Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Me Laboratory 1 Experiment No. 5A Orsat Apparatus: Answer/define The Following: 1. What Is Orsat Analysis?
Uploaded by
ANTHONETTE BERNABEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Me Laboratory 1 Experiment No. 5A Orsat Apparatus: Answer/define The Following: 1. What Is Orsat Analysis?
Uploaded by
ANTHONETTE BERNABECopyright:
Available Formats
ME LABORATORY 1
EXPERIMENT NO. 5A
ORSAT APPARATUS
Objectives of the Experiment:
This experiment is for the students to understand and define what an Orsat analysis is, and what an
Orsat Apparatus is and its working principle.
Procedure:
Answer/define the following:
1. WHAT IS ORSAT ANALYSIS?
A measurement of the oxygen, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide in a mixture of gases, usually from
the exhaust of combustion processes such as boilers, furnaces, fired heaters, and combustion engines.
Orsat analysis is a laboratory method used to determine the composition of a gas mixture, particularly
its oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen content. The analysis is named after its inventor, German
chemist Wilhelm Orsat, and is commonly used in industries such as power generation, petrochemicals,
and metallurgy.
In an Orsat analysis, a sample of gas is drawn into a specialized glass apparatus called an Orsat
apparatus. The apparatus typically consists of a gas burette, pipettes, and absorption bulbs containing
chemical solutions that selectively react with different components of the gas mixture. The gas is first
passed through a solution that removes any water vapor present in the sample, and then through a
series of absorption bulbs containing chemicals that react with specific components of the gas mixture.
ME LABORATORY 1 - RCRivero |EXPERIMENT NO. 5A 1
2. WHAT EQUIPMENT IS USED FOR ORSAT ANALYSIS? WHO INVENTED IT, AND WHAT IS ITS WORKING
PRINCIPLE?
The equipment used for Orsat analysis includes an Orsat apparatus, which consists of a gas burette,
pipettes, and absorption bulbs containing chemical solutions.
The gas burette is a graduated glass tube that allows the volume of gas being analyzed to be accurately
measured. The pipettes are used to measure and transfer precise volumes of chemical solutions into the
absorption bulbs. The absorption bulbs contain chemical solutions that react selectively with different
components of the gas mixture, allowing their concentration to be measured.
Louis Hengist Orsat was born 14/8/1837 in Paris.
The working principle of Orsat analysis is based on the selective absorption of different gas components
by chemical solutions. The gas sample is drawn into the Orsat apparatus, and any water vapor present in
the sample is removed by passing it through a solution of calcium chloride. The gas is then passed
through a series of absorption bulbs containing chemical solutions that react selectively with different
gas components.
3. ATTACH A PHOTO OF THE APPARATUS USED FOR ORSAT ANALYSIS AND LABEL EACH PART
ME LABORATORY 1 - RCRivero |EXPERIMENT NO. 5A 2
Consists of a water-jacketed measuring burette, connected in series to a set of three absorption
bulbs, each through a stop-cock.
The other end is provided with a three-way stop-cock, the free end of which is further
connected to a U-tube packed with glass wool (for avoiding the incoming of any smoke particles,
etc.)
The graduated burette is surrounded by a water-jacket to keep the temperature of the gas
constant during the experiment.
The lower end of the burette is connected to a water reservoir by means of a long rubber
tubing.
The absorption bulbs are usually filled with glass tubes, so that the surface area of contact
between the gas and the solution is increased.
ME LABORATORY 1 - RCRivero |EXPERIMENT NO. 5A 3
You might also like
- Calculating Flow Through An Orifice Using ASME MFC-3M-1989 and Irrecoverable Pressure Drop EquationsDocument5 pagesCalculating Flow Through An Orifice Using ASME MFC-3M-1989 and Irrecoverable Pressure Drop EquationsRaphael212219No ratings yet
- The System by Todd Valentine - Review & Summary - Power Dynamics™ PDFDocument33 pagesThe System by Todd Valentine - Review & Summary - Power Dynamics™ PDFshadowzack 509No ratings yet
- Abs 0678Document11 pagesAbs 0678Jorge OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Mine Gases - Sampling of Mine AirDocument9 pages1.8 Mine Gases - Sampling of Mine AirDeepakKattimaniNo ratings yet
- On Thi Di HC PHN Reading PassageDocument29 pagesOn Thi Di HC PHN Reading PassageTrần ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsFrom EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Orsat Gas AnalyserDocument3 pagesOrsat Gas AnalyserSandeep Mishra100% (1)
- ChromatographyDocument6 pagesChromatographyJyoti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Orsat Gas AnalysisDocument3 pagesOrsat Gas Analysisghambira100% (11)
- CHM260 Experiment 4Document11 pagesCHM260 Experiment 4Muhammad Azri Haziq57% (7)
- GAS IndicatorsDocument67 pagesGAS Indicatorssasikumarmarine100% (3)
- Handling Mercaptans in The LaboratoryDocument7 pagesHandling Mercaptans in The LaboratoryjoesuhreNo ratings yet
- On NCVET FunctioningDocument35 pagesOn NCVET Functioningsingh.darshan9100% (2)
- Sampling TechniquesDocument17 pagesSampling TechniquesDebjyoti SanyalNo ratings yet
- Action Plan ESP 2023 24Document2 pagesAction Plan ESP 2023 24Je-Ann EstriborNo ratings yet
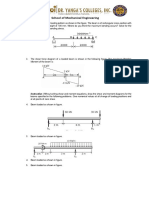
- ME139L Research 1Document10 pagesME139L Research 1goblinsbrideNo ratings yet
- Orsat Gas Analyser: ConstructionDocument2 pagesOrsat Gas Analyser: ConstructionCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- Orsat Gas Analyser: 2 Method of AnalysisDocument3 pagesOrsat Gas Analyser: 2 Method of AnalysisSandeep MishraNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Fuels PDFDocument3 pagesGaseous Fuels PDFTrisha ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gaseous FuelsDocument3 pagesGaseous FuelsTrisha ReyesNo ratings yet
- Orsat Gas AnalysisDocument3 pagesOrsat Gas AnalysisSandeep MishraNo ratings yet
- Orsat Gas AnalysisDocument3 pagesOrsat Gas AnalysisSAR_SuvroNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. - 3Document3 pagesExperiment No. - 3revendraojhaNo ratings yet
- 06 Flue Gas AnalysisDocument6 pages06 Flue Gas AnalysisJohannis ReyNo ratings yet
- Flue Gas Analysis - (1805240028)Document15 pagesFlue Gas Analysis - (1805240028)MohdNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrophotometerDocument22 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrophotometerJawad HafeezNo ratings yet
- Gastec FaqsDocument4 pagesGastec FaqsGufron MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy - WikipediaDocument16 pagesAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy - WikipediaDwika YanuariNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument2 pagesConstructionKelvin MshalieNo ratings yet
- Adsorption CompleteDocument20 pagesAdsorption Completehahaamin aminNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lab ConcentrationDocument24 pagesThermodynamics Lab ConcentrationIjazNo ratings yet
- Orsat Analysis ResearchDocument3 pagesOrsat Analysis ResearchEure Leigh BorjeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument9 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosKishore CivilNo ratings yet
- AaesDocument14 pagesAaesAbdeta BogaleNo ratings yet
- Orsat Gas AnalyserDocument6 pagesOrsat Gas Analyserاحمد كريم خلفNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument3 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosRohit KeoleNo ratings yet
- Group Members: Suhaidah Binti Nazori UK21425 Mohd Faizuddin Bin Abu Hasan UK21455 Siti Fasihah Binti Rameli UK21478Document27 pagesGroup Members: Suhaidah Binti Nazori UK21425 Mohd Faizuddin Bin Abu Hasan UK21455 Siti Fasihah Binti Rameli UK21478ah_16036566No ratings yet
- 397 FullDocument6 pages397 FullJossue LopezNo ratings yet
- Pervaporation A Useful Tool For Speciation AnalysisDocument9 pagesPervaporation A Useful Tool For Speciation AnalysischoifynNo ratings yet
- Astm D 4888-2006Document3 pagesAstm D 4888-2006JanethNo ratings yet
- Exeter Analytical, Inc. CE-440 Elemental Analyzer: Ce-440 Theory of OperationDocument3 pagesExeter Analytical, Inc. CE-440 Elemental Analyzer: Ce-440 Theory of OperationKhalid ZghearNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument12 pagesGas ChromatographyYaman Adnan QabajaNo ratings yet
- APC Module 3 APCDocument18 pagesAPC Module 3 APCVadiraj HathwarNo ratings yet
- Methods For Sampling Biogas and Biomethane For Assessment of The Gas Chemical and Physical PropertiesDocument2 pagesMethods For Sampling Biogas and Biomethane For Assessment of The Gas Chemical and Physical PropertiesJuan Enrique Vergel MarinNo ratings yet
- Mine GasesDocument10 pagesMine GasesMelford LapnawanNo ratings yet
- Analaytical Assignment Group-3Document10 pagesAnalaytical Assignment Group-3yilma wendayehuNo ratings yet
- Trace Analytics ISO 8573 White PaperDocument2 pagesTrace Analytics ISO 8573 White PaperDeepakNo ratings yet
- Chem400 LabW05Document11 pagesChem400 LabW05Vany Torres0% (1)
- Possibility of The Use Polish Soda Lime As The Absorbent in The Canisters of The Oxygen Breathing Apparatus Type Oxy-NGDocument11 pagesPossibility of The Use Polish Soda Lime As The Absorbent in The Canisters of The Oxygen Breathing Apparatus Type Oxy-NGindiomajaderoNo ratings yet
- Aeration UnitDocument5 pagesAeration UnitAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Determination in Oxygen-Supersaturated Drinking Waters by NMRDocument6 pagesOxygen Determination in Oxygen-Supersaturated Drinking Waters by NMRKahlil Schwanka SaloméNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Escombros de IncendiosDocument20 pagesAnalisis de Escombros de Incendiosuniversal0482No ratings yet
- Kitagawa Tube ListDocument16 pagesKitagawa Tube ListMehmet Ali TağNo ratings yet
- What Is Gas Chromatography AssignmentDocument10 pagesWhat Is Gas Chromatography AssignmentIsmi Fadli100% (1)
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument30 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosRashed BiswasNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Oily Dusts Emitted During Metal Surface Treatment in Laboratory ConditionsDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Oily Dusts Emitted During Metal Surface Treatment in Laboratory ConditionsResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document9 pagesChapter 4Kelkiyas TaurusNo ratings yet
- Measuring Toxic Gases Generated From Reaction of Guanidine Isothiocyanate-Containing Reagents With BleachDocument7 pagesMeasuring Toxic Gases Generated From Reaction of Guanidine Isothiocyanate-Containing Reagents With BleachAzmier AdibNo ratings yet
- Untitledyvhyfrc 6Document18 pagesUntitledyvhyfrc 6Lsk MatammuNo ratings yet
- Gas ChromatographyDocument4 pagesGas ChromatographyAgustin A.No ratings yet
- Ingles VocabularyDocument71 pagesIngles VocabularyESLYNo ratings yet
- M 03Document18 pagesM 03Ivan RosasNo ratings yet
- Flue Gas Analysis: By: Tugbong, Joemarie Guangco, Sean KelvinDocument26 pagesFlue Gas Analysis: By: Tugbong, Joemarie Guangco, Sean KelvinKen Denver MaglinteNo ratings yet
- Inert Purge VentingDocument14 pagesInert Purge VentingNurulNo ratings yet
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument28 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosvvrckumarNo ratings yet
- Pe AaDocument5 pagesPe AanedalllNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration, Compressed Air Systems & Efficient Use of EnergyDocument89 pagesRefrigeration, Compressed Air Systems & Efficient Use of EnergyANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Refrigerants Compressors: Refrigeration SystemDocument44 pagesRefrigerants Compressors: Refrigeration SystemANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Multi-Pressure: SystemDocument30 pagesMulti-Pressure: SystemANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Problems To ReviewDocument2 pagesProblems To ReviewANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Problems To ReviewDocument3 pagesProblems To ReviewANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument45 pagesUntitledANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Single Phase Transformer y Delta Conn.Document25 pagesTopic 11 Single Phase Transformer y Delta Conn.ANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Introduction To Refrigeration System OUTLINEDocument1 pageIntroduction To Refrigeration System OUTLINEANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Problems To ReviewDocument2 pagesProblems To ReviewANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Introduction in RefDocument68 pagesIntroduction in RefANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Blocky Hand-Drawn Stalls and Shopfronts InfographicDocument1 pageBlocky Hand-Drawn Stalls and Shopfronts InfographicANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Economic ExamsDocument3 pagesEconomic ExamsANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Parents ConsentDocument2 pagesParents ConsentANTHONETTE BERNABE100% (1)
- Performance Task #1Document1 pagePerformance Task #1ANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Episode 3 MultipressuresystemsDocument75 pagesEpisode 3 MultipressuresystemsANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Episode 8 SelectingtherefrigerantDocument58 pagesEpisode 8 SelectingtherefrigerantANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Episode2 BasicvaporcompressionrefrigerationsystemAutosavedDocument148 pagesEpisode2 BasicvaporcompressionrefrigerationsystemAutosavedANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Episode 9 ComputingforrighrtrefrigerantDocument95 pagesEpisode 9 ComputingforrighrtrefrigerantANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Episode1 IntrotorefrigerationsystemDocument98 pagesEpisode1 IntrotorefrigerationsystemANTHONETTE BERNABENo ratings yet
- Evrc Grade One-Math Dll-5thweek2ndquarterDocument8 pagesEvrc Grade One-Math Dll-5thweek2ndquarterAngelica Pastrana Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Bath Uni Coursework Cover SheetDocument8 pagesBath Uni Coursework Cover Sheetvtdvkkjbf100% (2)
- Fred Hymans and The Theory of Rope Traction, Part Two: HistoryDocument15 pagesFred Hymans and The Theory of Rope Traction, Part Two: Historyاحمد المقرميNo ratings yet
- Innovation Health and Wealth Report 2012dh - 134597Document36 pagesInnovation Health and Wealth Report 2012dh - 134597Alejandro CardonaNo ratings yet
- Microptic CatalogDocument8 pagesMicroptic CatalogMhd DamNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh's Population Part CDocument4 pagesBangladesh's Population Part CKemNo ratings yet
- Theory Summarized R1 To R5Document10 pagesTheory Summarized R1 To R5ALINDOGAN, KimleeNo ratings yet
- English Homework Sheets Ks1Document7 pagesEnglish Homework Sheets Ks1ewbp4y3s100% (1)
- Some Books For Stat 602XDocument1 pageSome Books For Stat 602XAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Acetone-Solution Casting Film of PMMADocument3 pagesCharacterization of Acetone-Solution Casting Film of PMMASyiera MujibNo ratings yet
- UVM Run-Time Phasing GuideDocument55 pagesUVM Run-Time Phasing GuideVictor David SanchezNo ratings yet
- Learning OrganizationDocument4 pagesLearning OrganizationAbdullah AzizNo ratings yet
- EXXXX 080 002, GGA and GTGS, Rev.4Document1 pageEXXXX 080 002, GGA and GTGS, Rev.4Mohamed HamdallahNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kandungan Vitamin C Bahan Makanan Dan Minuman Dengan Metode IodimetriDocument9 pagesAnalisis Kandungan Vitamin C Bahan Makanan Dan Minuman Dengan Metode IodimetriABDULLAH MHS ULMNo ratings yet
- Decimal Million & Fraction MillionDocument21 pagesDecimal Million & Fraction MillionSuganthi SupaiahNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument12 pagesProject ReportMuhammad SulemanNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes of RCC Beams Strengthened With NSM FRP TechniquesDocument9 pagesFailure Modes of RCC Beams Strengthened With NSM FRP TechniquesfelixNo ratings yet
- Raju ComparativePhilosophySpiritual 1963Document16 pagesRaju ComparativePhilosophySpiritual 1963Kent Jerson CasianoNo ratings yet
- PB Arang Aktif 11032020 BDocument2 pagesPB Arang Aktif 11032020 BSiti Sarifa YusuffNo ratings yet
- NDT Global Appoints New President - World PipelinesDocument2 pagesNDT Global Appoints New President - World PipelinesNutthakarn WisatsiriNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: K-W-L Chart: What I Know What I Want To Know What I LearnedDocument1 pageActivity 2: K-W-L Chart: What I Know What I Want To Know What I LearnedJuanito AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Development of The Indirect-Drive Approach To Inertial Confinement Fusion and The Target Physics Basis For Ignition and Gain - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFDocument92 pagesDevelopment of The Indirect-Drive Approach To Inertial Confinement Fusion and The Target Physics Basis For Ignition and Gain - REVIEW ARTICLE PDFAjit UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope LubricantsDocument12 pagesWire Rope LubricantsAlbert Aromin100% (1)
- The Strange Life of Nikola TeslaDocument8 pagesThe Strange Life of Nikola TeslaMohammad MetlejNo ratings yet