Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cl-THE CHEMICAL BOND
Uploaded by
Asif Ahnaf0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views45 pages(1) Chemical bonds form when atoms combine in order to achieve stable electron configurations like those of inert gases.
(2) Ionic bonds are formed via complete electron transfer between atoms, leaving positively and negatively charged ions that are attracted via electrostatic forces. Covalent bonds involve sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Coordination bonds involve both transfer and sharing of electrons.
(3) Ionic compounds have crystalline structures, are electrically conductive when molten or dissolved, have high melting/boiling points due to strong electrostatic attractions, and react quickly. Covalent compounds share electrons in pairs to achieve stable configurations.
Original Description:
Original Title
Cl-THE_CHEMICAL_BOND
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document(1) Chemical bonds form when atoms combine in order to achieve stable electron configurations like those of inert gases.
(2) Ionic bonds are formed via complete electron transfer between atoms, leaving positively and negatively charged ions that are attracted via electrostatic forces. Covalent bonds involve sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Coordination bonds involve both transfer and sharing of electrons.
(3) Ionic compounds have crystalline structures, are electrically conductive when molten or dissolved, have high melting/boiling points due to strong electrostatic attractions, and react quickly. Covalent compounds share electrons in pairs to achieve stable configurations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views45 pagesCl-THE CHEMICAL BOND
Uploaded by
Asif Ahnaf(1) Chemical bonds form when atoms combine in order to achieve stable electron configurations like those of inert gases.
(2) Ionic bonds are formed via complete electron transfer between atoms, leaving positively and negatively charged ions that are attracted via electrostatic forces. Covalent bonds involve sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Coordination bonds involve both transfer and sharing of electrons.
(3) Ionic compounds have crystalline structures, are electrically conductive when molten or dissolved, have high melting/boiling points due to strong electrostatic attractions, and react quickly. Covalent compounds share electrons in pairs to achieve stable configurations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 45
THE CHEMICAL BOND
Principles of Electronic Theory of
Chemical Bond
(1) Chemical combination between atoms of the
same or different elements takes place due
to the tendency by the outermost electron
groups to attain the stable arrangement of
inert gases.
(2) The attainment of inert gas electron
configuration may take place by complete
transference of electrons from one atom to
another. The resulting electrically charged
atoms (or ions) are held together by
electrostatic force of attraction. The chemical
bond so formed is known as electrovalent or
Ionic bond.
(3) The attainment of inert gas configuration
may occur by sharing of electrons (in pairs)
between two atoms. The chemical bond so
formed is called covalent bond.
(4) The attainment of electron groupings of inert
gases may also happen by both transference
and sharing of electrons between atoms in
pairs. The bond so formed is known as
coordination bond.
The Ionic Bond
The ionic bond is formed when one or more
electrons are transferred from one atom to
the other to complete the orbital's in each
case. In both cases, the electronic
arrangements of the resulting ions is identical
to that of an atoms of one of the inert gases.
The electronic configuration of Ne(10) and
Na(11) is 1s22s22p6 and 1s22s22p63s1
respectively.
It is noted that the gas neon(Ne) has 8
electrons in its outer energy level.
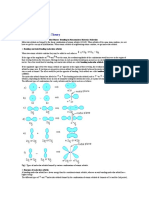
Similarly, the formation of negatively charged
fluorine ion (F-) may be illustrated as follows:
F(1s22s22p5) + 1e→ F-(1s22s22p6)
+ 1e →
Similarly, the bond between magnesium and
oxygen in magnesium oxide (MgO) involves
two electrons.
Mg ( 1s22s22p63s2 )
Mg+2 ( 1s22s22p6 ) Neon structure
O ( 1s22s22p4 )
O-2 ( 1s22s22p6 ) Neon structure
Mg + O → Mg+2 + O-2 → MgO
General Properties of the Ionic Bond
(1) Crystalline State: Ionic compound can form
crystalline structure. Crystals are composed of
ions in the crystal lattice or the atomic
network.
The structure of sodium chloride has been shown
in Fig. and gives cubic crystals.
(2) Electrical Conductivity: Ionic compounds
either in the fused state or in solutions are
good conductors of electricity. The ions are
free to move under the influence of electric
field.
(3) Isomorphism: The different compounds
containing ionic bonds have ions, which
assume the same electron arrangements in
their molecules and hence show similar
crystalline forms.
NaF is isomorphous with MgO, and K2S has the
same crystalline form as that of CaCl2
Na+ 1s22s22p6 F- 1s22s22p6
Mg+2 1s22s22p6 O-2 1s22s22p6
(4) Melting and Boiling Points: In the ionic
crystals the ions exert a powerful electrostatic
force on each other. A considerable amount of
work is needed to separate them from one
another. Ionic compounds have high melting
and boiling point.
(5) Reactivity: The reactions between ionic
compounds generally take place with great
speed.
(6) Solubility: Ionic compounds are generally
more soluble in polar than in non-polar
solvents.
The Covalent Bond
Atoms may combine with each other
chemically by sharing of electrons. A chemical
bond of this type is called a covalent bond,
and compounds containing these bonds are
called covalent compounds.
Sharing of electrons between atoms always
occurs in pairs, and in each pair of shared
electrons one is contributed by each atom.
Covalent bonds are, therefore, also known as
electron pair bonds.
The covalent bond may also link together
atoms of different elements to form a
molecule of a compound. The combination of
hydrogen atom with an atom of chlorine to
form a molecule of HCl may be shown as
follows:
In the molecule of HCl, both H and Cl are
surrounded by an electron cloud like that of
helium and argon atoms respectively.
An atom can combine by sharing electrons
with more than one atom.
Coordination Bond
In some molecules one of the atoms may
supply both electrons, i.e., both shared
electrons come from the same atom. A
covalent bond formed by the donation of a
pair of electrons from one atom to another
atom in the molecule is called a coordination
bond.
Ammonium ion also can be represented as
formed by the combination of H+ ion with
ammonia molecule by coordination bond.
You might also like
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 05Document10 pagesClass IX Chemistry Chapter 05Sam FisherNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument132 pagesChemical BondingKowser mahmudNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chem-Notes-Anil-Ch-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chem-Notes-Anil-Ch-4. Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRihab ShehzeenNo ratings yet
- CHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesCHM 112 Aspect Note-Chemical BondingOluwatosin KoyejoNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument13 pagesChemical BondingJonathan MathewNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureAthulRKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding & Molecular StructureDocument29 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding & Molecular StructureVighnesh0% (1)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFSudheesh Sudhakaran Nair100% (2)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureRIHAN ABDULKADERNo ratings yet
- XI CH 4 Chemistry Notes by AkDocument19 pagesXI CH 4 Chemistry Notes by AkappugmenonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureasinriazNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular ShapeDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Shapeshivakafle039No ratings yet
- VNKU Medical Chemistry Lecture on Chemical Bonding and Coordination CompoundsDocument31 pagesVNKU Medical Chemistry Lecture on Chemical Bonding and Coordination CompoundsAmirs AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding - Occurs When Two or More Ions Combine To Form An Electrically-NeutralDocument28 pagesChemical Bonding: Ionic Bonding - Occurs When Two or More Ions Combine To Form An Electrically-NeutralananntsharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument38 pagesChemical BondingBackup AccountNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NotesDocument13 pagesClass XI Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NoteseasaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument20 pagesChemical BondsAnbarin ParisaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Theory ExplainedDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding Theory Explainedarun iyer BitcoinminerandmathematicianNo ratings yet
- CHEM 212 Second LectureDocument2 pagesCHEM 212 Second LectureKazeem Ibrahim BelloNo ratings yet
- Note-02 (Chemical Bonding) PDFDocument27 pagesNote-02 (Chemical Bonding) PDFAnowar HossainNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Bond - I: Join Our Telegram Channel: @airjeeDocument37 pagesThe Chemical Bond - I: Join Our Telegram Channel: @airjeeVallabhNo ratings yet
- W) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXDocument10 pagesW) D5w$,yki3z . - (FXSav OliNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document42 pagesUnit 2Muktaar HassenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document77 pagesUnit 2sumeyaminNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Class11th by PS Sir IIT JEEDocument44 pagesChemical Bonding Class11th by PS Sir IIT JEEMahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Unit 4Document35 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Unit 4Rajiv Sharma100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding For B.tech 1st Year byJishnuNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondsDocument5 pagesIonic and Covalent BondsFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- CB 1Document4 pagesCB 1Mahmudur Rahman27No ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Chemical BondingDe AktivedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureM. MuvafficaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument46 pagesBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingHendri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Bond NoteDocument9 pagesChemical-Bond NoteDixit GautamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding Part 1Document93 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding Part 1Jimit Patel BankNo ratings yet
- Electronic Theory of Valency &bondingDocument12 pagesElectronic Theory of Valency &bondingshivakafle039No ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Struture - NotesDocument23 pages11 Chemistry-Chemical Bonding and Molecular Struture - NotesSumit MahatoNo ratings yet
- Bonding III.1-7Document7 pagesBonding III.1-7Kartik DuttaNo ratings yet
- EP101 Sen LNT 001 Bonding May11Document15 pagesEP101 Sen LNT 001 Bonding May11Sàtz ÑÖÑïtNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument42 pagesSolid StateM.AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Chapter - 04Document35 pagesChemical Bonding: Chapter - 04Harsh OthayothNo ratings yet
- Islamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyDocument29 pagesIslamic University, Kushtia-7003: Department of PharmacyRayhanuzzaman ShazibNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry RemedialDocument69 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry Remedialabdimoh7522100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond and Its TypesDocument5 pagesChemical Bond and Its TypesKhan NiaziNo ratings yet
- Q 2: Write A Note On Lewis Symbols.: Li Be B C N O F NeDocument23 pagesQ 2: Write A Note On Lewis Symbols.: Li Be B C N O F Neapi-233404189No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesChemical BondingRishu KumarNo ratings yet
- 04 Chemical Bonding Revision Notes QuizrrDocument80 pages04 Chemical Bonding Revision Notes QuizrrMONEY ALLNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDocument24 pagesAtomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDr-Sushant GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument94 pagesChemical BondingGagandeep WadhawanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument177 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureGanesh V GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument79 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureGanesh V GaonkarNo ratings yet
- NEET Revision Notes For Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument21 pagesNEET Revision Notes For Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureTanushree DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Lec 3 MSRDocument25 pagesChemical Bonding Lec 3 MSRsiam137032No ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidDocument6 pagesAtomic Bonding in SolidOjasviNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 NOTESDocument18 pagesChapter-4 NOTESAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 NotesHamza AminNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Document26 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE - 033838Gautam SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingDebasish BagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Lec 3 Plastic Deformation and Mechanical Properties of Metal PDFDocument57 pagesLec 3 Plastic Deformation and Mechanical Properties of Metal PDFAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- ME - 194 Engineering Materials SessionalDocument45 pagesME - 194 Engineering Materials SessionalAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Types, Concentration, and PropertiesDocument26 pagesSolutions: Types, Concentration, and PropertiesAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Valence Bond Theory VBTDocument32 pagesValence Bond Theory VBTAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Ode Lecture 1-5Document31 pagesOde Lecture 1-5Asif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Prob On DC MotorDocument9 pagesProb On DC MotorAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument13 pagesInduction MotorAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Prob On Transforme HaiderrDocument7 pagesProb On Transforme HaiderrAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- DC MachinesDocument54 pagesDC Machinessameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- DC GenDocument55 pagesDC GenAsif AhnafNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Fatigue Resistance of Endodontically Treated Incisors Without Ferrule Restored With CAD: CAM EndocrownsDocument20 pagesAccelerated Fatigue Resistance of Endodontically Treated Incisors Without Ferrule Restored With CAD: CAM EndocrownsBenjamin LucaNo ratings yet
- Seeleys Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition VanPutte Regan Russo Tate Stephens Seeley Test BankDocument89 pagesSeeleys Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition VanPutte Regan Russo Tate Stephens Seeley Test Bankedith100% (22)
- Ikatan IonikDocument229 pagesIkatan IonikGani PurwiandonoNo ratings yet
- Lxs Rubber Catalogue Eu Version Us 0219 WebDocument38 pagesLxs Rubber Catalogue Eu Version Us 0219 Webvlabat2017No ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chem CH19 Practice Question AnswersDocument1 pageAQA A Level Chem CH19 Practice Question AnswersMahebul MazidNo ratings yet
- A Microbial Transporter of The Dietary AntioxidantDocument34 pagesA Microbial Transporter of The Dietary Antioxidanth5wwgbvbvmNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument8 pagesEuropean Journal of Pharmaceutical SciencesSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Vant Hoff's Factor Calculation, by Elevation in Boiling PointDocument18 pagesChemistry Vant Hoff's Factor Calculation, by Elevation in Boiling PointMukesh Hacker63% (8)
- Pharmceutical Chemistry Part 1 (Prelim)Document11 pagesPharmceutical Chemistry Part 1 (Prelim)Majeddah Aliudin TalambunganNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Definitions ASDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Definitions ASShamima Begum Ali100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions of Copper LabDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions of Copper Labrikubean100% (1)
- MCQ Solubility Chapter One 20220403Document31 pagesMCQ Solubility Chapter One 20220403سراج الدين علي وفيق عليNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 4Document14 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 9 Chapter 4Rahul N BNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument12 pagesGen BioKhamil Kaye GajultosNo ratings yet
- Automated Blood Cell Analyzer (510712)Document34 pagesAutomated Blood Cell Analyzer (510712)ahsnupayaoNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Chapter Equilibrium Key ConceptsDocument10 pagesXI Chemistry Chapter Equilibrium Key ConceptsSridhar MarellaNo ratings yet
- Chem 31: Reviewer For 2 DepexDocument27 pagesChem 31: Reviewer For 2 DepexAlma PabilaneNo ratings yet
- Optronics - Single Loose Tube With Steel Tape Armour Fibre Optic CableDocument3 pagesOptronics - Single Loose Tube With Steel Tape Armour Fibre Optic CableblegedesNo ratings yet
- SPM - Chem ColoursDocument1 pageSPM - Chem Colourshannah100% (1)
- Module 2 - Hydrocarbons and DerivativesDocument121 pagesModule 2 - Hydrocarbons and DerivativesLouise AnneNo ratings yet
- THERMAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMER (Update)Document38 pagesTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMER (Update)Vĩ Lê QuangNo ratings yet
- Eamcet 2001Document35 pagesEamcet 2001Ashwin SriramojuNo ratings yet
- Part ІІ Microscopic World I: Ans: ADocument7 pagesPart ІІ Microscopic World I: Ans: AGabriel FungNo ratings yet
- Eco-Friendly Dyes and Dyeing: Asim Kumar Roy CHOUDHURYDocument33 pagesEco-Friendly Dyes and Dyeing: Asim Kumar Roy CHOUDHURYUtsho ParvezNo ratings yet
- Astm E3-11Document12 pagesAstm E3-11Alejandro OrtizNo ratings yet
- CO2 Conversion by Reverse Water Gas Shift Catalysis: Comparison of Catalysts, Mechanisms and Their Consequences For CO2 Conversion To Liquid FuelsDocument32 pagesCO2 Conversion by Reverse Water Gas Shift Catalysis: Comparison of Catalysts, Mechanisms and Their Consequences For CO2 Conversion To Liquid Fuelskishore dasmunshiNo ratings yet
- Final ColloidsDocument150 pagesFinal Colloidsmaheen aurangzaibNo ratings yet
- JEE Time Saver Course Planner FinalDocument24 pagesJEE Time Saver Course Planner FinalSadhak JainNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Faculty of Science and Mathematics: SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2021/2022Document4 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Faculty of Science and Mathematics: SEMESTER 1 SESSION 2021/2022Jojie KimaraNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7Document8 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7DikshantNo ratings yet