Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Galileo's Discoveries & Contributions
Uploaded by
Crystal JaundooOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Galileo's Discoveries & Contributions
Uploaded by
Crystal JaundooCopyright:
Available Formats
List of Discoveries of Galileo Galile
Galileo Galilei's Invention & Contributions
Earth's Orbit
Shortly after the telescope was invented in the Netherlands, Galileo fashioned his own from
makeshift spectacle lenses. He learned how to make increasingly powerful telescopes, which he
eventually used to to monitor the solar phases of the planet Venus. After noticing Venus went
through similar phases to the moon, he concluded the sun must be the central point of the solar
system, not the Earth as was previously assumed.
The Principle of the Pendulum
At just 20 years of age, Galileo was in a grand cathedral and noticed that a lamp swinging
overhead took exactly the same period of time for each swing, even as the distance of a swing
got progressively shorter. This principle of the pendulum made Galileo famous, and was
eventually used to regulate clocks. The law states that a pendulum will always take the same
amount of time to finish a swing because there is always the same amount of kinetic energy in
the pendulum -- it is merely transferred from one direction to the other.
The Law of Falling Bodies
This law states that all objects will fall at an equal rate, when accounting for relatively minor
differences in aerodynamics and weather conditions. Galileo demonstrated this theory by
climbing to the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa and dropping items of various weight off the
side. All items hit the ground at the same time. Contrary to the conventional wisdom established
by Aristotle, the speed of a heavy object's fall was found to not be proportional to its weight.
Astrological Discoveries
Galileo made several astronomical discoveries that people today simply accept as common
sense. He discovered that the surface of the moon is rough and uneven as opposed to smooth as
people had thought, and in 1610 he discovered four moons revolving around Jupiter. More
important than either of these was his finding that many more stars exist than are visible to the
eye, an assertion that came as a shocking surprise to the scientific community at the time.
Mathematical Paradigm of Natural Law
For centuries, natural philosophy, which at that time encapsulated such fields as physics and
astronomy, was discussed and theorized from a qualitative standpoint. Galileo didn't just
discover specific laws of the universe, he reformed the qualitative standpoint and established
mathematics as the language of scientific discovery. He pioneered the scientific method and
ushered in the modern practice of experimentation and calculated laws of nature. His doing so
led to the revelations that many of the laws of Greek philosophers such as Plato and Aristotle
were incorrect.
Galileo Facts
Galileo Galilei was born in Pisa, Italy, on the 15th of February 1564, he died on the 8th of January 1642.
Galileo was a ground breaking astronomer, physicist, mathematician, philosopher and inventor. Among his
inventions were telescopes, a compass and a thermometer.
Galileo enrolled to do a medical degree at the University of Pisa but never finished, instead choosing to study
mathematics.
Galileo built on the work of others to create a telescope with around 3x magnification, he later improved on this
to make telescopes with around 30x magnification.
With these telescopes, Galileo was able to observe the skies in ways previously not achieved. In 1610 he made
observations of 4 objects surrounding Jupiter that behaved unlike stars, these turned out to be Jupiter’s four
largest satellite moons: Io, Callisto, Europa and Ganymede. They were later renamed the Galilean satellites in
honor of Galileo himself.
The discovery of these moons was not supported by the scientific principles of the time and Galileo had trouble
convincing some people that he had indeed discovered such objects. This was similar to other ideas put forward
by Galileo that were very controversial at the time.
The Geocentric model of the universe which was embraced by earlier astronomers had the Earth at the center of
the universe with other objects moving around it. Work by Galileo, Nicolaus Copernicus and Johannes Kepler
helped to supercede this theory with the more accurate heliocentric model. Such a view of the universe differed
strongly with the beliefs of the Catholic Church at the time and Galileo was forced to withdraw many of his ideas
and even spent the final years of his life under house arrest.
Galileo refused to believe Kepler’s theory that the moon caused the tides, instead believing it was due to the
nature of the Earth’s rotation (helping prove that even the smartest people can make mistakes).
You might also like
- Estimation of Parameters - M11 - 12SP-IIIh-2, M11 - 12SP-IIIh-3 - Stat and Prob Chapter 4 (13 - 14) - FinalDocument10 pagesEstimation of Parameters - M11 - 12SP-IIIh-2, M11 - 12SP-IIIh-3 - Stat and Prob Chapter 4 (13 - 14) - FinalGerby GodinezNo ratings yet
- Friction, Gravity and Energy TransformationsDocument12 pagesFriction, Gravity and Energy TransformationsDaiserie LlanezaNo ratings yet
- (Week1 - Lesson 1) Origin of The UniverseDocument3 pages(Week1 - Lesson 1) Origin of The UniverseLysa TurredaNo ratings yet
- Origins of Modern Astronomy: Ancient Greeks and Kepler's LawsDocument70 pagesOrigins of Modern Astronomy: Ancient Greeks and Kepler's LawsDigie AspricNo ratings yet
- Final Summative Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesFinal Summative Physical ScienceCathy Fern GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DLL q1 Lesson6 Elses by LjescoteDocument3 pagesDLL q1 Lesson6 Elses by LjescoteLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- Stem12 Physics 1 q1 w1 LeapDocument4 pagesStem12 Physics 1 q1 w1 LeapGreg Aeron Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Kepler's Laws of Planetary MotionDocument3 pagesKepler's Laws of Planetary Motionkimberlyn100% (1)
- Budget of Work Earth Life ScienceDocument4 pagesBudget of Work Earth Life Scienceeugene medinaNo ratings yet
- Dll-Cot FinalDocument9 pagesDll-Cot FinalRevely DomdomNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 2.0Document4 pagesPerformance Task 2.0Norjanah H. M. AmbolaNo ratings yet
- Models of the Universe ExplainedDocument95 pagesModels of the Universe ExplainedJasmine Marie Estoque ArjinalNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Dielectric: A PPT For General Physics 2 STEM-12 2017-2018Document31 pagesCapacitors and Dielectric: A PPT For General Physics 2 STEM-12 2017-2018Jaylanie EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 3 - Stat and Proba Q3Document6 pagesDLL Week 3 - Stat and Proba Q3JESSIE GRACE DE LUNANo ratings yet
- Module 2Document13 pagesModule 2Lino Magbanua NavallascaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PhysicsDocument35 pagesLesson Plan Physicsare fiqsNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Eudoxus: Pythagoras PlatoDocument34 pagesAristotle Eudoxus: Pythagoras PlatoNicole PrimaNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of The Atom by Calvin O. DavidDocument24 pagesHistorical Development of The Atom by Calvin O. Davidgilbert datuNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Earth and Life Science Grade-11Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: Earth and Life Science Grade-11Ro ZenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Essential Learning Competencies Teaching-Learning Resources General Mathematics (Grade 11)Document28 pagesMathematics Essential Learning Competencies Teaching-Learning Resources General Mathematics (Grade 11)Monalisa Garcia BasañesNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Hich Among The Given Particles Will Complete CNO Cycle?Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Hich Among The Given Particles Will Complete CNO Cycle?adrian lozanoNo ratings yet
- 1ST Week DLLDocument5 pages1ST Week DLLJessa May MarcosNo ratings yet
- How Energy Is Produced AndManagedDocument34 pagesHow Energy Is Produced AndManagedIzumiNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaDocument42 pagesGeneral Physics 1.2b Moment of InertiaLADY SUZETTE LANDICHONo ratings yet
- S11ES IIh I 39Document2 pagesS11ES IIh I 39allanrnmanaloto50% (2)
- Physics Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesPhysics Reviewer 2nd QuarterCardinal RagerNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 15-EditedDocument24 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 15-EditedLove Joy JumawanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semester WEEK 11Document6 pages2nd Semester WEEK 11Queency Panaglima PadidaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesSummative Test Physical ScienceBrendick AbellaNo ratings yet
- Breathe In: Write Your Answer On These Activity SheetDocument4 pagesBreathe In: Write Your Answer On These Activity Sheetirah jane valentinoNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan For Peacscience8decDocument3 pagesLearning Plan For Peacscience8decMaam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- Learning Competencies With Code: Semester: First Quarter: 1st (Midterms) Subject: STEM 05 - General Physics 1Document3 pagesLearning Competencies With Code: Semester: First Quarter: 1st (Midterms) Subject: STEM 05 - General Physics 1Angel Abigail TapayanNo ratings yet
- Aristotelian MechanicsDocument86 pagesAristotelian MechanicsJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- WHLP Week 1 (Gen Math)Document2 pagesWHLP Week 1 (Gen Math)Glean VasquezNo ratings yet
- COT GM SolveLoan2Document7 pagesCOT GM SolveLoan2Venus Bayes QuiachonNo ratings yet
- Permit Christmas PartyDocument2 pagesPermit Christmas PartynyalimiNo ratings yet
- Phil Art Lesson Plan on Integrative Contemporary ArtDocument15 pagesPhil Art Lesson Plan on Integrative Contemporary ArtKler DaradarNo ratings yet
- DLL - G11 - Dec 9-13, 2019Document4 pagesDLL - G11 - Dec 9-13, 2019Cristina Maquinto0% (1)
- 1 Formation of The Elements During The Big BangDocument56 pages1 Formation of The Elements During The Big BangMary Ann GubanNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus Module 2Document4 pagesBasic Calculus Module 2Jocel Tecson LabadanNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 16-EditedDocument24 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 16-EditedLove Joy JumawanNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 STATS PROBABILITY DAILY LESSONDocument8 pagesGRADE 11 STATS PROBABILITY DAILY LESSONJESSIE GRACE DE LUNANo ratings yet
- New DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 8-12, 2019-2020Document2 pagesNew DLL SHS - Earth & Life Science July 8-12, 2019-2020BeeWinNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN IN PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Sample Only)Document2 pagesLESSON PLAN IN PHYSICAL SCIENCE (Sample Only)Charmine AbuanNo ratings yet
- psdll11 28 18Document2 pagespsdll11 28 18Christine De San JoseNo ratings yet
- Graphs of MotionDocument4 pagesGraphs of MotionJose Benavente100% (1)
- Summative 1st Quarter 2 PrecalculusDocument2 pagesSummative 1st Quarter 2 PrecalculusCarlo CutayNo ratings yet
- LH - Lesson 1.1 - 1.2Document3 pagesLH - Lesson 1.1 - 1.2joel gatanNo ratings yet
- DLL 1stQtr W1Document5 pagesDLL 1stQtr W1Rodalyn CastilloNo ratings yet
- Explicit Lesson-Plan SalardaDocument6 pagesExplicit Lesson-Plan SalardaJhon Ivy Jhon IvyNo ratings yet
- 7e's - Cellular RespirationDocument5 pages7e's - Cellular RespirationVea Patricia AngeloNo ratings yet
- Physical Science DLL q2 (Week 1) l9Document2 pagesPhysical Science DLL q2 (Week 1) l9Esmale RyaNo ratings yet
- Semi Aristtotle and Galileo MotionDocument3 pagesSemi Aristtotle and Galileo MotionAnna Marie San DiegoNo ratings yet
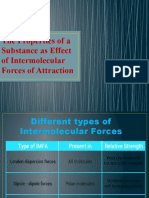
- Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument12 pagesIntermolecular Forces of AttractionCharles DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Color of Stars Reveals Their TemperatureDocument17 pagesColor of Stars Reveals Their TemperatureCarmilleah FreyjahNo ratings yet
- SCC Grade 12 Exam on Physical SciencesDocument2 pagesSCC Grade 12 Exam on Physical SciencesNil PadillaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Probability and Statistics 11Document17 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Probability and Statistics 11Ermm CaneteNo ratings yet
- DLL 3 PhysciDocument3 pagesDLL 3 PhysciJuliane Rebecca PitlongayNo ratings yet
- List of Discoveries of Galileo GalileiDocument2 pagesList of Discoveries of Galileo GalileiHenrissa Granado TalanNo ratings yet
- Galileo's Telescopic Discoveries Revolutionized AstronomyDocument8 pagesGalileo's Telescopic Discoveries Revolutionized AstronomyPanduka BandaraNo ratings yet
- ONLINE NATALNA KARTA DMDocument1 pageONLINE NATALNA KARTA DMAcimovic MarijanaNo ratings yet
- LL3 Universe and Solar SystemDocument31 pagesLL3 Universe and Solar SystemPrincess PabualanNo ratings yet
- Electronics 11 02021 v2Document39 pagesElectronics 11 02021 v2محمود محمد محمود عبدالقادرNo ratings yet
- Physical Education Center Infographics by SlidesgoDocument35 pagesPhysical Education Center Infographics by SlidesgoKate Hernández.No ratings yet
- GEO1111 Midterm 1 Practice Questions PDFDocument5 pagesGEO1111 Midterm 1 Practice Questions PDFfahfaNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Project ProposalDocument36 pagesSolar Power Project ProposalMuhammad Luqman100% (1)
- Solar Energy Fundamentals ExplainedDocument25 pagesSolar Energy Fundamentals ExplainedAvinesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Music Festival Marketing Plan by SlidesgoDocument48 pagesMusic Festival Marketing Plan by SlidesgoHanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pandit@jyotishi - com-Prof.K V Ramana Rao's Article On Raja Yogas, Planet Missing InformationDocument3 pagesPandit@jyotishi - com-Prof.K V Ramana Rao's Article On Raja Yogas, Planet Missing InformationsunderchandNo ratings yet
- The Milky Way Galaxy and The Solar SystemDocument4 pagesThe Milky Way Galaxy and The Solar SystemMae Baltera50% (2)
- Saral JyotishDocument296 pagesSaral JyotishTushar Chadha50% (2)
- ORBITER Credits & Contributions: Special ThanksDocument8 pagesORBITER Credits & Contributions: Special ThanksblanchoNo ratings yet
- Retrograde Motion of PlanetsDocument3 pagesRetrograde Motion of Planetsneha batraNo ratings yet
- Voyager 1 and 2 Atlas of Six Saturnian SatellitesDocument182 pagesVoyager 1 and 2 Atlas of Six Saturnian SatellitesBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Universe EssayDocument3 pagesUniverse EssayAndrijana J.No ratings yet
- Simple Blackboard Background - by SlidesgoDocument51 pagesSimple Blackboard Background - by SlidesgoLong Nguyen HoangNo ratings yet
- Menophres Was Merneferre Ay Not Menpehtire Ramesses I and His Sothic Rise Happened On May 23, 1385 BCDocument28 pagesMenophres Was Merneferre Ay Not Menpehtire Ramesses I and His Sothic Rise Happened On May 23, 1385 BCEulalio EguiaNo ratings yet
- 5 Wizard Year Pocket CalendarDocument24 pages5 Wizard Year Pocket Calendarermes100% (1)
- Factual Report TextDocument2 pagesFactual Report Textmikel haluNo ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 2.1 The Origin of Planet Earth.Document13 pagesEarth Science SHS 2.1 The Origin of Planet Earth.D GarciaNo ratings yet
- The Pleiades: The Celestial Herd of Ancient TimekeepersDocument6 pagesThe Pleiades: The Celestial Herd of Ancient TimekeepersNEOINFORMATION100% (1)
- 377674main Black Hole MathDocument127 pages377674main Black Hole MathAnonymous BPFIMnCdNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Science 6 Q4Document6 pagesSummative Test in Science 6 Q4Isil Albina100% (1)
- Multiwavelength Universe Poster All 8x11 PDFDocument10 pagesMultiwavelength Universe Poster All 8x11 PDFnabilanabnabNo ratings yet
- Gecaa - Theory Final Question Sheet: (Total 150 Points)Document11 pagesGecaa - Theory Final Question Sheet: (Total 150 Points)Rahul M-RanjanNo ratings yet
- The Sun: Distance, Composition, Light Travel TimeDocument2 pagesThe Sun: Distance, Composition, Light Travel TimeRatsel IsmeNo ratings yet
- Basic Delineation & Dynamic Configuration ICAS-BD&DC-001 R-0Document7 pagesBasic Delineation & Dynamic Configuration ICAS-BD&DC-001 R-0Veda GiriNo ratings yet
- Vedic Nadi Astrology For Career Amp ProfessionDocument6 pagesVedic Nadi Astrology For Career Amp ProfessionsubramanyaNo ratings yet
- Orbital Motion: Central Net Force Model Worksheet 4Document3 pagesOrbital Motion: Central Net Force Model Worksheet 4Justin DursoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cosmology: SEUE1002Document18 pagesFundamentals of Cosmology: SEUE1002Nurullah MertelNo ratings yet
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsFrom EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- In Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityFrom EverandIn Search of Schrödinger’s Cat: Quantum Physics and RealityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (380)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Paradox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsFrom EverandParadox: The Nine Greatest Enigmas in PhysicsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (57)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)