Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How computers process data in 4 steps
Uploaded by
mnbvcxzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How computers process data in 4 steps
Uploaded by
mnbvcxzCopyright:
Available Formats
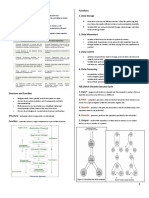
1 INPUT
Data is collected, transcribed, and converted into a computer-readable
format to enter the machine’s system. For it to process, it is verified for
validity by the program to minimize possible errors that may occur. Next,
data is sorted and arranged, then stored in a binary form inside the
computer. The data saved is now ready for the next cycle step.
2 PROCESSING
It involves coding data into information. The process includes calculations and
comparisons of values to arrive at an output. Collected data is grouped into
different classifications and arranged in a specific order for easier and quicker
access. Conversion of data occurs by using mathematical operations and logical
functions. As such, one can observe the process of calculating, classifying,
comparing, storing, etc.
HOW COMPUTER
PROCESSES DATA 3 OUTPUT
The output will now take its form. The desired result often referred to as
information, is tested following the system’s demand. It is then summarized
Feedback is given by comparing the output and the and stored in the device’s external memory, or any secondary storage
4 expected goal – it may or may not be up to the device, before displaying a copy of the output.
system’s standard; thus, the next process would
either be the repetition of the cycle’s steps or the
end of the pattern and the start of another one.
Failure to achieve the requirements in each step would result in repeating the abovementioned process.
You might also like
- Quiz Game DocumentationDocument33 pagesQuiz Game Documentationjayanand sidar71% (14)
- Google Cloud Platform for Data Engineering: From Beginner to Data Engineer using Google Cloud PlatformFrom EverandGoogle Cloud Platform for Data Engineering: From Beginner to Data Engineer using Google Cloud PlatformRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Project Report - Online ClassifiedsDocument149 pagesProject Report - Online ClassifiedsManoj Kumar80% (10)
- Computer Data ProcessingDocument4 pagesComputer Data ProcessingKimberly MolatoNo ratings yet
- 04 Data ProcessingDocument16 pages04 Data ProcessingVan ImperialNo ratings yet
- C-Org Midterm ReviewerDocument7 pagesC-Org Midterm ReviewerDen-Earl De DiosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Basic Operations and Components of A ComputerDocument18 pagesLesson 2: Basic Operations and Components of A ComputerNiña Mae C. QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Data Processing TaskDocument18 pagesData Processing TaskJericho HernanNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument4 pagesData ProcessingKwonyoongmaoNo ratings yet
- Data CapturingDocument7 pagesData Capturingodedeyi aishatNo ratings yet
- Simulation ProcessDocument5 pagesSimulation ProcessTeran PeñaNo ratings yet
- 1 ICT LiteracyDocument10 pages1 ICT Literacykurt palivinoNo ratings yet
- AT - Chapter 11-Notes - Part 1Document3 pagesAT - Chapter 11-Notes - Part 1hoxhiiNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Auditing the CIS EnvironmentDocument14 pagesAn Overview of Auditing the CIS EnvironmentRana LinNo ratings yet
- About Computers HomeworkDocument12 pagesAbout Computers HomeworkChi SantosNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Programming .NET NC III Quarter 1 Week 1 Computer OperationsDocument38 pagesSenior High School Programming .NET NC III Quarter 1 Week 1 Computer OperationsAileenD.EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Define Computer: 1. PC (Personal Computer) or Micro ComputerDocument2 pagesDefine Computer: 1. PC (Personal Computer) or Micro Computerraju dasNo ratings yet
- Ais Elect - ReviewerDocument5 pagesAis Elect - ReviewerWilbert Cunanan CapatiNo ratings yet
- Articol Disteibuted Data ProcessingDocument7 pagesArticol Disteibuted Data ProcessingAlexandru StefanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 27 Computer Based Data ProcessingDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 27 Computer Based Data ProcessingMelady Sison Cequeña100% (1)
- Data Processing CycleDocument2 pagesData Processing CycleAnonymous Id8iCMmWpNo ratings yet
- T2 and T3 - LD79876 - Liyana - NEWDocument19 pagesT2 and T3 - LD79876 - Liyana - NEWDennis TanjusayNo ratings yet
- Cpen ReviewerDocument8 pagesCpen Reviewerkeithleene trinidadNo ratings yet
- Basic computer components and data processing stepsDocument18 pagesBasic computer components and data processing stepsAbena, Kianne C.No ratings yet
- Auditing in A Computerized EnvironmentDocument40 pagesAuditing in A Computerized EnvironmentNCP Shem ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Sistem KomputerDocument15 pagesSistem KomputerNisa MislanNo ratings yet
- Comparing human and computer memory processesDocument2 pagesComparing human and computer memory processeszack frostNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Golden Gate ConfigurationDocument26 pagesStep by Step Golden Gate ConfigurationcbestNo ratings yet
- Information System and Its ModelsDocument15 pagesInformation System and Its ModelsSiddhant BanwatNo ratings yet
- Prepare and verify CIS input data controlsDocument6 pagesPrepare and verify CIS input data controlsMark Kenneth ParagasNo ratings yet
- Is - Chapter 1Document12 pagesIs - Chapter 1Lapa EtienneNo ratings yet
- Base Paper 2Document4 pagesBase Paper 2SanjayNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument14 pagesReviewerRhea MendozaNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument16 pagesData ProcessingLouella Vea HernandezNo ratings yet
- IT2106 Task Performance Processes OptimizedDocument4 pagesIT2106 Task Performance Processes OptimizedSean MaverickNo ratings yet
- The Telco Revenue Assurance Handbook: Figure 6.2.1 RA Architecture MonitoringDocument1 pageThe Telco Revenue Assurance Handbook: Figure 6.2.1 RA Architecture MonitoringMorad M SwidNo ratings yet
- The Data Processing CycleDocument22 pagesThe Data Processing CycleAnum KhursheedNo ratings yet
- MICROPROCESSORDocument8 pagesMICROPROCESSORSerj ObenzaNo ratings yet
- DA Unit 2Document13 pagesDA Unit 2Eswari KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Data Processing ReportDocument6 pagesData Processing ReportEmilie Ann SumalloNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONIC DATA PROCESSING and COMPUTER SYSTEMS BSCE 1A G3 - ReportDocument32 pagesELECTRONIC DATA PROCESSING and COMPUTER SYSTEMS BSCE 1A G3 - ReportcdaineredNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Information System in 40 CharactersDocument17 pagesBasic Accounting Information System in 40 CharactersMelady Sison CequeñaNo ratings yet
- Data Processing, Security, AntivirusDocument9 pagesData Processing, Security, AntivirusOgbo IsuNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in ItDocument8 pagesReviewer in Itpchu4019No ratings yet
- Reviewer in ItDocument10 pagesReviewer in Itpchu4019No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Auditing IT Governance ControlsKim Cristian MaañoNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Electronic Data Processing (EDP)Document6 pagesAuditing and Electronic Data Processing (EDP)Lizza Marie CasidsidNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect of Data Migration in Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCause and Effect of Data Migration in Cloud ComputingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- 1.1 About The ProjectDocument22 pages1.1 About The ProjectNaasif MNo ratings yet
- Auditing Ina Computerized EnvironmentDocument24 pagesAuditing Ina Computerized EnvironmentPrincessa LeeNo ratings yet
- Data ProcessingDocument14 pagesData Processingyleno_me0% (1)
- Itc Reviewer 1stsemmidDocument10 pagesItc Reviewer 1stsemmidkenneth.magsanay.2004No ratings yet
- Transforming Raw Data into Valuable InsightsDocument11 pagesTransforming Raw Data into Valuable InsightsMARSHA D.No ratings yet
- Ics 2105 - DsaDocument6 pagesIcs 2105 - DsaSteve Ouma100% (2)
- Introduction to Information Technology BasicsDocument54 pagesIntroduction to Information Technology BasicsDaniel100% (1)
- Auditing in CIS EnvironmentDocument16 pagesAuditing in CIS EnvironmentMart Roca LupigNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Structure and Execution ExplainedDocument2 pagesMicroprocessor Structure and Execution Explainedcjames vibe back upNo ratings yet
- The Processing Unit and Types of Processing: Week 2Document27 pagesThe Processing Unit and Types of Processing: Week 2VzHeronation 17 Queen™ KapLaxNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Operating SystemDocument32 pagesPresentation of Operating SystemSandeep Madhusudan SahooNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 The Computer EnvironmentDocument13 pagesChapter 20 The Computer EnvironmentClar Aaron Bautista100% (1)
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionFrom EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo ratings yet
- Range Gate Generator For FMCW Doppler Raradr PDFDocument5 pagesRange Gate Generator For FMCW Doppler Raradr PDFSrinivas CherukuNo ratings yet
- Serialization Tutorial6 PDFDocument36 pagesSerialization Tutorial6 PDFLoLo FernándezNo ratings yet
- Swa1801Z Repair Manual: ActiveDocument9 pagesSwa1801Z Repair Manual: ActiveEgger GüntherNo ratings yet
- C# OperatorsDocument60 pagesC# OperatorsGoutham KambleNo ratings yet
- STULZ WIB 67C 0811 en PDFDocument49 pagesSTULZ WIB 67C 0811 en PDFJaime MendozaNo ratings yet
- All Browser ElockClientNSE Installation GuideDocument9 pagesAll Browser ElockClientNSE Installation Guidenidhi jhunjhunwalaNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between PTH and NPTH in PCBDocument11 pagesThe Difference Between PTH and NPTH in PCBjackNo ratings yet
- EVoting SDS DocumentDocument58 pagesEVoting SDS DocumentKahfulwara MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Computer Science NotesDocument48 pagesComputer Science NotesaDEOlu AdesinaNo ratings yet
- Acceptance of Delivery: It Project Descriptions & ScopeDocument8 pagesAcceptance of Delivery: It Project Descriptions & ScopeAhmed ElhartyNo ratings yet
- Improve Reliability with Numerical RelayingDocument49 pagesImprove Reliability with Numerical RelayingBhargav PandyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Digit Sensor Counter Using Mcs51-AT89C1051Document6 pages4 Digit Sensor Counter Using Mcs51-AT89C1051Syed Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- CS210 Lab: 6-9 (400 Points) : TasksDocument10 pagesCS210 Lab: 6-9 (400 Points) : TasksSingam Setty S A DeshikNo ratings yet
- Clustering DocumentationDocument15 pagesClustering DocumentationNazifa KazimiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Operating SystemDocument9 pagesBasic Concepts of Operating SystemjohnNo ratings yet
- Embedded Projects ListDocument9 pagesEmbedded Projects ListAishwarya AishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Unix/Linux Commands and Shell Programming: Clemson University ParlDocument22 pagesUnix/Linux Commands and Shell Programming: Clemson University ParlSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- ADS7828 DataSheetDocument22 pagesADS7828 DataSheetEmanuel BaldisseraNo ratings yet
- Designing A SASE Architecture by NetskopeDocument66 pagesDesigning A SASE Architecture by NetskopeFrank TafurNo ratings yet
- TSN Time Sensitive NetworkingDocument12 pagesTSN Time Sensitive NetworkingDimas Alfredo GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 SepDocument701 pagesVol 2 Sepadityapankaj55No ratings yet
- ADSP-BF533 - HWR - Rev3.6 (Modelo Black Fin 533) PDFDocument884 pagesADSP-BF533 - HWR - Rev3.6 (Modelo Black Fin 533) PDFPaulo Henrique TrindadeNo ratings yet
- Motioneye CCTV Software On BalenacloudDocument33 pagesMotioneye CCTV Software On BalenacloudBandulaNo ratings yet
- F U L L - T I M e D I P L o M A C o U R S e I N I N F o R M A T I o N T e C H N o L o G yDocument62 pagesF U L L - T I M e D I P L o M A C o U R S e I N I N F o R M A T I o N T e C H N o L o G yBiplab DasNo ratings yet
- 0478 s19 Ms 13Document12 pages0478 s19 Ms 13Me RandomNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Computer Science 2210/13 October/November 2019Document14 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Computer Science 2210/13 October/November 2019Sarim JavedNo ratings yet
- Asiatech College: Bachelor of Science in Information TechnologyDocument10 pagesAsiatech College: Bachelor of Science in Information TechnologyJomar RebuladoNo ratings yet
- EPM AutomateDocument415 pagesEPM AutomateGolam Sarwar/INTERNATIONAL/BRACNo ratings yet
- Megaraid Sas 8888elp Raid Controller: Quick Installation GuideDocument3 pagesMegaraid Sas 8888elp Raid Controller: Quick Installation GuideJRochaNo ratings yet