Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summative Test in Grade 9 Science
Uploaded by
Apolonio Pamittan Jr.Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Summative Test in Grade 9 Science
Uploaded by
Apolonio Pamittan Jr.Copyright:
Available Formats
Summative Test in Grade 9 Science
Name: _________________________________________ Grade and Section: __________________ Score: _____
1. If a freely falling ball is somehow equipped with a speedometer, by how much would its speed-reading increase
for every second?
a. 0 m/s b. 9.8 m/s c. 10 m/s d. 20 m/s
2. A sepak takraw ball is hit vertically by a player. What is its acceleration after 1 second?
a. O b. 1 m/s2 c. 9 m/s2 d. -9 m/s2
3. A volleyball is tossed vertically upward, with an initial velocity of 5 m/s and caught back at the same level as
when it was thrown. What is the velocity of the ball at that point?
a. O m/s b. -5 m/s c. -9 m/s d. d. -9 m/s2
4. The motion of an object with constant acceleration is also known as
a. Motion b. uniform motion c. constant motion d. uniformly accelerated motion
5. A ball is thrown vertically upward. What is its instantaneous speed at its maximum height?
a. 0 b. 5 m/s c. 9.8 m/s d. -9.8 m/s
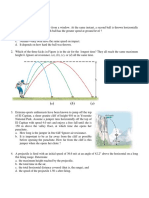
6. It is a combination of uniform horizontal motion and free fall.
a. Trajectory b. Range c. Projectile motion d. Height
7. It is the vertical distance traveled by a projectile.
a. Range b. Trajectory c. Projectile motion d. Height
For items 8-13 refer on the table below
8. If a water hose is aimed in order for the water to land with the greatest horizontal range, the angle of projection
should be
a. 0° b. 30° c. 45° d. 60°
9. If a water hose is aimed in order for the water to land with the greatest horizontal range, the angle of projection
should be
a. 0° b. 30° c. 45° d. 60°
10. When do we get maximum range in a simple projectile motion?
a. When θ = 45° b. When θ = 60° c. When θ = 90° d. When θ = 0°
11. When do we get maximum height in a simple projectile motion?
a. When θ = 45° b. When θ = 60° c. When θ = 90° d. When θ = 0°
12. At what angle of projectile (θ) is the horizontal range minimum?
a. . θ = 45° b. θ = 60° c. θ = 90° d. θ = 75°
13. Which two angles will produce the same range?
a. 35° and 65° b. 30° and 60° c. 45° and 15° d. 40° and 60°
14. A stand holds two white balls. At the same instant one ball is dropped straight down; the other ball is shot
straight out. Which ball will hit the ground first? (Neglect Air resistance)
a. the dropped ball b. the shot ball c. both d. none of the above
15. Which has more momentum, a heavy truck moving at 30 km/h or a light truck moving at 30 km/h?
a. heavy truck b. light truck c. both has the same momentum d. cannot be determined.
*For questions 16 and 17, refer to the data below:
16. In the table above, what is the momentum of the jeepney?
a. 6,000 kg•m/s b. 40,000 kg•m/s c. 20,000 kg•m/s d. 3,000 kg•m/s
17. Which has lesser momentum, the jeepney or the motorcycle?
a. jeepney b. motorcycle c. both have the same momentum d. cannot be determined
18. Two identical cars are travelling along EDSA. Which of the two cars would have a greater momentum?
a. the slower car b. the faster car c. both have the same momentum d. cannot be easily determined
19. A bus and a car are travelling along EDSA having the same velocity. Which of the two vehicles would have a
greater momentum?
a. the bus b. the car c. both have the same momentum d. cannot be easily determine
20. A 25-kg girl is riding a 5-kg with a velocity of 5 m/s the East. What is the total momentum of a girl and a bike
together?
a. 100 kg•m/s b. 125 kg•m/s c. 150 kg•m/s d. 200 kg•m/s
21. The impulse experienced by a body is equal to the change in its
a. velocity b. kinetic energy c. momentum d. potential energy
22. Which is a necessary condition for the total momentum of a system to be conserved?
a. Kinetic energy must not change. b. No external force is present.
c. An object must be at rest. d. Only the force of gravity acts on the system.
*For numbers 2 and 3: Two 0.5 kg balls approach each other with the same speed of 1.0 m/s.
23. What is the total momentum of the system before collision?
a. 0 b. 0.50 kg m/s c. 1.0 kg m/s d. -1.0 kg m/s
24. If there is no external force acting on the system, what is the total momentum of the system after collision?
a. 0 b. 0.50 kg m/s c. 1.0 kg m/s d. -1.0 kg m/s
25. Two billiard balls approach each other at equal speed. If they collide in a perfectly elastic collision, what would
be their velocities after collision?
a. zero b. same in magnitude and direction
b. c. same in magnitude but opposite in direction D. different in magnitude and opposite in direction
26. A 50-kg astronaut ejects 100 g of gas from his propulsion pistol at a velocity of 50 m/s. What is his resulting
velocity?
a. -0.10 m/s b. -0.50 m/s c. 0 m/s d. -100 m/s
You might also like
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A Practical Study For New Design of Essential OilsDocument17 pagesA Practical Study For New Design of Essential OilsEmmanuel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Assignment 2 - Soichiro HondaDocument7 pagesProject Management Assignment 2 - Soichiro HondaGladwin SamuelNo ratings yet
- Using Impact LX With ReaperDocument8 pagesUsing Impact LX With Reaper算踏空100% (1)
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Integration of SAP Into The Laboratory WorkflowDocument5 pagesIntegration of SAP Into The Laboratory WorkflowgvlaxmipathiNo ratings yet
- Use The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Document4 pagesUse The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Melvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- Physics Exit Exam ReviewDocument13 pagesPhysics Exit Exam ReviewJohn Mark Osias100% (1)
- Technical Documentation Engine Spare Parts CatalogueDocument347 pagesTechnical Documentation Engine Spare Parts CatalogueMateo Suarez Chulian100% (2)
- 4th Periodical Exam in ScienceDocument3 pages4th Periodical Exam in Scienceshermaine geniston50% (2)
- Print: 2Zr-Fe Engine Control Sfi System System DiagramDocument10 pagesPrint: 2Zr-Fe Engine Control Sfi System System DiagramAlfredo MedinaNo ratings yet
- MTA Capital Program 2015-19Document239 pagesMTA Capital Program 2015-19jcm23100% (1)
- NMAT Physics Review: Speed, Velocity, Forces & MoreDocument2 pagesNMAT Physics Review: Speed, Velocity, Forces & MoreEllah Gutierrez100% (1)
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionAlbert Ascher100% (34)
- Aspect Security The Unfortunate Reality of Insecure LibrariesDocument20 pagesAspect Security The Unfortunate Reality of Insecure Libraries99patinoNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 TQDocument9 pagesScience Grade 9 TQLae GadgudeNo ratings yet
- Important Indian Standard Codes: Civil Booster (Civil Ki Goli Publication 9255624029)Document34 pagesImportant Indian Standard Codes: Civil Booster (Civil Ki Goli Publication 9255624029)AKYNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter - Science 9Document7 pages4TH Quarter - Science 9MARIA THERESA TULALINo ratings yet
- 75 Civil Engineering Interview QuestionsDocument2 pages75 Civil Engineering Interview QuestionsZakir AliNo ratings yet
- FANUC Series 0M-D Machining Center ManualDocument406 pagesFANUC Series 0M-D Machining Center Manualcesar_abdd100% (1)
- Unified 4th Quarter Exam SCIENCE 9Document5 pagesUnified 4th Quarter Exam SCIENCE 9Lorraine Calvez Donio50% (2)
- Unit Test in General Physics Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesUnit Test in General Physics Multiple ChoiceDina Mita100% (1)
- Physics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsDocument9 pagesPhysics I Quiz #2 - Kinetic and Potential Energy ProblemsNathaly SosaNo ratings yet
- Law of Cosines: C A + B - 2 - A - B - Cos Law of Sines: A/sina B/sinß C/sin Fluid, Air Drag: FD 1/2CD - Ar - R - VDocument8 pagesLaw of Cosines: C A + B - 2 - A - B - Cos Law of Sines: A/sina B/sinß C/sin Fluid, Air Drag: FD 1/2CD - Ar - R - VrileyNo ratings yet
- SAP HCI DevGuideDocument168 pagesSAP HCI DevGuideSrinivasan SriNo ratings yet
- Code of Practice On Environmental Health (COPEH) 1998Document24 pagesCode of Practice On Environmental Health (COPEH) 1998Trang NgoNo ratings yet
- FINAL EXAMINATION FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCEDocument2 pagesFINAL EXAMINATION FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCEbernadeth m. barajasNo ratings yet
- Sem1 Exam GPDocument3 pagesSem1 Exam GPJumz BoNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Science 9Document3 pages4th Summative Test Science 9odette carzanoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 9-Q4Document6 pagesReviewer in Science 9-Q4katherine bacallaNo ratings yet
- ExIF04 PDFDocument13 pagesExIF04 PDFAB:brilliant thanks alot sir. G4MNo ratings yet
- Test in AdvDocument5 pagesTest in AdvvillarfranciaNo ratings yet
- BES 117 Dynamics FINALS 2ndsem2020 2021Document6 pagesBES 117 Dynamics FINALS 2ndsem2020 2021Rapzkie RapalNo ratings yet
- Vectors PhysicsDocument6 pagesVectors PhysicsFurqan HyderNo ratings yet
- Q4 Summative-1Document4 pagesQ4 Summative-1artNo ratings yet
- Physics 71 1 Long Sample ExamDocument4 pagesPhysics 71 1 Long Sample ExamManna Pinto100% (1)
- Nmat Review Physics 1 (Module 1 Exercise) : DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheDocument3 pagesNmat Review Physics 1 (Module 1 Exercise) : DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheMia0% (1)
- Aviation Physics GC02 ConceptsDocument10 pagesAviation Physics GC02 ConceptsyihesakNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 4th Q - ReviewerDocument1 pageSCIENCE 9 4th Q - ReviewerJonel RuleNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment1Document2 pagesSummative Assessment1Anjhiene Camba40% (5)
- Reviwer in Gen. Physics 1Document4 pagesReviwer in Gen. Physics 1Romero, Ken Angelo B.No ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter TestDocument2 pages4TH Quarter TestCathyNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1 TEST IDocument12 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1 TEST Izamora pegafiNo ratings yet
- GeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest2Document2 pagesGeneralPhysics1 Q1 ChapterTest2Jasmin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: KinematicsDocument38 pagesMultiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: Kinematics张书No ratings yet
- Long Test in Science Grade 9Document3 pagesLong Test in Science Grade 9Janet PagulayanNo ratings yet
- (UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestDocument14 pages(UPOU) PHYSICS Pre-TestMon Belle AmourNo ratings yet
- (Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Document14 pages(Momentum, Works and Power) Quiz2023Haigou WaaaahNo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- 4Q Science G9Document3 pages4Q Science G9Kimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- Phy 101 Past Questions by Adebayo Bim's 08112601259 God BledDocument33 pagesPhy 101 Past Questions by Adebayo Bim's 08112601259 God Bledtoluwanisola14No ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsDocument8 pagesPhysics QuestionsTheOnesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science 9Document3 pagesReviewer Science 9Jennica Grace EguiaNo ratings yet
- 4th Grading TestDocument8 pages4th Grading TestTEREMIE JOSEPH OBADONo ratings yet
- Gravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeDocument11 pagesGravity and Energy Multiple Choice PracticeJohnNo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument12 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- MT2 Practice Fall 07Document3 pagesMT2 Practice Fall 07Seljen AceNo ratings yet
- REVISION QUESTIONS PHY094 CHAPTER 1-4Document8 pagesREVISION QUESTIONS PHY094 CHAPTER 1-4NURUL FARRAH LIEYANA BT SHAMSUL BAHARINo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 2 - Test A: Multiple Choice Choose The Best Answer From The Options That Follow Each QuestionDocument4 pagesPhysics Chapter 2 - Test A: Multiple Choice Choose The Best Answer From The Options That Follow Each QuestionCamdrn WrightNo ratings yet
- Motion, Forces, and Energy Exam ReviewDocument18 pagesMotion, Forces, and Energy Exam ReviewJeff SuarezNo ratings yet
- Science9 RFQADocument5 pagesScience9 RFQATimothyNo ratings yet
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerNeil VelascoNo ratings yet
- CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDING TEST FinalDocument6 pagesCONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDING TEST FinalJanine Faye TagardaNo ratings yet
- AP Phys C Fall Final Web RevDocument12 pagesAP Phys C Fall Final Web RevNadhya FadlillahNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionlouisadonaldlwrNo ratings yet
- ST Joseph'S International College: Physics (AS) Multiple Choice: Practice Test - March, 2023 - Grade 12Document6 pagesST Joseph'S International College: Physics (AS) Multiple Choice: Practice Test - March, 2023 - Grade 12brought to inspire - faith silvaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 1 Summative ExamDocument4 pagesPHYSICS 1 Summative ExamLeizel MundoNo ratings yet
- Force QuestionsDocument12 pagesForce QuestionsZul Abror Bin Ya'akopNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 Practice FinalDocument32 pagesSem 1 Practice FinalJuanNo ratings yet
- Vector and Kinematics Problems AnswersDocument14 pagesVector and Kinematics Problems AnswersAhmed aliNo ratings yet
- Co Projectile Grade 9Document11 pagesCo Projectile Grade 9Apolonio Pamittan Jr.No ratings yet
- Heat Engine and Thermal EfficiencyDocument8 pagesHeat Engine and Thermal EfficiencyApolonio Pamittan Jr.No ratings yet
- Co-Heat Engine and Thermal Efficiency-Grade-9Document10 pagesCo-Heat Engine and Thermal Efficiency-Grade-9Apolonio Pamittan Jr.No ratings yet
- HEAT ENGINE EFFICIENCYDocument11 pagesHEAT ENGINE EFFICIENCYApolonio Pamittan Jr.No ratings yet
- Configure Switching FeaturesDocument28 pagesConfigure Switching FeaturesCinco PredragNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Sa-Ak350pl SMDocument103 pagesPanasonic Sa-Ak350pl SMEder Espinoza BajoneroNo ratings yet
- SAFIR 2011 ManualDocument58 pagesSAFIR 2011 ManualCZengenhariaNo ratings yet
- Coke FinalDocument80 pagesCoke Finaltwinkle_4259No ratings yet
- Critical Spare For Manitou MT X1840 New ManitouDocument3 pagesCritical Spare For Manitou MT X1840 New ManitouamonNo ratings yet
- Belt Conveyor BrochureDocument5 pagesBelt Conveyor BrochureMostafa Farahani100% (1)
- Ettus B100Document2 pagesEttus B100Philip GaddiNo ratings yet
- QCD-FS-G.Annex Rev2015 PDFDocument1 pageQCD-FS-G.Annex Rev2015 PDFvhin84No ratings yet
- Ae603 PS 3Document3 pagesAe603 PS 3JohnNo ratings yet
- 072-Log-Marine-Dpr-Vii-18 2018.08.05Document8 pages072-Log-Marine-Dpr-Vii-18 2018.08.05maya gosindoNo ratings yet
- Ball Drop ActivityDocument4 pagesBall Drop ActivityKogilan ChitranNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument199 pagesDBMS Lab ManualMoulika Chowdary100% (1)
- Operating Manual Contents for Airless Spraying UnitDocument30 pagesOperating Manual Contents for Airless Spraying UnitИли.Я Или.ТыNo ratings yet
- Project: Inventory Management System For Music Store: SynopsisDocument7 pagesProject: Inventory Management System For Music Store: SynopsisSoumitra ChakravartyNo ratings yet
- Study On The Strength of EarthbagsDocument28 pagesStudy On The Strength of EarthbagsZherrinore Rasay100% (1)
- Media Cloud: An Open Cloud Computing Middleware For Content ManagementDocument6 pagesMedia Cloud: An Open Cloud Computing Middleware For Content Managementmr_harisskumarNo ratings yet
- Scalding Documentation: Tutorials for Beginners and BeyondDocument89 pagesScalding Documentation: Tutorials for Beginners and BeyondrajaNo ratings yet