Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ecology and Enviroment
Uploaded by
pallavi maheshwari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views20 pagesOriginal Title
Ecology and enviroment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views20 pagesEcology and Enviroment
Uploaded by
pallavi maheshwariCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Ecology and enviroment
sumbited to – Ar gaurav agrawal
Sumbited by – lokesh prajapat
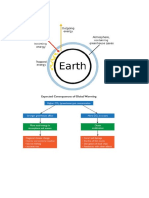
What is the global warming
Global Warming is the increase of Earth's
average surface temperature due to effect of
greenhouse gases,
such as carbon dioxide emissions from
burning fossil fuels or from deforestation
which trap heat that would otherwise escape
from Earth.
What are the main cause of global
warming
The Main causes of Global warming are:
Increase in co2 concentration
Ozone Depletion.Deforestation Methane and
Nitrous oxide emissions from agriculture,
Arctic sea beds and factories
Aerosols present in the Atmosphere Rise in
sea levels Plankton boom due to warming
seas.Water Vapour.
Why the global warming is problem
Global warming is primarily a problem of too
much carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere
which acts as a blanket, trapping heat and
warming the planet. ... Certain waste
management and agricultural practices
aggravate the problem by releasing other
potent global warming gases
such as methane and nitrous oxide.
What is the main resion for global
warming
Most climate scientists agree the main cause
of the current global warming trend is human
expansion of the "greenhouse effect
warming that results when the atmosphere
traps heat radiating from Earth toward space.
Certain gases in the atmosphere block heat
from escaping.
How do humans contribute to global
warming
Human activities contribute to climate change
by causing changes in Earth's atmosphere in
the amounts of greenhouse gas- es, aerosols
(small particles), and cloudiness.
The largest known contribution comes from
the burning of fossil fuels, which releases
carbon dioxide gas to the atmosphere.
How we can help stop global warming
Reduce Fossil Fuel Use. Burning fossil fuels
increases the levels of greenhouse gases in the
atmosphere. ...
Plant Trees. Because carbon dioxide is the most
important greenhouse gas, planting trees and
other plants can slow or stop global warming. ...
Reduce Waste. ...
Conserve Water.
Green house effect
What is the green house effect –
A phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a
planet traps radiation emitted by its sun,
caused by gases such as carbon dioxide, water
vapor.
and methane that allow incoming sunlight to
pass through but retain heat radiated back
from the planet's surface.
Green house effect on enviroment
Part of this energy is absorbed by the Earth's
surface, transformed into heat (longwave
radiation) and radiated back towards space.
But as this heat goes up through the
atmosphere, some of it is trapped by the
different greenhouse gases and doesn't
escape into space.
What is the result of green house effect
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse
gases act like a blanket, absorbing IR radiation
and preventing it from escaping into outer
space.
The net effect is the gradual heating of Earth's
atmosphere and surface, a process known as
global warming.
Who discovered the green house effect
The existence of the greenhouse effect was
argued for by Joseph Fourier in 1824.
The argument and the evidence were further
strengthened by Claude Pouillet in 1827 and
1838 and reasoned from experimental
observations by John Tyndall in 1859.
The effect was more fully quantified by
Svante Arrhenius in 1896.
What is the result of the green house effect
Svante Arrhenius (1859-1927) was a Swedish
scientist that was the first to claim in 1896
that fossil fuel combustion may eventually
result in enhanced global warming.
He proposed a relation between atmospheric
carbon dioxide concentrations and
temperature.
How can we help prevent global warming
Reduce Fossil Fuel Use. Burning fossil fuels
increases the levels of greenhouse gases in the
atmosphere. ...
Plant Trees. Because carbon dioxide is the most
important greenhouse gas, planting trees and
other plants can slow or stop global warming. ...
Reduce Waste. ...
Conserve Water.
What is the ozone depletion
Ozone layer depletion, is simply the wearing
out (reduction) of the amount of ozone in the
stratosphere.
Unlike pollution, which has many types and
causes, Ozone depletion has been pinned
down to one major human activity.
What are the effects of ozone depletion
If this ozone becomes depleted, then more UV
rays will reach the earth.
Exposure to higher amounts of UV radiation
could have serious impacts on human beings,
animals and plants.
such as the following: Harm to human health:
More skin cancers, sunburns and premature
aging of the skin.
How dose air pollution effect on ozone
depletion
One of the greatest and most dangerous
effects of pollution on the ozone layer
that it creates holes in the atmosphere,
which allow powerful ultraviolet rays from the
sun to reach the Earth's surface.
How dose the ozone depletion occur
When CFCs reach the stratosphere, the
ultraviolet radiation from the sun causes them
to break apart and release chlorine atoms
which react with ozone, starting chemical
cycles of ozone destruction that deplete the
ozone layer.
One chlorine atom can break apart more than
100,000 ozone molecules.
Who discovered ozone hole
The discovery of the annual depletion of
ozone above the Antarctic
first announced in a paper by Joe Farman,
Brian Gardiner and Jonathan Shanklin
which appeared in Nature in May 1985. Later,
NASA scientists re-analyzed their satellite data
and found that the whole of the Antarctic was
affected.
Where is the hole in ozone layer
Reactions that take place on polar
stratospheric clouds (PSCs) play an important
role in enhancing ozone depletion.
PSCs form more readily in the extreme cold of
the Arctic and Antarctic stratosphere.
This is why ozone holes first formed, and are
deeper, over Antarctica.
How to we protect ozone layer
While the vast majority of ODS usage is either
industrial or commercial, individuals can help
Buy air-conditioning and refrigeration
equipment that do not use HCFCs as
refrigerant.
Buy aerosol products that do not use HCFCs or
CFCs as propellants.
You might also like
- Global Warming & Ozone LayerDocument12 pagesGlobal Warming & Ozone LayerWayne JohannesNo ratings yet
- List of ContentsDocument9 pagesList of ContentsMaria JBieber BrandonizerNo ratings yet
- The Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesThe Greenhouse EffectDayanaNo ratings yet
- Envt Unit 1Document75 pagesEnvt Unit 1Divya GoelNo ratings yet
- What Are The Reasons For Global Warming?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Reasons For Global Warming?manirathinaNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect and GasesDocument4 pagesGreenhouse Effect and Gasespradeep aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument6 pagesGreen House EffectVir PatelNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectsDocument8 pagesGreen House Effectssme chemistryNo ratings yet
- TUGAS Global WarmingDocument4 pagesTUGAS Global WarmingPolsek Siantar SelatanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10 (1)Document15 pagesPresentation 10 (1)xoranek474No ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect Global WarmingDocument2 pagesGreenhouse Effect Global Warmingrajaafif LcNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument11 pagesGlobal Warmingghataksampa816No ratings yet
- Globle WarmingDocument87 pagesGloble WarmingVijay Maurya100% (1)
- Types of Pollution and Their EffectsDocument3 pagesTypes of Pollution and Their EffectsMe anNo ratings yet
- Global Warming2Document2 pagesGlobal Warming2aquistarNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueTANIA MILAGROS DELGADO CHOQQUENo ratings yet
- Commented (U1) : BURNING FOSSIL FUELDocument2 pagesCommented (U1) : BURNING FOSSIL FUELBusiness OnlyNo ratings yet
- Module For Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesModule For Climate ChangeReina DionsonNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument3 pagesGreen House EffectRavi Kanth M NNo ratings yet
- Cma433 Topics 2Document55 pagesCma433 Topics 2Muhammad AizatNo ratings yet
- The Greenhouse Effect and Thinning of The Ozone Layer On The EcosystemDocument21 pagesThe Greenhouse Effect and Thinning of The Ozone Layer On The EcosystemShahirah NsnNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse GasDocument5 pagesGreenhouse Gastanzim444No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument10 pagesGlobal WarmingYashraj RathiNo ratings yet
- Global Warming AND Greenhouse EffectDocument20 pagesGlobal Warming AND Greenhouse Effectphilip najeNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument8 pagesGlobal WarmingsamanNo ratings yet
- Green House Effect ExplainedDocument4 pagesGreen House Effect ExplainedAhilan KannanNo ratings yet
- Major Concern in Today's World!!!!Document8 pagesMajor Concern in Today's World!!!!Harsh Vardhan AroraNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument7 pagesGlobal WarmingHardik TankNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthDocument6 pagesGlobal Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthSaswataBhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate Change?Document12 pagesWhat Is Climate Change?ramneekNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document7 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- RA L9 Global Warming 9Document29 pagesRA L9 Global Warming 9md.daud.ul.islamNo ratings yet
- Environmental Imbalance:-: Global Warming and Green House Effect, Ozone Layer Depletion and Its EffectsDocument45 pagesEnvironmental Imbalance:-: Global Warming and Green House Effect, Ozone Layer Depletion and Its EffectsTanu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingDocument11 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Global WarmingA Aldika Farlis50% (2)
- How Does Global Warming Happen?Document10 pagesHow Does Global Warming Happen?Simran SomaiyaNo ratings yet
- The Greenhouse EffectDocument4 pagesThe Greenhouse EffectimienazNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesGreenhouse EffectAldo S. ArizaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document20 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect - 11º Zi2Document4 pagesGreenhouse Effect - 11º Zi2zi2turmaNo ratings yet
- Name: Dea Prameswari Class: 12 Ips 3 Nomor: 07Document2 pagesName: Dea Prameswari Class: 12 Ips 3 Nomor: 07Inez SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Global Change Manmade or NaturalDocument5 pagesGlobal Change Manmade or NaturalVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Rapid Global Warming andDocument6 pagesRapid Global Warming andshekki6No ratings yet
- Global Warming DefinitionDocument4 pagesGlobal Warming Definitionvidhyadevi888666No ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument4 pagesGreen House EffectHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect, Greenhouse Gases and Global WarmingDocument25 pagesGreenhouse Effect, Greenhouse Gases and Global WarmingAnnabelle Lee BanteguiNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangDocument27 pagesClimate ChangkashafNo ratings yet
- Assignment7 THE HUMAN IMPACT ON CLIMATE AND THE ATMOSPHEREDocument2 pagesAssignment7 THE HUMAN IMPACT ON CLIMATE AND THE ATMOSPHEREHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Env - Sci Assg. 4Document9 pagesEnv - Sci Assg. 4Rohit JindalNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Causes, Effects, and SolutionsDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming: Causes, Effects, and SolutionsTinu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry EssayDocument2 pagesChemistry Essayapi-410812167No ratings yet
- Greenhouse GassDocument4 pagesGreenhouse GassBella Yunita100% (1)
- Greenhouse EffectDocument20 pagesGreenhouse EffectRajalaxmi pNo ratings yet
- Chioma 2Document12 pagesChioma 2Udoye JoyNo ratings yet
- Biology FolioDocument12 pagesBiology Foliomuhd khobirNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Warming?Document4 pagesWhat Is Global Warming?Laikya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument11 pagesGreen House EffectChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument13 pagesGreen House Effectaruba anwarNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Effects & Solutions in 40 CharactersDocument7 pagesGlobal Warming Effects & Solutions in 40 CharactersmawarnisaputriNo ratings yet
- Architect Balkrishna Vithaldas Doshi: His Philosophy and WorksDocument42 pagesArchitect Balkrishna Vithaldas Doshi: His Philosophy and Workspallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Wall Finishes: Building MaterialsDocument29 pagesWall Finishes: Building Materialspallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Legislation Act-2Document18 pagesLegislation Act-2pallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- List of Indian Architects Database, Directory: WWW - Entrepreneurindia.coDocument25 pagesList of Indian Architects Database, Directory: WWW - Entrepreneurindia.copallavi maheshwari100% (1)
- Micro and Macro Climate: By: Rishabh Swaroop Ritika Aggarwal Aabhas Mathur Tarandeep Kaur Abhishek DagurDocument12 pagesMicro and Macro Climate: By: Rishabh Swaroop Ritika Aggarwal Aabhas Mathur Tarandeep Kaur Abhishek Dagurpallavi maheshwari100% (1)
- AdDocument2 pagesAdpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Ancient Architecture: Submitted By: Pallavi Maheshwari I Semester Section ADocument23 pagesAncient Architecture: Submitted By: Pallavi Maheshwari I Semester Section Apallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro Climate: By: Rishabh Swaroop Ritika Aggarwal Aabhas Mathur Tarandeep Kaur Abhishek DagurDocument12 pagesMicro and Macro Climate: By: Rishabh Swaroop Ritika Aggarwal Aabhas Mathur Tarandeep Kaur Abhishek Dagurpallavi maheshwari100% (1)
- Submitted To: Ar. Abhishek Verma Submitted By: Pallavi Maheshwari Aakansha DadDocument16 pagesSubmitted To: Ar. Abhishek Verma Submitted By: Pallavi Maheshwari Aakansha Dadpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Corrosion 130916000742 Phpapp01Document16 pagesCorrosion 130916000742 Phpapp01pallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Passive Thermal Control and ProtectionDocument1 pagePassive Thermal Control and Protectionpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Insulation and Heat TransferDocument2 pagesInsulation and Heat Transferpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT - Group 5thDocument16 pagesSOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT - Group 5thpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Warm and Humid Climate: Submitted by - Prateek Soni Sajal Sharma Faayez RajaDocument9 pagesWarm and Humid Climate: Submitted by - Prateek Soni Sajal Sharma Faayez Rajapallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Mud Architecture: Seema Makwana Priyanshi Desai Krupa Prajapati Shriyal JainDocument16 pagesMud Architecture: Seema Makwana Priyanshi Desai Krupa Prajapati Shriyal Jainpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- BOQDocument1 pageBOQpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- MB-13_Headboard FabDocument1 pageMB-13_Headboard Fabpallavi maheshwariNo ratings yet
- Borneanus (Roos Et Al. 2014 - Asian PrimatesDocument5 pagesBorneanus (Roos Et Al. 2014 - Asian PrimatesIda Bagus Ketut WedastraNo ratings yet
- Mushrooms That Can Eat PlasticDocument7 pagesMushrooms That Can Eat PlasticKaith Gallego100% (1)
- Environmental Ethics and Corporate ResponsibilityDocument10 pagesEnvironmental Ethics and Corporate ResponsibilityTaylor LeeNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Generation, Composition and Potentiality of Waste To Resource Recovery in Narayanganj City CorporationDocument8 pagesSolid Waste Generation, Composition and Potentiality of Waste To Resource Recovery in Narayanganj City CorporationMd. Jisan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Geo ASSDocument6 pagesGeo ASSTAMERATNo ratings yet
- Rights of Nature 2Document6 pagesRights of Nature 2Western Visayas Network of Social Development NGOsNo ratings yet
- Proposal For FYPDocument3 pagesProposal For FYPhaseebNo ratings yet
- 17 Sustainable Development GoalsDocument1 page17 Sustainable Development GoalsLaarnie QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment From Flooding in The Rivers of AlbaniaDocument1 pageRisk Assessment From Flooding in The Rivers of AlbaniaMscAlbanNo ratings yet
- Forest Resources Assessment ToolDocument135 pagesForest Resources Assessment ToolRhoderic M. AbacheNo ratings yet
- Brunner and God Bold J For Res 2007Document7 pagesBrunner and God Bold J For Res 2007Shanon DanielaNo ratings yet
- Barry Commoner's Four Laws of EcologyDocument5 pagesBarry Commoner's Four Laws of EcologyRachel AnneNo ratings yet
- Y8 - Geography - Landforms & Landscapes Assessment TaskDocument9 pagesY8 - Geography - Landforms & Landscapes Assessment TaskCaitlin MannixNo ratings yet
- Module - 11 EIA-1Document9 pagesModule - 11 EIA-1Faran MasoodNo ratings yet
- Guide to Biodiversity for MiningDocument2 pagesGuide to Biodiversity for MiningbelenNo ratings yet
- SMR Blank FormDocument18 pagesSMR Blank FormVinz SelabeNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 - Types of Outdoor Environment - 2022Document12 pages1.1.2 - Types of Outdoor Environment - 2022Matthew PringleNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Global WarmingDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Global Warmingdeep932100% (5)
- EIA in Oil & GasDocument24 pagesEIA in Oil & Gassonara mayurNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and ConservationDocument11 pagesBiodiversity and Conservationvennila-puviNo ratings yet
- Food WasteDocument2 pagesFood WasteosidiusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EnvironmentDocument20 pagesChapter 4 EnvironmentCarbelyn BarteNo ratings yet
- African Climate Response To Orbital and Glacial Forcing in 140,000-Y Simulation With Implications For Early Modern Human EnvironmentsDocument10 pagesAfrican Climate Response To Orbital and Glacial Forcing in 140,000-Y Simulation With Implications For Early Modern Human EnvironmentsTaakeNo ratings yet
- 45096Document12 pages45096Halusan MaybeNo ratings yet
- Home Gardens in Nepal: A Guide to Biodiversity, Nutrition and LivelihoodsDocument135 pagesHome Gardens in Nepal: A Guide to Biodiversity, Nutrition and Livelihoodshari balakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Non-Traditional AgricultureDocument22 pagesNon-Traditional AgricultureVaniel GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Keppel Seghers HardpelletiserDocument2 pagesKeppel Seghers Hardpelletisercumpio425428100% (1)
- Efficacy of Acm - 9 (Clodinafop Propargyl + Metribuzin) On WeedsDocument6 pagesEfficacy of Acm - 9 (Clodinafop Propargyl + Metribuzin) On WeedsJournal of Environment and Bio-SciencesNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentDocument11 pagesEnvironmentIT'S MD CREATIONNo ratings yet
- KMTR - A Hotspot for BiodiversityDocument34 pagesKMTR - A Hotspot for BiodiversityVinitha ArunNo ratings yet
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesFrom EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (21)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterFrom EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationFrom EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (37)
- The Future Earth: A Radical Vision for What's Possible in the Age of WarmingFrom EverandThe Future Earth: A Radical Vision for What's Possible in the Age of WarmingNo ratings yet
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- Chesapeake Requiem: A Year with the Watermen of Vanishing Tangier IslandFrom EverandChesapeake Requiem: A Year with the Watermen of Vanishing Tangier IslandRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (38)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersFrom EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo ratings yet
- Lessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”From EverandLessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- Winged Obsession: The Pursuit of the World's Most Notorious Butterfly SmugglerFrom EverandWinged Obsession: The Pursuit of the World's Most Notorious Butterfly SmugglerRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (67)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosFrom EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- How to Be Alive: A Guide to the Kind of Happiness That Helps the WorldFrom EverandHow to Be Alive: A Guide to the Kind of Happiness That Helps the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeFrom EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1002)
- Nature's Best Hope: A New Approach to Conservation that Starts in Your YardFrom EverandNature's Best Hope: A New Approach to Conservation that Starts in Your YardRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (42)