Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CM - Chemical
Uploaded by
Katrina Mae PatalinghugOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CM - Chemical
Uploaded by
Katrina Mae PatalinghugCopyright:
Available Formats
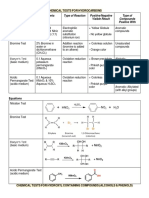
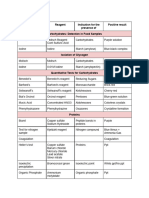
CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE
TEST PRINCIPLE REAGENT POSITIVE RESULT
ALBUMIN Heat & Acetic Acid Test Urinalysis protein is denatured by acid and heat so that it becomes less 10% Acetic Acid (+) cloudiness
Heller’s Test, Nitric Acid soluble & is precipitated & coagulated, respectively by acid & heat Conc. Nitric Acid
GLUCOSE Benedict’s Test When soluble copper sulfate is heated in strongly alkaline solution, the Benedict’s Reagent (+) orange to brick red precipitate
cupric ions are reduced to brick red insoluble cuprous ions (cuprous
oxide) by reducing agents such as glucose.
BENCE JONES Heat Precipitation Test The test involves heating the urine specimen with acetic acid and 5% acetic acid (+) precipitate dissolves upon
PROTEIN observing if the precipitate appears on heating, dissolves on further cooling to 56-60OC
heating and reappears on cooling.
ACETONE & Rothera’ Test Sodium nitroprusside is decomposed in alkaline solution. The resulting Ammonium sulfate (+) red-purple color
KETONE BODIES compounds are strong, oxidizing agents & in the presence and acetone Sodium nitroprusside
yield a rose- or purple- cpolred complex. The test is more sensitive for Ammonium hydroxide
diacetic acid than for acetone
Gunning’s Test Formation of yellow sediment of iodoform crystals results from the Strong ammonia (+) idoform crystals
reaction of Lugol’s solution Lugol’s solution
Gerthardt’s Test 10% chloride solution (+) Bordeaux red color
Hart’s Test 1 mL acetic acid (+) red ring
Hydrogen peroxide
LEVULOSE Seliwanoff’s Test Boiling urine with conc. HCl converts levulose to oxymethyl furfurol which Seliwanoff reagent (+) orange to red color
produces a red color when condensed with resorcinol
LACTOSE Rubner’s Test If lactose is present, the solution turns brick-red; red precipitate will Lead acetate (+) red precipitate & red
separate. The precipitate is the criterion for the test. Dextrose produces Strong ammonia water precipitate will separate
a red solution with yellow precipitate
BILE Gmelin’s Test Bile pigments are oxidized by acids forming a series of colored derivatives Nitric acid (+) play of colors: green on the
periphery, then red, and yellow
nearest the acid layer
BILIRUBIN Iodine-Smith Test 0.7% iodine & 95% ethyl (+) green ring
alcohol
UROBILINOGEN Ehrlich-Benzaldehyde Test The colorless urobilinogen is changed into a colored compound with Ehrlich-Benzaldehyde Cherry red color – increased
Ehrlich’s reagent Reagent amounts
Absence of cherry re od color –
decreased
UROBILIN Schlesinger Test Urobilinogen is oxidixzed to urobilin by the addition of Lugol’s Solution. Lugol’s Solution (+) fluorescent green color
The addition of zinc acetate leads to the production of a fluorescent green Zinc acetate solution
color
INIDICAN Obermayer’s Test Indoxyl potassium sulfate is hydrolyzed by strong metal and the resulting Obermayer’s reagent (+) indigo blue
indoxyl is oxidized tl indigo blue or to indigo red if the reaction is slow. Chloroform Normal: light blue
HEMOGLOBIN Guaiac Test 10% acetic acid, ether, 95% (+) blue color at the junction of
alcohol, guiac powder the guaiac and ether
Ammonium Sulfate Test Ammonium sulfate Clear supernatant – hemoglobin
Colored supernatant - myoglobin
MELANIN Thomalen Test Soidum nitroprusside is reduced to ferocyanide (Prussian blue) by 5% aqueous sodium (+) red color changes to blue
melanogen nitroprusside, 25% naOH, green
glacial acetic acid
CALCIUM Sulkowitch Test Calcium is precipated as calcium oxalate. This causes a milky turbidity Sulkowitch reagent (+) milky turbidity
CHLORIDE Fantus Test Silver nitrate reacts with chloride in the urine to precipitate silver chloride. Nitric acid (+) white precipitate
The nitric acid prevents the precipitation of silver phosphates Silver nitrate solution
You might also like
- M6 La1-Post Task Activity Sheet (Laboratory)Document5 pagesM6 La1-Post Task Activity Sheet (Laboratory)Mary Joeh LlarenaNo ratings yet
- Functional Group TestsDocument1 pageFunctional Group Testsnalla suhasNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument3 pagesBiochemPaulene Marie SicatNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument14 pagesReviewerpene reyezNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS For ACT 8910111213 and Coverage of Lab ExamDocument8 pagesANSWERS For ACT 8910111213 and Coverage of Lab ExamPearlregine Cianne MirandaNo ratings yet
- Tests for Carbohydrates, Lipids, GlycosidesDocument9 pagesTests for Carbohydrates, Lipids, GlycosidesDecemae FuentesNo ratings yet
- A. ANTHRAQUINONE GLYCOSIDE TESTDocument7 pagesA. ANTHRAQUINONE GLYCOSIDE TESTWestinNo ratings yet
- Group Iv Tests: Acetylation TestDocument7 pagesGroup Iv Tests: Acetylation TestAnanda VijayasarathyNo ratings yet
- Module 10 Lab ReportDocument5 pagesModule 10 Lab ReportVon Nilshen IlejayNo ratings yet
- Chem41 Postlabexpt.n0.3Document36 pagesChem41 Postlabexpt.n0.3HJakansjakkaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practical Help For XiiDocument16 pagesChemistry Practical Help For XiiMehjabin Abdurrazaque50% (8)
- Biochem LabDocument24 pagesBiochem Lab813 cafeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry TestsDocument46 pagesOrganic Chemistry TestsPriyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Screening by Dr. DV SirDocument4 pagesPhytochemical Screening by Dr. DV SirVaishnavi SahuNo ratings yet
- M4 Check in ActivityDocument2 pagesM4 Check in Activityjelly fishNo ratings yet
- Chemical Examination of UrineDocument6 pagesChemical Examination of UrinehermanskyNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Protein Tests SummaryDocument11 pagesQualitative Protein Tests SummaryLexi Evonne NacionalesNo ratings yet
- Biochem ProteinDocument40 pagesBiochem ProteinCharlene SibugNo ratings yet
- flashcards-for-neet-chemistry-dec20-aldehydes-ketones-and-carboxylic-acidsDocument5 pagesflashcards-for-neet-chemistry-dec20-aldehydes-ketones-and-carboxylic-acidsMinsha MohamedNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103L Santos Ronzel ANgelo M.Document3 pagesOrganic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103L Santos Ronzel ANgelo M.Akira SantosNo ratings yet
- Tests for CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesTests for CarbohydratesHans AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Carbohydrate Analysis TestsDocument6 pagesQualitative Carbohydrate Analysis TestsHalleli CastilloNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis Table For RecordDocument5 pagesQualitative Analysis Table For RecordAnanda VijayasarathyNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment NotesDocument2 pagesLab Experiment NotesHeily NicoleNo ratings yet
- MLS 5a - BSMLS2-E - Module4 - Group9Document8 pagesMLS 5a - BSMLS2-E - Module4 - Group9Lexi Evonne NacionalesNo ratings yet
- URINE EXMN With AnswersDocument12 pagesURINE EXMN With AnswersSivaani ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueDocument28 pagesAldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueMissy NalaunanNo ratings yet
- Experiment9 A011Document35 pagesExperiment9 A011Manas GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - Carbohydrates - Legario, M PDFDocument5 pagesTask 1 - Carbohydrates - Legario, M PDFMeddy LegarioNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and PhenolsDocument12 pagesAlcohols and PhenolsclarisseNo ratings yet
- Org Chem LabDocument3 pagesOrg Chem LabJocelyn AlunanNo ratings yet
- Chem 503 - Activity 5Document7 pagesChem 503 - Activity 5Aries Jay ReyesNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103LDocument4 pagesOrganic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103LPoll DaneNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryJaefar ShameemNo ratings yet
- CHM301 Lab Report 2Document14 pagesCHM301 Lab Report 2Nurul Adira FaziraNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions of Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument7 pagesColor Reactions of Proteins and Amino AcidsFARHANA ASDAIN INJAN100% (1)
- Biochem TestsDocument1 pageBiochem TestsJohn GreenNo ratings yet
- Kate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 12 Amines, Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument9 pagesKate Coleen D. Galera BS in Chemistry II May 4, 2017 Experiment 12 Amines, Amino Acids and ProteinsKateNo ratings yet
- 12stem B - Group No. 7 - Chapter IiiDocument4 pages12stem B - Group No. 7 - Chapter IiiMariel Generalao MacapazNo ratings yet
- KetonesDocument3 pagesKetonespixiedustNo ratings yet
- Qualitative TestsDocument36 pagesQualitative Testsanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Identification of The Unknown CarbohydrateDocument6 pagesIdentification of The Unknown CarbohydrateAngelica DangcoNo ratings yet
- Reactions Unknown Carbohydrates AnnotatedDocument19 pagesReactions Unknown Carbohydrates AnnotatedKkc KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Color Reactions and TestsDocument19 pagesCarbohydrates: Color Reactions and TestsAjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Explain Fehling's, Benedict's and Trommer's testsDocument2 pagesExplain Fehling's, Benedict's and Trommer's testsMa Anna Cris LumongsudNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONSDocument7 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONSASYRANI ZULAIKHANo ratings yet
- All Drugs - Chemical Tests1-3 PDFDocument3 pagesAll Drugs - Chemical Tests1-3 PDFALINo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Color ReactionsDocument3 pagesExperiment 2 - Color ReactionsPam GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chem LabDocument20 pagesChem LabKate Mae GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 2Document16 pagesPractical No. 2shahbazNo ratings yet
- Expt 8ADocument74 pagesExpt 8APearl Azucena100% (3)
- Radl Week 1Document36 pagesRadl Week 1Zeian Jacob BaylaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Lab Term01: Solubility TestDocument2 pagesBiochemistry - Lab Term01: Solubility TestJohn Daniel AriasNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidFrom EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Chemical Resistance Table: Page 1 of 14Document14 pagesChemical Resistance Table: Page 1 of 14FreddyPerazaNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry Reviews: Xiaoli Zhuang, Songtao Zhang, Yijian Tang, Feng Yu, Zhaomin Li, Huan PangDocument24 pagesCoordination Chemistry Reviews: Xiaoli Zhuang, Songtao Zhang, Yijian Tang, Feng Yu, Zhaomin Li, Huan PangBright MarchNo ratings yet
- A01 017Document41 pagesA01 017jaimeNo ratings yet
- Geology Chapter 2 UTHM NoteDocument3 pagesGeology Chapter 2 UTHM NoteFiqaAyobNo ratings yet
- The Recovery and Recycling of Mercury From Fluorescent Lamps Using Photocatalytic TechniquesDocument7 pagesThe Recovery and Recycling of Mercury From Fluorescent Lamps Using Photocatalytic TechniquesIna WhiteNo ratings yet
- IC No. 428 Page 2Document1 pageIC No. 428 Page 2aravinda aravindaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Molisch's TestDocument6 pagesPrinciple of Molisch's TestMg HNo ratings yet
- Catalogo GS 2018 PDFDocument116 pagesCatalogo GS 2018 PDFOcma MallidaNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts NotesDocument4 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts NotesMidhun Bhuvanesh.B 7A50% (2)
- Nitric AcidDocument7 pagesNitric AcidKuldeep BhattNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0011916414005761 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0011916414005761 MainAnca Maria CimbruNo ratings yet
- HN Chem Nomenclature Test Review Answer KeyDocument9 pagesHN Chem Nomenclature Test Review Answer KeyAdi ChhNo ratings yet
- Ionic PotentialDocument1 pageIonic PotentialGajanan HegdeNo ratings yet
- Module A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsDocument13 pagesModule A Chemistry: Contents: (A) Common Mistakes (B) Commands Task Answering Effectively (C) Sample QuestionsJOANNA MAGDALIN A/P JOSEPH MoeNo ratings yet
- Strong Acid-Strong Base TitrationDocument2 pagesStrong Acid-Strong Base TitrationSara KhalifehNo ratings yet
- HKFYG Lee Shau Kee College S4 Chemistry 2021-2022 Stoichiometry Part IDocument8 pagesHKFYG Lee Shau Kee College S4 Chemistry 2021-2022 Stoichiometry Part I(4C20) Chun Ting (Michael) LiNo ratings yet
- Diazonium Salts Azo DyesDocument8 pagesDiazonium Salts Azo DyesAnthony Basanta100% (1)
- Synthesis of ( ) - Menthol: Industrial Synthesis Routes and Recent DevelopmentDocument15 pagesSynthesis of ( ) - Menthol: Industrial Synthesis Routes and Recent DevelopmentLucas LiraNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Types and Uses (39Document13 pagesBiological Molecules: Types and Uses (39fatema buhussainNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Document16 pagesHydrocarbons (Alkanes and Alkenes)Soham NagNo ratings yet
- KCET 2024 Chemistry Study Plan PDFDocument5 pagesKCET 2024 Chemistry Study Plan PDFshirishgt02No ratings yet
- Brass PolishDocument11 pagesBrass PolishfsarfrazNo ratings yet
- Synergism in Solvent ExtractionDocument26 pagesSynergism in Solvent ExtractionabrahanNo ratings yet
- Vco Philippine National StandardDocument8 pagesVco Philippine National StandardTeenahNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry An Active Learning Approach 6th EditionDocument33 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry An Active Learning Approach 6th Editioncaulisdonatoryczdtt100% (14)
- Terjemahan Pembentukan Deposit BijihDocument8 pagesTerjemahan Pembentukan Deposit BijihIwan Makhwan HambaliNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Determining Oil and Grease For Raw and Treated EffluentDocument3 pagesLaboratory Manual For Determining Oil and Grease For Raw and Treated EffluentAnas YuzairiNo ratings yet
- GPP Company Insight 2018Document8 pagesGPP Company Insight 2018ady perdanaNo ratings yet
- SNAr Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazineDocument5 pagesSNAr Reaction Mechanism and Synthesis of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazineparadoxcomplexNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistrybliker182No ratings yet