Professional Documents
Culture Documents
An Acid Is A Substance
An Acid Is A Substance
Uploaded by
08Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria Wijaya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThe document discusses acid-base theories and properties. It defines acids as substances that can donate protons and bases as substances that can accept protons, according to the Bronsted-Lowry theory. A protophilic solvent is one that can accept protons from the solute. An acid that donates a proton and a base that accepts a proton is called a monoprotic electrolyte. In a solution containing only weak acids, the concentration of H3O+ is generally much larger than OH−. The concentration of OH− in a 0.2 M NaOH solution is 0.2 M. Substances with an acidity or alkalinity constant greater than 10−2 are considered strong acids or bases. Proton
Original Description:
Original Title
An Acid is a Substance
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses acid-base theories and properties. It defines acids as substances that can donate protons and bases as substances that can accept protons, according to the Bronsted-Lowry theory. A protophilic solvent is one that can accept protons from the solute. An acid that donates a proton and a base that accepts a proton is called a monoprotic electrolyte. In a solution containing only weak acids, the concentration of H3O+ is generally much larger than OH−. The concentration of OH− in a 0.2 M NaOH solution is 0.2 M. Substances with an acidity or alkalinity constant greater than 10−2 are considered strong acids or bases. Proton
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesAn Acid Is A Substance
An Acid Is A Substance
Uploaded by
08Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaThe document discusses acid-base theories and properties. It defines acids as substances that can donate protons and bases as substances that can accept protons, according to the Bronsted-Lowry theory. A protophilic solvent is one that can accept protons from the solute. An acid that donates a proton and a base that accepts a proton is called a monoprotic electrolyte. In a solution containing only weak acids, the concentration of H3O+ is generally much larger than OH−. The concentration of OH− in a 0.2 M NaOH solution is 0.2 M. Substances with an acidity or alkalinity constant greater than 10−2 are considered strong acids or bases. Proton
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
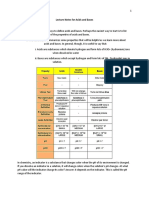
An acid is a substance, charged or uncharged, that can donate a proton, while a base is a substance,
charged or uncharged, that can accept a proton from an acid. The above statement
is a theory of...
A. Bronsted-lowry
B. Lewis.
C. Charles.
D. Van der Wale
The protophilic solvent is…
a. A solvent that can accept a proton from the solute
b. A solvent accepts protons and gives protons.
c. A proton-giving solvent of the solute.
d. A solvent that neither gives nor accepts protons from the solute
An acid that donates a proton and a base that accepts a proton is called
a.monoprotic electrolyte.
b.Polibasac.
c.Polyproticd.
d.Diprotic
If the solution contains only weak acids only weak acids,
so…
a.C️b is zero and H₃O⁺ is generally much larger than OH⁻
b.C️b is one and H₃O⁺ is generally much larger than OH⁻
c.Cb is zero and H₃O⁺ generally much smaller
than OH⁻
d.Cb is two and H₃O⁺ is generally much larger than OH⁻
What is the concentration of OH
–in 0.2 M NaOH solution?
a.0.2 Mb.
b.20Mc.
c.0.02Md.
d.2M
a substance that has a greater acidity and alkalinity constant than
10⁻² Called
a. strong acid and strong base
b. weak acid and weak base
c. strong acid and weak base
d. weak acid and strong base
Proton-donating compounds exhibited by acids such as formic acid, acetic acid, sulfuric acid, liquid
HCl. Is the definition of.
a.Protophilic
b.Protogenic
c.amphiprotic
d.Aprotic
You might also like
- Lab1 TeodoroDocument8 pagesLab1 TeodoroJherby Teodoro100% (1)
- Human Body in Health and Illness 6th EditionDocument12 pagesHuman Body in Health and Illness 6th EditiongetlearnlinkNo ratings yet
- Jack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryDocument25 pagesJack Westin MCAT Content General ChemistryLora100% (1)
- Lab1 TeodoroDocument9 pagesLab1 TeodoroJherby TeodoroNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2.docx Grade 12 Chemistry Note and WSDocument27 pagesUNIT 2.docx Grade 12 Chemistry Note and WSmesfin yonasNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - WEEK 6 MODULE GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2Document22 pagesGroup 6 - WEEK 6 MODULE GENERAL CHEMISTRY 2MOLINA, JULIANA A.No ratings yet
- LAcids and BasesDocument37 pagesLAcids and BasesAnonymous rFIshYy100% (1)
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Document12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 4 - Module 2Jirah GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Titrations PDFDocument31 pagesAcid Base Titrations PDFMuhammad Tariq RazaNo ratings yet
- Types of Acids and BasesDocument3 pagesTypes of Acids and BasesJadie Barringer IIINo ratings yet
- CH 16 Acid and Bases QuizDocument4 pagesCH 16 Acid and Bases QuizAindrila KaziNo ratings yet
- Chemo Tutor 28/6/2015Document1 pageChemo Tutor 28/6/2015Firaol GeremuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Notes-Acids and Bases Bronsted - Lowry Theory: Proton Donors Proton AcceptorsDocument7 pagesChapter 14 Notes-Acids and Bases Bronsted - Lowry Theory: Proton Donors Proton AcceptorsSarah MudaliarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument7 pagesChemistry NotesMARYA KHALIDNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Chemistry: Manasi MantriDocument16 pagesAcid-Base Chemistry: Manasi MantriSonam ChhedaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument2 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsusmanNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 6 (ن)Document22 pagesمحاضرة 6 (ن)انمي العراقNo ratings yet
- Requirements For A Titrimetric ReactionDocument11 pagesRequirements For A Titrimetric ReactionAbdo RaafatNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and BuffersDocument62 pagesAcids, Bases and BufferskolangyefrankbenleNo ratings yet
- 8.ionic EquilibriumDocument64 pages8.ionic EquilibriumhosifaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibria (Part 1)Document33 pagesIonic Equilibria (Part 1)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Module I INTRODUCTION BIOCHEMISTRYDocument53 pagesModule I INTRODUCTION BIOCHEMISTRYjoelle marie BaizasNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument33 pagesAcids and BasesFrancene Badana YepesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry G12 TestDocument6 pagesChemistry G12 TestNigatu MAmoNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument25 pagesAcid BaseMuhammad Yaser RayyanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank The Human Body Health Illness 5th Edition HerlihyDocument15 pagesTest Bank The Human Body Health Illness 5th Edition HerlihyRhonda Mosholder100% (22)
- Acid Base Review Honors ChemDocument6 pagesAcid Base Review Honors Chemhdlee888No ratings yet
- Bronsted Lowry ConceptDocument4 pagesBronsted Lowry ConcepttehseenullahNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BuffersDocument52 pagesAcid Base Buffersdinesh111180No ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and BuffersDocument23 pagesAcids, Bases and BuffersBhaveshwari WaghNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document5 pagesExp 4Crystal VangelineNo ratings yet
- Adge Handouts No. 3 2021Document8 pagesAdge Handouts No. 3 2021HILVANO, HEIDEE B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - General Chemistry - Asessment: Name: Score: Class SectionDocument1 pageChapter 8 - General Chemistry - Asessment: Name: Score: Class SectionReygemae Quitoras-ObsidNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium (8 Mark Questions)Document6 pagesIonic Equilibrium (8 Mark Questions)Nagesh NangiNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument15 pagesAcids and Baseslebogang0% (1)
- Chapter 4-Inorganic ChemDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Inorganic ChemMark Harold GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PH Curve SharingDocument34 pagesPH Curve SharingMuhammad Gibran Qudsy AlKautsarNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium Theory - EDocument33 pagesIonic Equilibrium Theory - Ethinkiit100% (2)
- Homework 4 of Analytical Chemistry (10 Points)Document1 pageHomework 4 of Analytical Chemistry (10 Points)coffewhore00No ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Module 1Document7 pagesAcids and Bases Module 1EPHRAIM JOSHUA SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Acidity and BasicityDocument89 pagesAcidity and Basicityjzllfrncsc100% (4)
- Chapter 16Document100 pagesChapter 16gycht672qdNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Equilibria & PH Calculations Analytical Chemistry: December 2018Document16 pagesAcid-Base Equilibria & PH Calculations Analytical Chemistry: December 2018King OzeedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Content Palm CardsDocument52 pagesChemistry Content Palm CardsMasonNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Note01-10 StudentDocument28 pagesAcid Base Note01-10 Studentc_66hsia7505No ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Acids and BasesDocument60 pagesTopic 8 - Acids and BasesLucia PesentiNo ratings yet
- Brønsted Concept of Acids and BasesDocument4 pagesBrønsted Concept of Acids and Basescayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Johnston Chapter 17 NotesDocument114 pagesJohnston Chapter 17 NotesRayna RamsinghNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceAicken Saga JosolNo ratings yet
- Proton - 2 - Acids and BasesDocument36 pagesProton - 2 - Acids and BasesFrancene Badana YepesNo ratings yet
- Bagasino, Almonry, Bscrim 2, BLK 1, Adge Midterm ExamDocument6 pagesBagasino, Almonry, Bscrim 2, BLK 1, Adge Midterm ExamHILVANO, HEIDEE B.No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document27 pagesLecture 1ramantocoolNo ratings yet
- 6-Acids and BasesDocument46 pages6-Acids and Basesnirvanjain212007No ratings yet
- Acid Bases Intro Asn AnswersDocument3 pagesAcid Bases Intro Asn AnswersvinaybharadwajbsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Part 1 ActivityDocument2 pagesChemical Equilibrium Part 1 ActivityMichael Dan Orejudos SottoNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Sec 2 WorksheetDocument3 pagesCH 14 Sec 2 Worksheet319991No ratings yet
- Acid and Base Review 3Document9 pagesAcid and Base Review 3Miguel A Alicea TrocheNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Acids and Bases-Theory & ExerciseDocument53 pagesConcepts of Acids and Bases-Theory & ExerciseRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- The Proton: Applications to Organic ChemistryFrom EverandThe Proton: Applications to Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- TI - Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) PDFDocument32 pagesTI - Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) PDF08Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaNo ratings yet
- How To Avoid Plagiarism Without Doing Labs or Fieldwork Research To Obtain DataDocument1 pageHow To Avoid Plagiarism Without Doing Labs or Fieldwork Research To Obtain Data08Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaNo ratings yet
- A23 - Pastae - Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaDocument9 pagesA23 - Pastae - Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria Wijaya08Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaNo ratings yet
- Interim Report Fareks Leonardo DemasDocument3 pagesInterim Report Fareks Leonardo Demas08Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaNo ratings yet
- Handout Syrup - Elixir 2023Document28 pagesHandout Syrup - Elixir 202308Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaNo ratings yet
- Drug Administration: Topic ResourcesDocument6 pagesDrug Administration: Topic Resources08Leonardo Demas Krisna Satria WijayaNo ratings yet