocument5 pagesThe Gene:: Eye Color BloodAbdullah SawalhaNo ratings yet
- GE 107 Semi-Finals Lessons: The Role of Genes in Heredity Lesson 3 Common Genetic DisorderDocument4 pagesGE 107 Semi-Finals Lessons: The Role of Genes in Heredity Lesson 3 Common Genetic DisorderErika Mae VillamorNo ratings yet
- DNA & Protein SynthesisDocument18 pagesDNA & Protein SynthesisLee da DonNo ratings yet
- Genetics and InheritanceDocument33 pagesGenetics and InheritanceLawrence Onthuga100% (1)
- 8th Grade Science-Genetics and HeredityDocument56 pages8th Grade Science-Genetics and Heredityleojohn275% (4)
- Bio Exam NotesDocument22 pagesBio Exam NotesThalia VladimirouNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Cell Differentiation and VariationDocument7 pagesTopic 3 Cell Differentiation and VariationdaniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Genetics (Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology For Nursing and Healthcare Students)Document87 pagesChapter 3 - Genetics (Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology For Nursing and Healthcare Students)Mary Grace MartinNo ratings yet
- Mana-Ay, Lawrence Angelo F. STEM 12-YA-12 Activity #4Document2 pagesMana-Ay, Lawrence Angelo F. STEM 12-YA-12 Activity #4Lawrence ManaayNo ratings yet
- PDF Document-3Document32 pagesPDF Document-3meryamNo ratings yet
- Cell DifferentiationDocument11 pagesCell DifferentiationMahmoud HeshamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Genetic Control of Cell FunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 3 - Genetic Control of Cell FunctionSADAVEJO100% (1)
- Section 4Document8 pagesSection 4Aaron RajeshNo ratings yet
- Mutations: Types and Causes: Mutations Are Recessive or DominantDocument4 pagesMutations: Types and Causes: Mutations Are Recessive or DominantUsman MaukNo ratings yet
- Gene and Its StructureDocument12 pagesGene and Its StructureABDUL HANANNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument4 pagesBiomoleculesEda, Haidee Gennie Anne R.No ratings yet
- Dob ColoDocument4 pagesDob ColoOmar AmatNo ratings yet
- 7 Gendev PDFDocument12 pages7 Gendev PDFJohn DeHansNo ratings yet
- According To Some WebsitesDocument3 pagesAccording To Some WebsitesJessa Mae OhaoNo ratings yet
- Differential Gene Expression and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesDifferential Gene Expression and DevelopmentShaher Bano Mirza100% (1)
- Topic 4Document7 pagesTopic 4Antonio López JiménezNo ratings yet
- Mendel's LawDocument4 pagesMendel's LawAngela Dez Therese AdefuinNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument25 pagesGeneticsLouel Mattew LagascaNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology CO.232471005Document4 pagesA Level Biology CO.232471005cidowu2006No ratings yet
- Genetics Ug IaDocument63 pagesGenetics Ug Iamuhammadnajaatu98No ratings yet
- Science Notes PDFDocument7 pagesScience Notes PDFakidelavega19No ratings yet
- Genetics and HeredityDocument56 pagesGenetics and HeredityHnin NandarNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Md. Murad Khan Lecturer Dept. of Microbiology Jagannath UniversityDocument68 pagesRegulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes: Md. Murad Khan Lecturer Dept. of Microbiology Jagannath UniversityCharls John ErcilloNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression and Genetics: MutationDocument23 pagesGene Expression and Genetics: Mutationprimal100% (1)
- Notes 221210 003035Document3 pagesNotes 221210 003035SWAGGANG 15No ratings yet
- Genomics and ProteomicsDocument2 pagesGenomics and ProteomicsJeremy BellNo ratings yet
- Aakaash Bio ProjectDocument7 pagesAakaash Bio ProjectHASHIRANo ratings yet
- Domesticated: A Gene Is The Basic Physical and Functional Unit of Heredity. Genes Are Made Up of DNA. Some Genes Act AsDocument2 pagesDomesticated: A Gene Is The Basic Physical and Functional Unit of Heredity. Genes Are Made Up of DNA. Some Genes Act AsLOVETH LAGMAYNo ratings yet
- Hua Final SolutionsDocument47 pagesHua Final SolutionsbrianhuaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes F4Document59 pagesBiology Notes F4Nathan SsekamatteNo ratings yet
- Multiple Alleles DefinitionDocument14 pagesMultiple Alleles DefinitionYoshimi MacahiloNo ratings yet
- Bio Module 3Document25 pagesBio Module 3ritika malikNo ratings yet
- Notes CHDocument3 pagesNotes CHeshalart12No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5-Genetics Lesson 1Document8 pagesCHAPTER 5-Genetics Lesson 1Stelio GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- In My "Own Words"Document6 pagesIn My "Own Words"Maria ZvolinskayaNo ratings yet
- Inherited Characteristics, Dna, Chromosomes, Genes, Selective Breeding, Mutations, Genitically Modifies Species, Clones and Natural Selection by EvolutionDocument11 pagesInherited Characteristics, Dna, Chromosomes, Genes, Selective Breeding, Mutations, Genitically Modifies Species, Clones and Natural Selection by EvolutionManya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument16 pagesGene ExpressionmidhunbonumahanthiNo ratings yet
- 1.02 Proteins Express DNA: Gene Expression Transcription TranslationDocument13 pages1.02 Proteins Express DNA: Gene Expression Transcription TranslationRoberta Soto IbarrecheNo ratings yet
- Glosario Biologia MolecularDocument11 pagesGlosario Biologia MolecularRicardo MataNo ratings yet
- Chromosome Structure & Dna Replication: Alu Sequences Can Be MutagenicDocument11 pagesChromosome Structure & Dna Replication: Alu Sequences Can Be MutagenicSuliman GarallehNo ratings yet
- 7.13C - Homologs, Orthologs, and Paralogs - Biology LibreTextsDocument2 pages7.13C - Homologs, Orthologs, and Paralogs - Biology LibreTextsVIDHI JAINENDRASINH RANANo ratings yet
- B12 Inheritance - Updated 2023Document15 pagesB12 Inheritance - Updated 2023Alejandro SotoNo ratings yet
- Genesandtheirrolein Animal ProductivityDocument3 pagesGenesandtheirrolein Animal ProductivityAbas S. AcmadNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Bin Naseem Roll Number: F16-0358 Section: A Department: Department of Agricultural Sciences University: University of Haripur EmailDocument4 pagesName: Muhammad Bin Naseem Roll Number: F16-0358 Section: A Department: Department of Agricultural Sciences University: University of Haripur EmailMuhammad Bin NaseemNo ratings yet
- Beyond DNA: The Epigenetic Revolution: From Cellular Mechanisms to Environmental Factors: How Epigenetics Shapes Our Biological Destiny and its Implications for Health, Behavior, and the Future of ResearchFrom EverandBeyond DNA: The Epigenetic Revolution: From Cellular Mechanisms to Environmental Factors: How Epigenetics Shapes Our Biological Destiny and its Implications for Health, Behavior, and the Future of ResearchNo ratings yet
- HomeschoolingDocument2 pagesHomeschoolingALMAR HarrisonNo ratings yet
- FriendshipDocument1 pageFriendshipALMAR HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Beneath The Pale BlueDocument1 pageBeneath The Pale BlueALMAR HarrisonNo ratings yet
- SatireDocument1 pageSatireALMAR HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Psychology NotesDocument6 pagesPsychology NotesALMAR HarrisonNo ratings yet
- What Is A GeneDocument11 pagesWhat Is A GeneetdsdgNo ratings yet
- Silvia - PCR ResultDocument1 pageSilvia - PCR Resultsilvia anandaNo ratings yet
- Somatic Mutations of The APC Gene in Colorectal Tumors: Mutation Cluster Region in The APC GeneDocument5 pagesSomatic Mutations of The APC Gene in Colorectal Tumors: Mutation Cluster Region in The APC GenemetteoroNo ratings yet
- 1 - Concept of Gene and Structure of ChromosomeDocument24 pages1 - Concept of Gene and Structure of Chromosomeharshit khareNo ratings yet
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument22 pagesAlcoholic Liver DiseasePierrotNo ratings yet
- Bioc 211 Complete NotesDocument158 pagesBioc 211 Complete NotesKevin KipropNo ratings yet
- Teknik ARMS PCRDocument4 pagesTeknik ARMS PCRliyanaNo ratings yet
- PORTFOLIO - BIOLOGICAL CELL Prepared by 1st Year MBBS Student-LEKSHMIDocument10 pagesPORTFOLIO - BIOLOGICAL CELL Prepared by 1st Year MBBS Student-LEKSHMIspillai11No ratings yet
- Long Test As Level Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesLong Test As Level Nucleic AcidPrisky Jofan SimbarNo ratings yet
- Gen BankDocument6 pagesGen BankJorge Luis ParraNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument2 pagesPDFLosang ChoephelNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Cell Lesson PlanAilyn Soria Ecot78% (37)
- LeaP Science 10 Q4 W3 4Document5 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q4 W3 4D Garcia100% (2)
- General Biology 1 Module 6Document19 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 6Vienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- USABO 19 Open Exam FinalDocument18 pagesUSABO 19 Open Exam FinalOnnNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BIOCHEMISTRY I (2230003) : Epimers Invert Sugar Muta-RotationDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank BIOCHEMISTRY I (2230003) : Epimers Invert Sugar Muta-RotationkbnarkhedeNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module 7 Q1Document23 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module 7 Q1Pril GuetaNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and Function: ScoreDocument4 pagesWORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and Function: ScoreCHONG KOK HIN MoeNo ratings yet
- GENDX AlleleSEQRDocument16 pagesGENDX AlleleSEQRCarola HernandezNo ratings yet
- The MDSiteDocument12 pagesThe MDSitealex_pitigoi100% (1)
- IGNOU Ph.D. Admission 2020 SyllabusDocument85 pagesIGNOU Ph.D. Admission 2020 SyllabusEswari GkNo ratings yet
- Parte 03Document100 pagesParte 03Pâmella PicançoNo ratings yet
- Sahabjada Assistant Professor CVDocument10 pagesSahabjada Assistant Professor CVCh GovardhanNo ratings yet
- Methods For Studying VirusesDocument24 pagesMethods For Studying VirusesFatima FarooqNo ratings yet
- Jefa (Rv2459), A Drug Efflux Gene in Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument3 pagesJefa (Rv2459), A Drug Efflux Gene in Mycobacterium TuberculosisaristyabudiarsoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map ScienceDocument4 pagesConcept Map ScienceNIMFA PALMERA100% (1)
- Biological Databases: DR Z Chikwambi BiotechnologyDocument47 pagesBiological Databases: DR Z Chikwambi BiotechnologyMutsawashe MunetsiNo ratings yet
- Gus Gene Assay in Transformed TissueDocument5 pagesGus Gene Assay in Transformed TissuekuangNo ratings yet
- m2 l2. Check in ActivityDocument2 pagesm2 l2. Check in ActivityTiffany SelirioNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Model LabDocument7 pagesProtein Synthesis Model Labmarisa corderoNo ratings yet