Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transcription-Translation Wksht1
Uploaded by
Jap (Dham) JiracharnchaisiriCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transcription-Translation Wksht1
Uploaded by
Jap (Dham) JiracharnchaisiriCopyright:
Available Formats
Name____________________________ Class __________________ Date __________
Transcription
In transcription, RNA polymerase splits the two halves of a strand
of DNA. RNA then uses one half as a template to make a copy of
the other half. RNA contains the nucleotide uracil instead of the
nucleotide thymine.
Label the DNA and RNA. Then, label the missing nucleotides marked on
the diagram.
C
A
G
T
RNA polymerase
Key
A = Adenine
C = Cytosine
G = Guanine
T = Thymine
U = Uracil
Use the diagram to answer the question. Circle the correct answer.
1. In RNA, which nucleotide is always paired with uracil?
adenine guanine
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
112
Name____________________________ Class __________________ Date __________
Comparing DNA Replication and Transcription
DNA replication is the process by which a cell copies its DNA.
During replication, both strands of the double helix are used as
templates to make complementary, or matching, strands of DNA.
DNA transcription is the process by which a single strand of DNA
is used as a template to generate a strand of mRNA.
Fill in the missing information. One row has been completed for you.
Template DNA Complementary DNA Messenger RNA
(mRNA)
TTACG AATGC AAUGC
GGCGG
ACGUAGC
AGACTC
GATAAGA
CUGGCUAC
Use the table to answer the question.
1. Give another example of a template DNA code that is at least
four base pairs long. Then give its matching complementary
DNA and mRNA codes.
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
113
Name____________________________ Class __________________ Date __________
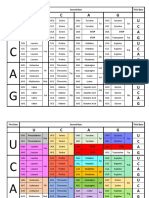
Decoding mRNA
The diagram shows the mRNA codes that correspond to amino
acids and stop codons. Read the diagram from the center out-
wards. For example, the mRNA code UAC corresponds to the
amino acid tyrosine.
Write the name of the amino acid that corresponds to each mRNA code.
The first one has been done for you.
Phenyl-
alanine
Glycin
cine
Glu cid ic
Leu
tam
a
e
As aci
in
e
pa d
Ser
G UC A G
ic
UC A
rt
e
G UC in
Ala A A os
A G U C
C r
nin
e
U G Ty
G U p
C
A C Sto
U C A AGU Cysteine
Valine A
C
U
G
U G U C
G AG TryStoptop phan
G U
Arginine A G U A Leucine
C
S e r i n e U
i n
C
G
e A
A A C C ACU
G
Lys C
A Pro
eU C G lin
rag
i n GA
C U G GA
C
U e
pa UG
Hi
e
As AC U G A C U
nin
sti
Glu
ine
di
reo
ine
Arginin
ne
tam
hion
Th
Isoleuc
ine
Met
mRNA Code Amino Acid
AAA lysine
GCG
GAU
CAA
Use the diagram to answer the questions.
1. Which two mRNA codes correspond to histidine?
2. How many different mRNA codes correspond to arginine?
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
114
Name____________________________ Class __________________ Date __________
Translation
During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) anticodons match to
messenger RNA (mRNA) codons. Each tRNA molecule can carry
one particular amino acid. The amino acids are joined to form
a polypeptide.
Number the four tRNA anticodons in the order in which they should
appear to match the codons in the mRNA strand.
A U G U U C A A A C U G
mRNA
phenylalanine leucine lysine methionine
A A G G A C U U U U A C
Use the diagrams to answer the question.
1. List the amino acids in the order they would appear in the
polypeptide coded for by the mRNA.
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
115
You might also like
- Label The The Diagram.: TranscriptionDocument4 pagesLabel The The Diagram.: TranscriptionLeonard PolancoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis - MechanismsDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis - MechanismsKhaled Turk100% (2)
- 14 Gene Expression Transcription SDocument6 pages14 Gene Expression Transcription SHelp Me Study TutoringNo ratings yet
- BCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMDocument55 pagesBCHS317 SU2.5 - Translation - FMKAGISO BRIAN MOTSHUPHINo ratings yet
- Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesGene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila CorvalanNo ratings yet
- 15 Gene Expression Translation SDocument6 pages15 Gene Expression Translation SHelp Me Study TutoringNo ratings yet
- DNA Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA Protein Synthesis WorksheetKate Nicole AndraNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Document6 pagesKami Export - Gene Expression-Translation-S.1617553074Camila Corvalan100% (5)
- 5.1 Molecular Biology Control of Gene ExpressionDocument31 pages5.1 Molecular Biology Control of Gene ExpressionGebby TrisaswithaNo ratings yet
- From Genes To ProteinsDocument2 pagesFrom Genes To ProteinsEderlyn ZateNo ratings yet
- Dna TranslationDocument19 pagesDna Translationandrefc98No ratings yet
- Genetic Material: Prodi Pendidikan Biologi UIN Walisongo Semarang 2019Document40 pagesGenetic Material: Prodi Pendidikan Biologi UIN Walisongo Semarang 2019elina lestariyanti UIN Walisongo SemarangNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation Exercise VER2 SolutionDocument3 pagesTranscription and Translation Exercise VER2 SolutionShanny McshannsNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Teknik Biologi Molekuler - CompressedDocument31 pagesAplikasi Teknik Biologi Molekuler - CompressedHelmawati PasombaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Rolling Circle Replication in Geminiviruses: Role of Replication Enhancer (Ren/Al3)Document18 pagesMechanism of Rolling Circle Replication in Geminiviruses: Role of Replication Enhancer (Ren/Al3)kalyankpy100% (1)
- Protein Synthesis Drag and Drop ActivityDocument6 pagesProtein Synthesis Drag and Drop ActivityGloria LaneNo ratings yet
- Translation and ModificationDocument49 pagesTranslation and ModificationYasmin BalochNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids 2012Document31 pagesNucleic Acids 2012Joana Marie Salinas-BeltranNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument20 pagesTranslationSherilyn MutoNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Biologi MolekulerDocument78 pagesKonsep Dasar Biologi MolekulerpipitNo ratings yet
- Konsep Dasar Biologi MolekulerDocument78 pagesKonsep Dasar Biologi Molekulerpipit100% (1)
- mRNAcodonchart PDFDocument2 pagesmRNAcodonchart PDFFerdinand Fremista JrNo ratings yet
- 16 - From-Gene-To-Protein-569f1f4a4ac56Document33 pages16 - From-Gene-To-Protein-569f1f4a4ac56Roaa SallamNo ratings yet
- Codon Bingo Game PDFDocument3 pagesCodon Bingo Game PDFCody DarrenNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Workflow Solutions BrochureDocument56 pagesMolecular Biology Workflow Solutions BrochureBishoy F. YoussefNo ratings yet
- 2022-04-26 L5 - Annealing Temperature & Primer DesignDocument3 pages2022-04-26 L5 - Annealing Temperature & Primer DesignTamara ElyasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20, RNA Synthesis TranscriptionDocument10 pagesLecture 20, RNA Synthesis TranscriptionNariopolusNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Examination-G10 ScienceDocument2 pages3rd Grading Examination-G10 ScienceMaria Conxedes GudesNo ratings yet
- Grafik 15 Patron Penyakit Puskesmas Binaus Bulan Januari 2016Document11 pagesGrafik 15 Patron Penyakit Puskesmas Binaus Bulan Januari 2016Sherly Haekase-TseNo ratings yet
- Sci Skill WKSHTDocument3 pagesSci Skill WKSHTsara gademNo ratings yet
- The First Injection in A Human Being of Macromolecules Whose Primary Structure Was Developed From A Religious TextDocument3 pagesThe First Injection in A Human Being of Macromolecules Whose Primary Structure Was Developed From A Religious TextHowTo HackNo ratings yet
- Codon Chart: U C A G UDocument3 pagesCodon Chart: U C A G UyesNo ratings yet
- Truce-: RazoleDocument65 pagesTruce-: RazoleShafinNo ratings yet
- Signature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1Document5 pagesSignature Assignment 4 Central Dogma 1api-709276885No ratings yet
- Fbs10 t3l #6ac - OppppDocument2 pagesFbs10 t3l #6ac - OppppHans Benedict PenaNo ratings yet
- Appendix I: IA IUPAC Nucleotide Ambiguity CodesDocument2 pagesAppendix I: IA IUPAC Nucleotide Ambiguity Codespeeps007No ratings yet
- Dna WsDocument1 pageDna WsLovryan Tadena AmilingNo ratings yet
- Gene Sequencing MethodsDocument41 pagesGene Sequencing MethodspavaniNo ratings yet
- Theorem 6.2.3Document9 pagesTheorem 6.2.3De SebNo ratings yet
- LEPOK 500g rm25Document1 pageLEPOK 500g rm25wan syazwanNo ratings yet
- Activity Title: Learning Targets: Reference (S)Document5 pagesActivity Title: Learning Targets: Reference (S)Jhev LeopandoNo ratings yet
- POGIL - Gene - Expression Translation SDocument8 pagesPOGIL - Gene - Expression Translation Sandrew fortneyNo ratings yet
- Biology VCE Unit 3, Chapter 3 TestDocument9 pagesBiology VCE Unit 3, Chapter 3 Testnidhi patelNo ratings yet
- Exam ConsolidatedDocument69 pagesExam ConsolidatedAnonymous jzlQevBxNo ratings yet
- HWA CHONG INSTITUTION 2021-2022 H2 BIOLOGY CORE IDEA 2 GENE AND CHROMOSOMAL MUTATIONS PRACTICE QUESTIONSDocument15 pagesHWA CHONG INSTITUTION 2021-2022 H2 BIOLOGY CORE IDEA 2 GENE AND CHROMOSOMAL MUTATIONS PRACTICE QUESTIONSErvin LimNo ratings yet
- Kirk Polka - Genetic Code WorksheetsDocument3 pagesKirk Polka - Genetic Code WorksheetsKirk PolkaNo ratings yet
- IndiaDocument1 pageIndiaanjanayanNo ratings yet
- Activity#1 Split DNA (Old Strand) New DNA Strand Split DNA (Old Strand) New Dna StrandDocument4 pagesActivity#1 Split DNA (Old Strand) New DNA Strand Split DNA (Old Strand) New Dna StrandfaithNo ratings yet
- NPM Directory - Upper Level 1.23.23Document1 pageNPM Directory - Upper Level 1.23.23ww18550No ratings yet
- signature assignment 4 central dogmaDocument6 pagessignature assignment 4 central dogmaapi-631586093No ratings yet
- Ambu QuixDocument1 pageAmbu QuixJose A AngelNo ratings yet
- Genetic code amino acid chartDocument3 pagesGenetic code amino acid chartESCUETA John RobertNo ratings yet
- My DnaDocument1 pageMy DnaAlmir BatacNo ratings yet
- PATH+Molecular Best Mohammad a Vasef MD, Aaron Auerbach MD MPH - Diagnostic Pathology_ Molecular Oncology (2019, Elsevier)Document1,005 pagesPATH+Molecular Best Mohammad a Vasef MD, Aaron Auerbach MD MPH - Diagnostic Pathology_ Molecular Oncology (2019, Elsevier)cristina.mazaroaieNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chem.Document6 pagesClass XI Chem.ImmortalNo ratings yet
- Achievement-Chartnew - Xls 1Document1 pageAchievement-Chartnew - Xls 1Sherry Ann C. CervantesNo ratings yet
- Achievement Chart BarDocument3 pagesAchievement Chart BarDM Riel0% (1)
- Review TestDocument5 pagesReview TestPoppy SmokeNo ratings yet
- APQP-ADVANCED PRODUCT QUALITY & CONTROL PLAN 2 ND Edi Manual 115 PagesDocument115 pagesAPQP-ADVANCED PRODUCT QUALITY & CONTROL PLAN 2 ND Edi Manual 115 PagesPaul RosiahNo ratings yet
- The Crimson Cowboys: The Remarkable Odyssey of the 1931 Claflin-Emerson ExpeditionFrom EverandThe Crimson Cowboys: The Remarkable Odyssey of the 1931 Claflin-Emerson ExpeditionNo ratings yet
- Proper Care and Use of Personal Dosimeters: HandlingDocument1 pageProper Care and Use of Personal Dosimeters: HandlingAshley JacksonNo ratings yet
- Public Stormwater Management With Green StreetsDocument90 pagesPublic Stormwater Management With Green StreetsPranay ManwarNo ratings yet
- How To Check A Capacitor With Digital Multimeter and Analog AVO Meter. by Four (5) Methods With Pictorial ViewDocument7 pagesHow To Check A Capacitor With Digital Multimeter and Analog AVO Meter. by Four (5) Methods With Pictorial ViewDivagar PNo ratings yet
- Payroll Accounting 2015 1st Edition Landin Test Bank 1Document106 pagesPayroll Accounting 2015 1st Edition Landin Test Bank 1dorothy100% (47)
- BD 1050 PartesDocument26 pagesBD 1050 PartesFelipe RojasNo ratings yet
- 20090716FoxReiki PDFDocument40 pages20090716FoxReiki PDFAgustina RomeroNo ratings yet
- Vetotop Doc Technical Map en 3573Document4 pagesVetotop Doc Technical Map en 3573Rebel XNo ratings yet
- Non-Digestible Oligosaccharides: A Review: Solange I. Mussatto, Ismael M. MancilhaDocument11 pagesNon-Digestible Oligosaccharides: A Review: Solange I. Mussatto, Ismael M. MancilhaPatrícia Felix ÁvilaNo ratings yet
- Manual Book IOG ConventionDocument17 pagesManual Book IOG ConventionTaufiq MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurs That Changed The Face of IndiaDocument4 pagesEntrepreneurs That Changed The Face of Indiamarykavitha_6No ratings yet
- Denawaka GangaDocument9 pagesDenawaka GangaErandikaNo ratings yet
- Urban Heat Island effect document answersDocument4 pagesUrban Heat Island effect document answersAlainDelonTahilLanaNo ratings yet
- Income Tax BasicsDocument48 pagesIncome Tax BasicsAzad Singh BajariaNo ratings yet
- 14 People V Manalo (Verba Legis)Document15 pages14 People V Manalo (Verba Legis)zeynNo ratings yet
- Agco - DBB - f68.f69Document6 pagesAgco - DBB - f68.f69Mohd Khairi Mohd NorzianNo ratings yet
- Hyperfunctional Voice DisordersDocument11 pagesHyperfunctional Voice DisordersJam PNo ratings yet
- CHEMDocument20 pagesCHEMValli RamalingamNo ratings yet
- SorghumDocument13 pagesSorghumMohaajanan AliNo ratings yet
- Help to Buy ISA GuideDocument4 pagesHelp to Buy ISA GuidefsdesdsNo ratings yet
- What Is A PronounDocument9 pagesWhat Is A PronounFanera JefferyNo ratings yet
- Cost Control ReviewerDocument13 pagesCost Control ReviewerMatthew Ivan HerreraNo ratings yet
- Bab 06 PindahPanasDocument41 pagesBab 06 PindahPanasPurna Satria NugrahaNo ratings yet
- The Strange ICA Stones of PeruDocument31 pagesThe Strange ICA Stones of PeruRoman Aleshkevich100% (1)
- Wrap Book A4Document27 pagesWrap Book A4doscribe100% (1)
- ANIMAL BEHAVIOR SCIENCEDocument37 pagesANIMAL BEHAVIOR SCIENCEZ AlbertNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument10 pagesResearch ProposalRonNo ratings yet
- Ecl7000 enDocument2 pagesEcl7000 ensuchaya tupyangNo ratings yet
- Mcqs of Family LawDocument24 pagesMcqs of Family LawVenugopal Mantraratnam32% (19)
- Health Behaviour: Current Issues and ChallengesDocument13 pagesHealth Behaviour: Current Issues and ChallengesK.A.No ratings yet
- GER Bangladesh EngDocument12 pagesGER Bangladesh Engfarhan.anjum20032004No ratings yet