Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fromm 3
Uploaded by
Alyssa Cabije0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesFeist FROMM
Original Title
FROMM 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFeist FROMM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesFromm 3
Uploaded by
Alyssa CabijeFeist FROMM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
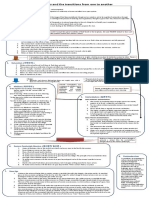
SUMMARY
ERICH FROMM: HUMANISTIC PSYCHOANALYSIS
I. OVERVIEW i. Between life and death (life after
a. Modern-day people have been torn away death)
from their prehistoric union with nature ii. Humans are capable of
and also with one another yet they have conceptualizing goal of complete self-
the power of reasoning, foresight, realization but also aware that life is
imagination. too short to reach that goal
b. “Freaks of Universe” iii. People are ultimately alone. Yet we
c. Self-awareness contributes to feelings of cannot tolerate isolation
loneliness, isolation, and homelessness. iv.
d. Reuniting with nature and with fellow IV. HUMAN NEEDS
human beings to escape those feelings a. Relatedness
e. Emphasizes the influence of i. Drive for union with another person/s
sociobiological factors, history, economics ii. 3 basic ways in w/c a person may
and class structure relate to the world
f. Humanistic Psychoanalysis: humanity’s 1. Submission
separation from the natural world has 2. Power
produced feelings of loneliness and 3. Love: only route by w/c a person
isolation—basic anxiety. can become united with the world
g. Looks at people from a historical and and achieve individuality and
cultural perspective rather than a strictly integrity
psychological one b. Transcendence
h. Less concerned with the individual and i. Urge to rise above a passive and
more concerned with those accidental existence and into the
characteristics common to a culture. “realm of purposefulness and
i. When humans emerged, as a separate freedom”
species in animal evolution, they lost ii. Malignant aggression: kill for reasons
most of their animal instincts but gained other than survival
“an increase in brain development that c. Rootedness
permitted self-awareness, imagination, i. The needs to establish roots or to feel
planning and doubt” at home again.
j. This combination of weal instincts and a ii. Fixation: tenacious reluctance to
highly developed brain makes humans move beyond the productive security
distinct from all other animals. provided by one’s mother
k. Personality: the totality of inherited and iii. People who strive for rootedness
acquired psychic qualities which are through fixation, are afraid to the next
characteristic of one individual and which step of birth, craving to be nurtured,
the individual unique nursed, protected by a motherly
II. BIOGRAPHY figure
a. Trained in Freudian psychoanalysis, iv. AGREED TO FREUD that incestuous
influenced by Karl Marx, Karen Horney… desires are universal but disagreed
b. View of human nature was shaped by with Freud that they are essential
childhood experiences v. Attracted to older woman—
c. Very neurotic parents—probably a rather Bachofen’s mother-centered theory
unbearably neurotic child d. Sense of Identity
d. Father: moody i. Capacity to be aware of ourselves as a
Mother: prone to depression separate entity.
e. Grew up in 2 distinct worlds—Traditional ii. Because we are torn away from
Orthodox Jewish and modern capitalist nature, we need to form a concept of
(seeing events from more than one our self, to be able to say, “I am I” or
perspective “I am the subject of my actions”
III. FROMM’S BASIC ASSUMPTIONS iii. Without a sense of identity, people
a. “Individual personality can be understood could not retain their sanity, and this
only in the light of human history.” threat provides a powerful motivation
b. Humans have been torn away from their to do almost anything to acquire a
prehistoric union with nature and left sense of identity.
with no powerful instincts to adapt to a iv. NEUROTICS: attach to powerful
changing world. But because humans people or to social or political
have acquired the ability to reason, they institutions
can think about their isolated condition — HEALTHY: lesser need to conform and
the human dilemma. to give up their sense of identity; do
c. EXISTENTIAL DICHOTOMIES not surrender their freedom and
individuality in order to fit in to the doubts, independent and yet an integral
society part of mankind; represents a successful
e. Frame of orientation solution to the human dilemma of being
i. Road map to make way through the part of the natural world and yet separate
world from it.
ii. Without it, humans would be VI. CHARACTER ORIENTATIONS: person’s
confused and unable to act relatively permanent way of relating to people
purposefully and consistently and things
iii. Enables people to organize the a. NON-PRODUCTIVE ORIENTATIONS
various stimuli that impinge them i. Receptive
iv. A road map without a goal or 1. Source of all good lies outside
destination is worthless. themselves and that the only way
v. Object of devotion: focuses people’s they can relate to the world is to
energies in a single direction, enables receive things (love, knowledge,
us to transcend our isolated existence materials)
and confers meaning to their lives; 2. Receiving than giving passively
you can only have the f.o.o if you have 3. Negative qualities: Passive,
the o.o.d submissive, lack of self-confidence
V. THE BURDEN OF FREEDOM Positive qualities: loyal,
Basic Anxiety: feeling of being alone in the acceptance, trust
world ii. Exploitative
a. MECHANISMS OF ESCAPE 1. Aggressively take what they desire
i. Authoritarianism rather than passively receive it
1. tendency to give up the 2. Negative qualities: egocentric,
independence of one’s own conceited, arrogant, seducing
individual self and to fuse one’s Positive qualities: impulsive,
self with somebody or something proud, charming, self-confident
outside oneself, in order to iii. Hoarding
acquire the strength which the 1. Seek to save that which they have
individual is lacking already obtained
2. Masochism: results from basic 2. Hold everything inside and do not
feeling of powerlessness, let go of anything
weakness and inferiority, aimed at 3. Possess loved one and preserve
joining the self to a more powerful the relationship rather than
person or institution; disguised as allowing it to change and grow
love or loyalty but can never 4. Tend to live in the past
contribute positively to 5. Similar to freud’s ANAL
independence and authenticity CHARACTER—excessively orderly,
3. Sadism: more neurotic and more stubborn and miserly.
socially harmful, aimed at 6. Negative qualities: rigidity,
reducing basic anxiety through sterility, obstinacy, compulsivity
achieving unity with another and lack of creativity
person. (1. Need to make others Positive qualities: Orderliness,
dependent on oneself and to gain cleanliness and punctuality
power over those who are weak 2. iv. Marketing
Compulsion to exploit others to 1. An outgrowth of modern
take advantage of them and use commerce in which trade is no
them for one’s benefit or pleasure longer personal but carried out by
3. Desire to see others suffer, large, fearless corporations
either physically or 2. See themselves as commodities,
psychologically.) with their personal value
ii. Destructiveness: rooted in the dependent on their exchange
feelings of aloneness, isolation and value, that is their ability to sell
powerlessness; seeks to do away with themselves
other people 3. They must make other believe
iii. Conformity: giving up their that they are skillful and salable
individuality and becoming whatever 4. Play many roles and guided by the
people desire them to be; seldom motto “I am as you desire me”
express opinion, robot-like, react
predictably, appear stiff and TWO KINDS OF UNPRODUCTIVE FAMILY:
automated
b. POSITIVE FREEDOM: can be free and not
alone, critical and yet not filled with
Symbiotic Family – members of the family are b. Fromm believed that patients come to
“swallowed up” by other so they do not develop therapy seeking satisfaction of their basic
their own personality human needs
c. Transference and Counter transference
Withdrawing Family – cool indifference if not cold
hatefulness
b. PRODUCTIVE IX. METHOD OF INVESTIGATION
i. has 3 dimensions a. Fromm's personality theory rests on data
1. working: value work not as an end he gathered from a variety of sources,
in itself, but as a means of creative including psychotherapy, cultural
self-expression and use work as a anthropology, and psychohistory.
means of producing life’s
necessities
2. loving: care, responsibility,
respect, and knowledge.
a. Biophilia: passionate love of
life and all that is alive
3. reasoning:
Three types of Relationship between Child and his
Parents:
Symbiotic Relatedness – failure to attain
independence and signifies immaturity and
pseudo-forms of love
Withdrawal Destructiveness – negative
relatedness or distance and indifference
Genuine Productive Love
VII. PERSONALITY DISORDERS
a. NECROPHILIA
i. love of death
ii. sexual perversion in which a person
desires sexual contact with corpse
iii. any attraction to death
iv. alternative character of biophilia
v. racists, warmongers, bullies that loves
bloodshed, destruction, terror and
torture and delight destroying life
vi. love to talk about sickness, death, and
burials
vii. fascinated by dirt, decay, corpses and
feces
b. MALIGNANT NARCISSISM
i. Interest in their own body
ii. Devalued others belonging
c. INCESTUOUS SYMBIOSIS
SYNDROME OF DECAY – combination of the three
personality disorders.
NOTE: The goal of therapy Fromm's psychotherapy
was to work toward satisfaction of the basic human
needs of relatedness, transcendence, rootedness, a
sense of identity, and a frame of orientation. The
therapist tries to accomplish this through shared
communication in which the therapist is simply a
human being rather than a scientist
VIII. PSYCHOTHERAPY
a. More interpersonal aspects of a
therapeutic encounter
You might also like
- ToP A5.5Document4 pagesToP A5.5Marielle Louisse MasinsinNo ratings yet
- Brown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationDocument24 pagesBrown and Beige Minimalist Vintage Scrapbook Self-Introduction PresentationLaine DerainNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 FROMM MyReviewerDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 7 FROMM MyReviewerFrances LouiseNo ratings yet
- UPDATED-UTS-REVIEWER (1)Document5 pagesUPDATED-UTS-REVIEWER (1)johnlemmar4No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Erich-Fromm-Long-NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Erich-Fromm-Long-NotesMaria RamirezNo ratings yet
- Instructions: A. Write The Letter of The Best Possible Answer in The AnswerDocument4 pagesInstructions: A. Write The Letter of The Best Possible Answer in The AnswerMariaJorjiyPonceNo ratings yet
- Fromm To BanduraaDocument28 pagesFromm To BanduraaKimNo ratings yet
- Theoper - MidtermsDocument15 pagesTheoper - MidtermsGene Ann ParalaNo ratings yet
- PSYC3400 Personality Exam 3Document10 pagesPSYC3400 Personality Exam 3PUBG TIPS & TRICKSNo ratings yet
- Sociological Views of The SelfDocument3 pagesSociological Views of The SelfRechiel Joy Espulgar LactaoenNo ratings yet
- Allport 2Document2 pagesAllport 2Alyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FrommDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Frommpatriciaroseayaay.igdonNo ratings yet
- Maslow 3Document4 pagesMaslow 3Alyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Early anal period multiple choice quizDocument12 pagesEarly anal period multiple choice quizKarla GraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PersonalityDocument6 pagesChapter 10 PersonalityAfiya KhanNo ratings yet
- Top 2Document12 pagesTop 2Karla Grace100% (1)
- Erich Fromm's HUMANISTIC Psychoanalysis Biography: Basic AssumptionsDocument22 pagesErich Fromm's HUMANISTIC Psychoanalysis Biography: Basic AssumptionsRRCaratNo ratings yet
- Caanamongan National High School: C. Has A Unique Relationship Between Distinct SubjectsDocument3 pagesCaanamongan National High School: C. Has A Unique Relationship Between Distinct Subjectschearly2008No ratings yet
- Erich Fromm: Humanistic PsychoanalysisDocument8 pagesErich Fromm: Humanistic PsychoanalysisGabriel Lance Ivan Manait100% (1)
- Karen Horney Psychoanalytic Social TheoryDocument3 pagesKaren Horney Psychoanalytic Social TheoryValerie ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Existential Psychology - Review QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesExistential Psychology - Review Questionnairerop serrNo ratings yet
- Erich Fromm 1900 1980 Print PDFDocument5 pagesErich Fromm 1900 1980 Print PDFMaria CabangonNo ratings yet
- Self Awareness & Human PersonDocument3 pagesSelf Awareness & Human PersonEzra LambarteNo ratings yet
- The Human PersonDocument2 pagesThe Human PersonAllyssa Nicole MabanoNo ratings yet
- Erich FrommDocument2 pagesErich FrommTina NavarroNo ratings yet
- ToP A5.4Document5 pagesToP A5.4Marielle Louisse MasinsinNo ratings yet
- Erikson 2Document2 pagesErikson 2Alyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Erich Fromm's Humanistic PsychoanalysisDocument3 pagesErich Fromm's Humanistic Psychoanalysisstephanie100% (1)
- Existential Psychology: Rollo Reese MayDocument2 pagesExistential Psychology: Rollo Reese MayRustumme Mirelle Reyes100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document12 pagesChapter 4Tasfia MeherNo ratings yet
- The Self in The Western and Orientaleastern ThoughtDocument6 pagesThe Self in The Western and Orientaleastern ThoughtPhee JhayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 3-Anthropological PerspectiveDocument4 pagesLecture Notes 3-Anthropological PerspectiveBej PascaNo ratings yet
- Diss Final ExamsDocument2 pagesDiss Final ExamsJohn Marlon EnglisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Sociological Perspective of The SelfDocument2 pagesLesson 3 Sociological Perspective of The SelfZionne TanafrancaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document2 pagesWorksheet 2Eric John About-ModillasNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Worldviews and The Transitions FromDocument2 pagesSummary of The Worldviews and The Transitions From노이완No ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document2 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2Katrina SupanNo ratings yet
- Erich Fromm's Humanistic Psychoanalysis TheoryDocument8 pagesErich Fromm's Humanistic Psychoanalysis TheoryHazel YebesNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Multifaceted Nature of the SelfDocument3 pagesUnderstanding the Multifaceted Nature of the SelfJC HilarioNo ratings yet
- Karen Horney: Psychoanalytic Social TheoryDocument10 pagesKaren Horney: Psychoanalytic Social TheoryGabriel Lance Ivan ManaitNo ratings yet
- CEEPED 401 Understanding The Self Answer KeyDocument5 pagesCEEPED 401 Understanding The Self Answer Keyabyr rabiaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer UtsDocument4 pagesReviewer UtsJYRAH COSENo ratings yet
- Lessons on Intersubjectivity and Underprivileged SectorsDocument3 pagesLessons on Intersubjectivity and Underprivileged SectorsHarvey Morales86% (7)
- Rich Romm: Natalie Curran Regina Munoz Kim OcanaDocument27 pagesRich Romm: Natalie Curran Regina Munoz Kim OcanaRhaine EstebanNo ratings yet
- IntersubjectivityDocument6 pagesIntersubjectivityVannete De VianaNo ratings yet
- 3eSSGCh9 PDFDocument22 pages3eSSGCh9 PDFMilton MakangeNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument29 pagesUnderstanding The SelfNiña Acebes Ampo-LontayaoNo ratings yet
- Solution For Advanced Lifespan Odyssey For Counseling Professionals 1st Edition by Erford PDFDocument43 pagesSolution For Advanced Lifespan Odyssey For Counseling Professionals 1st Edition by Erford PDFCB Orders0% (2)
- TOP Erich FrommDocument6 pagesTOP Erich FrommfourteenNo ratings yet
- Palonpon - Chapter 4 SummaryDocument3 pagesPalonpon - Chapter 4 SummaryShiela maeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document4 pagesLesson 2Rea Mae ElevazoNo ratings yet
- Existential MayDocument3 pagesExistential MayKentNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Hand OutDocument2 pages2nd Grading Hand Outjemel behaganNo ratings yet
- Erich Fromm: Humanistic Psychoanalysis: Lecture OutlineDocument7 pagesErich Fromm: Humanistic Psychoanalysis: Lecture OutlineChris Davis100% (1)
- UTSquiz 1Document4 pagesUTSquiz 1Mark Samuel Dela cruz100% (1)
- Top ZDocument41 pagesTop ZAika FaunilloNo ratings yet
- NMAT REINFORCEMENT SOCIAL SCIENCE REVIEWDocument2 pagesNMAT REINFORCEMENT SOCIAL SCIENCE REVIEWEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Erich FrommDocument5 pagesErich FrommJen BadanaNo ratings yet
- Erikson 2Document2 pagesErikson 2Alyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Allport 2Document2 pagesAllport 2Alyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Kohut 1Document1 pageKohut 1Alyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IODocument5 pagesChapter 5 IOAlyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 IODocument5 pagesChapter 4 IOAlyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Legal Issues in Employee SelectionDocument4 pagesLegal Issues in Employee SelectionAlyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IODocument4 pagesChapter 1 IOAlyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and EvaluationDocument4 pagesJob Analysis and EvaluationAlyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Alyssa Louise C. Cabije: BS Psychology University of MindanaoDocument52 pagesAlyssa Louise C. Cabije: BS Psychology University of MindanaoAlyssa CabijeNo ratings yet
- Packaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet SinghDocument48 pagesPackaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet Singharon demagiba100% (1)
- Aam April 2023Document198 pagesAam April 2023Adhitya DewantaraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Kingdom of GodDocument10 pagesWhat Is The Kingdom of GodSunil ChelladuraiNo ratings yet
- A Feminist Analysis of Habba Khatoon'S Poetry: Dr. Mir Rifat NabiDocument7 pagesA Feminist Analysis of Habba Khatoon'S Poetry: Dr. Mir Rifat NabiShabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- (New) Adjustable Voltage Power Supply 55 V - 20A High Power and Current - Automatic Fan On - OffDocument1 page(New) Adjustable Voltage Power Supply 55 V - 20A High Power and Current - Automatic Fan On - OffSek PyroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Statics FundamentalsDocument28 pagesEngineering Statics FundamentalsurwaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan Boyle's LawDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Boyle's LawTeacher Derick Daet86% (7)
- Chapter 16 - Gripping IFRS ICAP 2008 (Solution of Graded Questions)Document33 pagesChapter 16 - Gripping IFRS ICAP 2008 (Solution of Graded Questions)Falah Ud Din SheryarNo ratings yet
- 22 Imobilisasi Pada Usia LanjutDocument34 pages22 Imobilisasi Pada Usia LanjutGian KalalembangNo ratings yet
- Simply Supported Beam ReactionsDocument4 pagesSimply Supported Beam ReactionsRushi TutorNo ratings yet
- November 2010 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology A-Level PDFDocument12 pagesNovember 2010 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology A-Level PDFWiji NingNo ratings yet
- Eric Gamalinda - Amigo WarfareDocument88 pagesEric Gamalinda - Amigo Warfareenstone100% (1)
- Science: Pure Substances Vs MixturesDocument33 pagesScience: Pure Substances Vs MixturesElle Ma Rie100% (1)
- Hyundai-25 30 33L 35LN-9A19.01Rev.6 Eng-D4 PDFDocument20 pagesHyundai-25 30 33L 35LN-9A19.01Rev.6 Eng-D4 PDFVicente Antonio GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Revit Architecture - BeginnersDocument56 pagesUnderstanding Revit Architecture - BeginnersBudega100% (95)
- K2N Final Internship ReportDocument55 pagesK2N Final Internship ReportAceZeta0% (1)
- management of burns readingDocument28 pagesmanagement of burns readinghimanshugupta811997No ratings yet
- Analog Layout Design (Industrial Training)Document10 pagesAnalog Layout Design (Industrial Training)Shivaksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Blackmer Pump Parts ListDocument2 pagesBlackmer Pump Parts ListFelipe Ignacio PaillavilNo ratings yet
- Ac+lic Lab Manual 2018-19Document76 pagesAc+lic Lab Manual 2018-19Samanvi SaatviNo ratings yet
- Maersk QuestionnaireDocument43 pagesMaersk QuestionnaireSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Rational Use of AntibioticsDocument35 pagesRational Use of AntibioticsRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Solitaire Premier - Presentation (Small File)Document18 pagesSolitaire Premier - Presentation (Small File)Shrikant BadheNo ratings yet
- Ic M802 UDocument79 pagesIc M802 Uharis_fikriNo ratings yet
- IRIScan Book Executive 3 PDFDocument86 pagesIRIScan Book Executive 3 PDFssamplingNo ratings yet
- Golden Dawn 2 9 The Moon BreathDocument4 pagesGolden Dawn 2 9 The Moon BreathF_RCNo ratings yet
- Browning Belt Tension GaugeDocument2 pagesBrowning Belt Tension GaugeJasperken2xNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: Process Safety and Environment ProtectionDocument51 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Process Safety and Environment Protectionimran shaukatNo ratings yet
- Buckling TestDocument11 pagesBuckling Testsharusli100% (1)
- Solar Collectors Final WordDocument14 pagesSolar Collectors Final WordVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet