Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histopathlab Reviewer
Uploaded by
angela verayeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Histopathlab Reviewer
Uploaded by
angela verayeCopyright:
Available Formats
Histopathology
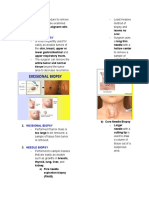
PROPER DONNING Biopsy Specimens
1. Inner gloves - Is a sub group of surgical specimens, however, these small
2. Gown tissue samples are obtained in procedures other than
3. Mask surgery.
4. Headcap
5. Facemask/ goggles Needle Aspiration Biopsy
6. Shoe cover - A biopsy obtained by inserting a hollow needle through the
7. Outer gloves skin into an internal organ.
Excision Biopsy
PROPER DOFFING - This involves the removal of a small lesions
1. Outer gloves
2. Shoe cover
Endoscopic Biopsy
3. Facemask/ googles
- A small specimen of digestive or respiratory tract obtained
4. Gown
by inserting an instrument periorally or perianally and
5. Headcap
removing a piece of tissue.
6. Mask
7. Innergloves
Wedge Biopsy
- This term describes a small pie shaped piece of a particular
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY organ obtained during exploratory surgery.
Sections:
Surgical Abrasion Biopsy
Cytology - A specimen received that is abraded from the surface of the
FNAB/ CNAB skin or mouth lesion done using a sponge or brush.
Slide Review
Breast Panel Cone Biopsy
Frozen Section - Special procedure for collection of specimen in which a
Surepath/ PAP smear cone shaped portion of the cervix is removed.
10 STEPS OF TISSUE PROCESSING GROSS EXAMINATION AND FIXATION
1. Fixation
2. Dehydration Gross examination
3. Clearing - assessment of tissue specimens by the unaided eye
4. Impregnation
5. Embedding Fixation
6. Trimming - The first and most critical step of tissue processing
7. Smearing
8. Staining Pathologist
9. Mounting - Gross examination is done by who
10. Labelling
Gross description and tissue block
5 LITERS 10% NBF (Neutrally Buffered Formalin) - The 2 end products of gross examination
1. 20g monobasic powder
2. 32.5g Dibasic powder Brain
3. 500mL 37% Formaldehyde - Tissues can be cut & trimmed without prior fixation except
4. 4.5L Distilled H2O for the?
GROSSING TISSUE SPECIMEN Photographs
- Provides a better 3-Dimensional understanding of the
Gross specimen
- A description and dissection of tissue specimen, done after
tissues are fixed or partially fixed. Millimeters
- A step that preceded tissue processing, embedding, - Unit for very small specimen in grossing
microtomy and staining.
Centimeter
Types of Specimen - The standard unit of measurement
Surgical specimens
Autopsy specimens 2-3mm
- Standard tissue thickness in gross examination
Surgical Specimens
- Specimens obtained during operative surgery Nitric Acid
- Discrete areas of calcification is decalcificied using this acid
Angela Obrique Veraye
Histopathology
Bread Loafing
- Knife technique for a live specimen. Non coagulant
- Create a gel that makes it difficult to penetrate by
1:20 subsequent solutions
- Ratio of tissue to fixative for routine exam
pH 6-8
1:50 - The satisfactory pH level of a fixative
- Ratio of tissue to fixative in museums
-60 °C
Fixation - The temperature required for rapid fixation
- A complex series of chemical events which bring about
changes in the cell-like hardening 400-450 mOsm
- The best result obtained in fixation is attained with—?
Crosslinking of proteins
- The ________ produces denaturation of coagulation of Mordant
proteins so that the semifluid state is converted into - Promotes staining or inhibit certain dyes in favor of another
semisolid state
Simple fixative
Primary aim - A fixative made up of only 1 component
- To preserve the morphologic and chemical integrity of the
cell in a life-like manner as possible Cytologic fixative
- A specific part and particular microscopic element of the
Secondary aim cell itself
- To harden and protect the tissue from trauma of further
handling 10% buffered formalin
- Most widely used fixative for routine histology
Autolysis
- A decomposition of a certain material due to hydrolytic 10% Formal Saline
enzymes - A simple microanatomical made up of 40% saturated
formaldehyde diluted to 10% sodium chloride (pH= 6.8)
Lysozome
- An example of a hydrolytic enzyme Alcoholic formalin
- Used for primary fixation specimens and for post fixation of
Putrefaction large fatty specimens
- The decomposition of a substance due to bacterial/fungal
colonization Glutaraldehyde
- Made up of two formaldehyde residues, linked by a three
Solidification carbon chain. It also doesn't cause dermatitis
- Converts the normal semifluid consistency of cells to an
irreversible semisolid consistency Carnoy’s fixative
- The fastest fixative
Optical Differentiation
- Alters the refractive indices to varying degrees so that Methanol 100%
unstained components are more easily visualized than - Excellent for fixing dry and wet smears, blood smears, and
when unfixed bone marrow
Formaldehyde ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL 95%
- This fixative intensifies the staining character of - Used for fixing touch preparations
hematoxylin
37-56°C ETHANOL
- What is the suggested heat temperature to hasten fixation - Used as a simple fixative and is incorporated into compound
fixatives for better results
Non additive
- Stabilizes the tissue by removing the bound water attached
to the hydrogen bond of a certain group within the protein CARNOY'S FIXATIVE
molecule - Permits good nuclear staining and differentiation
Additive
- Fixative is taken in and becomes a part of the tissue NEWCOMER'S FLUID
- Recommended for fixing mucopolysaccharide and nuclear
Coagulant proteins
- Creating a network that allows solutions to readily
penetrate the interior of the tissue
Angela Obrique Veraye
Histopathology
METALLIC FIXATIVES POST-CHROMATIZATION
- Fixes tissues through an unknown mechanism which - A form of secondary fixation whereby a primarily fixed
increases the staining brightness and gives excellent tissue is placed in an aqueous solution of 2.5-3% potassium
nuclear detail of our specimen dichromate for 24hrs
ZENKER'S SOLUTION
- Permits brilliant staining of nuclear and connective tissue WASHING OUT
fibers - the process of removing excess from the tissue after
fixation in order to improve staining and remove artifacts
from the tissue
HEIDENHAIN'S SUSA SOLUTION
- Permits most staining procedures to be done CADMIUM/COBALT SALT
- Prevents fat dispersal
FLEMMING'S SOLUTION
- Permanently fixes fat 3 MONTHS
- To prevent bleaching, change the fixative every _____
REGAUD'S
- Recommended for preservation of chromatin, mitochondria, 70%
mitotic figures, golgi bodies, RBC, and colloid-containing - To restore natural specimen color, what is the percentage
tissues of the alcohol solution that the specimen should be
immersed in?
ORTH'S FLUID
- Demonstrates rickettsiae and other bacteria MAGNESSIUM/CALCIUM CARBONATE
- Removes formic acid formation
3% POTASSIUM DICHROMATE
- Fixes but does not precipitate cytoplasmic structures,
preserves lipids and mitochondria BLEACHING, DISPERSAL OF FAT, DISSOLUTION
- Effects of prolonged fixation
PICRIC ACID
- Stains yellow, used for strong saturated aqueous solutions
LITHIUM CARBONATE
- Picric Acid's yellow stain may be removed by another acid
dye or ______
BOUIN'S SOLUTION
- Allows brilliant staining with trichrome method
BRASIL'S SOLUTION
- Better and less "messy" than Bouin's solution
4% LEAD ACETATE
- Takes up CO2 to form insoluble lead carbonate
ACETONE
- Used in fixing brain tissues (rabies)
SECONDARY FIXATIVE
- The process of placing an already fixed tissue in a second
fixative
Angela Obrique Veraye
You might also like
- Cataract And Small Pupil Management Manual Techniques: 2022, #1From EverandCataract And Small Pupil Management Manual Techniques: 2022, #1No ratings yet
- 5_Introduction to Tissue ProcessingDocument9 pages5_Introduction to Tissue Processingbsramos2023No ratings yet
- BIOPSYDocument7 pagesBIOPSYjmskdlnNo ratings yet
- Hstcyt1 Lcc1 Short Term NotesDocument33 pagesHstcyt1 Lcc1 Short Term NotesMHEKAELLA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination and Histological Techniques OverviewDocument4 pagesFresh Tissue Examination and Histological Techniques OverviewBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- Kim2016 Pdo MultifilamenDocument5 pagesKim2016 Pdo Multifilamenyolanda tejaNo ratings yet
- Tissue ProcessingDocument4 pagesTissue ProcessingSeon u 'No ratings yet
- Histopathological Techniques OverviewDocument5 pagesHistopathological Techniques OverviewNerdyPotatoNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lec MidetermsDocument48 pagesHistopath Lec MidetermsMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- Histology Lecture 2017 HandoutDocument11 pagesHistology Lecture 2017 HandoutqNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1Krizza UrmazaNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Tissue ProcessingDocument7 pages1 Introduction To Tissue ProcessingAngel RamosNo ratings yet
- Review On General HistoDocument50 pagesReview On General HistoVenice FuertesNo ratings yet
- Trans Histopath 3Document5 pagesTrans Histopath 33A PEÑA AndreaNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination - HistopathDocument4 pagesFresh Tissue Examination - HistopathIrish De VeraNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Fresh TissueDocument3 pagesPreparation of Fresh TissueMaster ChiefNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lab Rules and RegulationsDocument4 pagesHistopath Lab Rules and RegulationsFedz FederisoNo ratings yet
- BIOPSY Oral SurgeryDocument34 pagesBIOPSY Oral SurgeryNisha ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Cell and Embryology: Ii. Tissue Slide PreparationDocument9 pagesCell and Embryology: Ii. Tissue Slide Preparationashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Day Surgery BenefitDocument2 pagesDay Surgery BenefitSyafiq JasrinNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide To Day SurgeryDocument2 pagesA Quick Guide To Day SurgeryAprikot KapsulNo ratings yet
- Lec 1. Introduction to histology.AABDocument14 pagesLec 1. Introduction to histology.AABejekorangNo ratings yet
- Гистология, цитология, эмбриологияDocument125 pagesГистология, цитология, эмбриологияrysalievanurgul.tNo ratings yet
- Principles of BiopsyDocument4 pagesPrinciples of BiopsyTohin TurjoNo ratings yet
- Eyelid DisordersDocument6 pagesEyelid DisordersCamilo PerezNo ratings yet
- Ana 2142 Histology Lecture Note-2Document17 pagesAna 2142 Histology Lecture Note-2Malik timiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Specimen Processing in MycologyDocument7 pages2 - Specimen Processing in MycologyMariz MartinezNo ratings yet
- Histopathology: 1. Routine Histopathologic ExaminationDocument2 pagesHistopathology: 1. Routine Histopathologic ExaminationPat DazaNo ratings yet
- HPCT-LEC-MIDTERMSDocument25 pagesHPCT-LEC-MIDTERMSKRISTERLEX RUIZNo ratings yet
- Exfoliative CytologyDocument9 pagesExfoliative Cytologymiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LECDocument14 pagesHISTOPATHOLOGIC AND CYTOLOGIC TECHNIQUES (LECClair TugnaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Prosthetic SurgeryDocument26 pagesPre-Prosthetic SurgeryAhmed BarakatNo ratings yet
- BIO83A (LAB) Output#2 - BajadoDocument5 pagesBIO83A (LAB) Output#2 - BajadoMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Multifocal Pha Kic ImplantDocument6 pagesMultifocal Pha Kic ImplantArif MohammadNo ratings yet
- HCT Laboratory 1Document5 pagesHCT Laboratory 1Gwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic Comparison of Wound Closure TechniquesDocument3 pagesAesthetic Comparison of Wound Closure Techniquesluisrmg91No ratings yet
- FNAB Its Procedure and Method of Preserving SpecimenDocument12 pagesFNAB Its Procedure and Method of Preserving SpecimenNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lab (Module 2) : Receiving, Accessioning and Gross Examination of Tissue SamplesDocument5 pagesHistopath Lab (Module 2) : Receiving, Accessioning and Gross Examination of Tissue SamplesAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Immuno His To ChemistryDocument52 pagesImmuno His To ChemistryBagusHibridaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Laboratory Discussion 1Document4 pagesParasitology Laboratory Discussion 1FRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Compiled NotesDocument21 pagesCommunicable Disease Compiled NotesJoanne PaulineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Reconstructive Periodontal Surgery Part I PPT EsamDocument24 pagesLecture 6 - Reconstructive Periodontal Surgery Part I PPT EsamHaneen Al-HajjNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination EyeDocument2 pagesClinical Examination EyeKirti JamwalNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesModule 3 Lab ReviewerVince Nicole MoraNo ratings yet
- Incise Drapes UK GX750 6pDocument6 pagesIncise Drapes UK GX750 6pbouchra8blsNo ratings yet
- PARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Document5 pagesPARASITIC AMOEBAS (Lab)Xie LianNo ratings yet
- 4 Basic Human Tissue Types & Histopathology MethodsDocument12 pages4 Basic Human Tissue Types & Histopathology MethodsJanneth MendozaNo ratings yet
- His To Pathological InvestigationsDocument9 pagesHis To Pathological InvestigationsDeepak NingombamNo ratings yet
- OUTLINE - CytologyDocument4 pagesOUTLINE - CytologyMaria Renee Lian NobleNo ratings yet
- Student Notes: GPHCT: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument7 pagesStudent Notes: GPHCT: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentFedz FederisoNo ratings yet
- Surgery B PracticalDocument12 pagesSurgery B PracticalMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Articulo Ingles BiopsiaDocument9 pagesArticulo Ingles BiopsiaJamileth MartinezNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Gynecology Hysteroscopy and LaparosDocument5 pagesDiagnostic Gynecology Hysteroscopy and LaparosAlbert Francis BialaNo ratings yet
- Homo Gen IzationDocument5 pagesHomo Gen IzationDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaNo ratings yet
- OPHTHA - 1.07a - Lens and Cataract-2 PDFDocument7 pagesOPHTHA - 1.07a - Lens and Cataract-2 PDFNoel QuintonNo ratings yet
- Biopsy: Mahendraraj, M.T 110020599Document39 pagesBiopsy: Mahendraraj, M.T 110020599karinarakhmaNo ratings yet
- HISTOPATHDocument7 pagesHISTOPATHbella xiaoNo ratings yet
- Histopathology Procedures Fromtissue Samplingto Histopathological Evaluation DrugsafetyevaluationDocument15 pagesHistopathology Procedures Fromtissue Samplingto Histopathological Evaluation DrugsafetyevaluationDavindu AnushkaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Histology: Fixation, Staining and MicroscopyDocument2 pagesIntroduction to Histology: Fixation, Staining and MicroscopyKyla ValenciaNo ratings yet
- HPCT311 Midterms LecDocument16 pagesHPCT311 Midterms LecJuzhley Perez100% (1)
- MolBioLec Quiz3Document3 pagesMolBioLec Quiz3angela verayeNo ratings yet
- EXAM REVIEWER CCDocument1 pageEXAM REVIEWER CCangela verayeNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology (Prelim ReviewerDocument2 pagesImmunohematology (Prelim Reviewerangela verayeNo ratings yet
- Iso PrelimsDocument3 pagesIso Prelimsangela verayeNo ratings yet
- Parasitology lecture on stool examinationDocument7 pagesParasitology lecture on stool examinationangela verayeNo ratings yet
- Research Lec1Document2 pagesResearch Lec1angela verayeNo ratings yet
- Objective Assessment of YAG Laser VitreolysisDocument5 pagesObjective Assessment of YAG Laser VitreolysisPutri kartiniNo ratings yet
- SNB QuestionsDocument7 pagesSNB Questionshardie himerNo ratings yet
- Cell SaverDocument8 pagesCell SaverFrank QuitianNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Hysterectomy Vs Abdominal HysterectomyDocument6 pagesVaginal Hysterectomy Vs Abdominal HysterectomyValen Ying HuiNo ratings yet
- 4 EL Husseinys Essentials of Cardiovascular System @eduwaves360Document236 pages4 EL Husseinys Essentials of Cardiovascular System @eduwaves360ahmed_abu_alrobNo ratings yet
- Hemorragia Digestiva Baja: Lower Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument6 pagesHemorragia Digestiva Baja: Lower Gastrointestinal BleedingwiwiNo ratings yet
- Staff nurse coaching memory based questionsDocument8 pagesStaff nurse coaching memory based questionsVrindha VijayanNo ratings yet
- MCA - LAB - Sterile Technique Procedures - NotesDocument7 pagesMCA - LAB - Sterile Technique Procedures - NotesRaynelah AnnNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems - Overview, Anatomy, Functions - KenhubDocument13 pagesHuman Body Systems - Overview, Anatomy, Functions - Kenhubregina.rmsNo ratings yet
- Organ Sale and DonationDocument61 pagesOrgan Sale and DonationSachin PatelNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Drug Therapy QuizDocument4 pagesIntravenous Drug Therapy QuizcrossNo ratings yet
- Death Case Presentation StrokeDocument66 pagesDeath Case Presentation StrokeGrace SihotangNo ratings yet
- CBCTDocument19 pagesCBCTFernanda CombaNo ratings yet
- Borang Logbook - Inez Ann Marie 260219Document209 pagesBorang Logbook - Inez Ann Marie 260219AsepDarussalam0% (1)
- Nursing Care of a Client with Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument3 pagesNursing Care of a Client with Gastrointestinal BleedingnicoleNo ratings yet
- A. Loss of Deep Tendon ReflexesDocument15 pagesA. Loss of Deep Tendon Reflexes2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Bones of the Lower Limb AnatomyDocument42 pagesBones of the Lower Limb AnatomybnvjNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radiography - Merrills Atlas of Radiographic Positioning and ProceduresDocument30 pagesMobile Radiography - Merrills Atlas of Radiographic Positioning and ProceduresJonald Pulgo IcoyNo ratings yet
- Code Blue System: Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor BahruDocument15 pagesCode Blue System: Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor BahrumursidahanimNo ratings yet
- Peritoneal Dialysis.Document2 pagesPeritoneal Dialysis.alex_cariñoNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument11 pagesChest Paintashoy clarkeNo ratings yet
- Gent ConsensusDocument6 pagesGent ConsensusAlfonsoSánchezNo ratings yet
- GSRC Trans Resource Guide (2015-2016)Document19 pagesGSRC Trans Resource Guide (2015-2016)Merissa Taylor-Meissner100% (1)
- Trauma and Blast InjuriesDocument22 pagesTrauma and Blast InjuriesHafiz Mahruzza100% (1)
- Pathologic Obstetrics 100 Item Post TestDocument16 pagesPathologic Obstetrics 100 Item Post TestMomshie Felaih Binasoy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Handbook of General Surgical EmergenciesDocument3 pagesHandbook of General Surgical EmergenciesFarah MalaebNo ratings yet
- By DR.: Haitham Mokhtar Mohamed Abd AllahDocument101 pagesBy DR.: Haitham Mokhtar Mohamed Abd AllahMohamed ElkadyNo ratings yet
- A Prospective Study On The Maternal Outcome in Cases of Previous One Cesarean SectionDocument6 pagesA Prospective Study On The Maternal Outcome in Cases of Previous One Cesarean SectionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Thesis TopicsDocument6 pagesUltrasound Thesis Topicsdw9x1bxb100% (2)
- ECG UworldDocument4 pagesECG UworldBaebee LouNo ratings yet
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthFrom EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)