Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power System Protection Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Yousef ElsayedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power System Protection Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Yousef ElsayedCopyright:
Available Formats
POWER SYSTEM PROTECTION
Fourth year Electrical Power
Reference books:
*J. M. Gers and E. J. Holmes, 3rd edition, "Protection of Electricity Distribution Networks " , The
Institution of Engineering and Technology ,2011 .
*Walter A. Elmore ,"protective Relaying Theory and Applications" , Second edition , Marcel
Dekker ,New York ,2004.
*Power system protection , IEEE Electricity Training Association , 1997
*S. S. Rao,"Switchgear and Protection ", Khanna Publishers ,Delhi ,1986.
* ﻣﺣﻣود ﺟﯾﻼﻧﻲ, ﺣﻣﺎﯾﺔ اﻟﻧظم اﻟﻛﮭرﺑﯾﺔ
COURSE OUTLINE :
Electrical layout for power station and substation
Protective relays
Functional relays types
Protection systems for electrical power equipments
Circuit breakers
Switchgears
1 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
CHAPTER 1
Electrical Power system
• The purpose of an electrical power system is
to generate and supply electrical energy to
consumers.
• System should be designed and managed to
deliver this energy to the utilisation points
with both reliability and economy.
• It should be operated in a safe manner at all
times
2 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
Electrical Power system
• A power system comprises many diverse items of equipment.
• Many items of equipment are very expensive, and so the complete
power system represents a very large capital investment.
• The destructive power of a fault arc carrying a high current is very
great; it can burn through copper conductors or weld together core
laminations in a transformer or machine in a very short time – some
tens or hundreds of milliseconds.
• Even away from the fault arc itself, heavy fault currents can cause
damage to plant if they continue for more than a few seconds.
Why do we need protection?
• Electrical apparatus operates at various
voltage levels and may be enclosed or placed
in open.
• Under abnormal operating conditions
protection is necessary for
- Safety of electrical equipments.
- Safety of human personnel.
3 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
What protection system should do?
1) Prevent or limit damage during faults or
overloads.
2) Protection system should disconnect only
faulted parts but healthy parts of system should
be unaffected.
Blackouts
Characteristics
• Loss of service in a large area or population
region
• Hazard to human life
• May result in enormous economic losses
Main Causes
• Overreaction of the protection system
• Bad design of the protection system
4 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
Protection requirements
ART & SCIENCE OF PROTECTION
• Maximum and Reliable protection at minimum
equipment cost
• High Sensitivity to faults and insensitivity to
maximum load currents
• High-speed fault clearance with correct selectivity
• Selectivity in isolating small faulty area
• Ability to operate correctly under all predictable
power system conditions
Some definitions
a. Protection System: a complete arrangement of protection
equipment and other devices required to achieve a specified function
based on a protection principal (IEC 60255-20)
b. Protection Equipment: a collection of protection devices (relays,
fuses, etc.). Excluded are devices such as CT’s, CB’s, Contactors, etc.
c. Protection Scheme: a collection of protection equipment
providing a defined function and including all equipment required to
make the scheme work (i.e. relays, CT’s, CB’s, batteries, etc.)
5 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
Types of Protection
Apparatus Protection
• Transmission Line Protection
• Transformer Protection
• Generator Protection
• Motor Protection
• Busbar Protection
System Protection
One Line Diagram :
• Non-dimensioned diagram showing how
pieces of electrical equipment are connected
• Simplification of actual system
• Equipment is shown as boxes, circles and
other simple graphic symbols
• Symbols should follow ANSI “American “or IEC
“European “conventions
6 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
Line Symbols
Line Symbols
7 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
Line Symbols
How to protect
• Measure
• Think “detect a real problem”
• Action
8 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
Protection System Elements
• Protective relays
• Circuit breakers
• Current and voltage transducers
• Communications channels
• DC supply system
• Control cables
PROTECTION ZONES
• To limit the extent of the power system that is
disconnected when a fault occurs, protection is
arranged in zones.
• The point of connection of the protection with
the power system usually defines the zone and
corresponds to the location of the current
transformers
• Ideally, the zones of protection should overlap, so
that no part of the power system is left
unprotected
9 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
PROTECTION ZONES
• Generator or Generator-Transformer Units
• Transformers
• Buses
• Lines (transmission and distribution)
• Utilization equipment (motors, static loads,
etc.)
• Capacitor or reactor (when separately
protected)
PROTECTION ZONES
10 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
• BUT :
• For practical physical
and economic
reasons, this ideal is
not always achieved.
• ????????????????
• Example :
Accommodation for
current being in some
cases available only on
one side of the circuit
breakers,
• This leaves a section
between the current
transformers and the
circuit breaker A that is
not completely protected
against faults.
•
11 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
• A fault at F would cause the bus
bar protection to operate and
open the circuit breaker but the
fault may continue to be fed
through the feeder. The feeder
protection would not operate,
since the fault is outside its zone.
• This problem is dealt with by inter
tripping or some form of zone
extension, to ensure that the
remote end of the feeder is
tripped also.
Primary protection
• Primary protection should operate every time
an element detects a fault on the power
system.
• The protection element covers one or more
components of the power system.
12 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
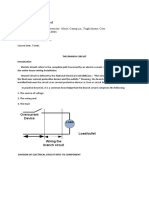
Back-up protection
• Back-up protection is installed to operate when,
for whatever reason, the primary protection does
not work.
• Back-up protection relay has a sensing element
that may or may not be similar to the primary
protection, but that also includes a time-delay
facility to slow down the operation of the relay so
as to allow time for the primary protection to
operate first.
Example :
13 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
14 Dr Ahmed Refai 2021/2022
You might also like
- SGP Unit 1 L2Document59 pagesSGP Unit 1 L2Samsung TabletNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power System ProtectionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Power System ProtectionHamzakhj100% (1)
- Basic of Switchgear and Protective DevicesDocument130 pagesBasic of Switchgear and Protective DevicesHafiziAhmadNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Uee2521 RRPDocument54 pages3.2 Uee2521 RRPmohammad2110959No ratings yet
- By: By: By: By: Er Er Er Er. - . - Rahul Rahul Rahul Rahul Sharma Sharma Sharma SharmaDocument69 pagesBy: By: By: By: Er Er Er Er. - . - Rahul Rahul Rahul Rahul Sharma Sharma Sharma SharmaAnand VRNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Program GoalsDocument31 pagesElectrical Safety Program GoalsJulios Charl Panuncialman TagupaNo ratings yet
- Feeder ProtectionDocument70 pagesFeeder Protectionmajid_altaf_042504100% (3)
- Basics of Power System ProtectionDocument17 pagesBasics of Power System ProtectionSharad_B_Patel100% (2)
- Re LAYDocument98 pagesRe LAYzsoso1796No ratings yet
- Topic 1 IntroductionDocument21 pagesTopic 1 IntroductionEngr Umer CheemaNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying IiDocument25 pagesPower System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying IiSampath AnbuNo ratings yet
- WindDocument46 pagesWindK Vijay Bhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Electrical ProtectionDocument94 pagesElectrical ProtectionNeil Summer100% (7)
- Lecture 3 Electrical Components Wiring AccessoriesDocument48 pagesLecture 3 Electrical Components Wiring AccessoriesMar VenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Protection Switchgear & Protection Unit 1Document150 pagesIntroduction To Protection Switchgear & Protection Unit 1padmajasiva100% (18)
- Ritchie Mar C. Ugsod: First Semester, A.Y. 2020-2021Document5 pagesRitchie Mar C. Ugsod: First Semester, A.Y. 2020-2021Gaming DeathNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection EssentialsDocument85 pagesPower System Protection EssentialsShivaditya singhNo ratings yet
- Prisma Plus and IEC 61439-1-2Document8 pagesPrisma Plus and IEC 61439-1-2FrancisautomacaoNo ratings yet
- Protection Schemes in Substation PresentationDocument28 pagesProtection Schemes in Substation PresentationAnil SainiNo ratings yet
- Electric Power System Protection BasicsDocument12 pagesElectric Power System Protection Basicseuge sylNo ratings yet
- PSP Chapter 1 of Module 1Document31 pagesPSP Chapter 1 of Module 1daveadeNo ratings yet
- Zone of ProtectionDocument17 pagesZone of ProtectionAkimeNo ratings yet
- Radial Feeder Protection: by N.Sarveshwar G.Ravikumar Panimalar Institute of TechnologyDocument35 pagesRadial Feeder Protection: by N.Sarveshwar G.Ravikumar Panimalar Institute of TechnologySarveshwar Nethaji100% (1)
- Sec14 - Electrical System and Equipment ProtectionDocument18 pagesSec14 - Electrical System and Equipment ProtectionYusufNo ratings yet
- PSP 02Document60 pagesPSP 02faizanNo ratings yet
- DAY 3 PresentationDocument12 pagesDAY 3 PresentationEgbin TransmissionNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Protection Using Microcontroller-Based RelayDocument66 pagesPower Transformer Protection Using Microcontroller-Based Relaybisanikumarbabu100% (5)
- Protective Relaying and SwitchgearDocument118 pagesProtective Relaying and SwitchgearSanyam BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Power System Basics: Tawsif Hossain Chowdhury Thchowdhury@seu - Edu.bdDocument21 pagesPower System Basics: Tawsif Hossain Chowdhury Thchowdhury@seu - Edu.bdMahmud HasanNo ratings yet
- Generator Protection - FDocument70 pagesGenerator Protection - Fengrsmabbasrizvi100% (2)
- Switch Gear and Protective Devices PDFDocument132 pagesSwitch Gear and Protective Devices PDFAnonymous m8oCtJBNo ratings yet
- Protection FundamentalsDocument12 pagesProtection FundamentalsGeorge AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Protection-Basics r3Document88 pagesProtection-Basics r3alimaghami100% (1)
- Lecture Material Template - FDocument3 pagesLecture Material Template - FNANDHAKUMAR ANo ratings yet
- BUILDING ELECTRICAL DESIGNDocument12 pagesBUILDING ELECTRICAL DESIGNShantilouwpNo ratings yet
- GE Multilin - 1craig Wester, John LevineDocument90 pagesGE Multilin - 1craig Wester, John LevineEduardo Salgado CarBajal100% (1)
- Guide To ProtectionDocument32 pagesGuide To ProtectionpjaengjaikulNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Uee2521 RRPDocument36 pages3.1 Uee2521 RRPmohammad2110959No ratings yet
- GE Consumer & Industrial Multilin document on generator protection devicesDocument70 pagesGE Consumer & Industrial Multilin document on generator protection devicesengrsmabbasrizvi100% (2)
- Module 2 - Safety and ProtectionDocument23 pagesModule 2 - Safety and ProtectionOlusegun OdubanjoNo ratings yet
- Power System ProtectionDocument38 pagesPower System ProtectionMuhd WariNo ratings yet
- Performance Tests For Protection Devices - MR ZALPYSDocument21 pagesPerformance Tests For Protection Devices - MR ZALPYSSalah SallamNo ratings yet
- Assignment of System Protection Eeg 806Document24 pagesAssignment of System Protection Eeg 806emechetasamuel27No ratings yet
- Class Notes - Introduction to Computer RelayingDocument8 pagesClass Notes - Introduction to Computer RelayingbiswajitsahooNo ratings yet
- The Branch Circuit: An OverviewDocument12 pagesThe Branch Circuit: An OverviewGaming DeathNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power System ProtectionDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Power System ProtectionHuzaifa WasimNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionDocument52 pages01 Introductionmohsin awanNo ratings yet
- 2.1.3 Lectura Recomendada Circuit Protection in HospitalDocument5 pages2.1.3 Lectura Recomendada Circuit Protection in HospitalGabrielNo ratings yet
- The IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedFrom EverandThe IEE Wiring Regulations Explained and IllustratedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Joint RES and Distribution Network Expansion Planning Under a Demand Response FrameworkFrom EverandJoint RES and Distribution Network Expansion Planning Under a Demand Response FrameworkNo ratings yet
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsFrom Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ultimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionFrom EverandUltimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- 10 - Bus Transfer System Retroffiting - Concept NoteDocument9 pages10 - Bus Transfer System Retroffiting - Concept Notevitthal01No ratings yet
- ADDC Standard For MV SwitchgearDocument47 pagesADDC Standard For MV SwitchgearAsif PervezNo ratings yet
- Siemens Indonesia Energy FactsheetDocument2 pagesSiemens Indonesia Energy Factsheetgina penyonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Service Minimum RequirmentDocument97 pagesElectrical Service Minimum RequirmentachniajosiNo ratings yet
- DWG-14-041 LUECO Wiring Diagram As Built 5 23 15 PDFDocument25 pagesDWG-14-041 LUECO Wiring Diagram As Built 5 23 15 PDFArmelita Tadifa DucusinNo ratings yet
- Eaton Power Distribution Product GuideDocument477 pagesEaton Power Distribution Product GuideRodrigo Alonso Rosales OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 5 Oase 2012 PowerDocument28 pages5 Oase 2012 PowerAdina BadeaNo ratings yet
- GIS Type Series 8DN8Document20 pagesGIS Type Series 8DN8Vishal Narkhede100% (1)
- Siemens - Power Engineering Guide - Transmission & DistributionDocument332 pagesSiemens - Power Engineering Guide - Transmission & DistributionAhmed Gaafer100% (10)
- Ten Questions and Answers of R&D SwithgearDocument3 pagesTen Questions and Answers of R&D Swithgearkwchan99No ratings yet
- ANSI C37.54-2002 (R2010) - Indoor AC HV Circuit Breakers Applied As Removable Elements in Metal-Enclosed Switchgear - Confromance Test ProceduresDocument46 pagesANSI C37.54-2002 (R2010) - Indoor AC HV Circuit Breakers Applied As Removable Elements in Metal-Enclosed Switchgear - Confromance Test ProceduresBryan SalamatNo ratings yet
- HLB1VHYJHFXXXXbtXpXX PRXFXXXPDocument10 pagesHLB1VHYJHFXXXXbtXpXX PRXFXXXPTauseef AlamNo ratings yet
- C 8201-1:2007 Standard for Low Voltage Switchgear and ControlgearDocument157 pagesC 8201-1:2007 Standard for Low Voltage Switchgear and Controlgearshen jianxinNo ratings yet
- 01 Manual de Planejamento Volume 1 - Princípios de PlanejamentoDocument130 pages01 Manual de Planejamento Volume 1 - Princípios de PlanejamentoRafael CarmoNo ratings yet
- Numerical Relays Protection Relays CatalogueDocument36 pagesNumerical Relays Protection Relays CatalogueRajeev ValunjkarNo ratings yet
- 36 KV, 2500A, 31.5 Ka Medium Voltage, Arc-Proof Switchgear: Unigear Zs2Document2 pages36 KV, 2500A, 31.5 Ka Medium Voltage, Arc-Proof Switchgear: Unigear Zs2KekKangLoong100% (1)
- GSTR001 - 1 (Rev1 - 2017 - 08 - 08)Document50 pagesGSTR001 - 1 (Rev1 - 2017 - 08 - 08)miguel1972No ratings yet
- Circuit Breakers Switchgear Handbook Vol 2Document115 pagesCircuit Breakers Switchgear Handbook Vol 2alexmuchmure2158No ratings yet
- Distribution Switchgear General CatalogueDocument294 pagesDistribution Switchgear General CatalogueGabriel210364No ratings yet
- ETS01-07-01 - Specs LV ABC & XLPE Cable Equipment & FittingsDocument61 pagesETS01-07-01 - Specs LV ABC & XLPE Cable Equipment & FittingsTerex14253No ratings yet
- Ca VD4G (En) B 1VCP000671 2018.09 PDFDocument46 pagesCa VD4G (En) B 1VCP000671 2018.09 PDFkienNo ratings yet
- Axera 5 Main Switchgear Maintenance ManualDocument22 pagesAxera 5 Main Switchgear Maintenance ManualAnonymous iu95trpxNNo ratings yet
- AREVA T&D Product RangeDocument10 pagesAREVA T&D Product RangeEduardo SolanoNo ratings yet
- Control TechnologiesDocument51 pagesControl TechnologiesrajuNo ratings yet
- Device Number Definition and Function: 1-1 Master ElementDocument6 pagesDevice Number Definition and Function: 1-1 Master ElementHamayoun MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Switches, Automatic TransferDocument44 pagesCommissioning Switches, Automatic Transferbookbum100% (5)
- EPE 12kV SwitchgearDocument48 pagesEPE 12kV Switchgearaimiza100% (1)
- M4-Approved Vendor ListDocument20 pagesM4-Approved Vendor Listisan.structural TjsvgalavanNo ratings yet
- Etu45b Unidad Disparo SiemensDocument48 pagesEtu45b Unidad Disparo SiemensNestor Guiza100% (2)
- ABB 2493 Is Limiter GB NewBrandingDocument20 pagesABB 2493 Is Limiter GB NewBrandingsf111No ratings yet