Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Green House Effect
Uploaded by
Huria Malik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesOriginal Title
yt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesGreen House Effect
Uploaded by
Huria MalikCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
GREEN HOUSE EFFECT
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the
Earth’s surface. When the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s
atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is
absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases.
Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide,
methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals
such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of
the Earth. This process maintains the Earth’s temperature at
around 33 degrees Celsius warmer than it would otherwise be,
allowing life on Earth to exist.
The ‘Greenhouse Effect’ is defined as the increase in Earth’s
surface temperature caused by the trapping of atmospheric heat.
This makes the earth’s temperature warmer than it actually
would, than getting warmer directly by the sun. Some of the heat
gets absorbed into the atmosphere and is bounced back into
space when sunlight reaches the earth. Now, this heat is
redirected back towards the Earth when greenhouse gases such
as carbon dioxide and methane that are present in the
atmosphere absorb this heat.
In 1827, Joseph Fourier discovered the greenhouse effect which
was experimentally verified in 1861 by John Tyndall and in
1896 was quantified by Svante Arrhenius.
Mechanism of the Greenhouse Effect
Sun gives out UV, infrared and visible radiation gets received by
the earth. The incoming solar energy from the sun is redirected
back towards space by the atmosphere and clouds and then some
of the solar energy gets absorbed by the atmosphere and clouds.
And the remaining energy gets absorbed by the Earth’s surface
making it warm.This energy then gets converted into heat.
Now once this heat gets absorbed by the earth’s surface, it is
trapped in the earth’s atmosphere and thereby adding to increase
the earth’s temperature. This effect is what we call the
‘Greenhouse Effect’.
Therefore, if the amount of greenhouse gases present in the
earth’s atmosphere is high then the earth’s temperature too will
keep getting higher; which is what has been happening lately
adding to the greenhouse effect and warming up earth than it
already is.
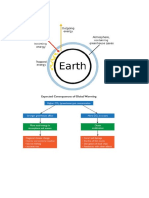
Extreme weather conditions, global warming, and rise in sea
levels are the results of the greenhouse effect.
Causes of the Greenhouse Effect
1. Burning of Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural
gas have become an integral part of our life. They are used on
large basis to produce electricity and for transportation. When
they are burnt, the carbon stored inside them is released
which combines with oxygen in the air to create carbon dioxide.
With the increase in the population, the number of vehicles have
also increased and this has resulted in increase in the pollution in
the atmosphere. When these vehicles run, they release carbon
dioxide, which is one the main gas responsible for increase in
greenhouse effect.
Apart from that, electricity-related emissions are high because
we are still dependent on coal for electricity generation which
releases large amount of CO2 into the atmosphere and is still the
primary source of fuel for generating electricity.
Deforestation, Increase in Population, Farming, Industrial
Waste and Landfills
Water vapor. The most abundant greenhouse gas, but
importantly, it acts as a feedback to the climate. Water vapor
increases as the Earth's atmosphere warms, but so does the
possibility of clouds and precipitation, making these some of the
most important feedback mechanisms to the greenhouse effect.
Carbon dioxide (CO2). A minor but very important component
of the atmosphere, carbon dioxide is released through natural
processes such as respiration and volcano eruptions and through
human activities such as deforestation, land use changes, and
burning fossil fuels. Humans have increased atmospheric CO2
concentration by more than a third since the Industrial
Revolution began. This is the most important long-lived
"forcing" of climate change.
Nitrous oxide. A powerful greenhouse gas produced by soil
cultivation practices, especially the use of commercial and
organic fertilizers, fossil fuel combustion, nitric acid
production, and biomass burning.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Synthetic compounds entirely
of industrial origin used in a number of applications, but now
largely regulated in production and release to the atmosphere
by international agreement for their ability to contribute to
destruction of the ozone layer. They are also greenhouse
gases.
You might also like
- Yotsubato Volume 1 GoiDocument66 pagesYotsubato Volume 1 Goijoe100% (2)
- Climate Change EssayDocument4 pagesClimate Change Essayyaz100% (4)
- The Greenhouse EffectDocument4 pagesThe Greenhouse EffectimienazNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test Science 8 SY 2019-2020Document6 pages1st Periodical Test Science 8 SY 2019-2020Dayen Bison100% (1)
- The Power of HR Analytics in Strategic Planning PDFDocument34 pagesThe Power of HR Analytics in Strategic Planning PDFviji100% (1)
- Global Warming Assignment (Final)Document8 pagesGlobal Warming Assignment (Final)Howard How100% (4)
- California Earth Science Grade6 ReadingWritingDocument176 pagesCalifornia Earth Science Grade6 ReadingWritingviswamanojNo ratings yet
- How To Review PV Elite Design ReportDocument9 pagesHow To Review PV Elite Design ReportBhaskar Shankar Chowdhury100% (2)
- Greenhouse Effect and Global WarmingDocument7 pagesGreenhouse Effect and Global WarmingmawarnisaputriNo ratings yet
- 4 .0 Result and Discussion: Table 4.1: Refractive Index For Each Acetone-Water MixturesDocument9 pages4 .0 Result and Discussion: Table 4.1: Refractive Index For Each Acetone-Water MixturesThrishnaa BalasupurManiamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Plant LocationDocument5 pagesChemical Plant LocationabdsalNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1196 PDFDocument3 pagesAstm D 1196 PDFSetyawan Chill Gates0% (1)
- Global WarmingDocument12 pagesGlobal Warmingshoeb100% (1)
- Maltese ArchitectureDocument13 pagesMaltese Architecturer_borgNo ratings yet
- Boluda Towing PlanDocument76 pagesBoluda Towing PlanManuel VaronNo ratings yet
- AL7 - The Elemental Lords AwakenDocument32 pagesAL7 - The Elemental Lords AwakenJavier67% (3)
- Exploring The Word of EnglishDocument210 pagesExploring The Word of EnglishSamiullah SadiqNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument10 pagesGlobal Warmingtusharbooks100% (34)
- Climate Change EssayDocument5 pagesClimate Change Essayyaz100% (4)
- Digital Media and Copyright Protection Under Copyright Ordinance 1962 & WIPO Internet TreatiesDocument19 pagesDigital Media and Copyright Protection Under Copyright Ordinance 1962 & WIPO Internet TreatiesHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect and GasesDocument4 pagesGreenhouse Effect and Gasespradeep aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Preventive Maintanance Interval 10 Whell Loader SDLGDocument40 pagesPreventive Maintanance Interval 10 Whell Loader SDLGAdy Prasetyo100% (2)
- Global Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueTANIA MILAGROS DELGADO CHOQQUENo ratings yet
- Teks Eksplanasi B.ingDocument1 pageTeks Eksplanasi B.ingAhmad ZiyaNo ratings yet
- TUGAS Global WarmingDocument4 pagesTUGAS Global WarmingPolsek Siantar SelatanNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument8 pagesGreenhouse EffectAmple CunananNo ratings yet
- BIOL 002 Global Warming: Beirut Arab University Faculty of Science Department of BiologyDocument65 pagesBIOL 002 Global Warming: Beirut Arab University Faculty of Science Department of BiologyYoumna ShatilaNo ratings yet
- What Are The Reasons For Global Warming?Document6 pagesWhat Are The Reasons For Global Warming?manirathinaNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument6 pagesGreen House EffectVir PatelNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Causes, Effects, and SolutionsDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming: Causes, Effects, and SolutionsTinu AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument11 pagesGreen House EffectChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Commented (U1) : BURNING FOSSIL FUELDocument2 pagesCommented (U1) : BURNING FOSSIL FUELBusiness OnlyNo ratings yet
- The Greenhouse Effect and Thinning of The Ozone Layer On The EcosystemDocument21 pagesThe Greenhouse Effect and Thinning of The Ozone Layer On The EcosystemShahirah NsnNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document20 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument7 pagesGlobal WarmingHardik TankNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document15 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument11 pagesGlobal Warmingghataksampa816No ratings yet
- How Does Global Warming Happen?Document10 pagesHow Does Global Warming Happen?Simran SomaiyaNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect Essay SPMDocument1 pageGreenhouse Effect Essay SPMcyberbat2008No ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument6 pagesGreenhouse EffectReshmi ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- PP 31 The Atmosphere and Climate ChangeDocument97 pagesPP 31 The Atmosphere and Climate ChangeOlerato NtsimaneNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4: The Greenhouse EffectDocument7 pagesBiology Form 4: The Greenhouse EffectNur Hidayatul Aliaa JustinNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary "Climate Change"Document5 pagesVocabulary "Climate Change"КатяNo ratings yet
- Presentation 10Document7 pagesPresentation 10xoranek474No ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument6 pagesGreenhouse Effectnimila gopiNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesGreenhouse Effectbbroy britainNo ratings yet
- Effect of Green House Gas Chem 12 ProjectDocument22 pagesEffect of Green House Gas Chem 12 ProjectMohak SubramanyaNo ratings yet
- History of The Greenhouse Effect PresentaseDocument7 pagesHistory of The Greenhouse Effect PresentaseIank M GoaNo ratings yet
- Aerith M. Adelante: Grade V-DaltonDocument10 pagesAerith M. Adelante: Grade V-DaltonElliot AldersonNo ratings yet
- Explanation TeksDocument4 pagesExplanation TeksDaniel SitanggangNo ratings yet
- List of ContentsDocument9 pagesList of ContentsMaria JBieber BrandonizerNo ratings yet
- NG One of The Biggest Threats To HumanityDocument2 pagesNG One of The Biggest Threats To HumanityRhea CabillaNo ratings yet
- HeyDocument7 pagesHeyHASHIM TRUNKWALANo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Sma N 1 KutaDocument4 pagesGlobal Warming: Sma N 1 KutaTL IGustiAgungAyuTrinadyaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument13 pagesGlobal WarmingRam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument8 pagesGlobal WarmingsamanNo ratings yet
- Green House EffectsDocument6 pagesGreen House EffectsLabal ListicNo ratings yet
- Environmental Imbalance:-: Global Warming and Green House Effect, Ozone Layer Depletion and Its EffectsDocument45 pagesEnvironmental Imbalance:-: Global Warming and Green House Effect, Ozone Layer Depletion and Its EffectsTanu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Green House Effect11Document19 pagesGreen House Effect11sayyadsajidaliNo ratings yet
- Global Warming & Climate Change: in The PhilippinesDocument23 pagesGlobal Warming & Climate Change: in The PhilippinesJannuhhhNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Scientific Basis and Impacts Lecture Part 1Document21 pagesClimate Change Scientific Basis and Impacts Lecture Part 1Muhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Lesson One: Global WarmingDocument7 pagesLesson One: Global WarmingALANNo ratings yet
- Causes Greenhouse EffectDocument1 pageCauses Greenhouse EffectYaiza Almengló OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Chioma 2Document12 pagesChioma 2Udoye JoyNo ratings yet
- Cma433 Topics 2Document55 pagesCma433 Topics 2Muhammad AizatNo ratings yet
- World Day For The Reduction of Co2 EmissionsDocument12 pagesWorld Day For The Reduction of Co2 Emissionsbanoon.sadiq1No ratings yet
- Green House EffectDocument13 pagesGreen House Effectaruba anwarNo ratings yet
- Climate Change ExplainedDocument2 pagesClimate Change ExplainedDexter RaboNo ratings yet
- The Earth Remembers: A Story of Warming, Damage, and HopeFrom EverandThe Earth Remembers: A Story of Warming, Damage, and HopeNo ratings yet
- Vanishing Peaks: Unveiling the Impact of Climate Change on Global SnowpacksFrom EverandVanishing Peaks: Unveiling the Impact of Climate Change on Global SnowpacksNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: 50 tips about the hot topic many people dismissFrom EverandGlobal Warming: 50 tips about the hot topic many people dismissNo ratings yet
- Widespread Distribution of Hormones in An Animal Permits CertainDocument20 pagesWidespread Distribution of Hormones in An Animal Permits CertainHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- The IMF Has Recently Predicted That The Percentage of Population Living in Poverty Will Grow To 40pc FromDocument1 pageThe IMF Has Recently Predicted That The Percentage of Population Living in Poverty Will Grow To 40pc FromHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Indo Pak RelationsDocument16 pagesIndo Pak RelationsHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Point Mutations: Silent Mutation: Although A Change in The DNA Sequence Occurs, ThisDocument3 pagesPoint Mutations: Silent Mutation: Although A Change in The DNA Sequence Occurs, ThisHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Alveena SynopsisDocument20 pagesAlveena SynopsisHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- HUria's Write Up After FeedbackDocument1 pageHUria's Write Up After FeedbackHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Human Beings and Their ExistenceDocument1 pageHuman Beings and Their ExistenceHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- File:///C:/Users/Arc/Desktop/Juvenile Delinquency - Theory, Practice, and Law (Pdfdrive) PDFDocument1 pageFile:///C:/Users/Arc/Desktop/Juvenile Delinquency - Theory, Practice, and Law (Pdfdrive) PDFHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Ecological RestorationDocument8 pagesEcological RestorationHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- 3 Innovative Solutions To Reducing Poverty in PakistanDocument5 pages3 Innovative Solutions To Reducing Poverty in PakistanHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Huria Malik: Career Objective Personal InformationDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae Huria Malik: Career Objective Personal InformationHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Challenges To SovereigntyDocument4 pagesChallenges To SovereigntyHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Anthropology 13% 105Document2 pagesAnthropology 13% 105Huria MalikNo ratings yet
- Poverty: CausesDocument11 pagesPoverty: CausesHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Food Security and Sustainable AgricultureDocument23 pagesFood Security and Sustainable AgricultureHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Can Democracy DeliverDocument34 pagesCan Democracy DeliverHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Prospects and Challenges of Online Education in Secondary Schools in Northern NigeriaDocument7 pagesProspects and Challenges of Online Education in Secondary Schools in Northern NigeriaHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- RespondentDocument20 pagesRespondentHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Write Better Speak Better HttpsDocument1 pageWrite Better Speak Better HttpsHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- A Criminal Investigation Is An Undertaking That SeeksDocument4 pagesA Criminal Investigation Is An Undertaking That SeeksHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- One Characteristic of Hybrid Rule Is The Duality of Power, and That Has Its Own Perils. The Present Political Disorder Is Symptomatic of ThisDocument5 pagesOne Characteristic of Hybrid Rule Is The Duality of Power, and That Has Its Own Perils. The Present Political Disorder Is Symptomatic of ThisHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Social Contract Theory of Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Thomas Hobbes, and John LockeDocument4 pagesComparison of Social Contract Theory of Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Thomas Hobbes, and John LockeHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- West Pakistan Family Courts Act 1964 PDFDocument11 pagesWest Pakistan Family Courts Act 1964 PDFAmmarNo ratings yet
- Aristotle'S Concept of Polity and Its Relevancy To The 2007 Constitution of The Kingdom of ThailandDocument11 pagesAristotle'S Concept of Polity and Its Relevancy To The 2007 Constitution of The Kingdom of ThailandamirNo ratings yet
- Defendant: Team Code: MDocument14 pagesDefendant: Team Code: MHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Huria MalikNo ratings yet
- The Political Theory of Communism and THDocument99 pagesThe Political Theory of Communism and THHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Similarity Between Monte PDFDocument7 pagesThe Fundamental Similarity Between Monte PDFHuria MalikNo ratings yet
- 40 Bài đọc hiểu - Cô Kiều Thắng - Tuyensinh247Document170 pages40 Bài đọc hiểu - Cô Kiều Thắng - Tuyensinh247phuong uyen tran hoangNo ratings yet
- The Happy Prince and Other Tales - Oscar Wilde PDFDocument41 pagesThe Happy Prince and Other Tales - Oscar Wilde PDFFiamma Del SartoNo ratings yet
- Artikel InternasionalDocument8 pagesArtikel InternasionalUmi KulsumNo ratings yet
- Ecology I: Population Ecology: Campbell Chapter 53Document33 pagesEcology I: Population Ecology: Campbell Chapter 53Amna BaigNo ratings yet
- The CipherDocument88 pagesThe CipherCarlos Eduardo AguirreNo ratings yet
- Demand Forecasting in A Supply ChainDocument10 pagesDemand Forecasting in A Supply ChainMd. Rezaul Islam TusharNo ratings yet
- The Cold Water Candy TestDocument3 pagesThe Cold Water Candy TestChristian Dave Tad-awan100% (1)
- Samsung 3000mah ICR18650-30ADocument14 pagesSamsung 3000mah ICR18650-30AStreet_skNo ratings yet
- 9814 Material 1 1625049897Document7 pages9814 Material 1 1625049897AadityaNo ratings yet
- Rosa de Vientos: Imata: Station # 01Document3 pagesRosa de Vientos: Imata: Station # 01Nataly AndradeNo ratings yet
- Forensic Entomology - AndersonDocument10 pagesForensic Entomology - AndersonSarah van WermeskerkenNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Equipos Paquetes PDFDocument8 pagesEspecificaciones Equipos Paquetes PDFDavid BallenNo ratings yet
- Typhoon Resilliency v.210Document19 pagesTyphoon Resilliency v.210Emerson BolibolNo ratings yet
- Hyouketsu Kyoukai No Eden Volume 1Document167 pagesHyouketsu Kyoukai No Eden Volume 1Matthew Dean RogersNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide On Aerokinesis - The Ability To Manipulate Air - Learn PowersDocument21 pagesUltimate Guide On Aerokinesis - The Ability To Manipulate Air - Learn PowersAmir Hossein RamezaniNo ratings yet
- (123doc) - De-On-Thi-Hsg-Tieng-Anh-Lop-10-Co-Dap-AnDocument19 pages(123doc) - De-On-Thi-Hsg-Tieng-Anh-Lop-10-Co-Dap-AnNguyễn T. KiênNo ratings yet
- How The World Was CreatedDocument1 pageHow The World Was CreatedRjvm Net Ca Fe100% (1)
- MA Sample Test B1Document12 pagesMA Sample Test B1Kartlosi NadiradzeNo ratings yet