Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reporttttt
Uploaded by
MILDRED VALEROS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesThe audio-lingual method is a language teaching technique that focuses on oral skills through repetition and memorization of dialogues. It was influenced by Leonard Bloomfield's techniques, the need for language training during WWII, and B.F. Skinner's behaviorism theories. Teachers use drills, substitution exercises, and dialogues to guide students' linguistic behavior while students practice pronunciation and respond quickly. While it helped improve oral skills, critics argued it placed too much emphasis on memorization and drills over understanding language.
Original Description:
Original Title
reporttttt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe audio-lingual method is a language teaching technique that focuses on oral skills through repetition and memorization of dialogues. It was influenced by Leonard Bloomfield's techniques, the need for language training during WWII, and B.F. Skinner's behaviorism theories. Teachers use drills, substitution exercises, and dialogues to guide students' linguistic behavior while students practice pronunciation and respond quickly. While it helped improve oral skills, critics argued it placed too much emphasis on memorization and drills over understanding language.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesReporttttt
Uploaded by
MILDRED VALEROSThe audio-lingual method is a language teaching technique that focuses on oral skills through repetition and memorization of dialogues. It was influenced by Leonard Bloomfield's techniques, the need for language training during WWII, and B.F. Skinner's behaviorism theories. Teachers use drills, substitution exercises, and dialogues to guide students' linguistic behavior while students practice pronunciation and respond quickly. While it helped improve oral skills, critics argued it placed too much emphasis on memorization and drills over understanding language.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Audio-Lingual Method
Reporter: Ivy Angel M. Valeros
Proponents: Charles Fries and Robert Lado
Background: The development of the audio-lingual technique was influenced by three crucial
historical events. First, Leonard Bloomfield's technique of memorizing and repetition centered
on this method, and it was the initial step in proposing the ALM.
The second situation occurred when World War II outbreak which urgently required the United
States to produce a group of orally fluent speakers of different languages. The linguist watched
the learning process while the instructor provided a languages source for mimicry.
B.F. Skinner’ behaviorism theory was the third component. In his imitation, repetition, and
positive or negative reinforcement theories for language learning. The main goal of the audio-
lingual method is to teach oral skills with accurate pronunciation, grammar, and the ability to
respond quickly and accurately.
Introduction: Audio-lingual is basically a method of language teaching that focuses on speaking
and listening. As the primary method of language presentation, it makes use of drills and
dialogues.
Discussion: The audio-lingual method is a verbal method for teaching language to pupils. The
audio-lingual approach emphasizes spoken language over students' native tongues in the
classroom. The primary method of teaching languages is through dialogues, with a focus on
specific practice methods including imitation, memorization, and pattern drills.
The teacher's role in the audio-lingual approach is in charge of guiding and managing students'
linguistic behavior. On the other hand, it is the responsibility of the pupils to follow the teacher's
instructions and react as correctly as quickly as they can. Better pronunciation and better
involvement as a result of the drilling activities are the benefits of this. However, some felt that
the approach had a weakness: It placed too much focus on the teacher, who was only able to
discuss the basic aspects of language.
In using the audio-lingual method in the classroom, every phrase of the dialog would be first
read out by the teacher or presented with a recording. Students read the dialogue aloud in chorus,
repeating each phrase over and over until they remember that this activity is based on the
dialogue. This other activity allows pupils to change the dialogue without changing the
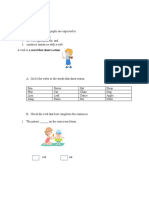
grammatical structure by using substitution drills. For example, I draw a rainbow, is a dialogue
statement that the teacher delivers. She then provides a prompt by mentioning clouds or by
flashing a cloud-related image. I draw clouds, should be the students' response. An option for
different alternatives that the teachers may use to expand pupils' vocabulary is the audio-lingual
method. This can assist pupils in developing their vocabularies in English-language content.
Strategies:
First, it focuses on practical pronunciation. Because the audio-lingual technique is focused on
language structure, the sounds of language are automatically considered to be crucial foundations
to produce words, that is, meaningful sequences of sounds. Regardless quantity of sounds the
language you teach uses, you must first know what they are, how they are formed, and how they
interact together to form phrases.
Second, engage structural drilling exercises. Since drilling is a valid and helpful method for
building strength and agility, you might wish to refer to this exercise as sentence practice. For
instance:
Teacher: I eat apple every day. She.
Students: She eats apple every day.
Teacher: She eats apple every day. They.
Students: They eat apple every day.
Third, is to employ dialogue practice, dialogue is the exchange of information among a group of
people. It is also a strategy for language production, from sound to phrase. Daily conversations
are most likely the most well-known relics of the original audio-lingual method. For example:
Buyer: Good morning.
Vendor: Hello.
Buyer: How much are the bananas?
Vendor: 70 pesos per kilo.
Buyer: Oh! That’s cheap! I’ll take two kilos.
Vendor: Good. That will be 210 pesos.
Buyer: Here you are.
Vendor: And here’s your change. Thank you.
Buyer: Thank you!
Vendor: Goodbye.
Buyer: Goodbye.
You might also like
- Audiolingual Method Background:: System of SignsDocument12 pagesAudiolingual Method Background:: System of SignsMelisa ParodiNo ratings yet
- Why Trust Your IntuitionDocument6 pagesWhy Trust Your IntuitionitachiiNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan Day I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan Day I. ObjectivesAbigail GoloNo ratings yet
- 5.Audio-Lingual Method. ApproachDocument4 pages5.Audio-Lingual Method. Approachgunay100% (1)
- Approaches and Methods of Teaching Foreign Language (EFL)Document6 pagesApproaches and Methods of Teaching Foreign Language (EFL)Choco DogNo ratings yet
- Communicative MethodsDocument5 pagesCommunicative MethodsDunas SvetlanaNo ratings yet
- 1800 Professional Education Practice DrillsDocument254 pages1800 Professional Education Practice DrillsHanna KhababNo ratings yet
- DLP-DEMO-closing RemarksDocument3 pagesDLP-DEMO-closing RemarksKelvin DecapiaNo ratings yet
- Teaching ListeningDocument26 pagesTeaching ListeningPolly AnnaNo ratings yet
- Teaching English to Speakers of Other LanguagesFrom EverandTeaching English to Speakers of Other LanguagesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Audio Lingual MethodDocument12 pagesAudio Lingual MethodMilton Martinez88% (8)
- Probability Lesson LogDocument5 pagesProbability Lesson LogJULIET AÑESNo ratings yet
- LK. 1.2 Eksplorasi Penyebab MasalahDocument6 pagesLK. 1.2 Eksplorasi Penyebab MasalahDesi MandasariNo ratings yet
- Audio-Lingual Method (Assignment)Document13 pagesAudio-Lingual Method (Assignment)Lisa Kwan100% (12)
- Approaches and Methods in Language TeachingDocument12 pagesApproaches and Methods in Language TeachingDushyant Nimavat100% (1)
- Guided Reading and Writing Lesson Plan ECS 580 Week 3Document6 pagesGuided Reading and Writing Lesson Plan ECS 580 Week 3Jacqueline MedinaNo ratings yet
- Audio-Lingual Method: Fitri Surya RahayuDocument4 pagesAudio-Lingual Method: Fitri Surya RahayuFitri Surya RahayuNo ratings yet
- The Practice of English Language Teaching (Chapter 4)Document4 pagesThe Practice of English Language Teaching (Chapter 4)katiaNo ratings yet
- Describing Language and TeachingDocument8 pagesDescribing Language and TeachingDobreanu SoranaNo ratings yet
- ALM-7Document3 pagesALM-7AhlemNo ratings yet
- ALM by Hajer and OualaDocument3 pagesALM by Hajer and OualaOuala MaafaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document9 pagesTopic 1Ainhoa Sempere IlazarriNo ratings yet
- Methods Approaches EflDocument29 pagesMethods Approaches Eflapi-317394066100% (1)
- C) Research Study Q3. With Reference To The Following Framework, Enumerate With Examples The Application of MethodologiesDocument6 pagesC) Research Study Q3. With Reference To The Following Framework, Enumerate With Examples The Application of MethodologiesNidhi MathurNo ratings yet
- Background and Characteristics of The AudioDocument6 pagesBackground and Characteristics of The AudioRika NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Style Audio Lingual Methods For Students With Special NeedsDocument6 pagesTeaching Style Audio Lingual Methods For Students With Special NeedsHani NovitasariNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction: Pre-Chapter QuestionsDocument3 pagesUnit 1: Introduction: Pre-Chapter QuestionsFranco KaaminoNo ratings yet
- Audio Lingual MethodDocument9 pagesAudio Lingual MethodGillaniNo ratings yet
- Man Aol 1Document5 pagesMan Aol 1cabuliwallahNo ratings yet
- Understanding T-WPS OfficeDocument9 pagesUnderstanding T-WPS OfficeEn RaniNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology1Document10 pagesResearch Methodology1Sara Kamal0% (1)
- Comments On The Audiolingual Method: Yang MeiDocument7 pagesComments On The Audiolingual Method: Yang MeiNurul RahmayaniNo ratings yet
- ALM Method Prioritizes Spoken SkillsDocument32 pagesALM Method Prioritizes Spoken SkillsMd SarroarNo ratings yet
- The Audio Lingual MethodDocument4 pagesThe Audio Lingual MethodVivian FernándezNo ratings yet
- TEFL Methodology DevelopmentDocument10 pagesTEFL Methodology DevelopmentHanoveraNo ratings yet
- Audiolingual MethodDocument13 pagesAudiolingual MethodJuli MerloNo ratings yet
- ALMDocument5 pagesALMFatin Nabihah RosliNo ratings yet
- Resume Tefl 1Document7 pagesResume Tefl 1Arin Dwi OktarindaNo ratings yet
- The Birth of The AudiolingualDocument3 pagesThe Birth of The AudiolingualWarda KhanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledELI KUSUMANo ratings yet
- Audiolingual Method AND Silent Way MethodDocument12 pagesAudiolingual Method AND Silent Way MethodRiani pohanNo ratings yet
- طرائق م ثالثهDocument8 pagesطرائق م ثالثهمظفر منعم ميران عباسNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal (FB)Document10 pagesResearch Proposal (FB)2157011177No ratings yet
- Teaching Oral Skills (Introduction)Document4 pagesTeaching Oral Skills (Introduction)Justine PalmaNo ratings yet
- Teaching English as a Second Language ApproachesDocument37 pagesTeaching English as a Second Language ApproachesPawan DhimanNo ratings yet
- 1401-Article Text-3637-1-10-20170517Document16 pages1401-Article Text-3637-1-10-20170517thwegraceNo ratings yet
- Describing Learning and TeachingDocument6 pagesDescribing Learning and TeachingSMK IT YASIN OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Method in English TeachingDocument31 pagesMethod in English TeachingStefani SiduppaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 (Teaching Speaking Using Short Story)Document13 pagesChapter2 (Teaching Speaking Using Short Story)Sayyidah BalqiesNo ratings yet
- Audio-Lingual Approach: Submitted By: Ortiz, Katerine A. Submitted To: Dr. Cecilia SaenzDocument5 pagesAudio-Lingual Approach: Submitted By: Ortiz, Katerine A. Submitted To: Dr. Cecilia SaenzKathy'totszki OrtizNo ratings yet
- 2017 Introduction To T.methodsDocument10 pages2017 Introduction To T.methodsVy TrầnNo ratings yet
- Selected ELT Methods Selected ELT MethodDocument5 pagesSelected ELT Methods Selected ELT MethodDiana Morilla AznaNo ratings yet
- The Direct Method BA 3rdDocument39 pagesThe Direct Method BA 3rdMan Bdr JoraNo ratings yet
- El Poder Del Pensamiento PositivoDocument8 pagesEl Poder Del Pensamiento PositivoWilliam Jurado VallejoNo ratings yet
- Direct Method Teaches English Through ImmersionDocument34 pagesDirect Method Teaches English Through ImmersioniLoveMarshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 PDFIrish BiatoNo ratings yet
- Imanul Buqhariah AlmDocument4 pagesImanul Buqhariah AlmImam BuqhariNo ratings yet
- English Language Teaching MethodDocument8 pagesEnglish Language Teaching MethodNadia Novernia Cristy KatuukNo ratings yet
- Topic AnalysisDocument4 pagesTopic AnalysisJade Dagondon BajaNo ratings yet
- Basic Classification of MethodsDocument5 pagesBasic Classification of MethodsсевинджNo ratings yet
- Oscar Alfredo Torres Apa Audiolingual MethodDocument10 pagesOscar Alfredo Torres Apa Audiolingual Methodoscar-30No ratings yet
- Audio-lingual method explainedDocument9 pagesAudio-lingual method explainedToqeer TumraniNo ratings yet
- Innovative Strategies For Language TeachingDocument32 pagesInnovative Strategies For Language TeachingMarissa UrnosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches MethodsDocument7 pagesTeaching Approaches MethodsCarlos VeraNo ratings yet
- Defferent ApproachesDocument8 pagesDefferent ApproachesElenaNo ratings yet
- Direct Method: ExampleDocument2 pagesDirect Method: ExampleMaite Ruiz Liza100% (1)
- XeddyDocument3 pagesXeddyMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- GE 07 Prelims To FinalsDocument56 pagesGE 07 Prelims To FinalsMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- History of GuidanceDocument6 pagesHistory of GuidanceMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- Lateness QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesLateness QuestionnaireMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Common Genre of EnglishDocument8 pagesCharacteristics and Common Genre of EnglishMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- Authors Matrix 2Document28 pagesAuthors Matrix 2MILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document2 pagesModule 3MILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument1 pageECOSYSTEMMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- DLL Quarter 3 WK 5 Lita VinzonDocument48 pagesDLL Quarter 3 WK 5 Lita VinzonMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- You SentDocument2 pagesYou SentMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- Mtah IntermediateDocument15 pagesMtah IntermediateMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Homeroom GuidanceDocument1 pageBenefits of Homeroom GuidanceMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument4 pagesVerbsMILDRED VALEROSNo ratings yet
- Statements of Inquiry in Physical and HealthDocument3 pagesStatements of Inquiry in Physical and HealthMillitiaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To CLILDocument5 pagesAn Introduction To CLILtonyNo ratings yet
- Using Tech Form 3Document11 pagesUsing Tech Form 3api-662490478No ratings yet
- 2 Entrepreneurial Mindset Part 2Document22 pages2 Entrepreneurial Mindset Part 2ATIENZA, CARYLLE JUSTINE B.No ratings yet
- 0.testing Introducation QH2021.D2Document10 pages0.testing Introducation QH2021.D2Nguyễn Minh Đức LêNo ratings yet
- Developing Lessons Using Bloom's TaxonomyDocument9 pagesDeveloping Lessons Using Bloom's TaxonomyDOMGIE LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Case Study of A Child Age 10Document22 pagesCase Study of A Child Age 10api-610745533No ratings yet
- Malutao - Output 1 Self Assessment of Interests and TalentsDocument3 pagesMalutao - Output 1 Self Assessment of Interests and TalentshaxadNo ratings yet
- Bloomfield's Contribution To LinguisticsDocument2 pagesBloomfield's Contribution To LinguisticsAsha MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter II - RRL WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesChapter II - RRL WPS Officelucille otanesNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Secondary Students' Listening ComprehensionDocument5 pagesEnhancing Secondary Students' Listening ComprehensionLIWANAGAN MARYJOICENo ratings yet
- Assessment Learning 2Document6 pagesAssessment Learning 2Karen Faith BedasuaNo ratings yet
- Literature Revie22Document6 pagesLiterature Revie22Antony OgemboNo ratings yet
- G8 READING Feb2 - Teaching Guide MAKATO AND COWRIE SHELLDocument3 pagesG8 READING Feb2 - Teaching Guide MAKATO AND COWRIE SHELLzyra rose leachonNo ratings yet
- Life Skills Module 1.2 FinalDocument20 pagesLife Skills Module 1.2 Finaljayanth62005No ratings yet
- Critical and Creative Thinking RelationshipDocument17 pagesCritical and Creative Thinking RelationshipAchmad Zultan MansurNo ratings yet
- 22 Supremely Powerful Tips For Highly Impressive Communication SkillsDocument7 pages22 Supremely Powerful Tips For Highly Impressive Communication SkillsGurusreenuNo ratings yet
- USW1 EDUC 3056 Elementary Education Lesson Plan TemplateDocument6 pagesUSW1 EDUC 3056 Elementary Education Lesson Plan TemplateRoopa NatarajNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping Technique ExplainedDocument5 pagesMind Mapping Technique Explainedviraaj pawarNo ratings yet
- DOSSIERDocument21 pagesDOSSIERMARÍA IGNACIANo ratings yet
- Reading Program SPARK ElemDocument4 pagesReading Program SPARK ElemJOANE PACATANGNo ratings yet
- 5 Main Reasons Why Education Is So ImportantDocument2 pages5 Main Reasons Why Education Is So ImportantМарія ДанильченкоNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension What WorksDocument8 pagesReading Comprehension What WorksDanielle BarettaNo ratings yet