Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hexose Monophosphate Pathway (HMP Shunt) / Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Uploaded by
Ahsan Ali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesHexose Monophosphate Pathway (HMP Shunt) / Pentose Phosphate Pathway
Uploaded by
Ahsan AliCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
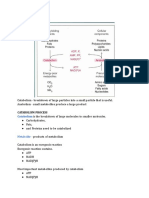
Hexose monophosphate pathway (HMP shunt) / Pentose phosphate
pathway
Hexose monophosphate pathway or HMP shunt is also called pentose phosphate pathway or
phosphogluconate pathway. This is an alternative pathway to glycolysis and TCA cycle for the oxidation of
glucose. However, HMP shunt is more anabolic in nature, since it is concerned with the biosvnthesis of
NADPH and pentose
HMP shunt-a unique multifunctional pathway:
The pathway starts with glucose 6-phosphate. As such, no ATP is directly utilized or produced in HMP
pathway. It is a unique multifunctional pathway, since there are several interconvertible substances
produced which may proceed in different directions in the metabolic reactions.
Location of the pathway:
The enzymes of HMP shunt are located in the cytosol. The tissues such as liver, adipose tissue, adrenal
gland, erythrocytes, testes and lactating mammary gland, are highly active in HMP shunt. Most of these
tissues are involved in the biosynthesis of fatty acids and steroids which are dependent on the supply of
NADPH.
Reactions of the pathway
The sequence of reactions of HMP shunt is divided into two phases-oxidative and non-oxidative.
1. Oxidative phase :
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is an NADP-dependent enzyme that converts glucose 6-
phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone The latter is then hydrolysed by the gluconolactone hydrolase to
6-phosphogluconate The next reaction involving the synthesis of NADPH is catalysed by
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase to produce 3 keto 6-phosphogluconate which then undergoes
decarboxylationt of give ribulose S-phosphate. G6PD regulates HMP shunt : The first reaction catalysed by
G6PD is most regulatory in HMP shunt. This enzyme catalyses an irreversible reaction. NADPH
competitively inhibits G6PD. It is the ratio of NADPH/NAD+ that ultimately determines the flux of this
cycle.
2. Non-oxidative phase :
The non-oxidative reactions are concerned with the interconversion of three, four, five and seven carbon
monosaccharides. Ribulose5 -phosphate is acted upon by an epimerase to produce xylulose 5-phosphate
while ribose5 -phosphate keto isomerase converts ribuloseS -phosphate to ribose 5-phosphate.
The enzyme transketolase catalyses the transfer of two carbon moiety from xylulose 5-phosphate to
ribose 5-phosphate to give a 3-carbon glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and a 7-carbon sedoheptulose 7-
phosphate. Transketolase is dependent on the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) and Mg2+ ions.
Transaldolase brings about the transfer of a 3-carbon fragment (active dihydroxyacetone) from
sedoheptulose 7-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to give fructose 6-phosphate and four carbon
erythrose 4-phosphate
Transketolase acts on xylulose 5-phosphate and transfers a 2-carbon fragment (glyceraldehyde) from it to
erythrose 4-phosphate to generate fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Fructose 6-
phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate can be further catabolized through glycolysis and citric acid
cycle. Glucose may also be synthesized from these two compounds. 6-phosphate to 6 CO2, we have to
start with 6 molecules of glucose-6-phosphate of these 6 , 5 moles are regenerated with the production
of 12 NADPH.
The overall reaction may be represented as
6 glucose-6-phosphate+ 12 NADP+ + 6H2O 6CO2 + 12 NADPH + 12H+ + 5 glucose-6-phosphate
Significance of HMP shunt
HMP shunt is unique in generating two important products pentoses and NADPH needed for the
biosynthetic reactions and other functions.
importance of pentoses
In the HMP shunt hexoses are converted into pentoses, the most important being ribose
5-phosphate. This pentose or its derivatives are useful for the synthesis of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA)
and many nucleotides such as ATP, NAD+, FAD and CoA. Skeletal muscle is capable of synthesizing
Pentoses, although only the first few enzymes of HMP shunt are active. It, therefore, appears that
the complete pathway of HMP shunt may not be required for the synthesis of pentoses.
Importance of NADPH
1. NADPH is required for the reductive biosynthesis of fatty acids and steroids hence HMP shunt is more
active in the tissues concerned with lipogenesis e.g. adipose tissue, liver etc.
2. NADPH is used in the synthesis of certain amino acids involving the enzyme glutamate dehydrogenase.
3. Microsomal cytochrome P450 system (in liver) brings about the detoxification of drugs and foreign
compounds by hydroxylation reactions involving NADPH.
5. Phagocytosis is the engulfment of foreign particles, including microorganisms carried out by white
blood cells. The process requires the supply of NADPH.
You might also like
- Encode SequenceDocument212 pagesEncode SequenceRaj Naithik100% (1)
- HMPDocument44 pagesHMPraanja2No ratings yet
- A New Route To Designer AntibioticsDocument2 pagesA New Route To Designer AntibioticsRaphael ContiNo ratings yet
- Second Aid USMLE Mnemonics PDFDocument19 pagesSecond Aid USMLE Mnemonics PDFTony Lǎo Hǔ ChenNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate PathwayDocument19 pagesHexose Monophosphate Pathwayspdharanimaran001No ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument38 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntKausik SenNo ratings yet
- BCH 312 Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument6 pagesBCH 312 Pentose Phosphate PathwayMARYJANE NZUBECHUKWU NJOKUNo ratings yet
- HMP ShuntDocument14 pagesHMP Shuntامجد حسين جواد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate Pathway: Oxidative ReactionsDocument3 pagesPentose Phosphate Pathway: Oxidative ReactionsCJ PorrasNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument43 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate Pathway (Aka Hexose Monophosphate Shunt or Phosphogluconate Pathway)Document2 pagesPentose Phosphate Pathway (Aka Hexose Monophosphate Shunt or Phosphogluconate Pathway)Dang CuevasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument15 pagesLecture 2 Pentose Phosphate PathwayWilliamNo ratings yet
- GlycogenolysisDocument6 pagesGlycogenolysisMituSamadderNo ratings yet
- 9 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Document18 pages9 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Doctor SonuNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument10 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayGonzarezu EmilyNo ratings yet
- HMP & Uronic Acid PathwaysDocument30 pagesHMP & Uronic Acid PathwaysAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument10 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwaySania SaeedNo ratings yet
- HMP ShuntDocument4 pagesHMP ShuntAmjad AlmousawiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Second PPP PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 10 Second PPP PDFMadani TawfeeqNo ratings yet
- HMP Pathway: Hexose Mono Phosphate PathwayDocument25 pagesHMP Pathway: Hexose Mono Phosphate PathwayAyoubMuhammadNo ratings yet
- MLS 218 HMPDocument8 pagesMLS 218 HMPZainabNo ratings yet
- Lec.6 PPP Pathway PDFDocument5 pagesLec.6 PPP Pathway PDFhawraaNo ratings yet
- Lec32 F08 HandoutDocument11 pagesLec32 F08 HandoutSarayu Ragavan NairNo ratings yet
- HMP Shunt Pathway: (Pentose Phosphate Pathway or Phospho Gluconate Pathway or Dickens-Horecker Pathway)Document5 pagesHMP Shunt Pathway: (Pentose Phosphate Pathway or Phospho Gluconate Pathway or Dickens-Horecker Pathway)Kausik SenNo ratings yet
- HMP-shunt MEDDocument37 pagesHMP-shunt MEDAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument3 pagesMetabolismSubrata KunduNo ratings yet
- PentosephosphateDocument38 pagesPentosephosphatesreya ghosalNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument4 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayCarry OnNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM-Carbohydrate Metabolism 3-Alternative PathwayDocument6 pagesBIOCHEM-Carbohydrate Metabolism 3-Alternative PathwayStd DlshsiNo ratings yet
- SMSP 23jan22 Ppe, Ed, PKDocument8 pagesSMSP 23jan22 Ppe, Ed, PKPravesh NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument22 pagesPentose Phosphate Pathwayjitendermcse9816No ratings yet
- Glycolytic PathwayDocument17 pagesGlycolytic PathwayramchinnaNo ratings yet
- 4 HMP ShuntDocument18 pages4 HMP ShuntAyoubMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument18 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntAbdul Jabbar Abdul JabbarNo ratings yet
- Describe La Vía Pentosas FosfatoDocument3 pagesDescribe La Vía Pentosas FosfatoDaniel SolanoNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument5 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntTheresaNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Oxidative Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument14 pagesRegulation of Oxidative Pentose Phosphate PathwayZain MazinNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis NotesDocument15 pagesGlycolysis and Gluconeogenesis NotesJohn Oliver AsiaNo ratings yet
- 6.metabolism in FungiDocument67 pages6.metabolism in FungiWahyuni Irmal100% (2)
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument2 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayClairyssa Myn D CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument2 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayGianneCarloGomedNo ratings yet
- HMP Pathway PDFDocument44 pagesHMP Pathway PDFHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Pentose and Uronic PathwayDocument28 pages2.2 Pentose and Uronic PathwayYared gebremedhinNo ratings yet
- The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Part 2Document3 pagesThe Pentose Phosphate Pathway Part 2Shiza TanveerNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of NucleotidesDocument24 pagesMetabolism of NucleotidesAditya NayakNo ratings yet
- PTS Phosphoenolpyruvate Dependent Phosphotransferase System. TPP Thiamine PyrophosphateDocument3 pagesPTS Phosphoenolpyruvate Dependent Phosphotransferase System. TPP Thiamine PyrophosphateShiva100% (2)
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument2 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- HMP ShuntDocument19 pagesHMP ShuntyaalinyNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument11 pagesUntitled PresentationIrene Regine DayandanteNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument8 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismChaudhari Saroj100% (1)
- Echevarria Jonille S BSP 2Document6 pagesEchevarria Jonille S BSP 2Jonille EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- HMP Shunt PathwayDocument12 pagesHMP Shunt Pathwaymuhammad noumanNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument38 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntJohn Raniel IsidroNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate Pathway 13Document8 pagesPentose Phosphate Pathway 13savinder singhNo ratings yet
- Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument17 pagesPentose Phosphate PathwayBlack man100% (1)
- Questions On HMP SHUNTDocument6 pagesQuestions On HMP SHUNTjmenchaca8080No ratings yet
- Glycolysis:: The Central Pathway of Glucose DegradationDocument23 pagesGlycolysis:: The Central Pathway of Glucose DegradationMohammad Noman AkramNo ratings yet
- Art:10 1007/BF00173913Document8 pagesArt:10 1007/BF00173913Leonardo SakamotoNo ratings yet
- Marc S. Wold, PHD: Bioc 3110Document31 pagesMarc S. Wold, PHD: Bioc 3110Giulia LiebovichNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018Document136 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018N A Anggriani WulandariNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument2 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntDr. SHIVA AITHAL100% (5)
- Non-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseFrom EverandNon-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Biosynthesis of CholesterolDocument4 pagesBiosynthesis of CholesterolAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument3 pagesBiosynthesis of Fatty AcidsAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Reactive Intermediates: Nimra AkmalDocument39 pagesReactive Intermediates: Nimra AkmalAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Oxidation Stages and TissuesDocument3 pagesFatty Acid Oxidation Stages and TissuesAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Location of GluconeogenesisDocument4 pagesLocation of GluconeogenesisAhsan AliNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression TranslationDocument10 pagesGene Expression TranslationManila MedNo ratings yet
- 6.conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized ProductsDocument8 pages6.conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized Productsقتيبه خالد دحام خلفNo ratings yet
- Protein-Synthesis-WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtein-Synthesis-WorksheetJohn SchwuchowNo ratings yet
- KTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFDocument24 pagesKTP Mcat Quicksheets PDFChristine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- PHA A ReviewDocument49 pagesPHA A ReviewFaez AbwaNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document31 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)sandrapaolamtzf100% (1)
- Chapter 16 Lippincott BiochemistryDocument57 pagesChapter 16 Lippincott BiochemistryMeysam SajjadiNo ratings yet
- MCQS On Protein Metabolism BY Siraj Ul IslamDocument12 pagesMCQS On Protein Metabolism BY Siraj Ul Islamsirajkhan93100% (2)
- MCQDocument9 pagesMCQpkm7929No ratings yet
- SOPs For AdmissionDocument19 pagesSOPs For AdmissionHafiza AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Polyamines: EditorsDocument324 pagesPolyamines: EditorsDIMAS PRAYOGANo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis ActivityDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis ActivityPrincess Raychel Delos AngelesNo ratings yet
- 5384 PDFDocument5 pages5384 PDFAngeline AguyenNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Dr. Muhammad Jalil AkhtarDocument133 pagesAmino Acids: Dr. Muhammad Jalil AkhtarAfnankh698No ratings yet
- Compendium On Pesticide Use in Vegetables PDFDocument146 pagesCompendium On Pesticide Use in Vegetables PDFRajan Kashyap100% (1)
- DNA and Protein PowerpointDocument13 pagesDNA and Protein PowerpointKashish ShahNo ratings yet
- Protein SysthesisDocument47 pagesProtein SysthesisPrincess Camille SorianoNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle PPT LecDocument52 pagesTCA Cycle PPT LecjaveriaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Stress Triggered Biochemical and Morphological Changes in TheDocument11 pagesNitrogen Stress Triggered Biochemical and Morphological Changes in TheDany CéspedesNo ratings yet
- Testbank 4e CH27 Protein MetabolismDocument13 pagesTestbank 4e CH27 Protein MetabolismKhristian Dom Ruam Cadabona100% (2)
- DNAmazing Challenge (Protein Synthesis)Document6 pagesDNAmazing Challenge (Protein Synthesis)DivineNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Other Amino Acids: GlycineDocument9 pagesMetabolism of Other Amino Acids: GlycineAsad AliNo ratings yet
- 2020 Molecular Biochemistry Handout PDFDocument12 pages2020 Molecular Biochemistry Handout PDFFlowerNo ratings yet
- Orgo 2 GuideDocument25 pagesOrgo 2 GuideRukiezillaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Syllabus PDFDocument220 pagesMarketing Syllabus PDFDeepikaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Ribosom Kloroplas EMBJ 36 475Document12 pagesRibosom Kloroplas EMBJ 36 475NovyKedungWilutNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Advanced Biochemistry. Introduction.Document70 pagesLecture 1. Advanced Biochemistry. Introduction.Cik Syin100% (1)