0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views26 pagesMachine Tool-I
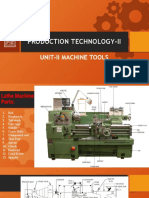
This document provides an overview of machine tools and lathe machines. It defines machining and machine tools, describing that machine tools use cutting tools to shape metal and rigid materials. It then classifies machine tools based on their purpose, motion type, automation, and energy used. The document focuses on lathe machines, defining them as rotating the workpiece while a fixed cutting tool shapes it. It describes the main parts of a lathe and different lathe types like engine, bench, and special purpose lathes. Finally, it lists important lathe specifications like swing diameter, spindle speeds, and machine dimensions and capabilities.
Uploaded by
Aman ModanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views26 pagesMachine Tool-I
This document provides an overview of machine tools and lathe machines. It defines machining and machine tools, describing that machine tools use cutting tools to shape metal and rigid materials. It then classifies machine tools based on their purpose, motion type, automation, and energy used. The document focuses on lathe machines, defining them as rotating the workpiece while a fixed cutting tool shapes it. It describes the main parts of a lathe and different lathe types like engine, bench, and special purpose lathes. Finally, it lists important lathe specifications like swing diameter, spindle speeds, and machine dimensions and capabilities.
Uploaded by
Aman ModanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd