Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8.1 Climate Change
Uploaded by
Unbound RacerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8.1 Climate Change
Uploaded by
Unbound RacerCopyright:
Available Formats
Vishal Thoutam
03/06/2023
Period 6
8.1: Climate Change
8.1.1
Greenhouse gases: Gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation
Ex. carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), hydrofluorocarbons
(HFCs) and ozone
8.1.2
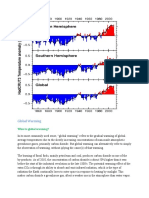
Over the last century, burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of
atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). This increase happens because the coal or oil burning process
combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO2. Deforestation and overpopulation are also other
causes of greenhouse gas emissions from humans.
8.1.3
Certain gases in the atmosphere absorb energy, slowing or preventing the loss of heat to space. Those
gases are known as “greenhouse gases.” They act like a blanket, making the earth warmer than it would
otherwise be. This process, commonly known as the “greenhouse effect,” is natural and necessary to
support life.
8.1.4
It is difficult to predict the size of the emissions of greenhouse gases in the coming decades as this can
be influenced by political decisions and technological advancements. Many of the effects of global
warming have been well documented and observations from real life are consistent with predictions.
The main challenge with predictions and projections is that we have models which are not yet perfect in
their representation of the climate system, and observations used to constrain these models still have
considerable uncertainties or do not have sufficiently long records.
You might also like
- What Are The Reasons For Global Warming?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Reasons For Global Warming?manirathinaNo ratings yet
- Bingemer 1987Document7 pagesBingemer 1987Alex GNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument24 pagesGreenhouse EffectSamarNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Evs Project-Class XiiDocument12 pagesAir Pollution: Evs Project-Class XiirijuNo ratings yet
- Indarto DecompositiongreenhousegasesbyplasmainpressDocument9 pagesIndarto DecompositiongreenhousegasesbyplasmainpressJosé Maria OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Gases 2017Document11 pagesGreenhouse Gases 2017AnusheenNo ratings yet
- 6 3essDocument50 pages6 3essDevanshi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument8 pagesClimate ChangeEmily Fitz GeraldNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument7 pagesGlobal Warmingcarlo78No ratings yet
- Montreal Prot enDocument24 pagesMontreal Prot enBoris PopovNo ratings yet
- Snapping Shrimp Make Flashing Bubbles: Brief CommunicationsDocument2 pagesSnapping Shrimp Make Flashing Bubbles: Brief Communicationsdimen_tNo ratings yet
- Outline For Report ENVIRONDocument6 pagesOutline For Report ENVIRONJoshua MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Energy in A High-Tech World: Term 3, 2012Document7 pagesEnergy in A High-Tech World: Term 3, 2012Alex WhittleNo ratings yet
- Component Percentage% Nitrogen Oxygen Argon Carbon Dioxide Neon Krypton Nitrogen Dioxide Methane Ozone Helium Hydrogen XenonDocument4 pagesComponent Percentage% Nitrogen Oxygen Argon Carbon Dioxide Neon Krypton Nitrogen Dioxide Methane Ozone Helium Hydrogen XenonVitor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mitigation of CO2 by Chemical ConversionDocument21 pagesMitigation of CO2 by Chemical Conversiona_abbaspourNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect Essay SPMDocument1 pageGreenhouse Effect Essay SPMcyberbat2008No ratings yet
- GWCC Key Cse June 2023Document20 pagesGWCC Key Cse June 2023srinivas kanakalaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document15 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- Environment Global Warming Conversation Topics Dialogs Oneonone Activities Re 90781Document3 pagesEnvironment Global Warming Conversation Topics Dialogs Oneonone Activities Re 90781Monica Maria DogaruNo ratings yet
- Answer These QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswer These Questionsmaiche amar100% (1)
- Fossil Fuel's: Consequences of Using Fossil FuelsDocument4 pagesFossil Fuel's: Consequences of Using Fossil FuelsDaniel FloresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 (22.08Document22 pagesLecture 11 (22.08api-3801916No ratings yet
- Air Pollution Causes and EffectsDocument16 pagesAir Pollution Causes and EffectshajaramirNo ratings yet
- Global Warming & Ozone LayerDocument12 pagesGlobal Warming & Ozone LayerWayne JohannesNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument2 pagesGlobal WarmingJoanna SaliganNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument26 pagesGlobal WarmingAishah AhmedNo ratings yet
- As Level - Green ChemistryDocument26 pagesAs Level - Green Chemistrysazy5100% (2)
- Fossil FuelsDocument3 pagesFossil FuelsKhawaja Ammar HussainNo ratings yet
- Page 2 Causes of Global WarmingDocument1 pagePage 2 Causes of Global Warmingdikoha1833No ratings yet
- Greenhouse GasDocument5 pagesGreenhouse Gastanzim444No ratings yet
- EPA Questions and Answers On Ozone DepletionDocument4 pagesEPA Questions and Answers On Ozone DepletionAndrew GrantNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument33 pagesAir PollutionSpencer VenableNo ratings yet
- Water Vapor, Not Carbon Dioxide, Is Major Contributor to the Earth's Greenhouse Effect: Putting the Kibosh on Global Warming AlarmistsFrom EverandWater Vapor, Not Carbon Dioxide, Is Major Contributor to the Earth's Greenhouse Effect: Putting the Kibosh on Global Warming AlarmistsNo ratings yet
- Project in EthicspicDocument19 pagesProject in EthicspicOdellien SajaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument8 pagesGlobal WarmingsamanNo ratings yet
- Course Id: ENV - 206 Sec-02: Submitted byDocument9 pagesCourse Id: ENV - 206 Sec-02: Submitted byMD. JULFIKER HASANNo ratings yet
- My Press TwoDocument10 pagesMy Press TwoNeriah Eam Veric PelarcoNo ratings yet
- Sustainable EngineeringDocument15 pagesSustainable EngineeringAbhijeeth AnilkumarNo ratings yet
- Generations of Crude Oil: March 2019Document6 pagesGenerations of Crude Oil: March 2019Aso SerwanNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel: Basra University of Oil and Gas Faculty of Oil and Gas EngineeringDocument4 pagesFossil Fuel: Basra University of Oil and Gas Faculty of Oil and Gas EngineeringAHMEDNo ratings yet
- Science Indiv PTDocument3 pagesScience Indiv PTKhloe Cristel Llanes TorresNo ratings yet
- Edexcel AS UNIT 2 Green Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesEdexcel AS UNIT 2 Green Chemistry NotesLakshan Selvarajah100% (1)
- Mod 2 Air Pollution Part 1Document50 pagesMod 2 Air Pollution Part 1rfgvgfNo ratings yet
- Eneregy and Environment Chapter ThreeDocument3 pagesEneregy and Environment Chapter ThreeMESAY MEKURIANo ratings yet
- 5.6 OzoneDocument22 pages5.6 Ozonetracyadjei28No ratings yet
- Topic B: Global Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesTopic B: Global Climate ChangeIvan CabroneNo ratings yet
- 1.3 The Enhanced GreenhouseDocument9 pages1.3 The Enhanced GreenhouseSpecial EffectNo ratings yet
- Climate Change ModuleDocument40 pagesClimate Change ModuleMohamed RafeesNo ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide Is A Greenhouse Gas That Makes A Planet WarmerDocument4 pagesCarbon Dioxide Is A Greenhouse Gas That Makes A Planet WarmerNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- LegacyprojectessayDocument8 pagesLegacyprojectessayapi-282614402No ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument101 pagesFuels and CombustionAlyssa Clarizze MalaluanNo ratings yet
- M7 Activity1 PimentelDocument3 pagesM7 Activity1 PimentelKenneth PimentelNo ratings yet
- Effects of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) (Final)Document5 pagesEffects of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) (Final)Luis RuizNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Causes and EffectsDocument6 pagesAir Pollution Causes and EffectsSandhya SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectsDocument8 pagesGreen House Effectssme chemistryNo ratings yet
- Ecology and EnviromentDocument20 pagesEcology and Enviromentpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Ddi11 Ss He3 NegDocument3 pagesDdi11 Ss He3 NegAtraSicariusNo ratings yet
- Carbon Trading in The City of Undoing.: September 2012Document24 pagesCarbon Trading in The City of Undoing.: September 2012Rizki DewaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change - Paper PresentationDocument45 pagesClimate Change - Paper PresentationVinoba SelvanduraiNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Crunch: How We're Getting Climate Change Wrong—and How to Fix ItFrom EverandThe Carbon Crunch: How We're Getting Climate Change Wrong—and How to Fix ItRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Discursive Writing On ProtestingDocument2 pagesDiscursive Writing On ProtestingUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy: By: Sofia Rosales, Gaurav Chaudhuri, Isabella Molina, Amy Van Hove, Vishal Thoutam, Isabella SantosDocument12 pagesNuclear Energy: By: Sofia Rosales, Gaurav Chaudhuri, Isabella Molina, Amy Van Hove, Vishal Thoutam, Isabella SantosUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Vishal ThoutamDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis - Vishal ThoutamUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Greenhouse Ozone Depletion - Vishal Thoutam 9-20-22Document4 pagesGlobal Warming Greenhouse Ozone Depletion - Vishal Thoutam 9-20-22Unbound RacerNo ratings yet
- March 14 Research Assignment - Vishal ThoutamDocument1 pageMarch 14 Research Assignment - Vishal ThoutamUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- Ecology Vocabulary - Vishal ThoutamDocument1 pageEcology Vocabulary - Vishal ThoutamUnbound RacerNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Acid DepositionDocument1 page7.1 Acid DepositionUnbound RacerNo ratings yet