Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osmosis in Plant & Animal Cells
Uploaded by
Brooke MorganCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Osmosis in Plant & Animal Cells
Uploaded by
Brooke MorganCopyright:
Available Formats
>» 4 Describe how your investigation has modelled the process of osmosis.
5 Outline any limitations of your model.
6 Discuss improvements that could be made to your model of osmosis.
EXees
Write a conclusion to link your results to the aim of the investigation.
A solution is formed when a solute dissolves in solvent.
KEY CONCEPTS
A concentrated solution has a high concentration of solute and a low concentration of water.
e@
A dilute solution has a low concentration of solute and a high concentration of water.
@
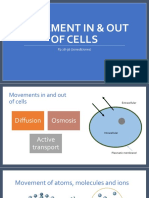
Osmosis is the process by which water moves from a region of high concentration of water
eo
(dilute —- low solute) to a region of low concentration of water (concentrated — high solute).
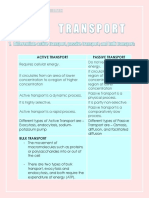
Osmosis requires no energy input.
e The more water that moves across the membrane, the higher the osmotic pressure created.
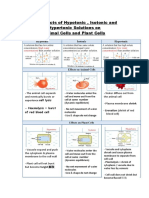
e Isotonic — fluids inside and outside a cell are of equal solute concentration — no net water
movement.
e Hypertonic - a solution of higher solute concentration (lower water concentration) that
surrounds a cell - net movement of water molecules will be out of the cell.
e Hypotonic—a solution of lower solute concentration (higher water concentration) that
surrounds a cell- net movement of water molecules will be into the cell.
Osmosis in animal cells
The cells of unicellular eukaryotes are surrounded only by a cell membrane. Hypertonic solutions, such
as fresh water, pose a problem because water moving into animal cells by osmosis can cause the cell to
swell and eventually burst the cell membrane, killing the organism.
Cells in most animals are not directly exposed to the external environment and are bathed in isotonic
extracellular fluid. This means that cells can function efficiently because water diffuses equally in both
directions, resulting in no net movement of water into or out of cells. The water concentration in animal
cells needs to be kept constant to coordinate biochemical reactions.
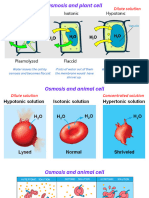
Osmosis in plant cells
Unlike animal cells, plant cells will not burst when soaked in fresh water (hypotonic solution), even
though water moves into the cells by osmosis.
Plant cells usually have large, fluid-filled vacuoles and firm, semipermeable cell walls that surround the
cell membrane. Plant cell vacuoles contain cell sap that has a high concentration of solutes and therefore
a low concentration of water. When a hypotonic solution surrounds a plant cell, water molecules move
by osmosis into the vacuole. This causes the vacuole to swell and pushes the cell membrane outwards
against the cell wall. The tough cell wall prevents the cell from bursting. When the cell wall stretches as
much as possible, no more water can enter and the cell is said to be turgid (Fig. 3.13a). In this state, the
osmotic pressure inside the cell is equal to the opposing pressure exerted by the cell wall.
Ifthe plant cells were to be placed into a hypertonic solution, the water in the cell would leave the cell
by osmosis, the vacuole would shrink and cause the cell membrane to move away from the cell wall ina
process called plasmolysis (Fig. 3.13b).
407281 CHAPTER 3 » CEl FUNCTION va
Water enters vacuole
Adapted from Biology: Prinicples & Processes by Roberts, Reiss & Monger (Nelson Thornes Ltd 2000)
by osmosis
Vacuole expands,
© Cell placed in external cytoplasm pushed outwards
solution whose solute
concentration is lower
than that of the cell sap
Cellulose wall Full turgor
Cytoplasm
Vacuole
containing
cell sap
Water leaves
Partially turgid vacuole by osmosis
plant cell
Vacuole shrinks,
© Cell placed in external cytoplasm moves inwards
solution whose solute
concentration is higher
than that of the cell sap
Full plasmolysis
FIGURE 3.13 The effect of immersing a partially turgid plant cell in a pure water (hypotonic solution) and b a high solute concentration (hypertonic solution)
CHECK YOUR
TMS See Draw a generalised diagram to represent a cell. On this diagram, indicate with arrows going into the cell
the substances that a cell requires. Also indicate the wastes that have to be removed from the cell, using
arrows pointing out of the cell.
2 Distinguish between a permeable membrane and a selectively permeable membrane.
3. a_ Identify and outline three characteristics of molecules that affect the permeability of the cell membrane
to them.
b |Indicate whether each of the following substances can move easily through the cell membrane or not.
Justify each of your answers.
i Neutral molecules such as carbon dioxide and oxygen gas
ii Sodium and potassium ions
iii, Water and ethanol
iv Large molecules such as proteins
4 Asugar solution is a mixture of sugar and water.
Identify the a solute and b solvent.
5 a Outline the process of diffusion.
b_ Identify two factors that could increase the rate of diffusion.
6 a Identify the substances that are able to move across the cell membrane by diffusion.
b Describe the process of facilitated diffusion.
c¢ Which substances move across the cell membrane using this process?
7 a Describe the process of osmosis.
b What is the relationship between diffusion and osmosis?
c Define the terms ‘isotonic; ‘hypotonic’ and ‘hypertonic’
78 MODULE ONE » CELLS AS THE BASIS OF LIFE
You might also like
- Unit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFDocument47 pagesUnit-I-IMTH-III (Osmosis, Types of Solution & Plasmolysis) PDFanuksha aroraNo ratings yet
- Final OsmosisDocument2 pagesFinal Osmosisapi-523278684No ratings yet
- Osmosis: + Factors Affecting The Rate of MovementDocument44 pagesOsmosis: + Factors Affecting The Rate of MovementCharlotte BurkeNo ratings yet
- 7 EbfcDocument3 pages7 EbfcRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- 1TheCellOsmosis - Diffusion 200825 123143 PDFDocument5 pages1TheCellOsmosis - Diffusion 200825 123143 PDFAlicia O CallaghanNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Class 9Document5 pagesBiology Notes Class 9lalitha muraliNo ratings yet
- IB Biology D Continuity and Change pt1Document5 pagesIB Biology D Continuity and Change pt1rellomharazNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: 1 MechanismDocument6 pagesOsmosis: 1 MechanismsnowflomanNo ratings yet
- Biology - Movement in and Out of CellsDocument3 pagesBiology - Movement in and Out of CellssimplyshriyaNo ratings yet
- Effect Solution On Plant CellsDocument9 pagesEffect Solution On Plant CellsNur FatihahNo ratings yet
- The Vacuole: What Is A Vacuole?Document3 pagesThe Vacuole: What Is A Vacuole?Amber L.No ratings yet
- LO: - Define Osmosis and Explain How Does It Work: Starter: (In The Back of Your Book)Document21 pagesLO: - Define Osmosis and Explain How Does It Work: Starter: (In The Back of Your Book)nidhiNo ratings yet
- 2 2 OsmosisDocument25 pages2 2 OsmosisAyah FNo ratings yet
- Topic 1-Osmosity and Tonicity - EditedDocument6 pagesTopic 1-Osmosity and Tonicity - Editedsalve joy villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document5 pagesLab Report 3Dunya FANo ratings yet
- 08T3 3OsmosisinCellsDocument4 pages08T3 3OsmosisinCellsprameetaNo ratings yet
- Movement of Substances Across A Plasma Membrane in Living OrganismsDocument25 pagesMovement of Substances Across A Plasma Membrane in Living OrganismsDewi SallehNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument11 pagesOsmosisIscariot PriestNo ratings yet
- Movement in & Out of Cells: PP 28-36 (Jones&Jones)Document13 pagesMovement in & Out of Cells: PP 28-36 (Jones&Jones)Matteo CacioppoNo ratings yet
- NCERT - Science - Lab - Manual - IX - Expt - 21Document3 pagesNCERT - Science - Lab - Manual - IX - Expt - 21Sunny ChopraNo ratings yet
- Biology CourseworkDocument13 pagesBiology CourseworkMiss_M90100% (1)
- Class 9 Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument30 pagesClass 9 Fundamental Unit of LifePravita K dasNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument25 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnNo ratings yet
- Notes - Movement of SubstancesDocument8 pagesNotes - Movement of SubstancesEricNo ratings yet
- 3 Movement Into & Out of CellsDocument4 pages3 Movement Into & Out of CellsmeerzasarahNo ratings yet
- Osmosis in Animal and Plant CellsDocument22 pagesOsmosis in Animal and Plant Cellsmaria virginia perlasNo ratings yet
- Osmosis QuestionsDocument13 pagesOsmosis QuestionsByambazaya ENo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 3.3Document4 pagesBiology Chapter 3.3Xinpei ShimNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Modes of Absorption and Conduction of WaterDocument60 pages4.3 Modes of Absorption and Conduction of WaterankurbiologyNo ratings yet
- Osmosis ReportDocument14 pagesOsmosis ReportKhai Zyann OcayNo ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument5 pagesCELLSJermaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Hypotonic, Isotonic N Hypertonic SolutionDocument41 pagesHypotonic, Isotonic N Hypertonic Solutionaida maro86% (7)
- Biology TestDocument7 pagesBiology TestAgustina GibautNo ratings yet
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranNo ratings yet
- Effect of Water Potential On Plant CellDocument2 pagesEffect of Water Potential On Plant CellWalwin HareNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument11 pagesOsmosisShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document3 pagesTopic 1Jonathan ObejaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNo ratings yet
- Plasma MembraneDocument66 pagesPlasma Membranenurul atika100% (2)
- Objectives: Elodea PlantDocument4 pagesObjectives: Elodea PlantEbby NisaNo ratings yet
- Applications of DiffusionDocument2 pagesApplications of DiffusionAmelia LimNo ratings yet
- Bio HomeworkDocument4 pagesBio HomeworkKamel BsaisoNo ratings yet
- PlasmolysisDocument2 pagesPlasmolysisRahman OlaitanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesTopic 3: Diffusion AND Osmosis: ObjectivesAidah JasniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture: Cells That Connect Body PartsDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture: Cells That Connect Body PartsGabriel EmperioNo ratings yet
- TonicityDocument27 pagesTonicityAirus SamaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEDocument37 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis - IGCSEJohnnie ZhangNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesCellular Structure and Functionsalmasadiq2008No ratings yet
- Transport MechanismDocument19 pagesTransport MechanismAaron Roxas100% (2)
- Membrane TransportDocument25 pagesMembrane TransportvvNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - TonicityDocument1 pageModule 1 - TonicitySam TagardaNo ratings yet
- 4-Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane in Everyday Life - 4Document34 pages4-Movement of Substances Across The Plasma Membrane in Everyday Life - 4nurulaznida50% (2)
- Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesPlasma MembraneNishi MenonNo ratings yet
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocument414 pagesMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaNo ratings yet
- Cellular TransportDocument51 pagesCellular TransportMarc Ian YoungNo ratings yet
- Active Transport Passive Transport: Perez, Jellie Lenn G. STM 14Document5 pagesActive Transport Passive Transport: Perez, Jellie Lenn G. STM 14Pangkat Lima Pagbasa at PagsusuriNo ratings yet
- S.O.P 1Document7 pagesS.O.P 1vishvendanNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 1 Activity 4Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 1 Activity 4CLAUDIA ELISABET BECERRA GONZALESNo ratings yet
- World Precision Instruments 2017 101 Things Catalog PDFDocument52 pagesWorld Precision Instruments 2017 101 Things Catalog PDFselleriverketNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Is No More A Mystery With Dilshad Sir Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesChemistry Is No More A Mystery With Dilshad Sir Chapter Practice ProblemsArnav AmbastaNo ratings yet
- M30 Normal - Mix Design With Trial SheetDocument4 pagesM30 Normal - Mix Design With Trial Sheetabir senguptaNo ratings yet
- PV - 1210 - EN 14482 - Corrosion Test PDFDocument5 pagesPV - 1210 - EN 14482 - Corrosion Test PDFAniruddha HawalNo ratings yet
- Applied ChemistryDocument300 pagesApplied ChemistryMohaideen SubaireNo ratings yet
- Index Phytosaniatire Maroc ONSSA 04 02 18Document669 pagesIndex Phytosaniatire Maroc ONSSA 04 02 18El Hachimi YacineNo ratings yet
- Easy Way To Score in Organic ChemistryDocument2 pagesEasy Way To Score in Organic ChemistryRoopa KhenedNo ratings yet
- ASSTM A882 - Epoxy Coated PC StrandDocument5 pagesASSTM A882 - Epoxy Coated PC StrandLai DieuNo ratings yet
- Give The Application and Scenarios Where Chemical and Physical Methods of Sterilization Are Best To UseDocument5 pagesGive The Application and Scenarios Where Chemical and Physical Methods of Sterilization Are Best To UseEarly SaribaNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Oil-Based Epoxy Resins and Their Composites With Bio-Based Hardener: A Short ReviewDocument17 pagesVegetable Oil-Based Epoxy Resins and Their Composites With Bio-Based Hardener: A Short ReviewbelkhamasNo ratings yet
- NCHE312Document11 pagesNCHE312Charmaine MoyoNo ratings yet
- Pore Classification in The Characterization of Porous Materials - A PerspectiveDocument24 pagesPore Classification in The Characterization of Porous Materials - A PerspectiveAnh Thơ Nguyễn QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Radiation Curing Os CoatingsDocument9 pagesRadiation Curing Os CoatingsLangleyNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Utilization of Crushed Solar Panel Waste As Sand Replacement in ConcreteDocument8 pagesExperimental Investigation On Utilization of Crushed Solar Panel Waste As Sand Replacement in ConcreteManoel HenriqueNo ratings yet
- 48 BD 08Document34 pages48 BD 08Mayur UrkudeNo ratings yet
- Hindawi Al Sulfat Accelerator 813052Document15 pagesHindawi Al Sulfat Accelerator 813052sanken ToshiNo ratings yet
- Week 3 & 4. Chemical Equilibria in Solution. TitrationDocument82 pagesWeek 3 & 4. Chemical Equilibria in Solution. TitrationChi NguyenNo ratings yet
- TechnicalspecificationsofheatexchangeralongwithSOI 20200314062818.362 XDocument78 pagesTechnicalspecificationsofheatexchangeralongwithSOI 20200314062818.362 XAvinash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Astm C 1602-2018Document5 pagesAstm C 1602-2018Mohammed Ali0% (1)
- Nucleate Boiling Heat Transfer Coefficients of Flammable Refrigerants On Various Enhanced TubesDocument5 pagesNucleate Boiling Heat Transfer Coefficients of Flammable Refrigerants On Various Enhanced TubesChinniRohithaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & Ether - AnswersDocument6 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & Ether - AnswersK. RupaNo ratings yet
- Cleanliness of Components For Use in Oxygen, Fuel, and Pneumatic Systems, Specification ForDocument27 pagesCleanliness of Components For Use in Oxygen, Fuel, and Pneumatic Systems, Specification ForOmNo ratings yet
- CH312 - COD Experiment ReportDocument3 pagesCH312 - COD Experiment ReportNarelle IaumaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Chemistry-I Assignment No 4: Hadia RaufDocument23 pagesIndustrial Chemistry-I Assignment No 4: Hadia RaufSIDRA NAZEER SAIFNo ratings yet
- 2 - Denaturation of ProteinDocument3 pages2 - Denaturation of ProteinnotshiroNo ratings yet
- Product Description Sheet Nordbak High Temperature Pneu-WearDocument2 pagesProduct Description Sheet Nordbak High Temperature Pneu-WearANDRESMARTESNo ratings yet
- Printing TextileDocument23 pagesPrinting TextileShresha DasNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Chemistry 9701/22 May/June 2017Document9 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Chemistry 9701/22 May/June 2017Javohirbek QobuljonovNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Lymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthFrom EverandLymph & Longevity: The Untapped Secret to HealthRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Change Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessFrom EverandChange Your Brain, Change Your Life (Before 25): Change Your Developing Mind for Real-World SuccessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)