Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Health Teaching Plan
Uploaded by
Sammy Jr Familar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
129 views3 pagesHTP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHTP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
129 views3 pagesHealth Teaching Plan
Uploaded by
Sammy Jr FamilarHTP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Level II AACUP Accredited
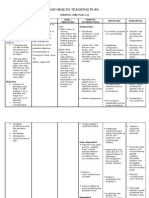
Topic: Prevention of pressure ulcers
Description/ Overview: Pressure ulcers are due to localized ischemia, a deficiency in the blood supply to the tissue. The
tissue is compressed between two surfaces, usually the surface of furniture such as the bed or chair and the bony skeleton.
When blood cannot reach the tissue, the cells are deprived of oxygen and nutrients, the waste products of metabolism
accumulate in the cells, and the tissue consequently dies. Prolonged, unrelieved pressure also damages the small blood
vessels. To reduce the likelihood of pressure ulcer development in all clients, the nurse employs a variety of preventive
measures to maintain the skin integrity and instructs the client; support people, and care giver in how to prevent pressure
ulcers.
Materials/ Equipment: Pamphlet
General Objective: The general objective of this health teaching plan is to prevent the patient to have pressure ulcers.
Objectives Learning Content Teaching Strategy Time Allotment Evaluation and
(in minutes) Assessment
Tool
COGNITIVE: I. What is pressure ulcer? Participative 5 minutes Active recalling
Within five (5) minutes of Lecture
health teaching, the Pressure ulcers consist of
patient and watcher will: injury to the skin and/or
Understand what underlying tissue, usually
is pressure ulcer over a bony prominence, as
How can the a result of force alone or in
patient acquire combination with
pressure ulcer movement. Pressure ulcers
are a problem in both acute
care settings and long-term
care settings, including
homes.
II. How can the patient
acquire pressure ulcer?
Pressure ulcers are due to
localized ischemia, a
deficiency in the blood
supply to the tissue. The
tissue is compressed
between two surfaces,
usually the surface of
furniture such as the bed or
chair and the bony skeleton.
When blood cannot reach
the tissue, the cells are
deprived of oxygen and
nutrients, the waste
products of metabolism
accumulate in the cells, and
the tissue consequently
dies. Prolonged, unrelieved
pressure also damages the
small blood vessels.
After the skin has been
compromised, it appears
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 1
pale, as if the blood had
been squeezed out of it.
When pressure relieved, the
skin takes on a bright red
flush, called reactive
hyperemia. The flush is due
to vasodilation, a process in
which extra blood floods to
the area to compensate for
the preceding period of
impeded blood flow.
Friction and shearing can
also cause pressure ulcers.
PSYCHOMOTOR: III. How to prevent pressure Participative 5 minutes Active recalling
After five (5) minutes of ulcers? Lecture and Q&A
health teaching, the
patient and watcher will To reduce the likelihood of
be able to: pressure ulcer development
Determine the in all clients, the nurse
preventions for employs a variety of
pressure ulcers preventive measures to
maintain the skin integrity
and instructs the client;
support people, and care
giver in how to prevent
pressure ulcers. For client’s
at risk, the nurse also
optimizes nutrition, and
hydration, inspects skin
daily, minimizes pressure,
and manages moistures by
keeping the client and dry
and moisturizing skin.
For the patient, these are
the things they need to do
to prevent pressure ulcers:
Have smooth, firm
and wrinkle-free
foundation on which
to sit or lie
Frequently shifts in
position
Keep skin clean
and dry.
Protect the skin.
Apply moisturizers
in dry skins.
Enhance nutrition
and hydration.
AFFECTIVE: Active recalling on the
Within three (3) minutes discussed topic. Participative lecture 3 minutes Self-reflection
of health teaching, the
patient and watcher will
be able to:
Incorporate their
own knowledge
to what they
have learn
Express
understand of
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 2
the health
teaching.
REFERRENCES:
1. Berman A., Snyder S., & Frandsen G.. KOZIER & ERB’S FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING Concepts, Process,
and Practice, Global Edition, Tenth Edition. Published by Pearson Education Limited (2018)
2. Mayo Clinic (2022) Bedsores (pressure ulcers). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bed-
sores/symptoms-causes/syc-20355893
3.
4.
Patient’s Name / Room No. | 3
You might also like
- Caso Clinico Electivas 3Document9 pagesCaso Clinico Electivas 3MARIANGEL LAFONTNo ratings yet
- Lonzaga Assessment PDFDocument7 pagesLonzaga Assessment PDFNiño Naryana Luke PanchoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Template for Student Fideli L. AbaquitaDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Template for Student Fideli L. AbaquitafabaquitaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions for Oral Mucosa InfectionDocument1 pageNursing Interventions for Oral Mucosa InfectionChriszanie CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionlinnaroueyakNo ratings yet
- SJMC - xi-nCP&HTP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument10 pagesSJMC - xi-nCP&HTP - Impaired Skin IntegrityJoy CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Risk For Falls Aeb Loss of BalanceDocument4 pagesRisk For Falls Aeb Loss of BalanceAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- Clinical Portrait Pertinent DataDocument9 pagesClinical Portrait Pertinent DataGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Er Journal HgeDocument3 pagesEr Journal HgeKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care PlanCaracel Cabrera SobionoNo ratings yet
- Types of Fractures, Traction, and Hip Dislocation SignsDocument3 pagesTypes of Fractures, Traction, and Hip Dislocation SignsDoyTanNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanTenth Ann ModanzaNo ratings yet
- NCP MRMDocument2 pagesNCP MRMKhloe Cristel Llanes Torres100% (1)
- RISK For INJURY Related To Regulatory Function (Sensory Difunction As Evidenced by Decrease Visual Acuity, Unable To Recognize Object 12-14 Inches Away, Not Wearing of Eyeglasses.Document2 pagesRISK For INJURY Related To Regulatory Function (Sensory Difunction As Evidenced by Decrease Visual Acuity, Unable To Recognize Object 12-14 Inches Away, Not Wearing of Eyeglasses.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Domperidone CompressDocument1 pageDrug Study Domperidone CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Introduction To Community Health Nursing Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts of Community Health NursingDocument134 pagesUnit 1: Introduction To Community Health Nursing Chapter 1: Fundamental Concepts of Community Health NursingMille Kaia100% (2)
- (Brand Name) & Date Ordered General Class and Family Specific IndicationDocument2 pages(Brand Name) & Date Ordered General Class and Family Specific IndicationNicole Grace VillegasNo ratings yet
- Actual NCPDocument2 pagesActual NCPbaki0146No ratings yet
- 3rd Year Nursing MS LEC MIDTERM QUIZESDocument18 pages3rd Year Nursing MS LEC MIDTERM QUIZESAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument21 pagesDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesASSESSMENTColeen PequitNo ratings yet
- University of Negros Occidental Student Clinical Training ReportDocument3 pagesUniversity of Negros Occidental Student Clinical Training ReportAzhly AntenorNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument2 pagesOMEPRAZOLEJenny Pearl PasalNo ratings yet
- AripiprazoleDocument2 pagesAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Sas 2 Cabahug, Victoria Mae IDocument4 pagesSas 2 Cabahug, Victoria Mae Ibekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument1 pageAspirinAmanda CoadNo ratings yet
- "Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" AsDocument4 pages"Nahadlok Naman Ko Sa Akong Gipambati, Ning-Undang Ko Sakong Work As QHSE and Training Manager, Nagdecide Ko Muuli Sa Pilipinas. Pag-Uli Nako Last Week, Ginabati Nako Mura Ko Makulbaan" Ashanna caballoNo ratings yet
- Risk for Infection Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesRisk for Infection Nursing Care PlanKarl-Ren LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- NCP Readiness RevisionDocument3 pagesNCP Readiness RevisionimnasNo ratings yet
- Surgery JournalDocument1 pageSurgery JournalPhilippe CANTORIA (SHS)No ratings yet
- Nursing Process in Drug TherapyDocument32 pagesNursing Process in Drug TherapyChaseNo ratings yet
- COMMUNITY-MANUSCRIPT SampleDocument84 pagesCOMMUNITY-MANUSCRIPT SampleCA SavageNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy For ElderlyDocument14 pagesDrugstudy For ElderlyJenniferP.BarrosoNo ratings yet
- DioxelDocument1 pageDioxelJosselle Sempio CalientaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process RecordingDocument5 pagesNursing Process RecordingErl Joy Montaño CañeteNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Prioritization After HysterectomyDocument2 pagesAcute Pain Prioritization After HysterectomyRuth Lea Cabrera100% (1)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care PlanDocument22 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis Nursing Care PlanLorelyn Santos Corpuz100% (1)
- Nursing responsibilities for ampicillinDocument3 pagesNursing responsibilities for ampicillinCharlene Serino JavierNo ratings yet
- LFDDocument3 pagesLFDVhince Norben PiscoNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge Plankim arrojado100% (1)
- LCPDDocument7 pagesLCPDakoismeNo ratings yet
- HEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Document3 pagesHEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Asterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- J.Paquit NCP ECCEDocument7 pagesJ.Paquit NCP ECCEJon Gab Paquit100% (1)
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Myonal, Eperisone DrugDocument4 pagesMyonal, Eperisone DrugDhaneswara Adhyatama100% (1)
- Case Study: Obstructive JaundiceDocument11 pagesCase Study: Obstructive JaundiceZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Ketorolac: Uses, Dosing, Side EffectsDocument14 pagesKetorolac: Uses, Dosing, Side EffectsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Improving Dental Hygiene in Grade III StudentsDocument3 pagesImproving Dental Hygiene in Grade III Studentsx483xDNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Document3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Tetracycline Drug StudyDocument5 pagesTetracycline Drug StudyEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Impaired MobilityDocument3 pagesImpaired MobilityYeana AlonNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice - Quiz #2 - 50 Questions - NurseslabsDocument52 pagesGastrointestinal System Disorders NCLEX Practice - Quiz #2 - 50 Questions - NurseslabsGypsy Joan TranceNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Community Health and Public Health NursingDocument1 pageThe Difference Between Community Health and Public Health NursingMelissa Briggs100% (1)
- Therapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesDocument35 pagesTherapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesKeith Clarence BunaganNo ratings yet
- Phenylephrine HydrochlorideDocument5 pagesPhenylephrine HydrochlorideRoger Jr PumarenNo ratings yet
- I. LearningsDocument5 pagesI. LearningsMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPVictor MurilloNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcer PamphletDocument2 pagesPressure Ulcer PamphletSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- 3 Pressure Ulcer (Bedsores) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsDocument12 pages3 Pressure Ulcer (Bedsores) Nursing Care Plans - NurseslabsJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- Assessing and Preventing Pressure UlcersDocument8 pagesAssessing and Preventing Pressure UlcersTamil VillardoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysioDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysioSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- Food WebDocument1 pageFood WebSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument25 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument1 pageBiogeochemical CyclesSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- Managing Pain in New Colostomy PatientDocument3 pagesManaging Pain in New Colostomy PatientSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcer PamphletDocument2 pagesPressure Ulcer PamphletSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- Case Study FinalDocument7 pagesCase Study FinalSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet
- OR Duty RLE RequirementsDocument5 pagesOR Duty RLE RequirementsSammy Jr FamilarNo ratings yet