Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7.1 Acid Deposition
Uploaded by
Unbound RacerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
7.1 Acid Deposition
Uploaded by
Unbound RacerCopyright:
Available Formats
Vishal Thoutam
2/13/23
0484825
Period 6
7.1: ACID DEPOSITION
7.1.1
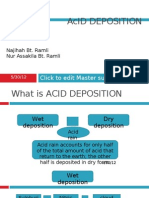
Acid Deposition – Mix of air pollutants that deposit from the atmosphere as acidic wet
deposition (with a pH <5.6) or acidic dry deposition.
7.1.2
Acid rain is a type of acid deposition, which can appear in many forms. Wet deposition is rain,
sleet, snow, or fog that has become more acidic than normal. Dry deposition is another form of
acid deposition, and this is when gases and dust particles become acidic.
7.1.3
Acid deposition, commonly known as acid rain, occurs when emissions from the combustion of
fossil fuels and other industrial processes undergo complex chemical reactions in the atmosphere
and fall to the earth as wet deposition (rain, snow, cloud, fog) or dry deposition (dry particles,
gas).
1. Acidic gases are released into the atmosphere
2. Gases carried upwards by the wind
3. Gases combine with water droplets to form acids
4. Acid rain
5. Acid rain destroys plants, pollutes water sources and soil and erodes buildings
7.1.4
The acidification of surface waters can lead to declines in the fish population. Acidic water also
affects aquatic plants and insects that are eaten by fish.
Dead or dying trees are a common sight in areas effected by acid rain. Acid rain also causes
aluminum to be released into the soil, which makes it difficult for trees to take up water. Acid
rain that seeps into the ground can dissolve nutrients, such as magnesium and calcium, that trees
need to be healthy.
When acid rain and dry acidic particles fall to earth, the nitric and sulfuric acid that make the
particles acidic can land on statues, buildings, and other manmade structures, and damage their
surfaces. The acidic particles corrode metal and cause paint and stone to deteriorate more
quickly.
You might also like
- Evaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksFrom EverandEvaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument7 pagesWhat Is Acid RainSai sasindhar MalapatiNo ratings yet
- Acid Deposition: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument15 pagesAcid Deposition: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAkie Kiela RamliNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument8 pagesAcid Rainmahi silvadasNo ratings yet
- ACID RAINS How They Form and Effect The WorldDocument19 pagesACID RAINS How They Form and Effect The WorldNOPEENo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument5 pagesWhat Is Acid RainHafiz hassanNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: By:Daniele Chisholm Tavia KamekaDocument8 pagesAcid Rain: By:Daniele Chisholm Tavia Kamekadaniele chisholmNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: HistoryDocument4 pagesAcid Rain: Historyrameesaali56No ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually Acidic, I.EDocument7 pagesAcid Rain: Acid Rain Is Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually Acidic, I.ESarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- ACID RAIN and Depletionof Ozone LayerDocument6 pagesACID RAIN and Depletionof Ozone Layerakshatraj873No ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityDocument20 pagesAcid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityManwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Fayza Kamal Khattab: Presented To: Dr. Sayed ShalabyDocument11 pagesPresented By: Fayza Kamal Khattab: Presented To: Dr. Sayed ShalabyMohamed Maher TorkyNo ratings yet
- AcidDocument1 pageAcidRantti AnwarNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument5 pagesWhat Is Acid RainUtari Dwi Alriyani YoshidaNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument6 pagesAcid Rainnot made with mematicNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain and Ozone Layer DepletionDocument5 pagesAcid Rain and Ozone Layer Depletionlekha1997No ratings yet
- Chemisty Project - 9 - F - 100383 - Acid Rain (Autosaved)Document8 pagesChemisty Project - 9 - F - 100383 - Acid Rain (Autosaved)Lakshya BhatiNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument20 pagesAcid RainNick ZeeNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument11 pagesAcid RainTEJAS JAINNo ratings yet
- 6.3.4. Acid Deposition - GEC 007-ARCH41S2 - Science, Technology and SocietyDocument3 pages6.3.4. Acid Deposition - GEC 007-ARCH41S2 - Science, Technology and SocietyKIRSTENNo ratings yet
- EnvDocument3 pagesEnv7.bharani12No ratings yet
- Acid Rain and OzoneDocument2 pagesAcid Rain and OzoneDevesh SawantNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument20 pagesAcid RainSmita Dhutraj100% (1)
- Acid Rain Description and Analysis: TreeboxDocument6 pagesAcid Rain Description and Analysis: TreeboxNanthini RajanderanNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument29 pagesAcid Rainapi-3706215100% (2)
- In The Name of ALLAH, The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful: A Threat To EnvironmentDocument24 pagesIn The Name of ALLAH, The Most Gracious, The Most Merciful: A Threat To EnvironmentMoeed KhanNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument5 pagesWhat Is Acid RainEhteshamNo ratings yet
- Photochemical Smog Effect On Atmosphere: How Is Smog Formed?Document3 pagesPhotochemical Smog Effect On Atmosphere: How Is Smog Formed?Rana IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Cala Component BDocument9 pagesCala Component BPeace MutombwaNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Prelim ReviewerDocument14 pagesENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Prelim ReviewerMichael MendozaNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Presented byDocument13 pagesAcid Rain: Presented byAnand AsiaNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument6 pagesAcid RainDeliaNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain NotesDocument2 pagesAcid Rain Notesapi-268159571No ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: By: Ratna Ayu Wulandari S2 - PKLHDocument20 pagesAcid Rain: By: Ratna Ayu Wulandari S2 - PKLHRatna Ayu WulandariNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: AssignmentDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Science: AssignmentRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain Cause & Prevention: Name Student IdDocument9 pagesAcid Rain Cause & Prevention: Name Student IdNur AsyikinNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument16 pagesAcid Rainhakimah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- ABE 137 Acid RainDocument31 pagesABE 137 Acid RainJackielou PachesNo ratings yet
- HTML Model2Document3 pagesHTML Model2Rathna MalaNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain Research PaperDocument15 pagesAcid Rain Research Paperaysilislam528No ratings yet
- What Are The Effects of Acid Rain?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Effects of Acid Rain?Tri Indriati ZiskiandaNo ratings yet
- Science Folio Form 2 (Acid Rain)Document6 pagesScience Folio Form 2 (Acid Rain)Nurul ImanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Acid RainDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Acid RainDevendarsingh rawatNo ratings yet
- Causes and History of Acid RainDocument12 pagesCauses and History of Acid RainJay PeeNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain and Ozone DepletionDocument40 pagesAcid Rain and Ozone DepletionmalarNo ratings yet
- Regional Outdoor Air PollutionDocument2 pagesRegional Outdoor Air Pollutionhunterkiller662No ratings yet
- What Is Acid Rain?Document4 pagesWhat Is Acid Rain?dhruvsuri17No ratings yet
- Enter Post Title HereDocument6 pagesEnter Post Title HereRohit ShalgarNo ratings yet
- Sources of Acid RainDocument1 pageSources of Acid RainMohd Najmi HakimNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number: 3: Submitted To: Muhammed Sahal Head of Chemistry Submitted By: Talha RafiqDocument6 pagesAssignment Number: 3: Submitted To: Muhammed Sahal Head of Chemistry Submitted By: Talha RafiqTalha RafiqNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Wet Deposition:-Dry DepositionDocument5 pagesAcid Rain: Wet Deposition:-Dry DepositionRycel De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument3 pagesAcid Raindeo2002No ratings yet
- What Is Acid Rain and What Causes ItDocument1 pageWhat Is Acid Rain and What Causes ItkhloudsaeidNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: What Is Acid Rain? How Does It Form?Document5 pagesAcid Rain: What Is Acid Rain? How Does It Form?DHARAMSAR HEMBRAMNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain, Cuases, Effects and SolutionsDocument4 pagesAcid Rain, Cuases, Effects and SolutionsChoudhry AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument12 pagesAcid RainUmesh Gaikwad100% (3)
- Acid Rain: by Samuel Quintero, Jeffry GilDocument4 pagesAcid Rain: by Samuel Quintero, Jeffry GilJaime Leal NavarroNo ratings yet
- Discursive Writing On ProtestingDocument2 pagesDiscursive Writing On ProtestingUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: By: Sofia Rosales, Gaurav Chaudhuri, Isabella Molina, Amy Van Hove, Vishal Thoutam, Isabella SantosDocument12 pagesNuclear Energy: By: Sofia Rosales, Gaurav Chaudhuri, Isabella Molina, Amy Van Hove, Vishal Thoutam, Isabella SantosUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Vishal ThoutamDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis - Vishal ThoutamUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Greenhouse Ozone Depletion - Vishal Thoutam 9-20-22Document4 pagesGlobal Warming Greenhouse Ozone Depletion - Vishal Thoutam 9-20-22Unbound RacerNo ratings yet
- March 14 Research Assignment - Vishal ThoutamDocument1 pageMarch 14 Research Assignment - Vishal ThoutamUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Ecology Vocabulary - Vishal ThoutamDocument1 pageEcology Vocabulary - Vishal ThoutamUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Climate ChangeDocument1 page8.1 Climate ChangeUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- The Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugFrom EverandThe Billion-Dollar Molecule: The Quest for the Perfect DrugRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionFrom EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsFrom EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)