Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equator It Is An Imaginary Line Drawn Around The Middle of The Earth
Uploaded by
Sadia AleemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equator It Is An Imaginary Line Drawn Around The Middle of The Earth
Uploaded by
Sadia AleemCopyright:
Available Formats
Equator It is an imaginary line drawn around the middle of the earth.
If we cut along the equator, the earth
separates into two hemisphere i.e. Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere. Most of the earth’s land is the
Northern Hemisphere.
Prime Meridian It is an imaginary line that runs from north to south poles. This creates eastern and western
hemisphere. The continents in the eastern hemisphere are traditionally called Old World, while those in the western
hemisphere called (U.S.A) Modern World.
Latitude :These are imaginary lines run east to west on the globe are called lines of latitude. OR The horizontal lines
on the globe are called lines of latitude. Total latitudes are 180, 90 in north of the equator and 90 in south of the
equator. Longitude :The vertical lines on the globe run from North to south between the poles are called lines of
longitude. Total longitudes are 360, 180 in east side and 180 in west side.
Introduction of Pakistan Pakistan emerged on the map of the world on 14th August 1947 as a result of the partition
of the Indian Sub-continent into two sovereign states namely Pakistan and India. Initially, Pakistan was comprised of
two distinct areas, namely East Pakistan and West Pakistan. In December 1971, East Pakistan was separated and
emerged as an independent state, ‘Bangladesh’. Location of Pakistan Pakistan is located between 24 to 37 North
latitudes and extends from 61 to 76.5 East longitudes. The total area of Pakistan is 796,096 square km, stretching
over 1600 km from north to south and about 885 km from east to west
Latitude & Longitude:
• Pakistan is located between 24⁰ 35 north and 37⁰ 05 north latitude.
• Its longitude extends from 61⁰ to 78⁰ east.
Area of Pakistan:
• Its total area is 796,096 sq kilometers.
• It is 1600 kilometers from north to south.
• 885 km from east to west.
Location of Pakistan:
Location Neighboring Country
North-East China (585 km long border)
West Afghanistan (2252 km long border) known as Durand Line.
North-West Wakkan (narrow strip of Afghanistan), it separates Pakistan from Tajikistan.
South-West Iran
South Arabian Sea
East India
Strategic Importance of Pakistan:
• The Khyber Pass provides a route to Afghanistan.
• The Karakoram Highway helps in trade & communication with China.
• The Gwadar and Karachi seaports provide crucial travel as well as trade facilities to north and north-west.
• Its coastline at the Arabian Sea facilitates trade with West, Middle East, Far East, and Southeast Asia.
• Pakistan has a central location that provides air routes from west to east and the Jinnah International Airport
facilitates it.
• It offers easy access to Central Asia (CAS) and its 6 republics through Afghanistan.
• Feasibility of Natural Gas Pipeline Projects from CAS, India, Iran and South East Asia.
Pakistan-Iran Gas Pipeline:
• If this project is completed, then Pakistan will get 21.5 cubic meters of natural gas from Iran.
• This can be used as a fuel (CNG) for vehicles.
• It can also be used to generate electricity from thermal power stations.
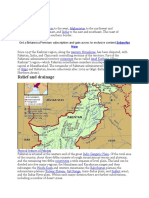
Location of Provinces & Cities
Provinces of Pakistan:
• It has Sindh, Punjab, Balochistan and NWFP provinces.
• It also includes FATA, Gilgit-Baltistan, and Kashmir.
• In 2009, the Federal Cabinet approved an ordinance that gave political autonomy to northern areas.
• A new name was also given to the Northern areas as Gilgit, Baltistan.
• In 2010, NWFP renamed as Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
FATA:
It stands fo federal administrated tribal areas
It is located between balochistan and khyber
Bolan
^Toba Kakar Range (Balochistan) …Connects Sibi with Quetta
Kojak
^Qila Abdullah, Chaman (Balochistan) …Quetta with Khandar Afghanistan
Khyber
^Sofad Koh …Peshawar with Kabul
Khunjerab
^Gilgit – Baltistan, Karakoram Mountains …Connects Gilgit Baltistan with China
Lowari
^KPK ….Chitral with Dir w
You might also like
- Notes On Geography (Paper 1, 2059/02) : Location of PakistanDocument4 pagesNotes On Geography (Paper 1, 2059/02) : Location of PakistanAmina AbidNo ratings yet
- Geography 2Document12 pagesGeography 2Youcef KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Land of PakistanDocument3 pagesIntroduction to the Land of PakistanMujtaba AamirNo ratings yet
- Geographical and Physical Features of PakistanDocument9 pagesGeographical and Physical Features of PakistanIqra Ashfaq100% (2)
- Geography of PakistanDocument6 pagesGeography of PakistanEiman UmerNo ratings yet
- Pakistan's Geography and International BoundariesDocument9 pagesPakistan's Geography and International BoundariesSaifMalikNo ratings yet
- Geography of Pakistan - WikipediaDocument16 pagesGeography of Pakistan - WikipediaSabir HussainNo ratings yet
- Location and Borders of PakistanDocument11 pagesLocation and Borders of PakistanEbaad SajidNo ratings yet
- Lec # 7, 8 Geography of PakistanDocument6 pagesLec # 7, 8 Geography of PakistannaeemsukheraNo ratings yet
- 1.1physical Features of PakistanDocument35 pages1.1physical Features of PakistanaNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Is Located at A Region Which Has A Great EconomicDocument9 pagesPakistan Is Located at A Region Which Has A Great EconomicMashal KhalilNo ratings yet
- 1-Landof Pak & Topography (Pakistan Studies Olevels)Document69 pages1-Landof Pak & Topography (Pakistan Studies Olevels)Shahzeen ShahNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentdanishfiverr182No ratings yet
- GeographyDocument16 pagesGeographyHayat Ullah shaheenNo ratings yet
- Pakistan: A Land of Strategic ImportanceDocument2 pagesPakistan: A Land of Strategic ImportanceArish altmishNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 1 NotesAmmar QureshiNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Location of PakistanDocument9 pages1 - The Location of Pakistandaud.agha2010No ratings yet
- Pakistan's Geo-Strategic Position Opportunity & ChallengesDocument36 pagesPakistan's Geo-Strategic Position Opportunity & ChallengesFajr MirNo ratings yet
- Opportunity & Challenges: Important For #Css / #PmsDocument33 pagesOpportunity & Challenges: Important For #Css / #PmsdanishNo ratings yet
- Geography: 1893, SeparatingDocument3 pagesGeography: 1893, SeparatingJeneferNo ratings yet
- Geographical Importance of PakistanDocument31 pagesGeographical Importance of Pakistanumerziabba100% (2)
- Geography Chapter 1Document36 pagesGeography Chapter 1Abdul WasayNo ratings yet
- Geography of PakistanDocument16 pagesGeography of PakistanAbu HuraraNo ratings yet
- 1-Landof Pak & Topography (Updated-2019)Document84 pages1-Landof Pak & Topography (Updated-2019)Shahzeen ShahNo ratings yet
- Geo-Strategic Importance of PakistanDocument21 pagesGeo-Strategic Importance of PakistanCh UsamaNo ratings yet
- OLevel - The Land of Pakistan - O Level Academy - Notes, Videos, Past Papers, Syllabus, Specimen, Examiner ReportDocument11 pagesOLevel - The Land of Pakistan - O Level Academy - Notes, Videos, Past Papers, Syllabus, Specimen, Examiner ReportMalahim BabarNo ratings yet
- Geography of PakistanDocument4 pagesGeography of PakistanMemer Hu yrrNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Location Importance Latitude LongitudeDocument14 pagesPakistan Location Importance Latitude LongitudePotatoNo ratings yet
- Solved Syllabus Pak - STDocument22 pagesSolved Syllabus Pak - STjshndNo ratings yet
- China Extreme North-EastDocument4 pagesChina Extreme North-Eastm1kuuuNo ratings yet
- Pakistan's Geography and LocationDocument2 pagesPakistan's Geography and LocationMuhammad Ahmad Noor100% (1)
- Indian Geography (Advanced)Document283 pagesIndian Geography (Advanced)Dorababu Mutyala100% (8)
- Iran Afghanistan China India Arabian Sea: Subscribe NowDocument3 pagesIran Afghanistan China India Arabian Sea: Subscribe Nownzgzxg mZMgfNo ratings yet
- Old Masters of Geodesy and Pakistan's Grids & DatumsDocument2 pagesOld Masters of Geodesy and Pakistan's Grids & DatumsBagaNo ratings yet
- Geo-Strategic Importance of PakistanDocument16 pagesGeo-Strategic Importance of Pakistanmasnsoor11011100% (2)
- O Notes Location and Importance of PakistanDocument5 pagesO Notes Location and Importance of Pakistand56pqxzqvgNo ratings yet
- Geography 1Document21 pagesGeography 1Irfan AliNo ratings yet
- Geography of Afghanistan: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesGeography of Afghanistan: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaTABIBI11No ratings yet
- Geopolitical Importance of PakistanDocument22 pagesGeopolitical Importance of PakistanNousheen Arshad95% (19)
- Geography of Pakistan in 40 CharactersDocument9 pagesGeography of Pakistan in 40 CharactersXain RanaNo ratings yet
- The Land of PakistanDocument54 pagesThe Land of Pakistanmina shamsNo ratings yet
- India: ©ramakrishna KongallaDocument55 pagesIndia: ©ramakrishna KongallaRita TripathiNo ratings yet
- Geo Physical Features of PakistanDocument47 pagesGeo Physical Features of PakistanFaiq AliNo ratings yet
- Geography of IndiaDocument15 pagesGeography of IndiaKhushal GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Land Scape of Pakistan PPT Grade 5Document4 pagesThe Land Scape of Pakistan PPT Grade 5ShahzadiSoha JawadNo ratings yet
- Fishing boats lashed together during approaching monsoon stormDocument1 pageFishing boats lashed together during approaching monsoon stormmlbslNo ratings yet
- Geography 32Document8 pagesGeography 32pramaniknitai99No ratings yet
- Geo Strategic Significance of PakistanDocument10 pagesGeo Strategic Significance of Pakistantassawarrehman184% (19)
- Indian Geography (Shashidthakur23.wordpress - Com) PDFDocument144 pagesIndian Geography (Shashidthakur23.wordpress - Com) PDFsingamsetty kavyaNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument144 pagesGeographyshiintu100% (1)
- Aits 4Document106 pagesAits 4ABHISHEK GUPTANo ratings yet
- Ahmad Subhani 2022-Ag-8037 (Geographical Importance of Pakistan)Document13 pagesAhmad Subhani 2022-Ag-8037 (Geographical Importance of Pakistan)ahmad tayyabNo ratings yet
- Geographical Features of PakistanDocument44 pagesGeographical Features of Pakistanmaqbool ur rehman50% (2)
- Geostrategic PakistanDocument30 pagesGeostrategic PakistanBaddiah JavaidNo ratings yet
- The Panjab, North-West Frontier Province, and KashmirFrom EverandThe Panjab, North-West Frontier Province, and KashmirNo ratings yet
- The Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India: Ethnological Study of the Caste SystemFrom EverandThe Tribes and Castes of the Central Provinces of India: Ethnological Study of the Caste SystemNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychology History AsgmtDocument3 pagesClinical Psychology History AsgmtSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Election of First CaliphDocument6 pagesElection of First CaliphSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Importance of isnad in authenticating HadithsDocument3 pagesImportance of isnad in authenticating HadithsSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- CharacterDocument3 pagesCharacterSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Chap 7.doxDocument5 pagesChap 7.doxSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Fever Day 1Document3 pagesFever Day 1Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Chap 7.doxDocument5 pagesChap 7.doxSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- By Fatima Aleem (Assignment # 01 HISTORY) PDFDocument3 pagesBy Fatima Aleem (Assignment # 01 HISTORY) PDFSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Chap 11Document3 pagesChap 11Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- First ReflectionDocument1 pageFirst ReflectionSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Practice File For P 1 AND P2Document31 pagesPractice File For P 1 AND P2Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Practice Questionsreal (4420)Document3 pagesPractice Questionsreal (4420)Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Chap 7.doxDocument5 pagesChap 7.doxSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- HADITH Teachings and Practices 1-5Document11 pagesHADITH Teachings and Practices 1-5Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Hadith 1 To 15Document7 pagesHadith 1 To 15Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Hazrat Umer AnswersDocument37 pagesHazrat Umer AnswersSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- 16 Wek Plan For RevisionDocument1 page16 Wek Plan For RevisionSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- CALIPHS (1) From Religious Std.Document23 pagesCALIPHS (1) From Religious Std.Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Islpastpaper2006 2013novDocument100 pagesIslpastpaper2006 2013novSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 Whole ContentDocument201 pagesPaper 2 Whole ContentSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Islamiyat Answers-Caliph 1Document2 pagesIslamiyat Answers-Caliph 1Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- CALIPHS (1) From Religious Std.Document23 pagesCALIPHS (1) From Religious Std.Sadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Life in Makkah 606 622 AdDocument7 pagesLife in Makkah 606 622 AdSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Hadith As Source of GuidanceDocument19 pagesHadith As Source of GuidanceSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- 2056 Islamic Religion and CultureDocument99 pages2056 Islamic Religion and CultureSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- JihaadDocument3 pagesJihaadSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Pillars of Islam References From Quran and HadithDocument8 pagesPillars of Islam References From Quran and HadithSadia AleemNo ratings yet
- Degrees of ComparisonDocument3 pagesDegrees of ComparisonThiru MoorthyNo ratings yet
- REYHER Technical Information 2010Document194 pagesREYHER Technical Information 2010andreiwlNo ratings yet
- Rexsteel English72Document10 pagesRexsteel English72Bogie Prastowo MahardhikaNo ratings yet
- Victory Over Sin Through Total ConsecrationDocument3 pagesVictory Over Sin Through Total ConsecrationJhon Ray OtañesNo ratings yet
- A High Capacity Floating LNG Design by Barend - PekDocument15 pagesA High Capacity Floating LNG Design by Barend - PekShaka Shalahuddin Shantika PutraNo ratings yet
- Eight Lane Vadodara Kim ExpresswayDocument11 pagesEight Lane Vadodara Kim ExpresswayUmesh SutharNo ratings yet
- Its Raining Idioms A Figurative Language ActivityDocument11 pagesIts Raining Idioms A Figurative Language ActivityTyrone MoogNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Role of Criminologists in Third World CountriesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding the Role of Criminologists in Third World Countriespaco kazunguNo ratings yet
- Albemarle Family YMCA Pool ScheduleDocument2 pagesAlbemarle Family YMCA Pool ScheduleYMCA of South Hampton RoadsNo ratings yet
- Body Condition Scoring of Dairy Cattle A Review - 2 PDFDocument8 pagesBody Condition Scoring of Dairy Cattle A Review - 2 PDFfrankyNo ratings yet
- Kenya Dieticians License ApplicationDocument5 pagesKenya Dieticians License ApplicationGrace NdutaNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual MSP DUCT - SLIM DUCT PDFDocument31 pagesInstallation Manual MSP DUCT - SLIM DUCT PDFutaiuliancatalinNo ratings yet
- Class Will and TestamentDocument4 pagesClass Will and TestamentAllan Tomas33% (3)
- Math TestDocument3 pagesMath TestGhalyanAtulNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Submitting An Article To Gesta: General InformationDocument1 pageGuidelines For Submitting An Article To Gesta: General InformationneddyteddyNo ratings yet
- 2019-Kubelka-Munk Double Constant Theory of Digital Rotor Spun Color Blended YarnDocument6 pages2019-Kubelka-Munk Double Constant Theory of Digital Rotor Spun Color Blended YarnyuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Health History SummaryDocument1 pageNursing Health History SummaryHarvey T. Dato-onNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of Soids5!1!13Document20 pagesBand Theory of Soids5!1!13Ravi Kumar BanalaNo ratings yet
- Cost MGMT Accounting U4Document74 pagesCost MGMT Accounting U4Kai KeatNo ratings yet
- Energy Savings White PaperDocument14 pagesEnergy Savings White PapersajuhereNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 Direct and Inverse ProportionsDocument22 pagesChapter-12 Direct and Inverse ProportionsscihimaNo ratings yet
- "Leadership Does Not Always Wear The Harness of Compromise." - Woodrow WilsonDocument3 pages"Leadership Does Not Always Wear The Harness of Compromise." - Woodrow WilsonAmbreen Zaineb/Lecturer BKR/Economics and BANo ratings yet
- 05-Program Design and AnalysisDocument78 pages05-Program Design and AnalysisTarq AbdullahNo ratings yet
- MGS 4301 Decision Making Sample ExerciseDocument1 pageMGS 4301 Decision Making Sample ExerciseMarielle AllouNo ratings yet
- 06Document11 pages06junaid_ishaqueNo ratings yet
- 2009 - Mazars Insight Ifrs 5 enDocument36 pages2009 - Mazars Insight Ifrs 5 enSahar FekihNo ratings yet
- Information Pack: Creative Media EducationDocument26 pagesInformation Pack: Creative Media EducationDaniel VladimirovNo ratings yet
- NB-CPR 17-722r8 - General Guidance On AVCP (Working Copy)Document25 pagesNB-CPR 17-722r8 - General Guidance On AVCP (Working Copy)halexing5957No ratings yet
- Accounting for Inventory Valuation Methods Research ProposalDocument66 pagesAccounting for Inventory Valuation Methods Research ProposalAyman Ahmed Cheema100% (1)
- Overcoming ChallengesDocument28 pagesOvercoming ChallengesDeutsche Mark CuynoNo ratings yet