Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supplydemand50 51
Uploaded by
Usman GhaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supplydemand50 51
Uploaded by
Usman GhaniCopyright:
Available Formats
____Z5.
_____
CHPibR 4: The Market Forces of Supply and Demand 51
50 PART II: Supply and Demand I: How Markets Work
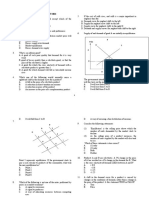
5. “Quantity Demanded” is a point on the demand curve. When there is a change in 12. An increase in supply accompanied by a proportionate decrease in demand
price, quantity demanded changes. but demand itself does not change. Quantity tends to decrease equilibrium price while leaving equilibrium quantity
I
demanded is synonymous with consumption, or sales, or quantity sold. unchanged.
— I3 . The market supply curve is the vertical summation of all the individual
6. “Supply” is the entire schedule or curve. Supply refers to the whole supply
supply curves.
schedule or supply curve, not just a point on the curve. For supply to shift, the
underlying factors that we hold constant in plotting a supply curve must change. 14. Assuming that pizza and beer are complements, a decrease in the price of
Changing the price simply means that we plot a new point on the existing supply pizza would increase the demand for beer.
curve, representing a new quantity. Of course an increase in price encourages
If pizza and hamburgers are substitutes, a decrease in the price of pizza would
suppliers to sell more; however, we call this response to higher price an increase in
increase the demand for hamburgers.
quantity supplied. rather than an increase (or shift) in supply.
B. Multiple-Choice Questions
7. “Quantity Supplied” is a point on the supply curve. When there is a change in
price. the quantity supplied changes, even though the supply curve itself does not
I . Which of the following would not increase the demand (shift the curve to the right)
shift. The quantity supplied at a particular price is the amount that sellers are
for beer?
willing to sell at that price.
a. A new Health Canada study concludes that beer cures colds and skin disorders.
II. Self-Testing Challenges b. A price war results in beer selling for $,05/bottle.
c. Bars begin giving away spicy snacks to their customers.
A. True/False Questions d. The price of a substitute, hard liquor, rises.
e. There is an increase in the drinking-age population.
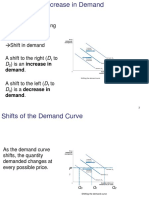
1 . A decrease in the price of soft drinks will increase their demand (shift the 2. If buyers believe that the price of automobile antifreeze will rise soon, due to an
curve to the right). increase in the price of ethylene glycol, which is used to make antifreeze, the most
likely immediate result will be:
2. The supply of petroleum is fixed, because there is only a finite amount in the
ground. a. a decrease (shift to the left) in the demand for antifreeze, due to a change in
tastes.
3. At the equilibrium price, the amount that sellers are willing to provide is just b. a decrease (shift to the left) in the demand for antifreeze, due to a shift to
equal to the amount that buyers are willing to buy. substitutes.
C. an increase in the quantity demanded, due to the change in supply.
4, An improvement in technology tends to reduce the supply (shift it to the left).
d. an increase (shift to the right) in the demand for antifreeze, due to a change in
5. An increase in raw materials prices tends to reduce the supply (shift it to the expectations.
left). e. no change in demand; only supply will change.
6. If sellers expect prices to rise in the future, this could cause prices to rise
today by encouraging sellers to reduce their current supply in anticipation of 3. If a new technological breakthrough in genetic engineering makes it possible to
a price hike. grow twice as much corn per hectare as had been possible in the past, the most
likely result will be:
7. A market refers to a physical location in which buyers and sellers interact. a. a decrease (shift to the left) in the supply of corn, due to the increased costs
8. A pnce below equilibrium results in excess supply. associated with the new technology
b. an increase (shift to the right) in the supply of corn, due to the reduced cost of
9. Excess demand tends to drive price up until the market reaches equilibrium production.
price and quantity. c. an increase in the demand for corn, due to the greatly reduced price.
10. An increase in supply tends to increase equilibrium price and quantity. d. an increase in quantity supplied, due to the increased willingness to sell corn.
e. a shift from corn production to wheat production, using all of the extra land not
11. An equal increase in both supply and demand tends to increase equilibrium needed for corn production.
price and quantity.
You might also like
- Lifecycle Investing: 0465018291-Ayres - 1stpages 2/22/10 12:03 PM Page IDocument236 pagesLifecycle Investing: 0465018291-Ayres - 1stpages 2/22/10 12:03 PM Page IJovan Sajov100% (1)
- International Economics by Thomas Pugel - 15e, TEST BANK 0073523178Document20 pagesInternational Economics by Thomas Pugel - 15e, TEST BANK 0073523178jksnmmm100% (1)
- Applied Assessment. Demand and Supply BumanglagDocument4 pagesApplied Assessment. Demand and Supply BumanglagClinton John BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Notes On Demand, Supply, Single Shifts, and Double Shifts Principle of Microeconomics Notes On DemandDocument7 pagesNotes On Demand, Supply, Single Shifts, and Double Shifts Principle of Microeconomics Notes On DemandJoel C. BaccayNo ratings yet
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Chapter 3 - Seminar (Answer)Document8 pagesChapter 3 - Seminar (Answer)Misheel MinannNo ratings yet
- Final SHS 12 Applied Econ. Q1 Module 3pdfDocument14 pagesFinal SHS 12 Applied Econ. Q1 Module 3pdfML TuTorNo ratings yet
- Supply, Demand, and Equilibrium Assessment Questions - MRU (With Answers)Document13 pagesSupply, Demand, and Equilibrium Assessment Questions - MRU (With Answers)Jimmy RoblesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ch4demandsupplyDocument62 pagesTutorial Ch4demandsupplyTuran, Jel Therese A.No ratings yet
- Extra Credit - Supply and Demand Infographic - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesExtra Credit - Supply and Demand Infographic - Answer Keyrowena vocesNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 - Seminar (Answer)Document5 pagesChapter-4 - Seminar (Answer)Misheel MinannNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 2Document10 pagesIndividual Assignment 2Tran Nguyen Diem Quynh (K17 HCM)No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Economics PracticeDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Economics PracticeJoe StoneNo ratings yet
- Demand and Elasticity of DemandDocument7 pagesDemand and Elasticity of DemandaakaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Document64 pagesIntroduction To Economics (Econ. 101)Ali HassenNo ratings yet
- Exercise - Chapter 5 - QuestionDocument7 pagesExercise - Chapter 5 - QuestionIzzah AdninNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document1 pageQuiz 3ZielNo ratings yet
- REVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 4 PDFDocument6 pagesREVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 4 PDFKiệt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- A Movement Along A Demand Curve Means?: This Question Requires An Understanding of DemandDocument22 pagesA Movement Along A Demand Curve Means?: This Question Requires An Understanding of DemandChie IbayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: (Market Forces of Supply and Demand) Section ADocument11 pagesChapter 4: (Market Forces of Supply and Demand) Section APhạm HuyNo ratings yet
- Review PT 1Document10 pagesReview PT 1Quỳnh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Review-BBDocument4 pagesCh.4 Review-BBRHB ALNo ratings yet
- Principles SSG Ch5Document13 pagesPrinciples SSG Ch5Tingwei HuangNo ratings yet
- Tugas EkonomiDocument28 pagesTugas Ekonomi12mipa1 Yudha Dwi putraNo ratings yet
- Principles 2e SSG Ch5Document14 pagesPrinciples 2e SSG Ch5VivienNo ratings yet
- A Change in Something Other Than Price:: DemandDocument29 pagesA Change in Something Other Than Price:: DemandWajahat AliNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3: Chapter 3Document5 pagesExercise 3: Chapter 3ying huiNo ratings yet
- ECO202 Practice Test 3 (Ch.3)Document2 pagesECO202 Practice Test 3 (Ch.3)Aly HoudrojNo ratings yet
- Be Stu - Tutorial 2Document18 pagesBe Stu - Tutorial 2Gia LinhNo ratings yet
- AIM03Document17 pagesAIM03Kifah CharafNo ratings yet
- Quiz M.A 1Document1 pageQuiz M.A 1KEHKASHAN NIZAMNo ratings yet
- ECON 200. Introduction To Microeconomics Homework 3 Part I Name: - (Multiple Choice)Document12 pagesECON 200. Introduction To Microeconomics Homework 3 Part I Name: - (Multiple Choice)Ifrah AtifNo ratings yet
- Teacher's SampleDocument13 pagesTeacher's SampleDaniyal AghaNo ratings yet
- Econ Demand and Supply NotesDocument2 pagesEcon Demand and Supply NotesjemimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Dai Huu0% (1)
- Tutorial 4-Chapter 4-Elasticity of DD & SsDocument3 pagesTutorial 4-Chapter 4-Elasticity of DD & SskrsuicideNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4: Chapter 20Document5 pagesExercise 4: Chapter 20ying huiNo ratings yet
- Sec 4.4Document10 pagesSec 4.4Dạ Phong CốNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Answers 3Document4 pagesWorksheet Answers 3Gavin SkittNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-1Document33 pagesLecture 4-1ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz Theory of DemandDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz Theory of DemandMahi YadavNo ratings yet
- 2.1 CasesDocument2 pages2.1 CasesAkshay ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Supply, Elasticity of SupplyDocument4 pagesSupply, Elasticity of SupplySaurabhNo ratings yet
- REVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 2Document12 pagesREVIEW 01 - Microeconomics - Chapter 2Kiệt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MIC 3e SSG Ch4 PDFDocument14 pagesMIC 3e SSG Ch4 PDFJina NjNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document59 pagesLecture 4Zong Zheng SunNo ratings yet
- 1 Economics May 2018Document9 pages1 Economics May 2018Hanze MacasilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Demand, Supply and PricesDocument6 pagesChapter 4: Demand, Supply and PricesRohinNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 AKDocument10 pagesHomework 2 AKTrang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document36 pagesLecture 6ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Answerstohomework 2 Summer 2010Document10 pagesAnswerstohomework 2 Summer 2010Abul KashemNo ratings yet
- 1 Economics ARTS PRTC October 2018Document9 pages1 Economics ARTS PRTC October 2018Bea LamanilaoNo ratings yet
- Economics October 2013 PRTCDocument8 pagesEconomics October 2013 PRTCGelyn CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Lesson 2Document16 pagesUnit 8 Lesson 2shermatt0No ratings yet
- Econ Supply and DemandDocument3 pagesEcon Supply and DemandSamuel EviaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Lesson 2.2 - Predicting The Shift of The Demand Curve - SCDocument3 pagesChapter 2 - Lesson 2.2 - Predicting The Shift of The Demand Curve - SCElijah DizonNo ratings yet
- Describe The Terms Below, and Each Give An Example: Assignment-2: Demand and Supply EquilibriumDocument3 pagesDescribe The Terms Below, and Each Give An Example: Assignment-2: Demand and Supply EquilibriumArizal Dwi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Economics 14: Lecture 5: Supply and Demand, Part 2Document7 pagesEconomics 14: Lecture 5: Supply and Demand, Part 2Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Quizizz - Supply and DemandDocument7 pagesQuizizz - Supply and DemandBollah MariameNo ratings yet
- Summary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleFrom EverandSummary of Austin Frakt & Mike Piper's Microeconomics Made SimpleNo ratings yet
- Principles Of Political Economy Abridged with Critical, Bibliographical, and Explanatory Notes, and a Sketch of the History of Political EconomyFrom EverandPrinciples Of Political Economy Abridged with Critical, Bibliographical, and Explanatory Notes, and a Sketch of the History of Political EconomyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 FinanceDocument1 pageAssignment 3 FinanceUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Sensitivity Analysis and The Simplex Method PDFDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Sensitivity Analysis and The Simplex Method PDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Overall TemplateDocument5 pagesOverall TemplateUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Overall TemplateDocument2 pagesOverall TemplateUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 3: AssetsDocument7 pagesAssignment # 3: AssetsUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Assign #03 FNNDocument11 pagesAssign #03 FNNUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Job TitleDocument2 pagesJob TitleUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Apple Goes Global Dah Edit Untuk ZatiDocument11 pagesApple Goes Global Dah Edit Untuk ZatiUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument12 pagesPDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (LP Models)Document2 pagesAssignment 1 (LP Models)Usman GhaniNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument2 pagesDocxUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- QDocument1 pageQUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Optimization and LP PDFDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Optimization and LP PDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Ob Case StudyDocument4 pagesOb Case StudyUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To DEcision Models PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Intro To DEcision Models PDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Emails Plus AttendanceDocument2 pagesEmails Plus AttendanceUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- The COVIDDocument3 pagesThe COVIDUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Case 1 (Patrix Paradox) PDFDocument2 pagesCase 1 (Patrix Paradox) PDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- 1st AssDocument3 pages1st AssUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- 1st AssDocument4 pages1st AssUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- OM320 - Decision Models - Spring 2023 PDFDocument5 pagesOM320 - Decision Models - Spring 2023 PDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 03-09-2023 04.53Document1 pageCamScanner 03-09-2023 04.53Usman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Leadership AssignmentDocument3 pagesLeadership AssignmentUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 03-09-2023 04.53Document1 pageCamScanner 03-09-2023 04.53Usman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Apple Goes Global Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesApple Goes Global Case Study PDFUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Usman GhaniNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 03-09-2023 04.54Document1 pageCamScanner 03-09-2023 04.54Usman GhaniNo ratings yet
- F StateDocument1 pageF StateUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- J StateDocument1 pageJ StateUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Fmma Midterm Activity 121123Document2 pagesFmma Midterm Activity 121123gerald paduaNo ratings yet
- UNI 20230306154519093616 781498 uniROC IpayobDocument7 pagesUNI 20230306154519093616 781498 uniROC IpayobxidaNo ratings yet
- Annual Report GEMS 2022Document319 pagesAnnual Report GEMS 2022firman manaluNo ratings yet
- Dissertation AyushiDocument32 pagesDissertation AyushiTaseen MbNo ratings yet
- Mss SCMDocument16 pagesMss SCMMyat Su SanNo ratings yet
- Supplimentary Guidelines CIE2 - Project On Capital StructureDocument2 pagesSupplimentary Guidelines CIE2 - Project On Capital StructureVrushieNo ratings yet
- 5-9642.revised Final Exam Schedule (MBA and EMBA Program) - 232Document3 pages5-9642.revised Final Exam Schedule (MBA and EMBA Program) - 232mirza.bari.232No ratings yet
- 3c Orange County CaseDocument19 pages3c Orange County Caseannabellekd123No ratings yet
- Tute-9 FMTDocument6 pagesTute-9 FMTHiền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Present Value ExcelDocument17 pagesPresent Value ExcelSanjai CttNo ratings yet
- FM Cia 1.1 - 2123531Document15 pagesFM Cia 1.1 - 2123531Rohit GoyalNo ratings yet
- FIN301 - Financial ManagementDocument8 pagesFIN301 - Financial ManagementSHANILA AHMED KHANNo ratings yet
- Treasury and Risk Management PDFDocument25 pagesTreasury and Risk Management PDFShanidNo ratings yet
- Artikel - Menuju Sinta 2-1Document13 pagesArtikel - Menuju Sinta 2-1andiamin311263No ratings yet
- Case Study 1Document2 pagesCase Study 1Manasi VermaNo ratings yet
- BstfinalDocument5 pagesBstfinalpriya singhNo ratings yet
- Final Report of Engro PDF FreeDocument58 pagesFinal Report of Engro PDF FreeMadni Enterprises DGKNo ratings yet
- Ebook Economics For Managers Global Edition 3Rd Edition Farnham Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesEbook Economics For Managers Global Edition 3Rd Edition Farnham Test Bank Full Chapter PDFenstatequatrain1jahl100% (11)
- 4.discounted Cash Flows and Fundamentals of ValuationDocument5 pages4.discounted Cash Flows and Fundamentals of Valuationjoel pvargheseNo ratings yet
- ECI Business Model CanvasDocument3 pagesECI Business Model CanvasScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- May StatementsDocument4 pagesMay Statementszubairniazi304No ratings yet
- 10.annual Report FY 2023Document115 pages10.annual Report FY 2023faarehaNo ratings yet
- Suntrust VeronaDocument12 pagesSuntrust Veronalyanca majanNo ratings yet
- Emarketer Report Email Marketing Benchmarks Relevancy Frequency Deliverability Mobility 5Document18 pagesEmarketer Report Email Marketing Benchmarks Relevancy Frequency Deliverability Mobility 5CHRISTIAN DAVID PALACIOS YANEZNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 SVT Possible Questions All UnitsDocument9 pagesPaper 1 SVT Possible Questions All UnitsPearl NarangNo ratings yet
- Volatility Contraction Pattern (VCP)Document5 pagesVolatility Contraction Pattern (VCP)Steve HatolNo ratings yet
- Strategy 6 Trading Gaps Down and Gaps Up at The Open BrianDocument26 pagesStrategy 6 Trading Gaps Down and Gaps Up at The Open Brianarun pingaleNo ratings yet
- PitchBook Benchmarks As of Q3 2022 With Preliminary Q4 2022 Data GlobalDocument60 pagesPitchBook Benchmarks As of Q3 2022 With Preliminary Q4 2022 Data GlobalNoe De DieuNo ratings yet
- DRF RequestDocument3 pagesDRF Requestjitender.singh29No ratings yet