Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 7
Uploaded by
Hesham Ebrahim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views14 pagesThe Wien-bridge oscillator uses a lead-lag circuit in the positive feedback loop of an op-amp. At lower frequencies, the lead circuit dominates due to the high reactance of C2. As frequency increases, XC2 decreases, allowing the output voltage to increase. At a specified frequency, the lag circuit takes over and XC1 decreases, causing the output voltage to decrease. The circuit oscillates at the frequency where the phase shift through the lead-lag circuit is 0 degrees.
Original Description:
Electronics 3
Original Title
Lecture_7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe Wien-bridge oscillator uses a lead-lag circuit in the positive feedback loop of an op-amp. At lower frequencies, the lead circuit dominates due to the high reactance of C2. As frequency increases, XC2 decreases, allowing the output voltage to increase. At a specified frequency, the lag circuit takes over and XC1 decreases, causing the output voltage to decrease. The circuit oscillates at the frequency where the phase shift through the lead-lag circuit is 0 degrees.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views14 pagesLecture 7
Uploaded by
Hesham EbrahimThe Wien-bridge oscillator uses a lead-lag circuit in the positive feedback loop of an op-amp. At lower frequencies, the lead circuit dominates due to the high reactance of C2. As frequency increases, XC2 decreases, allowing the output voltage to increase. At a specified frequency, the lag circuit takes over and XC1 decreases, causing the output voltage to decrease. The circuit oscillates at the frequency where the phase shift through the lead-lag circuit is 0 degrees.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Prepared by
The Wien-Bridge Oscillator
One type of sinusoidal feedback oscillator is the Wien-bridge
oscillator.
The operation of this lead-lag circuit is as follows. At lower
frequencies, the lead circuit dominates due to the high reactance of
C2.
As the frequency increases,XC2 decreases, thus allowing the output
voltage to increase.
At some specified frequency, the response of the lag circuit takes
over, and the decreasing value of causes XC1 the output voltage to
decrease.
The Wien-Bridge Oscillator
The Wien-Bridge Oscillator
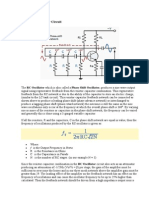
The lead-lag circuit is used in the positive feedback loop of an
opamp, as shown in Figure 16–7(a). A voltage divider is used in
the negative feedback loop.
The Wien-Bridge Oscillator
The Wien-bridge oscillator circuit can be viewed as a
noninverting amplifier configuration with the input signal fed
back from the output through the lead-lag circuit. Recall that
the voltage divider determines the closed-loop gain of the
amplifier.
The circuit is redrawn in Figure 16–7(b) to show that the op-amp is
connected across the bridge circuit. One leg of the bridge is the lead-
lag circuit, and the other is the voltage divider.
The Wien-Bridge Oscillator
Positive Feedback Conditions for Oscillation As you know, for the circuit to
produce a sustained sinusoidal output (oscillate), the phase shift around the positive
feedback loop must be 0° and the gain around the loop must equal unity (1).
The 0° phase-shift condition is met when the frequency is fr because the phase shift
through the lead-lag circuit is 0° and there is no inversion from the noninverting (+)
input of the op-amp to the output. This is shown in Figure 16–8(a).
The Wien-Bridge Oscillator
The Wien-Bridge Oscillator
The Phase-Shift Oscillator
Figure 16–13 shows a sinusoidal feedback oscillator called the phase-shift oscillator.
Each of the three RC circuits in the feedback loop can provide a maximum phase shift
approaching 90°.
Oscillation occurs at the frequency where the total phase shift through the three RC
circuits is 180°.
The inversion of the op-amp itself provides the additional 180° to meet the requirement
for oscillation of a 360° (or 0°) phase shift around the feedback loop.
The Phase-Shift Oscillator
OSCILLATORS WITH LC FEEDBACK CIRCUITS
You might also like
- Lab 8 ReportDocument8 pagesLab 8 ReportSHUBHAM GARGNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OscillatorsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Oscillatorsmrana_56No ratings yet
- OscillatorssDocument21 pagesOscillatorssrishiNo ratings yet
- ch16 - Oscilator Theory PDFDocument21 pagesch16 - Oscilator Theory PDFruslaninstNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document35 pagesLecture 14Hanzala DaarNo ratings yet
- CH 16 Part 2 by DR - Nouf T. MahmoodDocument24 pagesCH 16 Part 2 by DR - Nouf T. MahmoodNoof Al GhareebNo ratings yet
- Tribhuwan University: Lab No:..... Sinusoidal OscillatorsDocument5 pagesTribhuwan University: Lab No:..... Sinusoidal OscillatorsKRSTNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge Oscillator ReportDocument5 pagesWien Bridge Oscillator ReportDerrick Sibusiso KuneneNo ratings yet
- Oscillator CircuitsDocument19 pagesOscillator Circuits21-08523No ratings yet
- Assignment No.2: Topic: OscillaDocument6 pagesAssignment No.2: Topic: OscillaMuhammad Mubashar AwaisiNo ratings yet
- AEC NotesDocument271 pagesAEC Notes1DS19EC726- Pankaj Ashok M.No ratings yet
- 3.2 RC Phase Shift Oscillator Using TransistorDocument21 pages3.2 RC Phase Shift Oscillator Using Transistorksreddy2002No ratings yet
- Oscillator NotesDocument11 pagesOscillator NotesHarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Source. The Key To Oscillator Operation Is Positive Feedback. A Positive FeedbackDocument11 pagesSource. The Key To Oscillator Operation Is Positive Feedback. A Positive FeedbackDrLaxya Singla100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - OscillatorsDocument37 pagesChapter 4 - OscillatorsnawaralseelawiNo ratings yet
- IC Questions With Ans AnilsirDocument22 pagesIC Questions With Ans AnilsirAniil J Kumaar50% (2)
- The Wien Bridge OscillatorDocument8 pagesThe Wien Bridge OscillatorSamuel ArthurNo ratings yet
- Analog Lab 8 1904132Document13 pagesAnalog Lab 8 1904132SHUBHAM GARGNo ratings yet
- Basic RC Oscillator CircuitsDocument8 pagesBasic RC Oscillator CircuitsZsori CorinaNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal OscillatorsDocument2 pagesSinusoidal OscillatorsAmrendra Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Voltage Controlled OscillatorDocument9 pagesVoltage Controlled Oscillatorbezabwm100% (4)
- Sinusoidal OscillatorDocument22 pagesSinusoidal OscillatorChandrika Reddy100% (1)
- Wien Bridge Oscillator:: RC Phase Shift Network (Lead Lag Network)Document6 pagesWien Bridge Oscillator:: RC Phase Shift Network (Lead Lag Network)Rashid ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document38 pagesPart 1Anupam ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - OscillatorDocument60 pagesChapter 2 - OscillatorNURUL NADHIRAH ROSDINo ratings yet
- Lic Unit 2,3,4Document53 pagesLic Unit 2,3,4suresh mNo ratings yet
- My Lecture Note The OscillatorDocument17 pagesMy Lecture Note The OscillatorVictor AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Oscillators SowmiyaDocument24 pagesOscillators SowmiyaOcakachon InnocentNo ratings yet
- V Unit OscillatorsDocument91 pagesV Unit OscillatorsÑaýaň ŇăwğhårēNo ratings yet
- 1Document15 pages1PandaNo ratings yet
- Oscillators: de La Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Engineering, Architecture, and Technology Engineering ProgramDocument9 pagesOscillators: de La Salle University - Dasmariñas College of Engineering, Architecture, and Technology Engineering ProgramJaneNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument3 pagesWein Bridge OscillatorT BlackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Op-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpDocument11 pagesChapter 1: Op-Amps: I. Practical Op-Amprockrockyrocker123No ratings yet
- 6.design A Wien Bridge Oscillator Using OpDocument5 pages6.design A Wien Bridge Oscillator Using OpSudeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Current Mirrors Differential Amplifier Class A: Input StageDocument4 pagesCurrent Mirrors Differential Amplifier Class A: Input StagebarnamalaNo ratings yet
- Adjustable Wien Bridge OscillatorDocument5 pagesAdjustable Wien Bridge OscillatorKatrina DuranNo ratings yet
- Lec06-Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument9 pagesLec06-Wein Bridge OscillatorRoknuzzaman RikonNo ratings yet
- Op-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpDocument7 pagesOp-Amps: I. Practical Op-AmpSteven Nelson100% (1)
- Oscillator 2020Document39 pagesOscillator 2020Apek OweNo ratings yet
- The RC OscillatorDocument6 pagesThe RC OscillatorBerri M PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers (Revision) : OutputDocument19 pagesOperational Amplifiers (Revision) : OutputAndrewWerdnaNo ratings yet
- OscillatorDocument59 pagesOscillatorMaretha rhea AlmyraNo ratings yet
- The RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument12 pagesThe RC Phase Shift OscillatorvikashrahiNo ratings yet
- (WB) AC - UNIT II - 10 - Wien Bridge OscillatorDocument20 pages(WB) AC - UNIT II - 10 - Wien Bridge OscillatorDugasani UshasreeNo ratings yet
- RC Oscillator: DescriptionDocument5 pagesRC Oscillator: DescriptionTomoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Analog CircuitsDocument92 pagesAnalog Circuitsmaganga magangaNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: Experiment 6: Study of A Wein Bridge Oscillator CircuitDocument2 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: Experiment 6: Study of A Wein Bridge Oscillator CircuitshajibNo ratings yet
- Oscillators 1Document14 pagesOscillators 1diya shajiNo ratings yet
- Oscillators - EDC PDFDocument21 pagesOscillators - EDC PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document6 pagesLab 4Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Mit Aec Labmanula 10esl37Document45 pagesMit Aec Labmanula 10esl37anon_70724250No ratings yet
- Weign Bridge OscillatorDocument4 pagesWeign Bridge Oscillatormanojkumar9No ratings yet
- 04 Osc100Document17 pages04 Osc100CauVong JustinNo ratings yet
- Multivibrator Manual PDFDocument73 pagesMultivibrator Manual PDFAvijitRoyNo ratings yet
- Note Topic 2Document32 pagesNote Topic 2nurul iqinNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)