Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
Mikay CatacataOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Uploaded by
Mikay CatacataCopyright:
Available Formats
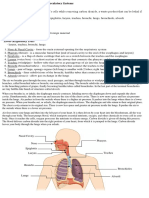
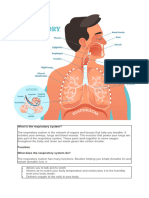
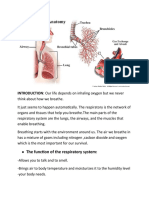
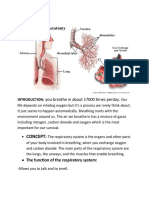
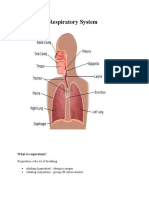
Mouth and nose: Openings that pull air from outside your body into your respiratory
system.
Sinuses: Hollow areas between the bones in your head that help regulate the
temperature and humidity of the air you inhale.
Pharynx (throat): Tube that delivers air from your mouth and nose to the trachea
(windpipe).
Trachea: Passage connecting your throat and lungs.
Bronchial tubes: Tubes at the bottom of your windpipe that connect into each lung.
Lungs: Two organs that remove oxygen from the air and pass it into your blood.
From your lungs, your bloodstream delivers oxygen to all your organs and other
tissues.
Muscles and bones help move the air you inhale into and out of your lungs. Some of
the bones and muscles in the respiratory system include your:
Diaphragm: Muscle that helps your lungs pull in air and push it out.
Ribs: Bones that surround and protect your lungs and heart.
When you breathe out, your blood carries carbon dioxide and other waste out of the
body. Other components that work with the lungs and blood vessels include:
Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
takes place.
Bronchioles: Small branches of the bronchial tubes that lead to the alveoli.
Capillaries: Blood vessels in the alveoli walls that move oxygen and carbon
dioxide.
Lung lobes: Sections of the lungs — three lobes in the right lung and two in the
left lung.
Pleura: Thin sacs that surround each lung lobe and separate your lungs from the
chest wall.
Some of the other components of your respiratory system include:
Cilia: Tiny hairs that move in a wave-like motion to filter dust and other
irritants out of your airways.
Epiglottis: Tissue flap at the entrance to the trachea that closes when you swallow
to keep food and liquids out of your airway.
Larynx (voice box): Hollow organ that allows you to talk and make sounds when air
moves in and out.
You might also like
- Vi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureDocument5 pagesVi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument1 pageLungstasuki_fernandez25No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesScience Reviewer - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemMaribeth Villanueva100% (2)
- Activity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesActivity On The Respiratory and The Circulatory SystemFheby ValerieNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory Systemjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory System.Document3 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory System.Alvin Patrick Colobong AsisNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemAsher Eby VargeeseNo ratings yet
- What Is The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Respiratory SystemacNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesRespiratory SystemKrizza Dawn QueNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System BpeDocument2 pagesRespiratory System BpeRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 7062113972923606793Document4 pagesAnatomy 7062113972923606793Domato Ayaon NawalNo ratings yet
- Anatomi InggrisDocument6 pagesAnatomi InggrisNur DianaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ExplanationDocument3 pagesAnaphy Explanationdanicamarieparado018No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesRespiratory SystemMesheil TaladroNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FinalDocument3 pagesRespiratory FinalSittie Bashma DiamaodenNo ratings yet
- Covid Ana - Phy DiscussionDocument3 pagesCovid Ana - Phy DiscussionFrance Llana CueNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System What Is The Respiratory System?: LungsDocument3 pagesRespiratory System What Is The Respiratory System?: LungsMami JdenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesRespiratory System: Anatomy and PhysiologyMykadi UnoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesRespiratory SystemKrizNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJEMZPERNo ratings yet
- Circulatory & Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesCirculatory & Respiratory SystemReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- The RespiratoryDocument11 pagesThe RespiratoryJellaine Anne Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory SystemMinh Phương HoàngNo ratings yet
- Respiratory TractsDocument2 pagesRespiratory TractsMervis ChandaNo ratings yet
- Et 2.-Anatommy PhisiologyDocument17 pagesEt 2.-Anatommy Phisiologyanisa93No ratings yet
- Path FitDocument21 pagesPath FitChris Timothy TurdanesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 46: The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 46: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systemapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Concept::: You Breathe in About 17000 Times PerdayDocument4 pagesConcept::: You Breathe in About 17000 Times PerdayMinh Phương HoàngNo ratings yet
- Vi. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesVi. Anatomy and PhysiologyJoeven HilarioNo ratings yet
- Science Week 1 (Bil)Document6 pagesScience Week 1 (Bil)shashaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Biological System Organs Respiration Organism Exchange Oxygen Carbon DioxideDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Biological System Organs Respiration Organism Exchange Oxygen Carbon DioxideAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Grade 9Document5 pagesRespiratory System Grade 9Ramos JayjayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: What Is Respiration?Document25 pagesRespiratory System: What Is Respiration?Perla AlejandresNo ratings yet
- Glosarium B.ing BiologiDocument5 pagesGlosarium B.ing BiologiAnita HandayaniNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument4 pagesRespiratoryNurul FikriNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Respiratory System: What Is Respiration?Document3 pagesAnatomy of Respiratory System: What Is Respiration?Adrian PunongbayanNo ratings yet
- Lungs: Importance of The LungsDocument4 pagesLungs: Importance of The Lungsdg100% (1)
- Science Reviewer (MID)Document53 pagesScience Reviewer (MID)Francesca KatigbakNo ratings yet
- What Is RespirationDocument2 pagesWhat Is RespirationEjay ObarNo ratings yet
- Every Cell in Your Body Needs Oxygen To LiveDocument12 pagesEvery Cell in Your Body Needs Oxygen To LiveSeraphim CamposNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYS-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesRESPIRATORY SYS-WPS OfficeRina Catubo100% (1)
- Reviewer in Science 9..Document4 pagesReviewer in Science 9..nanami's ChildNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SytemDocument2 pagesRespiratory SytemJanet BantigueNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument7 pagesLungsMelanie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Respiratory SystemCarlos Alfonso Borromeo AmoresNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument5 pagesReproductiveJason Vinluan CarinanNo ratings yet
- Review in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryDocument3 pagesReview in Science Circulatory System PulmonaryElvie Jane P. MolatoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - Respi & LiverDocument13 pagesAnaphy - Respi & LiverANAMAZING CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Respiratory SystemDocument1 pageVocabulary Respiratory SystemGAIA BACCANINo ratings yet
- Respiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsDocument3 pagesRespiration Is A Chemical Reaction That Happens in All Living CellsKani KurmanbekovaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology PneumoniaDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology PneumoniaJohnson MallibagoNo ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument26 pagesDiscussionCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemRoland Jacques AlconisNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemruben diwasNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Respiratory SystemMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument5 pagesRespiratoryKintina MorataNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Members: Tiffany Claire V. Anisco Blessie Faith S. Estifano Heart Nathalie D. OlasoDocument31 pagesRespiratory System: Members: Tiffany Claire V. Anisco Blessie Faith S. Estifano Heart Nathalie D. OlasoClairity KimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyLorraine Gambito100% (1)
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet