Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arrhythmia Recognition Poster Part 2
Uploaded by
Gwen LylesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arrhythmia Recognition Poster Part 2
Uploaded by
Gwen LylesCopyright:
Available Formats
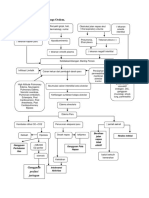
Arrhythmia Recognition
Premature Ventricular Conduction Pacemaker Lead Placement ST Segment Depression
Pacing Lead Pacing Lead
v1 v1
J point
Atrial Ventricular AV Sequencial
Pacing Pacing Pacing Downsloping ST Upsloping ST Horizontal ST
The pacing lead is The pacing lead is The pacing lead is The J point occurs at the end of the QRS complex.
inserted into the inserted into the inserted into the The ST segment begins at the J point and extends to a user-defined interval.
Right Ventricular PVC Left Ventricular PVC atrium to cause ventricle to cause both the atrium and
atrial depolarization. ventricular ventricle stimulating
depolarization. at set intervals.
Ventricular Rhythms Pacemaker Rhythms
Premature Ventricular Complex - PVC Ventricular Fusion Beat Electronic Pacemaker Spikes Failure to Capture
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds)
N/A Irregular with N/A N/A ≥ 0.12
PVCs
Unifocal PVCs: Identical shapes
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds) Electrical stimuli delivered by the electronic pacemaker to the
N/A N/A Present Same as sinus ≥ 0.12 endocardium are seen as a spike on the surface ECG.
rhythm or shorter The pacemaker generates a pacemaker spike
but does not cause an intrinsic beat (P wave or QRS).
Ventricular Escape Beat Ventricular Pacemaker (single chamber)
Failure to Sense
Multifocal PVCs: More than one shape
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds)
< 40 bpm Irregular Absent Absent ≥ 0.12
Single spike producing a wide QRS complex
(ventricular capture).
Idioventricular Rhythm
Atrial Pacemaker (single chamber)
The pacemaker does not recognize the intrinsic beats
and generates an unnecessary pacemaker spike.
Failure to Fire
Paired PVCs (Couplet)
Single spike producing paced P wave
(atrial capture) followed by an intrinsic QRS complex.
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds)
20 - 40 bpm Regular Absent or not related N/A ≥ 0.12 AV Sequential Pacemaker (dual chamber)
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm (AIVR)
The pacemaker does not generate
a pacemaker spike when it is needed.
R on T Phenomenon: PVC occurs at the peak
of the of T wave of the preceding beat
First spike followed by a paced P wave (atrial capture)
followed by a second spike producing a wide QRS complex
(ventricular capture).
ECG Artifact
Paced Fusion Beat Any waveform on the ECG
that is not related to the patient’s cardiac events
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Calibration Pulses
(in seconds) (in seconds)
40 - 100 bpm Regular Absent, not related N/A ≥ 0.12
Ventricular Bigeminy: Every other beat is a PVC or retrograde
conduction
Ventricular Tachycardia
(3 or more consecutive ventricular complexes)
The electronic pacemaker and the patient’s own cardiac
rhythm occurs simultaneously producing a combination Deliberate artifact caused to show the interpreter the
of a paced beat and an intrinsic beat. relationship of the complexes with a known electrical
stimulus (standardization procedure).
AC Interference (60 cycle)
Full Compensatory Pause
vs. Noncompensatory Pause
Ventricular Trigeminy: Every third beat is a PVC
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds)
> 100 bpm Regular Absent, not related N/A ≥ 0.12
or retrograde
conduction 1:1. 1:2, Sixty even, regular spikes in a one-second interval
or VA Wencheback
caused by electrical current near the patient.
Ventricular Fibrillation Muscle Tremor (Somatic)
Full Compensatory Pause
Ventricular Quadrigeminy:
Every fourth beat is a PVC
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
(in seconds) (in seconds)
300 - 600 bpm Extremely Absent Absent Absent
irregular
Ventricular Asystole Noncompensatory Pause Electrical interference
caused by the patient’s tensed muscles.
To measure a Full Compensatory Pause:
Wandering Baseline (Draft)
Heart Rate Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS preceding the premature complex.
(in seconds) (in seconds) 3. The third mark should fall exactly on the P wave following
Absent Absent Absent or present Absent Absent the premature complex to be called a compensatory pause.
Normal ECG Standards for Children Age
Arrhythmia Recognition (poster 2 of 2) 0-1d 1-3d 3-7d 7 - 30 d 1 - 3 mo 3 - 6 mo 6 - 12 mo 1-3y 3-5y 5-8y 8 - 12 y 12 - 16 y The most common ECG rate, interval, and duration measurements
This is part two of two posters to assist healthcare professionals in Heart 94 - 155 91 -158 90 - 166 106 - 182 120 - 179 105 - 185 108 - 169 89 - 152 73 - 137 65 - 133 62 - 130 60 - 120 are from the following publications:
Rate/Min (122) (122) (128) (149) (149) (141) (131) (119) (109) (100) (91) (80)
recognizing basic arrhythmias. According to the Practice Standards for PR Interval
• Clinical Electrocardiography (Post Graduate Institute for Medicine).
0.08 - 0.16 0.08 - 0.14 0.07 - 0.15 0.07 - 0.14 0.07 - 0.13 0.07 - 0.15 0.07 - 0.16 0.08 - 0.15 0.08 - 0.16 0.09 - 0.16 0.09 - 0.17 0.09 - 0.18
Electrocardiographic Monitoring in Hospital Settings (Circulation. Lead II
(seconds)
(0.107) (0.108) (0.102) (0.100) (0.098) (0.105) (0.106) (0.113) (0.119) (0.123) (0.128) (0.135) • Understanding Electrocardiography (Mary Boudreau Conover).
2004;110;2721-2746) in general, the mechanisms of arrhythmias are the QRS Interval 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.07 0.02 - 0.08 0.02 - 0.08 0.02 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.08 0.03 - 0.07 0.03 - 0.08 0.04 - 0.09 0.04 - 0.09
• How to Quickly and Accurately Master Arrhythmia Interpretation (Dale Davis).
same in both adults and children. However, the ECG appearance of the Lead V5 (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.05) (0.06) (0.06) (0.06) (0.06) (0.07)
• Principles of Clinical Electrocardiography (M. J. Goldman).
(seconds) An undulating baseline
All values 2nd – 98th percentile; numbers in parentheses, means. Adapted from
Pediatr Cardiol. 1979;1:123. • Basic Dysrhythmias Interpretation and Management (Robert Huszar).
baseline heart rate, sinus and AV node function, and automatic with waveform present.
Innervation. • An Introduction to Electrocardiography (Leo Shamroth).
This poster includes Premature Ventricular Conduction, Pacemaker Lead Placement, ST Segment • Interpretation of Arrhythmias (Emanual Stein ).
ECG terminology and diagnostic criteria often vary from text to text and Depression, Ventricular Rhythms, Pacemaker Rhythms, Full Compensatory Pause and ECG Artifact.
from one teacher to another. There are often several terms describing The ECG rhythm Strips display lead II as the top waveform and lead V1 as the bottom waveform.
Classic examples are shown for each rhythm to provide basic visualization and avoid complexities.
Premature Complex, Atrial Extrasystole, Supraventricular Ectopic Beat, The intended use of this poster is to complement a text and/or course – in addition to a reference
etc.) It is important to correlate the ECG interpretation with the clinical guide for arrhythmia recognition
observation of the patient.
gehealthcare.com © 2019 General Electric Company – All rights reserved.
DOC1178264 Rev2
You might also like
- Ccu Survival GuideDocument10 pagesCcu Survival Guideomegasauron0gmailcom100% (1)
- The 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsFrom EverandThe 12-Lead Electrocardiogram for Nurses and Allied ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- EKG Quick Reference ChartDocument4 pagesEKG Quick Reference ChartMildaNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG: Dr. Rita A. Dello StrittoDocument18 pages12 Lead EKG: Dr. Rita A. Dello Strittocuteralph1972No ratings yet
- Ecg CookbookDocument2 pagesEcg CookbookCalin Popa100% (1)
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYDocument75 pagesELECTROCARDIOGRAPHYMeliaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - 4th - EdDocument35 pagesRespiratory System - 4th - EdJen100% (1)
- How To Interpret An ECG in Seven StepsDocument5 pagesHow To Interpret An ECG in Seven StepsCM NajitoNo ratings yet
- Normal Pediatric RR and HRDocument1 pageNormal Pediatric RR and HRRick FreaNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms SlideDocument26 pagesACLS Algorithms SlidehrsoNo ratings yet
- 11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFDocument16 pages11 Steps of ECG - Ali Alnahari PDFBìnhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECG RhythmsDocument59 pagesIntroduction To ECG RhythmsIvona RagužNo ratings yet
- Ekg Panum or OsceDocument69 pagesEkg Panum or OsceGladish RindraNo ratings yet
- CCU Clinical GuidelinesDocument63 pagesCCU Clinical GuidelinesHAMMYER ALROKHAMINo ratings yet
- Cardio - ECGDocument13 pagesCardio - ECGSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Ecg Reading NotesDocument17 pagesEcg Reading NotesMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- EKG Quick Reference Chart: Route Rate Rhythm Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Rate Regularity Life Threatening CausesDocument4 pagesEKG Quick Reference Chart: Route Rate Rhythm Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS Rate Regularity Life Threatening CausesGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Practice StripsDocument9 pagesPractice StripsErica Yamamoto50% (4)
- Coumadin Dosing GuideDocument3 pagesCoumadin Dosing Guidemorale28No ratings yet
- Chest Tube Explanation by AllnursesDocument3 pagesChest Tube Explanation by AllnursesYemaya84No ratings yet
- Poster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFDocument1 pagePoster1 Arrhythmia Recognition e PDFSergio ChangNo ratings yet
- Acls Seminar MeDocument62 pagesAcls Seminar MeAbnet Wondimu100% (1)
- ACLS Provider Manual Supplementary MaterialDocument86 pagesACLS Provider Manual Supplementary MaterialEma0% (2)
- Basic Ecg: - Department of Medicine BIMC Hospital 2013Document60 pagesBasic Ecg: - Department of Medicine BIMC Hospital 2013LexadkNo ratings yet
- LS Identifying ArrhythmiasDocument5 pagesLS Identifying ArrhythmiasClaudia Park100% (1)
- Thoracic Spine and Ribs PDFDocument334 pagesThoracic Spine and Ribs PDFSurender DhillonNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNDocument34 pagesBasic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNMavic Martinez BuntalesNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Document6 pagesACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cases in Right Heart FailureFrom EverandClinical Cases in Right Heart FailureLana TsaoNo ratings yet
- Basic EKG Interpretation ExamDocument13 pagesBasic EKG Interpretation Examtwdroppoint100% (1)
- CH 11 Cardiovascular-SystemDocument113 pagesCH 11 Cardiovascular-SystemHazel Banday100% (1)
- Sample Acls For DummiesDocument3 pagesSample Acls For DummiesTodd Cole100% (1)
- Adult Early Warning Score Observation Chart For High Dependency UnitDocument2 pagesAdult Early Warning Score Observation Chart For High Dependency Unitalexips50% (2)
- St. John ICU ReportDocument2 pagesSt. John ICU ReportbouncedNo ratings yet
- Sinus Rhythm DisturbancesDocument3 pagesSinus Rhythm DisturbancesMarcus Philip GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Assessment: General ImpressionDocument2 pagesPediatric Assessment: General ImpressionAghnia Nafila100% (1)
- ECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersDocument7 pagesECG Quiz Review and Practice Strip AnswersAANo ratings yet
- Cs-Cardiac-023-Essential Cardiac LabsDocument2 pagesCs-Cardiac-023-Essential Cardiac LabsColeen YraolaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities For The Patient Will Undergo Cardiac CatheterizationDocument4 pagesNursing Responsibilities For The Patient Will Undergo Cardiac CatheterizationCharlene Jacobe Cornista100% (1)
- A Cardiomyopathy PPT NEWDocument62 pagesA Cardiomyopathy PPT NEWShetal Sharma100% (1)
- ECG Fast and Easy PPDocument38 pagesECG Fast and Easy PPTara McNeillNo ratings yet
- Systems BookletDocument8 pagesSystems Bookletapi-383568582No ratings yet
- Ecg Practice TestDocument1 pageEcg Practice TestSoySauceNo ratings yet
- 1008 1400 ACLS - StudyGuide Print PDFDocument54 pages1008 1400 ACLS - StudyGuide Print PDFWaqar HassanNo ratings yet
- HO - Burns Environmental EmergenciesDocument7 pagesHO - Burns Environmental EmergenciesSteven Paul DaclesNo ratings yet
- Anesthesiology Pre-Op Evaluation: ExovsrtsDocument1 pageAnesthesiology Pre-Op Evaluation: Exovsrtssabbo morsNo ratings yet
- Newborn Hal ManualDocument74 pagesNewborn Hal ManualPedz RomanoNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Ventilation 2014Document62 pagesBasic Mechanical Ventilation 2014dragon66No ratings yet
- The WHO Manual of Diagnostic Imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of The Chest and The Pulmonary SystemDocument154 pagesThe WHO Manual of Diagnostic Imaging Radiographic Anatomy and Interpretation of The Chest and The Pulmonary SystemAdiel Ojeda100% (1)
- Emergency Department Nursing Flow SheetDocument2 pagesEmergency Department Nursing Flow SheetDessi KayNo ratings yet
- A. WOC Acute Lungs Oedem.: Gangguan Perfusi JaringanDocument1 pageA. WOC Acute Lungs Oedem.: Gangguan Perfusi Jaringanrizki vitaNo ratings yet
- Zero Based BudgetDocument9 pagesZero Based Budgetapi-447860598No ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Critical Thinking in Patient Care Single Volume 4th Edition Lemone Test BankDocument4 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Critical Thinking in Patient Care Single Volume 4th Edition Lemone Test BankRebeccaGilliamNo ratings yet
- ACAQ Crit Care Nursing CurriculumDocument91 pagesACAQ Crit Care Nursing CurriculumAnne Julia Agustin100% (1)
- Arterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNDocument34 pagesArterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNinuko1212No ratings yet
- The Easy R's EKG Interpretation FinalDocument9 pagesThe Easy R's EKG Interpretation FinalMatar PaneerNo ratings yet
- Heart BlocksDocument6 pagesHeart BlocksMark Hammerschmidt100% (1)
- Dysrhythmia Instructor 2018 2 PDFDocument105 pagesDysrhythmia Instructor 2018 2 PDFtvrossyNo ratings yet
- Integrated ChecklistDocument2 pagesIntegrated ChecklistKena BenNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics For The Bedside Nurse 1CEUDocument7 pagesHemodynamics For The Bedside Nurse 1CEURN333100% (1)
- ACLS ChartDocument1 pageACLS ChartJev DespiNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Medication ChartDocument1 pageBlood Pressure Medication CharttmleNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Lungs BLACKWOODDocument360 pagesDiseases of Lungs BLACKWOODG AnshuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Mitral ValveDocument6 pagesAnatomy of Mitral ValvesrhubanbabuNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure Et Causa Rheumatic Heart Disease: (Laporan Kasus)Document7 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Et Causa Rheumatic Heart Disease: (Laporan Kasus)FerinaDwiMarindaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi PleuraDocument31 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi PleuraAjie LateNo ratings yet
- Folio 2022Document10 pagesFolio 2022fila markNo ratings yet
- Heart HistologyDocument11 pagesHeart HistologyAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationsDocument14 pagesBody Fluids and CirculationsNikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tricuspid AtresiaDocument44 pagesTricuspid Atresiadoctorsaty7539No ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument6 pagesCirculatory System NotesShayan UzzamanNo ratings yet
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument22 pagesCyanotic Congenital Heart DiseaseRaviNo ratings yet
- 1 Thoracic and Abdominal AneurysmDocument37 pages1 Thoracic and Abdominal AneurysmErneslito LucasNo ratings yet
- Fuctions of The Parts of The HeartDocument3 pagesFuctions of The Parts of The Heartsonia1519No ratings yet
- Chest TraumaDocument47 pagesChest Traumafrenee aradanasNo ratings yet
- Basicinterpretationofcxr 110913060449 Phpapp01Document84 pagesBasicinterpretationofcxr 110913060449 Phpapp01Alexandra DîrțuNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPleural EffusionRensa ArdsNo ratings yet
- Breast ScriptDocument2 pagesBreast ScriptKrysstal GerongaNo ratings yet
- The StethoscopeDocument2 pagesThe Stethoscopetanishkagupta002No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System-Heart: Miss Wheeler Unit 8Document29 pagesCardiovascular System-Heart: Miss Wheeler Unit 8Ngatchou GaelleNo ratings yet
- Disectii AorticeDocument61 pagesDisectii AorticeMadalinaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Blunt Chest Trauma With Multidetector Computed TomographyDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Blunt Chest Trauma With Multidetector Computed TomographyasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: Maryhill College College of Nursing Lucena City (ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-laboratory)Document6 pagesCirculatory System: Maryhill College College of Nursing Lucena City (ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-laboratory)Christa Villanueva MalinaoNo ratings yet