Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rate of Photosynthesis: Science Inquiry
Uploaded by
Jono ThanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rate of Photosynthesis: Science Inquiry
Uploaded by
Jono ThanCopyright:
Available Formats
3.6 Rate of photosynthesis 3.
6
3 Recall photosynthesis by writing its:
(a) word equation
Science inquiry
(b) balanced chemical equation.
Verbal/linguistic Logical/mathematical
4 Identify the limiting factor that stops photosynthesis from proceeding at night.
As the chemical equations below show, carbon dioxide and water have to be present
before photosynthesis can take place.
carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen
5 Plants don’t grow well in a drought. They may even die. Use your knowledge of
6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 photosynthesis to explain why this happens.
Although it is not a reactant, chlorophyll needs to be present. Sunlight is also needed,
because it powers the reaction. If any one of these is not available, then photosynthesis
slows down or stops. The factor that is missing or in short supply is called the limiting
6 Most caves have no plants in them. Identify the limiting factors of this environment
factor. In times of drought, water could be a limiting factor. If the stomata are closed to
save water, then carbon dioxide cannot enter the leaf, and carbon dioxide could become
the limiting factor.
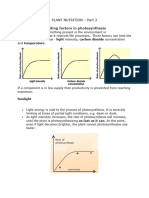
At night, light is the limiting factor and there is no photosynthesis. As the sun rises, the
rate of photosynthesis increases as the light intensity increases. Then, at some point, 7 (a) State the temperature that photosynthesis stops above.
the rate of photosynthesis does not increase any further. Something other than light is (b) Explain why photosynthesis stops above this temperature.
controlling the rate. When light is no longer the limiting factor, it is often the amount of
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, and the rate at which it can diffuse into the leaf, that
limits the rate of photosynthesis. This is shown in Figure 3.6.1.
8 Compare lines X and Y on the graph shown below.
No further increase can occur
without more CO2
Rate of photosynthesis
Oxygen produced
Carbon dioxide levels begin
to limit the reaction
As light intensity increases, more energy is X
available and the rate of photosynthesis increases
Figure
3.6.1 Light intensity Light intensity
The speed (rate) of most chemical reactions increases as the temperature increases. 9 Summarise what both lines on the graph show about photosynthesis as light
This is true of photosynthesis too, but only up to a point. The rate of photosynthesis intensity increases.
increases until the temperature reaches about 30°C. At this temperature, photosynthesis
decreases and then stops. This is because the enzymes that help photosynthesis along
are destroyed at temperatures greater than 30°C. Above 30°C the enzymes can no longer
function. 10 Discuss possible reasons for the difference in the lines.
1 For the photosynthesis reaction, list the names and chemical formulas of the:
11 Explain why the amount of oxygen produced is a good measure of the rate of
(a) reactants
photosynthesis taking place.
(b) products.
2 State what else is required for photosynthesis to occur.
You might also like
- b4 Bioenergetics Mastery Booklet Arb v2Document22 pagesb4 Bioenergetics Mastery Booklet Arb v2laurnawhittakerNo ratings yet
- 2.9 Photosynthesis WSDocument9 pages2.9 Photosynthesis WS한서현No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- IB Biology Notes - 38 PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesIB Biology Notes - 38 PhotosynthesisJohn Philip D. NapalNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Document8 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESIS-Student Worksheet (With Answers)Daniella Gabrielle Gerodias50% (10)
- 2.photosynthesis QusDocument7 pages2.photosynthesis QusAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractiveDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Hhmi BiointeractivemariaNo ratings yet
- PLANT NUTRITION Part 2Document10 pagesPLANT NUTRITION Part 2dineo kabasiaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Section 2 Lesson 2Document56 pagesIgcse Biology Section 2 Lesson 2treeker10No ratings yet
- Topic 2.9 W.SDocument11 pagesTopic 2.9 W.SChristie Fadi MARDININo ratings yet
- Kami Export - ALEXA CADENA - PhotosynthesisLabSE - Google Doc VersionDocument5 pagesKami Export - ALEXA CADENA - PhotosynthesisLabSE - Google Doc VersionALEXA CADENANo ratings yet
- Leaf in DepthDocument49 pagesLeaf in DepthTarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Photosynthesis Lab: OxygenDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Photosynthesis Lab: OxygenAnthony HernandezNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument14 pagesCalvin CycleWahyu ArifNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Extended EssayDocument28 pagesChemistry Extended EssayDarren Tan50% (2)
- Photosynthesis Study GuideDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study GuideLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Session BookletDocument21 pagesPlant Physiology Session BookletDeepak BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- B8 - PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageB8 - PhotosynthesisShalini MishraNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryKhubaib BaryaalNo ratings yet
- 3.10 Plants and Food - PhotosynthesisDocument23 pages3.10 Plants and Food - PhotosynthesisChi In SoNo ratings yet
- I. Photosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) : Quarter 2 / Semester 1, Week 2Document6 pagesI. Photosynthesis (Light and Dark Reaction) : Quarter 2 / Semester 1, Week 2Monica SolomonNo ratings yet
- How Light Intensity Affects The Rate of Photosynthesis in PondweedDocument3 pagesHow Light Intensity Affects The Rate of Photosynthesis in PondweedLovin JoseNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: STEP Grade 9Document14 pagesPhotosynthesis: STEP Grade 9Lo ViNo ratings yet
- BioA4 09. Nutrition and Gas Exchange in PlantDocument8 pagesBioA4 09. Nutrition and Gas Exchange in Plantthanks btNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Rates of Reaction: Chemguide - QuestionsDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Rates of Reaction: Chemguide - QuestionsFatma MoustafaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (3 Meetings) OkDocument27 pagesPhotosynthesis (3 Meetings) Okshanta gintingNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument4 pagesBiologyMai Nhiên Lê NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of PhotosynthesisNurul AthirahNo ratings yet
- 2022 Metabolism and EnergyDocument35 pages2022 Metabolism and EnergyClaire WeerepasNo ratings yet
- Photo Synths GDocument8 pagesPhoto Synths Gno moovNo ratings yet
- ESEN 340 Slide4-PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesESEN 340 Slide4-PhotosynthesisAyda SipahioğluNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NotesDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesis Notesapi-544344393100% (2)
- Limiting FactorsDocument14 pagesLimiting FactorsAdam ChiangNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument2 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISVivien LancinNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio W2Document3 pagesGen Bio W2Alyson EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Knowledge OrganiserDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis Knowledge Organiserapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Plant Metabolism Stern's Plant Biology Flashcards - QuizletDocument21 pagesChapter 10 - Plant Metabolism Stern's Plant Biology Flashcards - QuizletChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- C1.3 PhotosynthesisDocument42 pagesC1.3 PhotosynthesisteddyenNo ratings yet
- 3.8 Chemical Reactions Human BiologyDocument9 pages3.8 Chemical Reactions Human Biologygienoa ablaoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Part 1Document27 pagesPhotosynthesis Part 1m4h1rstNo ratings yet
- ChI06 Rates of Reaction TMA B 0817Document21 pagesChI06 Rates of Reaction TMA B 0817Husnul YaqinNo ratings yet
- 14 Photosynthesis and Respiration-KEYDocument6 pages14 Photosynthesis and Respiration-KEYsenjics100% (1)
- (Final) PhotosynthesisDocument10 pages(Final) PhotosynthesisAmanKukreja100% (1)
- Gizmos: Photosynthesis LabDocument5 pagesGizmos: Photosynthesis LabRandom DooodNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsDineth Gunasekera - Chinguacousy SS (2422)No ratings yet
- Essay Questions On PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesEssay Questions On Photosynthesislhydupvcf100% (1)
- PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesisShannen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document11 pagesChapter 13ririrachma fitriahNo ratings yet
- Chem12 c06 6 2Document4 pagesChem12 c06 6 2ehaxhaj2006No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis: Animations Student WorksheetChelsea MansuetoNo ratings yet
- 9ba-5 PhotosynthesisDocument1 page9ba-5 PhotosynthesisUmraan AhmadNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesisalyaainsyirah04No ratings yet
- Rates of Reaction Revision CardDocument1 pageRates of Reaction Revision Cardagentdog175No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Plant Nutrition - Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Plant Nutrition - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (5)
- CH 2 - PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesCH 2 - PhotosynthesisnawarakanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Part 2: Calvin Cycle Adaptations Factors Affecting RateDocument50 pagesPhotosynthesis Part 2: Calvin Cycle Adaptations Factors Affecting RateCik NursharwaniNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 - What Is PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesTopic 9 - What Is PhotosynthesisHoulin HuangNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Let The Sun Shine in WorksheetDocument7 pagesKami Export - Let The Sun Shine in WorksheetMitchell WhitworthNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Work BookDocument10 pagesPhotosynthesis Work BookFederica TrevisanNo ratings yet
- Toro Wheelhorse Demystification Electical Wiring Diagrams For All WheelHorse TractorsDocument546 pagesToro Wheelhorse Demystification Electical Wiring Diagrams For All WheelHorse TractorsKevins Small Engine and Tractor Service69% (32)
- Control Valves Data Sheet: Client: PlantDocument1 pageControl Valves Data Sheet: Client: PlantAnoNo ratings yet
- Corekit User Manual EmulexDocument63 pagesCorekit User Manual Emulexprakashv44No ratings yet
- DCN Manual 2019Document74 pagesDCN Manual 2019Suhani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- HIGHWAY AND RAILROAD ENG'G (Lesson 1-4)Document15 pagesHIGHWAY AND RAILROAD ENG'G (Lesson 1-4)Xienlyn BaybayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DSADocument11 pagesIntroduction To DSAdhiraj1223353No ratings yet
- 10385-J UTBI-001 ManualDocument2 pages10385-J UTBI-001 ManualMatias GiammariniNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Lakshmi Narain College of Technology BHOPAL-462021 (INDIA)Document48 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Lakshmi Narain College of Technology BHOPAL-462021 (INDIA)Vikash SinghNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current QuestionsDocument2 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current QuestionsVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- 480-1 (Manski, Northwestern) PDFDocument3 pages480-1 (Manski, Northwestern) PDFInvestNo ratings yet
- E220-400M30S UserManual EN v1.0-1Document14 pagesE220-400M30S UserManual EN v1.0-1Predrag VisnjicNo ratings yet
- WIND LOADS (Computation of QH For MWFRS, Low Rise BuildingDocument2 pagesWIND LOADS (Computation of QH For MWFRS, Low Rise BuildingRomeo QuerubinNo ratings yet
- Xenon LampDocument25 pagesXenon LampJamaica Peñaloza NatuelNo ratings yet
- Fkeyrouz@ndu - Edu.lb: Systems Using MATLAB, Second Edition, Prentice Hall 2002Document2 pagesFkeyrouz@ndu - Edu.lb: Systems Using MATLAB, Second Edition, Prentice Hall 2002Elio EidNo ratings yet
- Web Technology QuantumDocument335 pagesWeb Technology QuantumabhishekgsNo ratings yet
- Ees ManualDocument191 pagesEes ManualMohd Jamal Mohd MoktarNo ratings yet
- 100 Notes 2 XPDocument53 pages100 Notes 2 XPJIGSNo ratings yet
- DMM172Document2 pagesDMM172Mauricio GarayzarNo ratings yet
- ME:5160 (58:160) Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids Fall 2021 - HW6 SolutionDocument6 pagesME:5160 (58:160) Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids Fall 2021 - HW6 SolutionDiki AgungNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument12 pagesWater TreatmentSata AjjamNo ratings yet
- Titanic EdaDocument14 pagesTitanic EdaDeepak SemwalNo ratings yet
- Example Paper CC270 SpontaneousGenDocument14 pagesExample Paper CC270 SpontaneousGenLaert VeliaNo ratings yet
- 200 Important Quantitative Aptitude QuestionsDocument50 pages200 Important Quantitative Aptitude Questionsjamil ahmedNo ratings yet
- Jay BirdDocument37 pagesJay Birdvlcmstne04100% (1)
- SAP SD Interview QuestionsDocument130 pagesSAP SD Interview QuestionsPraveen Kumar100% (1)
- Understand and Troubleshoot IP Address Management (IPAM) in Windows Server 8 BetaDocument102 pagesUnderstand and Troubleshoot IP Address Management (IPAM) in Windows Server 8 Betacalin bNo ratings yet
- HX 16-Data SheetDocument2 pagesHX 16-Data SheetRaul SebastiamNo ratings yet
- Elbi Vessel Data SheetDocument20 pagesElbi Vessel Data SheetMAZENNo ratings yet
- Remy Hvh250 Application Manual: Preliminary Draft Hvh250 Motormanual20110407.Doc Page 1 of 31Document31 pagesRemy Hvh250 Application Manual: Preliminary Draft Hvh250 Motormanual20110407.Doc Page 1 of 31David WalshNo ratings yet
- PetDocument15 pagesPetAhmed RhifNo ratings yet