Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Preparation of Fresh Tissue
Uploaded by
Master ChiefOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Preparation of Fresh Tissue
Uploaded by
Master ChiefCopyright:
Available Formats
HISTOPATHOLOGY LABORATORY
PREPARATION OF FRESH TISSUE
LECTURER: Mr. John Marke Bernardo
DATE | A.Y. 2022 – 2023 | PRELIMS | 2ND SEMESTER
OUTLINE and into the subcutaneous fat, yielding a 3- to 4-
I. Introduction mm cylindrical core of tissue sample.
II. Fresh Tissue Sample Techniques ● Shave biopsy - where small fragments of tissue
A. Teasing & Dissociation are “shaved” from a surface (usually skin).
B. Squash Preparation ● Curettings - where tissue is scooped or spooned
C. Smear Preparation to remove tissue or growths from body cavity such
a. Streaking
as endometrium or cervical canal.
b. Spreading
c. Pull-Apart (From the book)
d. Touch or Impression Smear
D. Frozen Section
FRESH TISSUE SAMPLE TECHNIQUES
INTRODUCTION
Histology is the microscopic study of the normal TEASING AND DISSOCIATION
tissues of the body while histopathology is the microscopic ● A process whereby a selected tissue specimen is
study of tissues affected by disease. The procedures immersed in isotonic salt solution such as normal
adopted for the preparation of material for such studies are saline or Ringer’s solution in a petri dish or watch
known as histologic or histopathologic techniques. The glass, carefully dissected with a needle and separated
tissues are usually obtained during surgery, biopsy, or by direct or zigzag spread using an applicator stick.
autopsy. They range from very large specimens or whole Selected pieces of the tissue are transferred carefully
organs to tiny fragments of tissue. The following surgical to a microscope slide and mounted as a wet
procedures are usually performed to obtain the preparation underneath a cover glass, careful to avoid
forming bubbles. It is either stained with a supravital
specific-types of tissue that are submitted to a histology
dye or examined unstained by Phase Contrast or
laboratory for processing:
Bright Field microscopy. It has the advantage of
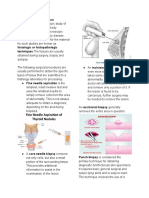
● Fine needle aspiration is the simplest, least
permitting the cells to be examined in the living state.
invasive test and uses the smallest needle to
● Procedure for Teasing and Dissociation:
simply remove cells from the area of abnormality. 1. From the frozen block of tissue, cut several small,
This is not always adequate to obtain a diagnosis, thin slices of tissue.
depending on the area to be biopsied. 2. Immerse the tissue slices in a petri dish filled with
● A core needle biopsy removes not only cells, but saline solution.
also a small amount of the surrounding tissue. This 3. Using a dissecting needle, carefully tease the
provides additional information to assist in the tissue slices until they unfold and spread out.
examination of the lesion. 4. Carefully mount a teased slice on a slide and cover
● An incisional biopsy takes out even more it with a coverslip.
surrounding tissue. It takes out some of the
abnormality, but not all. The doctor will slice into
the lesion and remove only a portion of it. If the
lesion is found to be cancerous, further surgery
may be needed to remove or excise the entire
lesion.
● An excisional biopsy generally removes the entire SQUASH PREPARATION (CRUSHING)
area in question. ● A process whereby small pieces of tissue (not more
● Punch biopsy is considered the primary technique than one mm. in diameter) are placed in a
for obtaining diagnostic full-thickness skin microscopic slide and forcibly compressed with
specimens. It requires basic general surgical and another slide or with a cover glass. If necessary, a
suture-tying skills and is easy to learn. The supravital stain may be placed at the junction of the
technique involves the use of a circular blade that slide and the cover glass, and allowed to be absorbed
is rotated down through the epidermis and dermis, by the tissue through capillary attraction.
Transes Warriors: HISTOFRAT_RAV: Pacres, Tee │ 2K │Page 1 of 3
HISTOPATHOLOGY LABORATORY
PREPARATION OF FRESH TISSUE
LECTURER: Mr. John Marke Bernardo
DATE | A.Y. 2022 – 2023 | PRELIMS | 2ND SEMESTER
1. Add 1-2 drops of methylene blue stain directly on length of the slide. If a wire loop is used instead,
the tissue slice on the glass slide. 2. Cover the collect a loopful of the material and smear the
stained tissue with a cover slip or another glass slide. material on the slide. A relatively uniform
3. Applying enough pressure to crush the tissue flat. distribution of the material should be obtained.
4. Label your slide with your name, group number and Cover it with a cover slip.
section and submit it to your instructor 3. Label your slide with your name, group number
and section and submit it to your instructor.
SPREADING
SMEAR PREPARATION
1. Transfer a small amount of the sediments on
● The method of preparing the smear differs
one end of a clean glass slide.
depending on the nature of the material to be
2. Using an applicator stick, spread the sediments
examined. As a general rule, smears are made
throughout the slide (similar to how butter is
either by spreading the selected portion of the
spread on bread). Another technique is to place the
specimen over the surface of the slide with a
drop of sediments at the center of the slide. Then
platinum loop. Smears may be examined either as
with a circular motion, gently spread it into a
fresh preparations similar to that described for
moderately thick film.
teased preparations, or by using a supravital
3. Label your slide with your name, group number
staining technique. Smear preparations can be
and section and submit it to your instructor.
made permanent by fixing them while still wet,
staining them to demonstrate specific structures
and inclusions, and mounting the cleared specimen
beneath a cover glass with a suitable mounting
medium. This is useful for preparing smears of
thick secretions such as serous fluids,
concentrated sputum, enzymatic lavage sample
from the gastrointestinal tract, and blood smears.
This technique is especially useful in cytological ● It is a little more tedious than streaking, but has the
examinations, particularly for cancer diagnosis. advantage of maintaining cellular interrelationships
(from the book) of the material to be examined. It is especially
recommended for smear preparations of fresh
● Note: Centrifuge body fluid samples and decant the sputum and bronchial aspirates, and also for thick
supernatant. Save the sediments for the mucoid secretions. (from the book)
procedures below. Avoid making smears that are
too thin or too thick since this will render your
PULL-APART
smears unsuitable for examination. 1. Place a drop of the sediments at one end of a
glass slide.
STREAKING 2. Cover it with the end of another glass slide.
1. Pour a small amount of the sediments on one Allow the sediments to spread evenly between the
end of a clean glass slide. attached surfaces of the two slides.
2. Using an applicator stick, streak the sediments in
a straight or zigzag line throughout the remaining
Transes Warriors: HISTOFRAT_RAV: Pacres, Tee │ 2K │Page 2 of 3
HISTOPATHOLOGY LABORATORY
PREPARATION OF FRESH TISSUE
LECTURER: Mr. John Marke Bernardo
DATE | A.Y. 2022 – 2023 | PRELIMS | 2ND SEMESTER
3. With a single, uninterrupted motion, pull the two technique (around 10 minutes vs 16 hours). However, the
slides apart in opposite directions. Cover the technical quality of the sections is much lower.
smear with a cover slip.
4. Label your slide with your name, group number
and section and submit it to your instructor.
TOUCH OR IMPRESSION SMEAR
1. Retrieve the block of tissue from the first
procedure. Cut the block in half, exposing a
fresher surface.
2. Allow the freshly cut surface to come in contact
with the surface of a clean glass slide. Apply
gentle pressure, allowing the cells to be transferred
directly to the slide. Cover the smear with a cover
slip.
3. Label your slide with your name, group number
and section and submit it to your instructor.
Frozen Section
The technical name for this procedure is cryosection.
With the cryostat, the usual histology slice is cut at 5 to 10 µm.
The surgical specimen is placed on a metal tissue disc which
is then secured in a chuck and frozen rapidly to about –20 to
–30°C. The specimen is embedded in a gel like medium
consisting of polyethylene glycol and polyvinyl alcohol; this
compound is known by many names and when frozen has the
same density as frozen tissue. Subsequently it is cut frozen
with the microtome portion of the cryostat, the section is
picked up on a glass slide and stained. The preparation of the
sample is much more rapid than with traditional histology
Transes Warriors: HISTOFRAT_RAV: Pacres, Tee │ 2K │Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Biopsy - PPT Oral PathologyDocument40 pagesBiopsy - PPT Oral PathologyDr.Neethu Salam100% (4)
- Trans Histopath 3Document5 pagesTrans Histopath 33A PEÑA AndreaNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue ExaminationDocument6 pagesFresh Tissue ExaminationHenessey Palisoc ResuelloNo ratings yet
- Mod 2.1Document7 pagesMod 2.1Pauline Louise S. DURANNo ratings yet
- Tissue ProcessingDocument4 pagesTissue ProcessingSeon u 'No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Fresh Tissue ExaminationzDocument10 pagesChapter 2 - Fresh Tissue ExaminationzMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination - HistopathDocument4 pagesFresh Tissue Examination - HistopathIrish De VeraNo ratings yet
- Cytology Sample Collection and Preparation For Veterinary PractitionersDocument8 pagesCytology Sample Collection and Preparation For Veterinary PractitionersKmo mastnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1Krizza UrmazaNo ratings yet
- HPCT311 Midterms LecDocument16 pagesHPCT311 Midterms LecJuzhley Perez100% (1)
- Gregorios-Histopathologic-Techniques Ch3 and 29Document78 pagesGregorios-Histopathologic-Techniques Ch3 and 29EllaineSonejaNo ratings yet
- F) Microtomy: Procedure of Section Cutting/ MicrotomyDocument6 pagesF) Microtomy: Procedure of Section Cutting/ MicrotomyJes CarreonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Bacterial Identification and Processing ModuleDocument20 pagesLesson 2 Bacterial Identification and Processing ModuleTinNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesHistopath Lab ActivityRakia PillayNo ratings yet
- HistopathDocument6 pagesHistopathRichell VillacarlosNo ratings yet
- HistotechniquesDocument47 pagesHistotechniquesJean VipinosaNo ratings yet
- Modules 7 12 HistopathologyDocument9 pagesModules 7 12 HistopathologyKrystelle Anne PenaflorNo ratings yet
- Act. 2 - Proper Processing of Fresh Tissue Samples For Microscopic ExaminationDocument6 pagesAct. 2 - Proper Processing of Fresh Tissue Samples For Microscopic ExaminationBSMLS TINGZNo ratings yet
- Skin Collection Act4 Group 3 FinalDocument9 pagesSkin Collection Act4 Group 3 FinalIvan Jay DomingoNo ratings yet
- 02 HP Lab - Fresh Tissue ExaminationDocument30 pages02 HP Lab - Fresh Tissue ExaminationLaiza Fathma AbilosaNo ratings yet
- Animal Cytology (Compatibility Mode)Document13 pagesAnimal Cytology (Compatibility Mode)AdarshBijapurNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument27 pagesTissuesAngela Nicole Udan100% (1)
- 1 Introduction To Tissue ProcessingDocument7 pages1 Introduction To Tissue ProcessingAngel RamosNo ratings yet
- Leishmaniasis Guide Collection 2021Document3 pagesLeishmaniasis Guide Collection 2021Amii CcNo ratings yet
- BIOPSY Oral SurgeryDocument34 pagesBIOPSY Oral SurgeryNisha ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Bacteria, Virus, Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Mycoplasma, Parasite, Toxin, PoisonsDocument5 pagesBacteria, Virus, Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Mycoplasma, Parasite, Toxin, PoisonsNerdyPotatoNo ratings yet
- Guide: PracticalDocument4 pagesGuide: PracticalAli SamanthaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Cytology: 10.1 Methods of Specimen AttainmentDocument54 pagesDiagnostic Cytology: 10.1 Methods of Specimen AttainmentSuraj_Subedi100% (3)
- HPCT Lec MidtermsDocument25 pagesHPCT Lec MidtermsKRISTERLEX RUIZNo ratings yet
- Panduan Diagnosis KulitDocument16 pagesPanduan Diagnosis Kulitjonatan314No ratings yet
- Sop Od DermatophytosisDocument10 pagesSop Od DermatophytosisAnanyaNo ratings yet
- Denmark V.Micro Exercise 2Document2 pagesDenmark V.Micro Exercise 2JM&MC TV ninjaNo ratings yet
- Press BookDocument4 pagesPress Bookalibinahmed2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (Bacte)Document7 pagesChapter 7 (Bacte)Jessica PontanaresNo ratings yet
- Routine Histotechniques - Lecture 1Document47 pagesRoutine Histotechniques - Lecture 1Gerald John Paz100% (1)
- 5 - Introduction To Tissue ProcessingDocument9 pages5 - Introduction To Tissue Processingbsramos2023No ratings yet
- Module 3 Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesModule 3 Lab ReviewerVince Nicole MoraNo ratings yet
- Smear PreparationDocument4 pagesSmear PreparationDavid WolfyNo ratings yet
- Lab Excercise 5 (Fungi) (2023-2024)Document7 pagesLab Excercise 5 (Fungi) (2023-2024)ps.pcpc221No ratings yet
- Lesson 30 PDFDocument5 pagesLesson 30 PDFLaura B.No ratings yet
- Activity No. 2: Title of The ActivityDocument8 pagesActivity No. 2: Title of The ActivitymasorNo ratings yet
- Histopathology and CytologyDocument26 pagesHistopathology and CytologyKirsten ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- The Acquisition and Management of Cytology Specimens: Denny J. MeyerDocument15 pagesThe Acquisition and Management of Cytology Specimens: Denny J. MeyerzvegaNo ratings yet
- 9 Practical - 1Document5 pages9 Practical - 1anubh50No ratings yet
- Lec 1. Introduction To Histology - AABDocument14 pagesLec 1. Introduction To Histology - AABejekorangNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue ExaminationDocument23 pagesFresh Tissue ExaminationMarissa CordovaNo ratings yet
- Micro - Power PointDocument48 pagesMicro - Power PointGalana BiratuNo ratings yet
- Varney - Pap SpecimenDocument3 pagesVarney - Pap SpecimenevillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Proceedings - J Brazzell1Document130 pagesProceedings - J Brazzell1Ganesh Dasara100% (1)
- HistopathologyDocument21 pagesHistopathologyjuliaisabelzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tissue ProcessingDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Tissue ProcessingELIEZER MAYAPITNo ratings yet
- Fresh Tissue Examination: Mark Lester B. Cauan, RMTDocument22 pagesFresh Tissue Examination: Mark Lester B. Cauan, RMTMarissa CordovaNo ratings yet
- Wound Dressing Cesarean SectionDocument7 pagesWound Dressing Cesarean Sectionneo natalNo ratings yet
- Biopsy: Mahendraraj, M.T 110020599Document39 pagesBiopsy: Mahendraraj, M.T 110020599karinarakhmaNo ratings yet
- TinciónDocument23 pagesTinciónedicius líaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory - Viewing Animal and Plant Cell Under The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesLaboratory - Viewing Animal and Plant Cell Under The MicroscopeCortez Faye Nicole L.No ratings yet
- H G M O Y C S: C P T: Ow To Et The Ost Ut of Our Ytologic Ample Ollection and Rocessing EchniquesDocument8 pagesH G M O Y C S: C P T: Ow To Et The Ost Ut of Our Ytologic Ample Ollection and Rocessing EchniquesSusi SulistyowatiNo ratings yet
- Hstcyt1 Lcc1 Short Term NotesDocument33 pagesHstcyt1 Lcc1 Short Term NotesMHEKAELLA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Dehydration - SPC MLS 2K - Histopathology LabDocument6 pagesDehydration - SPC MLS 2K - Histopathology LabMaster ChiefNo ratings yet
- Nature of Analytical ChemistryDocument3 pagesNature of Analytical ChemistryMaster ChiefNo ratings yet
- Chemical StoichiometryDocument2 pagesChemical StoichiometryMaster ChiefNo ratings yet
- P2.1 Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocument1 pageP2.1 Introduction To Analytical ChemistryMaster ChiefNo ratings yet
- Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry Chapter 3Document5 pagesCalculations Used in Analytical Chemistry Chapter 3Master ChiefNo ratings yet
- Buffer SolutionsDocument5 pagesBuffer SolutionsMaster ChiefNo ratings yet