Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam Reviewer
Uploaded by
Vanessa Jimenez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesOriginal Title
GEN-BIOLOGY-1-deptal-2nd-quarter-exam-reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesGEN BIOLOGY 1 Deptal 2nd Quarter Exam Reviewer
Uploaded by
Vanessa JimenezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
GEN BIOLOGY 1
Lactose intolerance happens when your small
nd
2 Quarter intestine does not make enough of a digestive
enzyme called lactase. Lactase breaks down
REVIEWER FOR DEPARTMENTAL EXAMINATION the lactose in food so your body can absorb it.
People who are lactose intolerant have
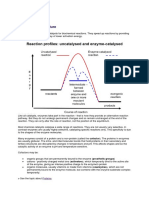
An enzyme is a biological catalyst and is almost unpleasant symptoms after eating or drinking
always a protein. It speeds up the rate of a specific milk or milk products. These symptoms include
reaction in the cell. Since enzymes are proteins, they are bloating, diarrhea and gas.
composed of monomers known as amino acids.
Enzymes speed up the rate of chemical reactions Enzymes need optimal conditions
because they lower the energy of activation, the
energy that must be supplied in order for molecules to Each enzyme works within quite a small pH
react with one another. range. There is a pH at which its activity is
greatest (the optimal pH). This is
Enzymes are a type of protein found in because changes in pH can make and break
cells. Enzymes create various chemical reactions in the intra- and intermolecular bonds, changing
body. The function of enzymes in the body is very the shape of the enzyme and, therefore, its
important, namely creating a reaction for the body such effectiveness.
as building muscles, destroying toxins, and breaking
down food particles during the digestive Enzymes need the right conditions to work. If
process. Enzymes are produced naturally in the body. conditions aren't right, enzymes can change
shape. Then, they no longer fit with substrates,
so they don't work correctly.
This response is considered appropriate, in the absence These are chemicals or compounds
of enzymes, higher temperatures will complete the that resemble the normal substrate
reactions necessary to sustain life. This is because an molecule and compete for admission
increase in temperature will increase the rate of a into the active site.
reaction, where the reaction will stimulate energy
stimulation activity (in the reaction process) so that a The enzyme inhibitor closely resembles the
higher increase in temperature can replace the role substrate in its molecular structure and inhibits
of enzymes in a body reaction. enzyme activity by binding to the active site of the
enzyme.
The Active Site
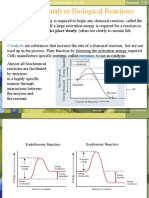
An endothermic process absorbs heat and
The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds is cools the surroundings of the starting reactants;
called the active site (since that's where the catalytic it is very unstable and is referred to as the
“action” happens). transition state.
Energy flow in the life of a cell
What is lactose intolerance?
Lactose intolerance is when your body can't break down
or digest lactose. Lactose is a sugar found in milk and
milk products.
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that accelerate
chemical reactions, enzymes that happen to be made of
RNA rather than protein.
Substances that speed up a reaction without being used
up destroyed or incorporated into the product is a
catalyst.
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—
without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. The
catalysts for biochemical reactions that happen in living
organisms are called enzymes.
The
Cofactors are inorganic species or at least nonprotein The substrate is the reactant an enzyme act
compounds that aid enzyme function by increasing the
rate of catalysis. Typically, cofactors are metal ions. The substance an enzyme works on is a
substrate. The substrate also has a unique
The increase of reaction rate of enzymes: shape. The enzyme and the substrate must fit
together to work.
The increase of the reaction rate of an enzyme-
catalyzed reaction increases with an increase in the When an enzyme binds its substrate, it forms
concentration of an enzyme. Increasing the number an enzyme-substrate complex.
of enzymes or adding more enzymes.
The part of the enzyme where the substrate
binds is called the active site (since that's
where the catalytic “action” happens).
The lock-and-key model suggests that the
substrate is completely complementary in
shape to the active site so that it fits
in 'perfectly' - i.e. the way a key (the substrate)
fits into a lock (the enzyme). There is no
change in the shape of the active site when
the substrate binds.
Protein Structure Intr0duction
The term “protein” originates from the Greek word
proteios, meaning “primary” or “of the first rank”.
The name was adopted by Jon Berzelius in 1838 to
emphasize the importance of this class of molecules.
Quaternary structure: Quaternary structure is the
three-dimensional structure of a protein macromolecule
formed by the aggregation of two or more individual
polypeptide chains.
The sequence in which amino acids are arranged in a
protein is called the primary structure. The linear
sequence of amino acids constitutes a protein's primary
structure. The sequence is written from the amino- The tightening of the binding after initial
terminal end (the first amino acid) to the carboxyl- contact is called induced fit. This brings
terminal end. chemical groups of the active site into
positions that enhance their ability to catalyze
The monomers or building blocks of proteins are known the chemical reaction. 10.
as amino acids. Amino acids come together during the
process of translation and form peptide bonds with one Activation Energy is the minimum amount of
another. energy needed to start a chemical reaction. All
chemical reactions need a certain amount of
Each enzyme typically binds only one substrate. activation energy to get started.
Enzymes are not consumed during a reaction; instead,
they are available to bind new substrates and catalyze Get a banana, remove the banana peel,
and then take a bite. Observe the bitten part
the same reaction repeatedly.
of the banana for a few minutes.
The term “protein” originates from the Greek word proteios,
meaning “primary” or “of first rank”
Enzymes are organic or biological catalysts that are
essential to live organisms.
Questions:
1. What do you observe?
As the banana peels and takes a bite, the
bitten part of the banana becomes brown
as it was exposed to air for a few minutes.
2. Did the bitten part of the banana turn brown?
Yes, bananas turned brown when exposed to air for a
few minutes because Bananas contain the enzyme
polyphenol oxidase, and when the enzyme interacts
with oxygen, it causes a chemical reaction. This
chemical reaction, known as enzymatic browning,
changes the banana's peel and fruit to brown.
3. What caused the browning?
Bananas contain polyphenol oxidase and other iron-
containing chemicals which react with the oxygen in the
air when the cells are cut open. When exposed to the
air, these chemicals react in a process known as
oxidation, turning the fruit brown.
You might also like
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Unit 3 A EnzymesDocument3 pagesUnit 3 A EnzymesseecatpNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document6 pagesEnzymes 1zarszNo ratings yet
- Unit EnzimDocument6 pagesUnit EnzimSUNARDINo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab: Investigating Factors that Impact Reaction RateDocument15 pagesEnzyme Lab: Investigating Factors that Impact Reaction RateAshalee JonesNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ChemistryDocument9 pagesEnzyme ChemistryVictor OmoloNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Free Energy and Metabolism RegulationDocument29 pagesGibbs Free Energy and Metabolism RegulationMaya AwadNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory (Study of Enzymes) - 3Document18 pagesBio Investigatory (Study of Enzymes) - 3Deepa Singh0% (1)
- Biology Notes CHPTR 5Document4 pagesBiology Notes CHPTR 5Wan HasliraNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting ActivityDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Structure, Function and Factors Affecting Activitytiyf mojaleedNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: - Sucrase - Lactase - MaltaseDocument4 pagesEnzymes: - Sucrase - Lactase - MaltaseKate Nicole EjercitoNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument40 pagesEnzymesVeronica HanyNo ratings yet
- Lecture On EnzymesDocument26 pagesLecture On EnzymesDAVIE MATIASNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Principles of BiologyDocument18 pagesEnzymes: Principles of BiologyNaskar SouvikNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and The Active SiteDocument23 pagesEnzymes and The Active SiteLaura GambaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes speed up reactionsDocument3 pagesEnzymes speed up reactionsAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12Document7 pagesEnzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12almira garciaNo ratings yet
- Bio t4 KSSM Chap 5 DLPDocument34 pagesBio t4 KSSM Chap 5 DLPRaynieNo ratings yet
- Genes & Inheritance SeriesDocument58 pagesGenes & Inheritance SeriesKim HoangNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Material PDFDocument7 pagesEnzymes Material PDFSalma AhmedNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymesVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument3 pagesMetabolismFans TimeNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Are Proteins A Definitive Guide of 4000+ Words (Updated)Document15 pagesEnzymes Are Proteins A Definitive Guide of 4000+ Words (Updated)mammmmNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument35 pagesGen Biomikechristian073No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biological Catalysts that Speed Up ReactionsDocument6 pagesEnzymes: Biological Catalysts that Speed Up ReactionsSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- Enzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesDocument26 pagesEnzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesAyesha JamilNo ratings yet
- Enzyme, A Substance That Acts As ADocument5 pagesEnzyme, A Substance That Acts As Amuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Efficient Catalysts for Biochemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesEnzymes: Efficient Catalysts for Biochemical ReactionsLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- Bio Sem 1Document123 pagesBio Sem 1HALFAH BT HASSANNo ratings yet
- Enzymes .Document6 pagesEnzymes .Nathan SsekamatteNo ratings yet
- 5 - EnzymesDocument5 pages5 - EnzymesIce CoffeeNo ratings yet
- Enzymes (As Biology)Document42 pagesEnzymes (As Biology)Muhtasim FarhanNo ratings yet
- GCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME NoteDocument11 pagesGCE AS Biology 3 ENZYME Notengnicole090607No ratings yet
- Chidrawi M1 C PDFDocument33 pagesChidrawi M1 C PDFZA AustraliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter EnzymesDocument2 pagesChapter EnzymesJaved SohawonNo ratings yet
- Notes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanDocument10 pagesNotes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanLanz MoenNo ratings yet
- Scienze e Rapporto Uomo NaturaDocument2 pagesScienze e Rapporto Uomo NaturaEmilia EspositoNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalysis ExplainedDocument9 pagesEnzyme Catalysis ExplainedMaira. BalsaNo ratings yet
- Inhibition and RegulationDocument28 pagesInhibition and RegulationRoyal MindNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Enzymes PDFDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Enzymes PDFJenny GoNo ratings yet
- Bio-Ch 5-EnzymesDocument6 pagesBio-Ch 5-EnzymesHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- 1.3b Enzymes EditedDocument10 pages1.3b Enzymes EditedSoleil R.No ratings yet
- 1. C 1.1 SL EnzymesDocument37 pages1. C 1.1 SL Enzymesswapnaboddu666No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument23 pagesEnzymessamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (HL)Document26 pagesMetabolism (HL)Sapreen KaurNo ratings yet
- Claret College of Isabela: Senior High SchoolDocument7 pagesClaret College of Isabela: Senior High SchoolLatifah EmamNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument22 pagesEnzymesRohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- Enzyme StructureDocument17 pagesEnzyme Structureام احمدNo ratings yet
- Bio EnzDocument8 pagesBio EnzbhzeenatNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition EnzymesDocument7 pagesHuman Nutrition EnzymesMihika SpamNo ratings yet
- Sample 63Document9 pagesSample 63Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument43 pagesEnzymesMaryam SabirNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivityDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Function, Structure, and Factors Affecting ActivitySameer ButtNo ratings yet
- Protein Denaturation: EnzymesDocument7 pagesProtein Denaturation: EnzymescharlesNo ratings yet
- Enzymes ...Document13 pagesEnzymes ...Glen MangaliNo ratings yet
- S.5 EnzymesDocument16 pagesS.5 Enzymesmusokelukia6No ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanDocument11 pagesEnzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- About The Nomenclature of Enzymes: Everything You Need To KnowDocument4 pagesAbout The Nomenclature of Enzymes: Everything You Need To KnowIva ColterNo ratings yet
- Bio-Organic Chemistry (Unit-V)Document32 pagesBio-Organic Chemistry (Unit-V)PG ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Document 2 Safety in The WorkplaceDocument1 pageDocument 2 Safety in The WorkplaceVanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Literature REVIEWERDocument4 pages21st Century Literature REVIEWERVanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document1 pageLesson 7Vanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- Network Router: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Coaxial CableDocument3 pagesNetwork Router: Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Coaxial CableVanessa JimenezNo ratings yet
- Some Tensile Properties of Unsaturated Polyester Resin Reinforced With Varying Volume Fractions of Carbon Black NanoparticlesDocument8 pagesSome Tensile Properties of Unsaturated Polyester Resin Reinforced With Varying Volume Fractions of Carbon Black NanoparticlesMamoon ShahidNo ratings yet
- Xii Chemistry Patna RegionDocument235 pagesXii Chemistry Patna RegionPrashant Jain100% (1)
- Kimyasal Tepk - Müh 1Document8 pagesKimyasal Tepk - Müh 1Merve YönyülNo ratings yet
- Top 27 Engineering BooksDocument4 pagesTop 27 Engineering BooksSai Subrahmanyam PvkNo ratings yet
- Chem 1701 Practice Test 1Document10 pagesChem 1701 Practice Test 1api-535167759No ratings yet
- MCQ ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesMCQ ThermodynamicsNaughty PAPANo ratings yet
- Amines - JEE Main 2023 AprilDocument15 pagesAmines - JEE Main 2023 AprilSajjan BalasubramanyanNo ratings yet
- Inj Mold CalculateDocument9 pagesInj Mold CalculateGiap NguyenNo ratings yet
- Process Design II Lecture on Distillation ColumnsDocument32 pagesProcess Design II Lecture on Distillation Columnsmasroor ahmed laghariNo ratings yet
- Technip - Process Engineering Design GuideDocument302 pagesTechnip - Process Engineering Design Guideanghel_florin82No ratings yet
- Koteeswaran, MythiliDocument79 pagesKoteeswaran, MythilimadhavanssnNo ratings yet
- Conservation Laws of Fluid Motion and Boundary Conditions: Ibrahim SezaiDocument20 pagesConservation Laws of Fluid Motion and Boundary Conditions: Ibrahim Sezairamy86No ratings yet
- Werner Vogel Glass Chemistry PDFDocument478 pagesWerner Vogel Glass Chemistry PDFJéssica Notório100% (1)
- Process Dynamics and Control: By: Gemechu Bushu (AAU)Document32 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control: By: Gemechu Bushu (AAU)gebreslassie gereziherNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas TreatementDocument73 pagesNatural Gas Treatementهشام حدودNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument45 pagesThermodynamics and Kinetic Theory of GasesSanthosh PotluriNo ratings yet
- Project No. 3 Case Study - Cumene Production Plant SimulationDocument3 pagesProject No. 3 Case Study - Cumene Production Plant SimulationRizal YansyahNo ratings yet
- APIChem Featured Products PDFDocument5 pagesAPIChem Featured Products PDFTezozómocNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Aromatic Compounds: Chemistry Molecule ConjugatedDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Aromatic Compounds: Chemistry Molecule ConjugatedBobby RedianNo ratings yet
- Franck-Hertz Experiment Determines Argon Excitation EnergyDocument3 pagesFranck-Hertz Experiment Determines Argon Excitation EnergyBattiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer TheoryDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer TheoryKTINE08No ratings yet
- Confronting Crystallization IssuesDocument8 pagesConfronting Crystallization IssuesBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- Chapter 09 - Two-Component System (Binary Systems)Document21 pagesChapter 09 - Two-Component System (Binary Systems)Jean D. MARIN PADILLLANo ratings yet
- QB 10 Chapter 5&6Document4 pagesQB 10 Chapter 5&6Nitin SNo ratings yet
- PH ParadoxDocument6 pagesPH ParadoxSofiaMylonaNo ratings yet
- R2B-P3-206-02-A-FO-00001 - Rev.1 - Operation Philosophy - EngDocument290 pagesR2B-P3-206-02-A-FO-00001 - Rev.1 - Operation Philosophy - Engdaniel contreras0% (1)
- Icho 15Document28 pagesIcho 15los sabiosNo ratings yet
- Vapour Pressure TestingDocument2 pagesVapour Pressure TestinglbNo ratings yet
- Integrate Process Simulation and Process SynthesisDocument0 pagesIntegrate Process Simulation and Process SynthesisSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- Laser DissertationDocument7 pagesLaser DissertationPayForAPaperCanada100% (1)