Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heart Histology
Uploaded by
Carlotta ranalliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heart Histology
Uploaded by
Carlotta ranalliCopyright:
Available Formats
CELLS
NARROWER & SHORT
10-100 micrometri in diameter
80-100 micrometri in length
heart
LOCATIONS pulmonary veins
superior & inferior vena cava
DIFFERENZE SCHELETRICO-CARDIACO
FIBERS linear BRANCHES of several cardiac muscle cells STRIATIONS
CARDIAC FUNCTION IS LOST IN THE SITE OF
DEATH OF CELLS
INJURY STRUCTURE
INJURY AND REPAIR
released 3-12h after the MI REPLACEMENT OF FIBROUS
TnI and TnT in the blood markers NONFATAL MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION (MI) this pattern is see in
remain in the blood up to 2 week CONNECTIVE TISSUE SUBENDOCARDIAL
CONNECTIVE TISSUE COMPONENTS ENDOMYSIUM
SUBPERICARDIAL
MATURE CARDIAC CELLS ARE ABLE TO single & central
just 0.1%
DIVIDE
BICONIC REGION MYOFIBRILS OF C.M SEPARATE TO PASS AROUNT THE NUCLEUS
to recapture enerhy
INCREASE FREQUENCY OF IMPULSES ACCELERATES THE HEARTBEAT SYMPATHETIC PARASYMPATHETIC AND SYMPATHETIC NUCLEUS
both terminate in the NODES MITHOCONDRIA posses closely packed CRISTAE
DECREASE FREQUENCY OF IMPULSES DECELERATE THE HEARTBEAT PARASYMPTHETIC SYSTEM
AUTONOMOUS NERVOUS SYSTEM INNERVATION often full length of asarcomere
FREQUENCY
just modify CANNOT INITIATE THE CONTRACTION GLYCOGEN GRANULES store energy
STRENGTH
GOLGI APPARATUS
juxtanuclear space 0.3-0.4 micrometri of diameter
CELL MEM DEPOLARIZATION REACHES
ten arrive at CARDIAC MYOCYTES 1 enrich in organelles
PURKINJE FIBERS ATRIAL NATRIURETIC FACTOR (ANF/
CONTRACTION CARDIAC MUSCLE L.NATRIUM SODIUM)
OPENING of Na+ channels and INFLUX of Na+ 2 types
BRAIN NATRIURETIC FACTOR (BNF) in congestive heart failure, increase its level
LONG-LASTING DEPOLARIZATION of t- LIPOFUSCIN PIGMENTS GRANULES in the ATRIA ATRIAL GRANULES
200 microsec of delay 3
tubules contains 2 polypetide hormones what diuretic affecting urinary excretion of Na+
SLOW CONF.CHANGE of DHSR into functional inhibit renin secretion by the kidney and
4 aldosterone secretion by adrenal gland
Ca2+ channels function
inhibit contraction of vascular smoot muscle
CALCIUM-TRIGGERED CALCIUM
RELEASE MECHANISM (aka calcium formation of DIAD
induce, calcium release/ CICR PENETRATE INTO MYOFILAMENTS
mecchanism) BUNDLES at the level of the Z-line in skeletal the triad is at the A-I junction
5 SMALLER TERMINAL CISTERNAE than skeletal muscle
in the sER
PASSAGE OF Ca2+ from te lumen
T-TUBULES 1 x SARCOMERE
RISE in cytoplasmic Ca2+ of t-tubules to te sarcoplasm is both are btw LARGER than T-TUBULES of
essential to start the contraction LARGER and MORE in CARDIAC VENTRICULAR SKELETAL MUSCLE
opening of RYR2 gated-release cannels MUSCLE
Ca2+ released from the sER and increase the pool SMALLER and LESS in CARDIAC ATRIAL
6
of Ca2+ in the cytoplasm MUSCLE
Events similar to the skeletal muscle 7
JUNCTION btw CARDIAC CELLS
CROSS at 90° the MYOFIBERS
VISIBLE TRANSVERSE COMPONENTS
have less or no T-TUBULES like risers of the stairs
LARGER than cardiac muscle cells characteristics CROSS PERPENDICULARLY the transverse
STEP-LIKE FASHION 2 parts analysis with TEM
MYOFIBRILS are located PERIPHERICALLY components
characteristics PURKINJE FIBERS NON-VISIBLE LATERAL COMPONENTS
NUCLEI are ROUND and LARGER than CROSS PARALELLY the MYOFIBERS
they nuclei of cardiac muscle like steps of the stairs
CYTOPLASM stains poorly due to the RICH just TRANSVERSE COMPONENTS
in the dehydratation step shrink away during te biopsy preparation
AMOUNT OF GLYCOGEN where
responsable x staining in H&E of transverse
hold cardiac cells to the end to form functional
cardiac fibers
SINGLE NETWORK FASCIA ADHERENTES/ ADHHERING
why transverse boundaries btw cardiac cells
EXTENDING FROM Z LINE TO Z LINE characteristics JUNCTION
CELL-TO-CELL CONNECTION site of attachment of thin filament of
LESS WELL ORGANIZED
terminal sarcomere onto te plasma mem
it does not separate bundles of myofilaments into sER
function space filled with material similar to the zonula
discrete myofibrils characteristics
adherent of epithelium
the external lamina adheres the invaginated containing
penetrate in the cytoplasm of muscle cells both LATERAL and TRANSVERSE
plasma mem of T TUBULE
where COMPONENTS
INTERCALATED DISCS
bind individual muscle cells to one other
MACULA ADHERENTES/ DESMOSOMES
renforce the fascia adherent
why prevent the cells from pulling apart under the strain
of regular repetive contraction
the position is functional to allow their protection
where just LATERAL COMPONENTS
during contraction
GAP JUNCTION
allow to behave as a FUNCTIONAL # FROM STRUCTURAL SYNCHITIUM OF
why IONIC CONTINUITY cell to cell passage pf macromolecules
SYNCHITIUM SKELETAL MUSCLE
You might also like
- W 00 ADocument1 pageW 00 ADHANAPALNo ratings yet
- 30x20 Title Block ReferenceDocument1 page30x20 Title Block ReferencelyzersehjNo ratings yet
- Structural 1Document9 pagesStructural 1manglicmotabigail11No ratings yet
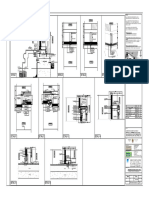
- Anatomy HeartDocument1 pageAnatomy HeartCarlotta ranalliNo ratings yet
- Boundary Wall DetailsDocument2 pagesBoundary Wall DetailsSuha ModakNo ratings yet
- 1.detail One (Black-White)Document1 page1.detail One (Black-White)maxNo ratings yet
- Front Side Guard Room Front Side Guard Room Front Side Guard RoomDocument1 pageFront Side Guard Room Front Side Guard Room Front Side Guard RoomLalitBagoriaNo ratings yet
- Jetstream Brochure EUDocument2 pagesJetstream Brochure EUBruno ZanuttiniNo ratings yet
- S-3.0 3723 Noah ST - Lot 1 - Windstorm Ties & NotesDocument1 pageS-3.0 3723 Noah ST - Lot 1 - Windstorm Ties & NotesTAIQ MASROORNo ratings yet
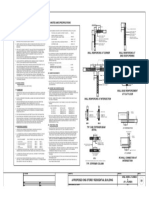
- Load Bearing Wall On Slab: Detail 03Document1 pageLoad Bearing Wall On Slab: Detail 03Anthonio MaraghNo ratings yet
- AB-036914 - Support Details of Nozzle & Manways For Castable - SAUDI ARAMCODocument1 pageAB-036914 - Support Details of Nozzle & Manways For Castable - SAUDI ARAMCOAkhil GeorgeNo ratings yet
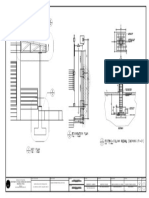
- Handrail DetailsDocument2 pagesHandrail DetailsVivianNo ratings yet
- Notes:-A: D R 20 KN/M Ø 30° &Document2 pagesNotes:-A: D R 20 KN/M Ø 30° &PavanNo ratings yet
- GW 02 Elevation &detailsDocument1 pageGW 02 Elevation &detailsMiteshSuneriyaNo ratings yet
- 950G Series II and 962G Series II Electrical System IT62G Series II Integrated Toolcarrier Wheel LoaderDocument4 pages950G Series II and 962G Series II Electrical System IT62G Series II Integrated Toolcarrier Wheel LoaderHector VallesNo ratings yet
- Avoiding Heart Attacks and Strokes: Don't Be A Victim Protect YourselfDocument48 pagesAvoiding Heart Attacks and Strokes: Don't Be A Victim Protect YourselfkaruturiNo ratings yet
- Uecp-Sd-Cul - 12.1-R00Document3 pagesUecp-Sd-Cul - 12.1-R00Anuradha KoswaththaNo ratings yet
- Welders Range SincroDocument5 pagesWelders Range SincroOPAZOSCNo ratings yet
- Revision History: 10-V-101 Oil Water Separation DrumDocument1 pageRevision History: 10-V-101 Oil Water Separation DrumShyamPanthavoorNo ratings yet
- Revision History: 10-V-101 Oil Water Separation DrumDocument1 pageRevision History: 10-V-101 Oil Water Separation DrumKarwanNo ratings yet
- S1.03 - Structural Symbols and NotationsDocument1 pageS1.03 - Structural Symbols and NotationsMarie Ariadne MurilloNo ratings yet
- Structural Plan 3 StoreyDocument6 pagesStructural Plan 3 StoreyJulie Anne Flores IINo ratings yet
- Kz01-Cv-Lay-14-6010-001 - Master Point 2Document1 pageKz01-Cv-Lay-14-6010-001 - Master Point 2Admin UTSNo ratings yet
- Revised Pargola DetailDocument1 pageRevised Pargola Detailreddi.demullu007No ratings yet
- Shiplift Docking Plan For ICGS VIKRAM - 23032018 (Keel Beam) 1Document2 pagesShiplift Docking Plan For ICGS VIKRAM - 23032018 (Keel Beam) 1Kyaw Win TunNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor GW 07Document1 pageGround Floor GW 07MiteshSuneriyaNo ratings yet
- G 1646 A-5 Stair Section Details May 01 2018Document1 pageG 1646 A-5 Stair Section Details May 01 2018autocadplease6213No ratings yet
- 3000 StationsDocument79 pages3000 Stationsahong100No ratings yet
- American March Pump 460 ODSDocument24 pagesAmerican March Pump 460 ODSjuan davidNo ratings yet
- C&C FoldupChrSheet Final1 - 51Document2 pagesC&C FoldupChrSheet Final1 - 51dox348361No ratings yet
- Septic Tank Details: General NotesDocument1 pageSeptic Tank Details: General NotesRycca DeeNo ratings yet
- BLDG PlanDocument1 pageBLDG PlanMax BenizaNo ratings yet
- Tolea Poster01Document1 pageTolea Poster01jbrusselNo ratings yet
- Clean-Out Detail Air Chamber Detail: General NotesDocument1 pageClean-Out Detail Air Chamber Detail: General NotesJem CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Plan A: Department of Public Works and Highways Regional Office 4 S100.0Document1 pagePlan A: Department of Public Works and Highways Regional Office 4 S100.0Adrian PachecoNo ratings yet
- P1926 (E1) 1 001Document1 pageP1926 (E1) 1 001Se Jin CoohNo ratings yet
- Ewan Engineering Consultancy: Engineered/Contractor To Verify and Submit Calculation For The Approval of EngineersDocument1 pageEwan Engineering Consultancy: Engineered/Contractor To Verify and Submit Calculation For The Approval of EngineersAbid AyubNo ratings yet
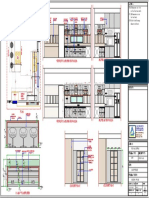
- A1.1 - Floor Plan and Elevations Rev.0 MarkupDocument1 pageA1.1 - Floor Plan and Elevations Rev.0 MarkupAstria Elena Lopez AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Plano Electrico 420E Pra0917Document4 pagesPlano Electrico 420E Pra0917Luis Gustavo Escobar Machado0% (1)
- Garage Electical Plan Smoke Alarm Notes:: WH AC Bedroom 1Document1 pageGarage Electical Plan Smoke Alarm Notes:: WH AC Bedroom 1IamJace C.No ratings yet
- Sapang E1Document1 pageSapang E1Christian - Ian FarnacioNo ratings yet
- A Proposed One-Storey Residential Building S1Document1 pageA Proposed One-Storey Residential Building S1Jezreel FlotildeNo ratings yet
- Detalle - Cubierta Verde - KarolDocument1 pageDetalle - Cubierta Verde - KarolKAROL DAYANA GONZALEZ MAYORGANo ratings yet
- Kitchen DrawingDocument1 pageKitchen DrawingAMAZE INTERIORNo ratings yet
- DB 000 13302 0301 001 01 Member List For Module Steel StructureDocument1 pageDB 000 13302 0301 001 01 Member List For Module Steel StructurekohilanrkNo ratings yet
- CB3 Me-13Document1 pageCB3 Me-13J-R MERLIN CabatoNo ratings yet
- Corbel Reinforcement Detail 'X': Reinforcement Details of Approach SlabDocument1 pageCorbel Reinforcement Detail 'X': Reinforcement Details of Approach SlabTari IslamNo ratings yet
- Tier-I Metro: Produced by An Autodesk Educational ProductDocument1 pageTier-I Metro: Produced by An Autodesk Educational Productbhaseen photostateNo ratings yet
- Water Installations Code CS-CSI-P1/C2 Water Installations Code CS-CSI-P1/C2Document2 pagesWater Installations Code CS-CSI-P1/C2 Water Installations Code CS-CSI-P1/C2NAHEEMA KPNo ratings yet
- Location Plan: Perimeter Fence DetailsDocument1 pageLocation Plan: Perimeter Fence DetailsLucio AdaNo ratings yet
- 772B Tractor & 773B Truck Electrical System: Machine Harness Connector and Component LocationsDocument2 pages772B Tractor & 773B Truck Electrical System: Machine Harness Connector and Component LocationsjesusNo ratings yet
- General Notes: Legend & Symbols:: Schedule of Loads: Pp1Document1 pageGeneral Notes: Legend & Symbols:: Schedule of Loads: Pp1ven villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall Notes:: Fin. Flr. 0'-0" A.F.FDocument1 pageShear Wall Notes:: Fin. Flr. 0'-0" A.F.FIamJace C.No ratings yet
- Split Type Air Conditioning Units ScheduleDocument1 pageSplit Type Air Conditioning Units ScheduleMahmoud ElturkyNo ratings yet
- Circuit Map V12Document1 pageCircuit Map V12Senseu MasterNo ratings yet
- Wf-1 Detail: Foundation PlanDocument1 pageWf-1 Detail: Foundation PlanJezzrel SumalinogNo ratings yet
- HTTPS://WWW - scribd.com/document/342895369/NAM PHAN 05 06 14 KvsDocument1 pageHTTPS://WWW - scribd.com/document/342895369/NAM PHAN 05 06 14 KvsKhủng Long ConNo ratings yet
- Curtain WallDocument1 pageCurtain WallKalyani sonekarNo ratings yet
- USITT 07 Lighting Plot Standards PDFDocument1 pageUSITT 07 Lighting Plot Standards PDFBenji ArrigoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry II End of Semester Exam QuestionsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry II End of Semester Exam Questionsnima00No ratings yet
- Tissues MCQDocument9 pagesTissues MCQtraptisharma3342No ratings yet
- Use of The Program Module To Analyse RDCDocument3 pagesUse of The Program Module To Analyse RDCRigel_TNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper2Document28 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper2Alexis OkosunNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Course Notes PDFDocument131 pagesExercise Physiology Course Notes PDFPRAJINIKUMARNo ratings yet
- ImmunochemistryDocument44 pagesImmunochemistryJowe VarnalNo ratings yet
- Expert MdcatDocument4 pagesExpert Mdcathely shahNo ratings yet
- Passive Transport - Virtual LabDocument27 pagesPassive Transport - Virtual LabHalleli CastilloNo ratings yet
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument3 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsLux Sanchez DarlyNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Cell Transport - Lesson - Review - WorkbookDocument4 pages7.3 Cell Transport - Lesson - Review - WorkbookSsslayny 26100% (1)
- Biomimetic Liposomes Hybrid With ErDocument8 pagesBiomimetic Liposomes Hybrid With Erash0406No ratings yet
- The Effect of Ascorbic Acid On The Nature and Production of Collagen andDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Ascorbic Acid On The Nature and Production of Collagen andfgonzalezNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Microbiology 1st Edition Wessner Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Microbiology 1st Edition Wessner Solutions Manual PDFyoreoakling.9vtk0y100% (8)
- 1.analyses of Chemical Components and Their Functions in Single Species Plant-Derived Exosome Like VesicleDocument11 pages1.analyses of Chemical Components and Their Functions in Single Species Plant-Derived Exosome Like Vesiclesnow silverNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular BiologyDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Molecular BiologyAbbinaya100% (9)
- Media File 4: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMedia File 4: PathophysiologyhazeeeNo ratings yet
- Structure of Cell - Dakha BDocument19 pagesStructure of Cell - Dakha Bapi-3731257No ratings yet
- B Vitamins 1Document1 pageB Vitamins 1api-245692797No ratings yet
- Receptors: Types Structure FunctionsDocument44 pagesReceptors: Types Structure Functionsmaham1085No ratings yet
- 71 - WigginsBen STEM Exams Can Be Inspiring and Challenging NOTESPDF (ASU Remote) v1Document14 pages71 - WigginsBen STEM Exams Can Be Inspiring and Challenging NOTESPDF (ASU Remote) v1Alicia AbundisNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesCell The Unit of LifeSREE GANESHNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Histology - Fawcett, Don W. (Don Wayne), 19Document1,048 pagesTextbook of Histology - Fawcett, Don W. (Don Wayne), 19Heinz Mae PadillaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis IIDocument36 pagesSodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis IIYUEALVIN17No ratings yet
- Transcription Errors in Aging and DiseaseDocument8 pagesTranscription Errors in Aging and DiseaseIngri CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Virtual Cell WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Virtual Cell WorksheetRafael CunetaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes VS EukaryotesGamu GamuNo ratings yet
- Applications of DiffusionDocument2 pagesApplications of DiffusionAmelia LimNo ratings yet
- Gene Families of Plants Plant BiotechnoloDocument26 pagesGene Families of Plants Plant BiotechnoloNiniva GhoshNo ratings yet
- 5384 PDFDocument5 pages5384 PDFAngeline AguyenNo ratings yet
- Organisation of The Organism 3 MSDocument6 pagesOrganisation of The Organism 3 MSJ.Chang ChangNo ratings yet