0% found this document useful (0 votes)
274 views14 pagesUnderstanding Triangle Angles Explained
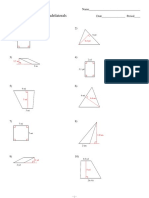
- Angles in a triangle always add up to 180 degrees. This fact can be used to find missing angles by adding the known angles and subtracting from 180.
- There are different types of triangles such as right, isosceles, equilateral, and scalene triangles which have specific angle properties.
- Examples show how to find missing angles using properties like equal angles in isosceles triangles or angles on a straight line adding to 180 degrees. Algebra can also be used to set up and solve equations for missing angles.
Uploaded by
Naeem RazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
274 views14 pagesUnderstanding Triangle Angles Explained
- Angles in a triangle always add up to 180 degrees. This fact can be used to find missing angles by adding the known angles and subtracting from 180.
- There are different types of triangles such as right, isosceles, equilateral, and scalene triangles which have specific angle properties.
- Examples show how to find missing angles using properties like equal angles in isosceles triangles or angles on a straight line adding to 180 degrees. Algebra can also be used to set up and solve equations for missing angles.
Uploaded by
Naeem RazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd