Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zinnat 500mg X 10 Film
Zinnat 500mg X 10 Film
Uploaded by
Ana AlbuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zinnat 500mg X 10 Film
Zinnat 500mg X 10 Film
Uploaded by
Ana AlbuCopyright:
Available Formats
Zinnat 500mg x 10 film-coated tablets. Zinnat 500mg prospect.
What is Zinnat and what is it used for?
Zinnat contains cefuroxime, which is an antibiotic belonging to the cephalosporin class.
Antibiotics are used to kill bacteria or germs that cause infections.
The usual dose is:
Adults and adolescents
For upper respiratory tract infections such as tonsillitis, acute otitis media, sinusitis, and
pharyngitis: one 250 mg Zinnat tablet or 500 mg Zinnat tablet twice a day for 5-10 days.
For lower respiratory tract infections such as bronchitis: one 250 mg Zinnat tablet twice a day
for 5-10 days.
For more severe infections of the lower respiratory tract such as pneumonia: one 500 mg
Zinnat tablet twice a day for 5-10 days.
For urinary tract infections: one 125 mg Zinnat tablet or 250 mg Zinnat tablet twice a day for
7-10 days.
For infections of the kidneys and urinary tract: one 250 mg Zinnat tablet twice a day.
For skin infections: one 250 mg Zinnat tablet or 500 mg Zinnat tablet twice a day for 5-10
days.
For the treatment of early stages of Lyme disease: one 500 mg Zinnat tablet twice a day for
20 days.
Children aged 6 to 12 years
For the above mentioned indications: one 125 mg Zinnat tablet or 250 mg Zinnat tablet twice
a day for 5-10 days.
For acute middle ear infection: take one 250 mg Zinnat tablet twice daily for 5-10 days. For
children under 6 years old, other forms of cefuroxime are recommended. There is no
experience with the use of cefuroxime in children under 3 months old. Sometimes, your
doctor may need to increase your dosage. Treatment usually lasts for 7 days, but may be
longer in the case of severe infections.
Common side effects:
• Candidiasis;
• Increase in certain white blood cells (eosinophils);
• Headache;
• Dizziness;
• Diarrhea;
• Nausea;
• Abdominal pain;
• Temporary increases in liver enzyme values.
Less common side effects: • Decrease in certain white blood cells (leucopenia,
thrombocytopenia);
• False positive results on the Coombs test;
• Temporary skin rash; • Vomiting.
Rare side effects: • Hives; • Itching; • Pseudomembranous colitis.
Very rare side effects: • Decrease in certain red blood cells (hemolytic anemia); •
Drug fever;
• Serum sickness; •
Anaphylaxis;
• Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice);
• Hepatitis; •
Polymorphous erythema; •
Stevens-Johnson syndrome; •
Toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Other side effects have been reported, particularly in patients with impaired renal function:
nervousness, restlessness, confusion, increases in plasma creatinine and urea
concentrations, acute interstitial nephritis.
You might also like
- Interpretation of The Reptile Blood ProfileDocument8 pagesInterpretation of The Reptile Blood ProfileAndre NgoNo ratings yet
- The Essential Kidney Disease Cookbook: Over 150 Delicious Kidney-Friendly Meals to Ensure You Manage Your Kidney DiseaseFrom EverandThe Essential Kidney Disease Cookbook: Over 150 Delicious Kidney-Friendly Meals to Ensure You Manage Your Kidney DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. 1Document20 pagesAcute Upper Respiratory Tract Infection. 1Joana Carolina QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For Medical RepresentativesDocument74 pagesTraining Manual For Medical RepresentativesAman Ghayas50% (4)
- Medications To Avoid in Retinitis PigmentosaDocument7 pagesMedications To Avoid in Retinitis PigmentosasosoNo ratings yet
- Rhizin (Cetirizine Hydrochloride)Document3 pagesRhizin (Cetirizine Hydrochloride)El Min ForoNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument5 pagesPrednisoneMarcus Philip GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Dry Eye Disease, (Keratitis Sicca) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDry Eye Disease, (Keratitis Sicca) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin (Levan)Document2 pagesLevofloxacin (Levan)jackNo ratings yet
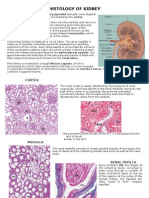
- Histology of KidneyDocument4 pagesHistology of KidneyIzzi FekratNo ratings yet
- Brenner Pocket 08Document871 pagesBrenner Pocket 08adry100% (2)
- Severe Trauma and Sepsis Organ Damage and Tissue Repair by Xiaobing Fu, Liangming LiuDocument392 pagesSevere Trauma and Sepsis Organ Damage and Tissue Repair by Xiaobing Fu, Liangming LiuDavid Avellaneda TalledoNo ratings yet
- DNB QUESTION PAPER-Topic Wise (Author DR - Sirisha)Document92 pagesDNB QUESTION PAPER-Topic Wise (Author DR - Sirisha)Sirisha CkvNo ratings yet
- HematuriaDocument32 pagesHematuriaSurya Nirmala DewiNo ratings yet
- RHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Document14 pagesRHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Jm Jm100% (1)
- Citrine's Holistic Flu Remedies: Boost Your Immunity Naturally Using Nutrition, Herbs, Homeopathy and AromatherapyFrom EverandCitrine's Holistic Flu Remedies: Boost Your Immunity Naturally Using Nutrition, Herbs, Homeopathy and AromatherapyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AntibioticsDocument58 pagesAntibioticsKamal GhimireNo ratings yet
- Dry Eyes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDry Eyes, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument3 pagesLevofloxacinkezia_reyes67% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyShayne Jessemae Almario100% (1)
- PMLS 1 Lesson 8 Nature of Clinical LabDocument200 pagesPMLS 1 Lesson 8 Nature of Clinical Labangelica fayeNo ratings yet
- Quinton ApplicationsDocument13 pagesQuinton ApplicationsfaarhadhamidNo ratings yet
- Zinnat Tablets NaDocument12 pagesZinnat Tablets NaLeonid BitanNo ratings yet
- Zinnat PIDocument10 pagesZinnat PIfsdfNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime AxetilDocument4 pagesCefuroxime AxetilSebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- MedicinesDocument6 pagesMedicinesMARJINA A. UDDAHNo ratings yet
- Zinnat TabletsDocument5 pagesZinnat TabletsAndrei Marian BorcescuNo ratings yet
- Zednad Tablet LeafletDocument2 pagesZednad Tablet LeafletAli KhNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument4 pagesAzithromycinBrittany ClontzNo ratings yet
- Cerox ADocument3 pagesCerox AAkash ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- CiproflaxacinDocument3 pagesCiproflaxacindonnas1128No ratings yet
- HomeDocument2 pagesHomeJerecel Gapi VigoNo ratings yet
- CyclophosphamideDocument4 pagesCyclophosphamiderizky31No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studymaryhiromi10No ratings yet
- Obat Untuk Gondok, Cara Mengobati Penyakit Gondok, Obat Gondok Dalam.20131030.230445Document2 pagesObat Untuk Gondok, Cara Mengobati Penyakit Gondok, Obat Gondok Dalam.20131030.230445wave3sideNo ratings yet
- Betnesol Oral DropsDocument8 pagesBetnesol Oral DropsAnamika VatsalNo ratings yet
- AmoxcillinDocument7 pagesAmoxcillinMohamed FarahatNo ratings yet
- VIGOCIDDocument2 pagesVIGOCIDKaren DamoNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesSumate KittiNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Tuberculosis .2Document59 pagesTreatment of Tuberculosis .2Alexander Santiago Parel0% (1)
- ZithromaxDocument2 pagesZithromaxianecunar100% (2)
- What Is FAMVIRDocument5 pagesWhat Is FAMVIRMustfa PanchoNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin 3Document12 pagesCiprofloxacin 3Odiit StephenNo ratings yet
- Zinobest PIL 27122016Document7 pagesZinobest PIL 27122016Kochu KuchuNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K:: PhytonadioneDocument11 pagesVitamin K:: Phytonadionehiral mistryNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Lecture Notes 2013 2Document140 pagesPharmacology Lecture Notes 2013 2muleyazegetNo ratings yet
- Pemphigus: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical Collage Physiotherapy Department 2020 - 2021 2 StageDocument20 pagesPemphigus: Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical Collage Physiotherapy Department 2020 - 2021 2 StageZA IDNo ratings yet
- Steroids in DentistryDocument4 pagesSteroids in DentistryrazasiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tamiflu, FlagylDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Tamiflu, Flagylmark_gain100% (1)
- ErythromycinDocument6 pagesErythromycinapi-3797941100% (1)
- Fungi PDFDocument59 pagesFungi PDFChaku LambarNo ratings yet
- Patient Information Leaflet CiproDocument3 pagesPatient Information Leaflet CiproRuth LessNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmacology: NTA Level 4 Semester 2Document16 pagesBasic Pharmacology: NTA Level 4 Semester 2MabusiNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides Streptomycin Is An: Streptomyces GriseusDocument7 pagesAminoglycosides Streptomycin Is An: Streptomyces GriseusVian ArccenioNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: Summary of CDC Treatment GuidelinesbenzveewitNo ratings yet
- Anti TuberDocument16 pagesAnti TuberpgfhgfgfNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Disease 4th YearsDocument77 pagesSexually Transmitted Disease 4th YearsAakashNo ratings yet
- Diphenhydramine - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesDiphenhydramine - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfKomang SubitaNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument12 pagesAzithromycinReygie MataNo ratings yet
- Levofloxacin 500mg Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC)Document10 pagesLevofloxacin 500mg Film-Coated Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC)OdunlamiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneAfidz Azuddin HaziqNo ratings yet
- Nepal Essential MedicationsDocument103 pagesNepal Essential MedicationsPriya SahNo ratings yet
- ClarithromycinDocument3 pagesClarithromycinapi-3797941No ratings yet
- التهاب الجيوب الانفية والاذن الوسطىDocument2 pagesالتهاب الجيوب الانفية والاذن الوسطىDavid HosamNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO 10 MG Once Daily or 5 MG Bid. Oral: Pregnancy Category (US FDA)Document4 pagesAdult: PO 10 MG Once Daily or 5 MG Bid. Oral: Pregnancy Category (US FDA)widiyaNo ratings yet
- DiclofenacDocument9 pagesDiclofenacIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- FlagylDocument2 pagesFlagylianecunarNo ratings yet
- VIVO - Dialysis Technician: Course DescriptionDocument1 pageVIVO - Dialysis Technician: Course Descriptionpushp00No ratings yet
- Anaphy CKDDocument3 pagesAnaphy CKDSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Physiology Course Structure - at A GlanceDocument13 pagesVeterinary Physiology Course Structure - at A Glancemohit jainNo ratings yet
- Soal Seleksi Impsq Tahap 1Document3 pagesSoal Seleksi Impsq Tahap 1sanjayahalim123No ratings yet
- Renal Mini Case StudyDocument7 pagesRenal Mini Case Studyapi-242589113No ratings yet
- NPB 10 - Midterm 2 - Va - Fa17 - Sa KeyDocument4 pagesNPB 10 - Midterm 2 - Va - Fa17 - Sa KeyVamsi Krishna ThiriveedhiNo ratings yet
- The Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease in Ilorin, NigeriaDocument5 pagesThe Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease in Ilorin, NigeriaMuhammad A MakusidiNo ratings yet
- General Biology Q4 M3Document16 pagesGeneral Biology Q4 M3Delfin LeeNo ratings yet
- Asam BasaDocument47 pagesAsam BasaMilikPremiumstock90No ratings yet
- TIVA in CKDDocument7 pagesTIVA in CKDfixheartNo ratings yet
- KT/V CalculationDocument1 pageKT/V CalculationNor Nadiah Mohd NawawiNo ratings yet
- Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies On The AqueoDocument13 pagesAcute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies On The AqueoEmmanuel OwonaNo ratings yet
- Kode Simpus PTT EMIDocument18 pagesKode Simpus PTT EMIfauziahNo ratings yet
- ریفرنس امتحان انترنس اکمال تخصص پرنسپ داخله و جراحی برای سال ۱۳۹۸ PDFDocument3 pagesریفرنس امتحان انترنس اکمال تخصص پرنسپ داخله و جراحی برای سال ۱۳۹۸ PDFAli Rahimi100% (1)
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaDasep PadilahNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Human BeingsDocument2 pagesExcretion in Human BeingsDwi Apriyanti SumantriNo ratings yet
- Heather Zwickey, PHD - Important Clarifications Regarding Covid-19 and Natural Medicine - Dispelling Myths and MisconceptionsDocument9 pagesHeather Zwickey, PHD - Important Clarifications Regarding Covid-19 and Natural Medicine - Dispelling Myths and Misconceptionstahuti696No ratings yet
- Quiz MRIDocument7 pagesQuiz MRIMark M. AlipioNo ratings yet
- Urinary Histology SlidesDocument24 pagesUrinary Histology SlidesHera Vinandika PNo ratings yet
- 4BI1/2BR: BiologyDocument24 pages4BI1/2BR: BiologyEsionNo ratings yet
- KMB Diabetes InsipidusDocument24 pagesKMB Diabetes InsipidusNuryuyunNo ratings yet
- Anemia Renal - BDF 2018-2Document38 pagesAnemia Renal - BDF 2018-2Buku Tama WaingapuNo ratings yet