Professional Documents
Culture Documents
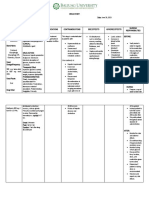
TABLE 17-29 - Causes of Hypophosphatemia
Uploaded by
Rashmeeta ThadhaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TABLE 17-29 - Causes of Hypophosphatemia
Uploaded by
Rashmeeta ThadhaniCopyright:
Available Formats
Tintinalli’s Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e >Fluids and Electrolytes
Judith E. Tintinalli, J. Stephan Stapczynski, O. John Ma, Donald M. Yealy, Garth D. Meckler, David M. Cline+
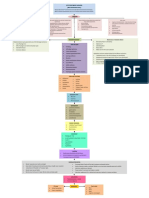
TABLE 17-29Causes of Hypophosphatemia
Glucose
Insulin
Shift from ECF to ICF without depletion of PO43–
Catecholamines
Respiratory alkalosis
Hyperalimentation
Shift from ECF to ICF with depletion of PO43–
Refeeding syndrome
Low intake
Malabsorption
Decreased intestinal absorption
Chronic use of calcium acetate or bicarbonate, aluminum hydroxide
Vitamin D deficiency
Hyperparathyroidism
Increased fibroblast growth factor (FGF-23)
Genetic hypophosphatemia mutations
Tubular acidosis
Increased renal loss Fanconi's syndrome
Hypokalemia
Hypomagnesemia
Polyuria
Acidosis
Alcoholism (poor intake, vitamin D deficiency)
Miscellaneous causes Diabetic ketoacidosis (osmotic diuresis)
Toxic shock syndrome
Drugs See Table 17-30
Date of download: 03/26/23 from AccessEmergency Medicine: accessemergencymedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- 4 Diabetes MellitusDocument26 pages4 Diabetes MellitusnomiskemalNo ratings yet
- The Billionaire Brain WaveDocument3 pagesThe Billionaire Brain WavelittlebirdshomeeducationNo ratings yet
- DECLAMATIONDocument19 pagesDECLAMATIONJohn Carlos Wee67% (3)
- Notes-Indolence of The Filipino PeopleDocument3 pagesNotes-Indolence of The Filipino PeopleKayes MNo ratings yet
- Blood Loss: Acute Chronic Inadequate Production of Normal Blood CellsDocument11 pagesBlood Loss: Acute Chronic Inadequate Production of Normal Blood CellsSheila Amor BodegasNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesPathophysiologyJerica Mae VenoyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesNathaniel John Rebollos SuladayNo ratings yet
- Dental MneumonicDocument30 pagesDental Mneumonictmle44% (9)
- Hypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypophosphatemia, (Low Phosphate) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy: Chapter 6: Comparison and Selection Among AlternativesDocument25 pagesEngineering Economy: Chapter 6: Comparison and Selection Among AlternativesBibhu R. TuladharNo ratings yet
- For Printing Pathophysiology DMDocument1 pageFor Printing Pathophysiology DMkat garciaNo ratings yet
- Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Mid La Union CampusDocument5 pagesDon Mariano Marcos Memorial State University Mid La Union CampusSam Bernardo100% (2)
- Ir21 Geomt 2022-01-28Document23 pagesIr21 Geomt 2022-01-28Master MasterNo ratings yet
- Newborn Screening Panel of Disorders: Management ProtocolDocument56 pagesNewborn Screening Panel of Disorders: Management ProtocolRay Arvin DyNo ratings yet
- 1st-Year ObliconDocument10 pages1st-Year ObliconIts SaoirseNo ratings yet
- NCP DM Ii Part 2Document14 pagesNCP DM Ii Part 2Elay PedrosoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixDocument16 pagesAssessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixNalzaro Emyril89% (19)
- EDICTO Acute Metabolic Alkalosis (FINAL)Document1 pageEDICTO Acute Metabolic Alkalosis (FINAL)GLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesSodium BicarbonateMikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- filePV 26 12 940 PDFDocument9 pagesfilePV 26 12 940 PDFzikryauliaNo ratings yet
- Food-Drug Interaction: Presented By: Deepika Baranwal PHD ScholarDocument29 pagesFood-Drug Interaction: Presented By: Deepika Baranwal PHD ScholarUncu LiviaNo ratings yet
- Refeeding SyndromeDocument10 pagesRefeeding SyndromePhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Kelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enDocument14 pagesKelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enhilan sasewaNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocument3 pagesDrug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsSurria Suguna15No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyFelizandra MicuNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument3 pagesAnemiaGhadeer AbedNo ratings yet
- 31.chronic Diarrhea and MalabsorbtionDocument14 pages31.chronic Diarrhea and MalabsorbtionSajjal AliNo ratings yet
- Kelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enDocument16 pagesKelompok Bhs Inggrtios .Id - enAgustinusNo ratings yet
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedDocument1 pagePathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- Pa Tho Physiology CherryDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology CherryMervin Ezekiel Amistoso FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Egaloblastic Naemia Acrocytic Anaemia: Ihsanil HusnaDocument9 pagesEgaloblastic Naemia Acrocytic Anaemia: Ihsanil HusnafikriNo ratings yet
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocument2 pagesChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Furosemide ChlorthalidoneDocument5 pagesFurosemide ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- ElectrolytesDocument2 pagesElectrolytesVenus Amoroso BaguiosoNo ratings yet
- Ipd - Kelas Ac - Kad Dan Hhs - DR - DR.K Heri Nugroho HS, SP - PD, K-EmdDocument51 pagesIpd - Kelas Ac - Kad Dan Hhs - DR - DR.K Heri Nugroho HS, SP - PD, K-EmdTeresia MaharaniNo ratings yet
- OB PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesOB PathophysiologyCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- AcidDocument6 pagesAcidfisiruadama88No ratings yet
- Type 2 DM PathoDocument5 pagesType 2 DM PathoPearl JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Starvation and Refeeding SyndromeDocument11 pagesPhysiology of Starvation and Refeeding SyndromeUCI COVID Pediátrico HNGAINo ratings yet
- m.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Document3 pagesm.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Dasha VeeNo ratings yet
- Class: Calcium Salts: Agent(s) Common Uses Contraindications Route/Dosage Onset of Action InteractionsDocument8 pagesClass: Calcium Salts: Agent(s) Common Uses Contraindications Route/Dosage Onset of Action InteractionsAlano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Potassium - Hypokalaemia - Emergency Care InstituteDocument3 pagesPotassium - Hypokalaemia - Emergency Care InstituteLauraNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument24 pagesBio NotesIslam MansourNo ratings yet
- Lecturio 3663 JaundiceDocument12 pagesLecturio 3663 JaundicePranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseImnot YouNo ratings yet
- Pathway DMDocument1 pagePathway DMwahyuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study.: Generic NameDocument1 pageDrug Study.: Generic NameMichael James PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Environmental FactorsDocument7 pagesEnvironmental FactorsjayrchinNo ratings yet
- Prefinals Overall TopicDocument8 pagesPrefinals Overall TopicClarke GriffinNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- Esrd Diagram PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesEsrd Diagram PathophysiologySTEPHANIE JOSUE100% (1)
- Surgical JaundiceDocument15 pagesSurgical Jaundicedrrohit1756No ratings yet
- Liver CirrhosisDocument1 pageLiver CirrhosisJAMES PATRICK MONTEMAYORNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Vitamin DDocument1 pageDrug Study Vitamin DErica VelascoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drug Study CL Med PBL IDocument11 pagesGroup 3 Drug Study CL Med PBL IDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Fanconi SyndromeDocument9 pagesFanconi SyndromeEmilio AldreteNo ratings yet
- Hipocalemia e Hipercalemia. 2015 PDFDocument17 pagesHipocalemia e Hipercalemia. 2015 PDFMiguel Angel Manotas CañasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Mineral Reference GuideDocument2 pagesVitamin Mineral Reference GuideEleni KostaraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Diet Stress Hereditary AgeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: Diet Stress Hereditary AgeChucky VergaraNo ratings yet
- Inbumin PDFDocument12 pagesInbumin PDFresa dianNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Expected: IncreasedDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibility Expected: IncreasedMichaella MalimitNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Metabolism-Disorders-1Document19 pagesAmino Acids Metabolism-Disorders-1lucky mbaselaNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-27 - Causes of HypercalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Surgery Open Digestive Advance: G. Pasinato, J.-M RegimbeauDocument7 pagesSurgery Open Digestive Advance: G. Pasinato, J.-M RegimbeauRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-19 - Emergency Therapy of HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-19 - Emergency Therapy of HyperkalemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-26 - Symptoms and Signs of HypocalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-26 - Symptoms and Signs of HypocalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument1 pageTintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of HypocalcemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-24 - Some Causes of HypocalcemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-30 - Drugs That Cause Hypophosphatemia and UnderlyingDocument1 pageTABLE 17-30 - Drugs That Cause Hypophosphatemia and UnderlyingRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TableDocument3 pagesTableRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Chp8 Diagrams by The One and OnlyDocument3 pagesChp8 Diagrams by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- TABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaDocument1 pageTABLE 17-34 - Causes of HyperphosphatemiaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- 2011 Article 195Document6 pages2011 Article 195Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- (Sici) 1520 6823 (1997) 5:3 93::aid Roi1 3.0.co 2 DDocument4 pages(Sici) 1520 6823 (1997) 5:3 93::aid Roi1 3.0.co 2 DRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Primer: Head and Neck Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument22 pagesPrimer: Head and Neck Squamous Cell CarcinomaRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument1 pageTintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide, 8e Fluids and ElectrolytesRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach of Fever in Childhood - Aug 19Document31 pagesDiagnostic Approach of Fever in Childhood - Aug 19Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers October 2016Document25 pagesTuberculosis: Nature Reviews Disease Primers October 2016Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- PKMDocument10 pagesPKMRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2020 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument23 pagesEconomics ALevel 2020 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- KS 1405 WB03A Energy Systems Modeling Workshop BriefDocument9 pagesKS 1405 WB03A Energy Systems Modeling Workshop BriefRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Pemberton Sign in Diagnosis of Retrosternal GoiterDocument3 pagesPemberton Sign in Diagnosis of Retrosternal GoiterRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2019 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument24 pagesEconomics ALevel 2019 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Economics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyDocument31 pagesEconomics ALevel 2018 Mark Scheme by The One and OnlyRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- List ObatDocument9 pagesList ObatRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Document18 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Document18 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (Dr. Michael, August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Cardiology: Micaela Gliozzi, Natalia Malara, Saverio Muscoli, Vincenzo MollaceDocument5 pagesInternational Journal of Cardiology: Micaela Gliozzi, Natalia Malara, Saverio Muscoli, Vincenzo MollaceRashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Trial of Invasive Versus Medical Therapy in Elderly Patients Wit 2001Document7 pagesTrial of Invasive Versus Medical Therapy in Elderly Patients Wit 2001RodrigoSachiFreitasNo ratings yet
- Joint Pain (Dr. Stevent, 27th August 2020)Document3 pagesJoint Pain (Dr. Stevent, 27th August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Confusion and Delirium (Dr. Euphemia, 24th August 2020)Document8 pagesConfusion and Delirium (Dr. Euphemia, 24th August 2020)Rashmeeta ThadhaniNo ratings yet
- Dde 23Document3 pagesDde 23omboyeNo ratings yet
- MHS Week 3. Quality Culture-KWODocument37 pagesMHS Week 3. Quality Culture-KWOKevin SinagaNo ratings yet
- SanamahismDocument7 pagesSanamahismReachingScholarsNo ratings yet
- Rayya Abdallah David Abdallah, As Next of Kin of Baby Boy Abdallah, and On Their Own Personal Behalf v. Wilbur Callender, M.D. Government of The Virgin Islands, 1 F.3d 141, 3rd Cir. (1993)Document13 pagesRayya Abdallah David Abdallah, As Next of Kin of Baby Boy Abdallah, and On Their Own Personal Behalf v. Wilbur Callender, M.D. Government of The Virgin Islands, 1 F.3d 141, 3rd Cir. (1993)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Buad 306 HW 2Document4 pagesBuad 306 HW 2AustinNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Engineering Company Limited (KECL)Document13 pagesKarnataka Engineering Company Limited (KECL)miku hrshNo ratings yet
- PhysicsssssDocument1 pagePhysicsssssSali IqraNo ratings yet
- Tourism Signs & Symbols Published by World Tourism OrganizationDocument244 pagesTourism Signs & Symbols Published by World Tourism OrganizationJemima Pontino0% (1)
- Aja052550590 786Document13 pagesAja052550590 786EugeneSeasoleNo ratings yet
- Socscipi PPT2Document9 pagesSocscipi PPT2DKY SYSNo ratings yet
- 2008-12-16Document32 pages2008-12-16CoolerAdsNo ratings yet
- National Social Protection Strategy GhanaDocument95 pagesNational Social Protection Strategy GhanaSisiraPinnawalaNo ratings yet
- Theatrical Script Legend of La LloronaDocument2 pagesTheatrical Script Legend of La LloronaScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- DCF Calculation of Dabur India Ltd.Document6 pagesDCF Calculation of Dabur India Ltd.Radhika ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- Social Defence Vision 2020: Dr. Hira Singh Former Director National Institute of Social DefenceDocument19 pagesSocial Defence Vision 2020: Dr. Hira Singh Former Director National Institute of Social DefencePASION Jovelyn M.No ratings yet
- Gender Roles As Seen Through Wedding Rituals in A Rural Uyghur Community, in The Southern Oases of The Taklamakan Desert (#463306) - 541276Document26 pagesGender Roles As Seen Through Wedding Rituals in A Rural Uyghur Community, in The Southern Oases of The Taklamakan Desert (#463306) - 541276Akmurat MeredovNo ratings yet
- Module2.Shs CGPDocument54 pagesModule2.Shs CGPRommelyn Perez Pelicano75% (4)
- Purification and Detection of Linamarin From Cassava Root Cortex by HPLCDocument5 pagesPurification and Detection of Linamarin From Cassava Root Cortex by HPLCJohn Eiver BelalcazarNo ratings yet
- BM AssignmentDocument7 pagesBM AssignmentAntony LawrenceNo ratings yet
- The Right MindDocument8 pagesThe Right Mindwaltor makuvireNo ratings yet
- Information Analyzer Data Quality Rules Implementations Standard Practices - 01052012Document94 pagesInformation Analyzer Data Quality Rules Implementations Standard Practices - 01052012abreddy2003No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Final OkDocument43 pagesCHAPTER 1 Final Okroneldayo62No ratings yet