Professional Documents
Culture Documents
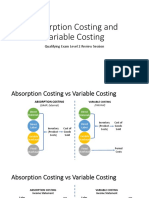
Variable and Absorption Costing Income Statements
Uploaded by
Monica GarciaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Variable and Absorption Costing Income Statements
Uploaded by
Monica GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
Manila * Cavite * Laguna * Cebu * Cagayan De Oro * Davao
Since 1977
MANAGEMENT SERVICES TRINIDAD
MS 3405 – Variable and Absorption Costing MAY 2023
LECTURE NOTES
1. Variable costing treats only those costs of released to the income statement as a charge
production that vary with output as product costs. against income as well as all of the current fixed
Ordinarily, direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs. Since only the
variable manufacturing overhead costs would be current fixed manufacturing overhead costs are
included in product costs under variable costing. expensed under variable costing, the net income
Fixed manufacturing overhead is treated as a reported under absorption costing will be less than
period cost and is immediately charged off against the net income reported under variable costing.
revenue each period. 4. Long-term differences in income. Over an
2. Absorption costing treats all costs of production as extended period of time, the cumulative net
product costs, regardless of whether they are income figures reported under absorption costing
variable or fixed in nature. Under the absorption and variable costing will be about the same; they
costing method, a portion of fixed manufacturing will differ only by the amount of fixed
overhead is allocated to each unit of product. manufacturing overhead cost in ending inventories
under absorption costing. Cumulative net income
Comparison of Absorption and Variable Costing. figures will be identical whenever ending
When comparing absorption costing and variable inventories are reduced to zero.
costing income statements, the following points should 5. Changes in production volume. Variable costing
be noted: net income is not affected by changes in
1. Deferral of fixed manufacturing costs under production volume. Absorption costing net income
absorption costing. Under the absorption is affected by changes in production volume. For a
costing method, if inventories increase then a particular level of sales, net income under
portion of the fixed manufacturing overhead costs absorption costing will increase as the level of
of the current period is deferred to future periods output increases and hence inventories increase.
through the inventory account. When the units are
later taken out of inventory and sold, the deferred Advantages of the Contribution Approach. There
fixed costs flow through to the income statement. are several advantages in using variable costing (and
2. Differences in inventories under the two the contribution approach) in internal reports and
methods. The ending inventory figures under the analysis.
variable costing and absorption costing methods 1. More useful for CVP analysis. Variable costing
are different. Under variable costing, only the statements provide data that are immediately
variable manufacturing costs are included in useful for CVP analysis since they categorize costs
inventory. Under absorption costing, both variable based on their behavior.
and fixed manufacturing costs are included in 2. Income is not affected by changes in production
inventory. volume. Under absorption costing, reported net
income is affected by changes in production since
Suitability for CVP analysis. The absorption costing fixed costs are spread across more or fewer units.
income statement is not well suited for providing data This can distort income and may even result in
for CVP computations since it makes no distinction income moving in an opposite direction from sales.
between fixed and variable costs. In contrast, the This does not occur under variable costing.
variable costing method classifies costs by behavior 3. Avoids misunderstandings concerning unit product
and is very useful in setting-up CVP computations. costs. Absorption costing unit product costs can be
easily misinterpreted as variable costs since they
Extended Comparison of Income Data. are stated on a per unit basis. Such a
1. Production equals sales (no change in inventories). misperception can lead to serious errors in making
When production equals sales, there is no change decisions. Variable costing avoids this problem
in inventories. If there is no change in inventories, since unit costs include only variable costs.
then there is no change in the fixed manufacturing 4. Fixed costs are more visible. The impact of fixed
overhead costs in inventories under absorption costs on profits is emphasized because the total
costing. amount of such costs for the period appears
2. Production exceeds sales (inventories increase). separately and is highlighted in the income
When production exceeds sales, inventories grow. statement rather than being buried in cost of
If inventories grow, then some of the current fixed goods sold and ending inventory.
manufacturing overhead costs will be deferred in 5. Understandability. Managers may find it easier to
inventories under absorption costing. Since all of understand variable costing reports because data
the current fixed manufacturing overhead costs are organized by behavior and because variable
are expensed under variable costing, the net costing is much closer to a cash flow concept.
income reported under absorption costing will be 6. Control is facilitated. Variable costing ties in with
greater than the net income reported under cost control methods such as flexible budgets.
variable costing. 7. Incremental analysis is more straight-forward.
3. Sales exceeds production (inventories decrease). Variable cost corresponds closely with the current
When sales exceeds production, inventories shrink. out-of-pocket expenditure necessary to produce
If inventories decrease, then some of the fixed and sell products and services and can therefore
manufacturing overhead costs that had been be used more readily in incremental analysis than
deferred in inventories in previous periods will be absorption costing data. And since variable costing
Page 1 of 5 www.teamprtc.com.ph MS.3405
EXCEL PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC.
net income is closer to net cash flow than PROBLEM NO. 4.
absorption costing net income, it is likely to be Golden Gate Company makes network connectors that
more useful to companies that have cash flow sell for P500. Standard variable manufacturing cost is
problems. P200, and the standard fixed manufacturing cost is
STRAIGHT PROBLEMS P100, based on budgeted fixed cost of P10 millions
and budgeted production of 100,000 units. During
PROBLEM NO. 1. 2020, the company produced 96,000 units sold
Baker Company produced 30,000 units and sold 90,000. Actual fixed manufacturing costs were
28,000 units. Beginning inventory was zero. During P9,870,000; actual variable manufacturing costs were
the period, the following costs were incurred: P19,300,000. Selling and administrative expenses
Indirect labor P60,000 were P11,350,000, all fixed. There were no beginning
Indirect materials 30,000 inventories.
Other variable overhead 90,000
Fixed manufacturing 180,000 Requirements:
overhead 1. Prepare in income statement for Golden Gate
Fixed administrative 150,000 using standard variable costing.
expenses 2. Prepare a standard absorption costing income
Fixed selling expenses 120,000 statement.
Variable selling expenses, per unit 40
Direct labor, per unit 80 PROBLEM NO. 5.
Direct materials, per unit 20 Shark Company began operations on January 1 to
produce a fishing rods. It used a standard absorption
Requirements: costing system with a planned production volume of
Compute the peso amount of ending inventory using: 100,000 units. During its first year of operations, no
1. Absorption costing variances were incurred and there were no fixed
2. Variable costing selling or administrative expenses. Inventory on
December 31 was 20,000 units, and net income for
PROBLEM NO. 2. the year was P480,000. If Shark had used variable
Luzon Manufacturing Company began its operations on costing, its net income would have been P440,000.
January 1, 2020 and it produces a single product that Compute the breakeven point in units.
sells for P45 per unit. During 2020, 60,000 units of
the product were produced, 55,000 of which were PROBLEM NO. 6.
sold. There was no work in process inventory at the During its first year of operations, Gold, Inc. produced
end of the year. Manufacturing and marketing and 27,000 units. Unit sales were 26,400. Fixed overhead
administrative expenses for 2020 were as follows: was applied at P0.75 per unit produced. Fixed
Fixed Variable overhead was underapplied by P3,000. This fixed
Materials P12 per unit produced overhead variance was closed to Cost of Goods Sold.
Direct labor P8 per unit produced There was no variable overhead variance. The results
Factory OH P420,000 P6 per unit produced of the year’s operations are as follows (on an
Marketing & P180,000 P4 per unit sold absorption-costing basis):
admin.
Sales (26,400 units @ P12) P 316,800
Requirements: Less: Cost of goods sold 161,400
1. Compute the unit cost using variable costing. Gross margin P 155,400
2. Compute the unit cost using absorption costing. Less: Selling and administrative
3. Compute the amount of income under: expenses (all fixed) 120,000
a. Traditional costing Operating income P 35,400
b. Variable costing
c. Throughput costing Requirements:
1. Give the cost of the firm’s ending inventory under
PROBLEM NO. 3. absorption costing. What is the cost of the
RV Corporation has fixed manufacturing cost of P8 per ending inventory under variable costing?
unit. Consider the three independent cases that follow. 2. Prepare a variable-costing income statement.
Case A: Absorption- and variable costing net
income each totaled P160,000 in a period MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
when the firm produces 20,000 units.
Case B: Absorption-costing net income totaled 1. If a firm produces more units than it sells,
P180,000 in a period when finished-goods absorption costing, relative to variable costing, will
inventory level rises by 5,000 units. result in
Case C: Absorption-costing net income and a. higher income and assets
variable-costing net income respectively b. lower income but lower assets
totaled P240,000 and P272,000 in a period c. higher income but lower assets
when the beginning finished-goods inventory d. lower income and assets
was 14,000 units.
2. Under absorption costing, if sales remain constant
Requirements: from period 1 to period 2, the company will report a
1. In Case A, how many units were sold during the larger income in period 2 when
period? a. period 2 production exceeds period 1 production
2. In Case B, how much income would RV Company b. period 1 production exceeds period 2 production
report under variable costing?
3. In Case C, how many units were in the ending
finished-goods inventory?
Page 2 of 5 www.teamprtc.com.ph MS.3405
EXCEL PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC.
c. variable production costs are larger in period 2 a. Direct period costs.
than period 1 b. Indirect period costs.
d. fixed production costs are larger in period 2 than c. Direct product costs.
period 1 d. Indirect product costs.
3. The variable costing format is often more useful to 10. Which of the following groups prefer variable
managers than the absorption costing format costing for their reporting?
because A. Internal decision maker
a. costs are classified by their behavior B. Bureau of Internal Revenue
b. it is required for external reporting C. Stockholders
c. costs are always lower D. Securities & Exchange Commission
d. it justifies higher product prices
11. How will a favorable volume variance affect net
4. When a firm prepares financial reports using income under each of the following methods?
absorption costing Absorption Variable
a. profits will always increase with increase in sales a. Reduce No effect
b. profits will always decrease with decreases in b. Reduce Increase
sales c. Increase No effect
c. profits may decrease with increased sales even if d. Increase Reduce
there is no change in selling prices and costs
d. decreased output and constant sales result in 12. Assuming absorption costing, which of the following
increased profits columns includes only product costs?
A B C D
5. Which of the following statements is true for a firm Direct labor X X X
that uses variable costing? Direct materials X X X
a. The cost of a unit of product changes because of Sales materials X
changes in the number of units manufactured Advertising costs X
b. Profits fluctuate with sales Indirect factory materials X X X
c. An idle facility variation is calculated
Indirect labor X X X
d. None of the given choices
Sales commissions X
Factory utilities X X X
6. Net income determined using full absorption costing
Administrative supplies X
can be reconciled to net income determined using
expense
variable costing by computing the difference
between: Administrative labor X
A. fixed manufacturing overhead costs deferred in Depreciation on X
or released from inventories. administration building
B. inventoried discretionary costs in the beginning Cost of research on X
and ending inventories. customer demographics
C. gross margin (absorption costing method) and A. A. C. C.
contribution margin (variable costing method). B. B. D. D.
D. sales as recorded under the variable costing
method and sales as recorded under the 13. Which of the following is(are) closely related to
absorption costing method. variable costing than to absorption costing?
1. Predetermined fixed overhead
7. Which of the following statements is correct? 2. Unit sales
A. When production is higher than sales, absorption 3. Production units
costing net income is lower than variable costing 4. Contribution margin
net income 5. Gross margin
B. If all products manufactured during the period 6. Volume variance
are sold in that period, variable costing net 7. Cost behavior
income is equal to absorption costing net 8. Management accounting
income.
C. When production is lower than sales, variable A. 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8
costing net income is lower than absorption B. 2, 4, 7, 8
costing net income C. 1, 3, 4, 7, 8
D. When production and sales level are equal, D. 1, 3, 5, 6
variable costing net income is lower than
absorption costing net income. 14. At its present level of operations, a small
manufacturing firm has total variable costs equal to
8. As compared with total absorption costing profit 75% of sales and total fixed costs equal to 15% of
over the entire life of a company, total variable sales. Based on variable costing, if sales change by
costing profit will be P1.00, income will change by
A. less a. P0.25 c. P0.75
B. greater b. P0.10 d. Undeterminable
C. equal
D. substantially greater or less depending upon 15. Gabbert Company, which has only one product, has
external factors provided the following data concerning its most
recent month of operations:
9. Using absorption costing, fixed manufacturing Units sold @ P90 per unit 3,400
overhead costs are best described as Units produced 3,600
Beginning inventory 0
Page 3 of 5 www.teamprtc.com.ph MS.3405
EXCEL PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC.
19. Company B produces a single product. The
Costs Variable Fixed Cost company had 16,000 units in its beginning
Cost inventory. During the year, the company's variable
Direct materials P23 production costs were P6 per unit and its fixed
Direct labor 11 manufacturing overhead costs were P4 per unit. The
Manufacturing overhead 2 P 93,600 company's net operating income for the year was
Selling and administrative 8 61,200 P24,000 higher under absorption costing than it was
expenses under variable costing. Given these facts, the
What is the total period cost for the month under number of units in the ending inventory must have
the variable costing approach? been:
a. P93,600 a. 22,000 units c. 6,000 units
b. P154,800 b. 10,000 units d. 4,000 units
c. P88,400 20. This year, Roberts Company's income under
d. P182,000 absorption costing was P2,000 lower than its
income under variable costing. The company sold
16. Three new companies (X, Y, and Z) began 8,000 units during the year, and its variable costs
operations on January 1. Consider the following were P8 per unit, of which P2 was variable selling
operating costs that were incurred by these expense. If production cost was P10 per unit under
companies during the complete calendar year: absorption costing, then how many units did the
Company X Company Y Company Z company produce during the year?
Production in A. 7,500 units.
units 10,000 10,000 10,000 B. 7,000 units.
Sales price per C. 9,000 units.
unit P10 P10 P10 D. 8,500 units.
Fixed
production costs P10,000 P20,000 P30,000 21. Southseas Corp. uses a standard cost system. The
Variable standard cost per unit of one of its products are as
production costs P30,000 P20,000 P10,000 follows:
Variable SG&A P10,000 P20,000 P30,000
Direct Materials P4.00
Fixed SG&A P30,000 P20,000 P10,000
Direct labor 6.00
Based on sales of 7,000 units, which company will Factory overhead
report the greater income before income taxes Variable 3.00
under variable costing? Fixed (based on a normal
a. Company X capacity of 10,000 units) 2.00
b. Company Y Total 15.00
c. Company Z
d. All of the companies will report the same income. Beginning inventory 2,000 units
Production 8,000 units
17. A company manufactures a single product for its Units sold (selling price P50) 7,000 units
customers by contracting in advance of production. Actual costs:
Thus, the company produces only units that will be Direct materials P 35,000
sold by the end of each period. For the last period, Direct labor 50,000
the following data were available: Variable overhead 23,000
Sales P40,000 Fixed overhead 18,000
Direct materials 9,050 Variable selling and administrative 60,000
Direct labor 6,050 Fixed selling and administrative 35,000
Rent (9/10 factory, 1/10 office) 3,000
Depreciation on factory equipment 2,000 Variances are closed to cost of sales monthly.
Supervision (2/3 factory, 1/3 office) 1,500 How much are the net income under absorption
Salespeople’s salaries 1,300 costing and variable costing methods?
Insurance (2/3 factory, 1/3 office) 1,200 Absorption Variable
Office supplies 750 a. 144,000 143,000
Advertising 700 b. 143,000 144,000
Depreciation on office equipment 500 c. 144,000 142,000
Interest on loan 300 d. 142,000 144,000
The gross profit margin percentage (rounded) was
a. 34% c. 44% Use the following information for the next two
b. 41% d. 46% questions.
The following data are available for X Co. for its first
18. Lauder Company produces a single product. During year of operations:
March, the company had net operating income Sales in units 5,000
under absorption costing that was P3,500 lower Production in units 8,000
than under variable costing. The company sold Manufacturing costs:
7,000 units in March, and its variable costs were P7 Direct labor P3 per unit
per unit, of which P3 was variable selling expense. Direct materials P5 per unit
If fixed manufacturing overhead was P2 per unit Variable overhead P1 per unit
under absorption costing, then how many units did Fixed overhead P100,000
the company produce during March? Net income (absorption method) P30,000
a. 5,250 units c. 6,500 units Sales price per unit P40
b. 8,750 units d. 6,125 units
Page 4 of 5 www.teamprtc.com.ph MS.3405
EXCEL PROFESSIONAL SERVICES, INC.
22. What would X Co. have reported as its income Units produced 20,000
before tax if it had used variable costing? Units sold 12,000
a. P30,000 c. P67,500 Unit sales Price P12
b. P(7,500) d. P45,000
26. What is Cost of Goods Sold for Soconfused Co.’s
23. What was the total amount SG&A expense incurred first year?
by X Co.? a. P80,000 c. P48,000
a. P30,000 c. P6,000 b. P90,000 d. Undeterminable
b. P62,500 d. P45,000
27. If Soconfused Co. had used variable costing in its
Use the following information for the next two questions. first year of operations, how much income (loss)
Sales and costs data for Maripaz Corporation’s new before taxes would they have reported?
product are as follows: a. P(6,000) c. P26,000
Sales (P22.50 per unit) P225,000 b. P54,000 d. P 2,000
Unit Fixed Cost
Variable 28. Based on variable costing, if Soconfused had sold
Cost* 12,001 units instead of 12,000, its income before
Manufacturing cost P12.00 P37,500 taxes would have been
Administrative cost 4.50 22,500 a. P9.50 higher c. P8.50 higher
* per unit of production. b. P11.00 higher d. P8.33 higher
There was no inventory at the beginning of the year.
Normal capacity of the plant is 12,500 units. During the Use the following information for the next two questions.
year, 12,500 units were manufactured. Reusser Company produces wood statues. Management
24. The total fixed cost charged to expense for the year has provided the following information:
under the absorption costing shall be Actual sales 80,000 statues
a. P48,000 Budgeted production 100,000 statues
b. P52,500 Selling price P20.00 per statue
c. P55,500 Direct material costs P5.00 per statue
d P60,000. Variable manufacturing costs P1.50 per statue
Variable administrative costs P2.50 per statue
25. The cost of ending inventory under the direct Fixed manufacturing overhead P2.00 per statue
costing and absorption costing shall be as follows:
a. b. c. d. 29. What is the cost per statue if throughput costing is
Direct costing P30,000 P30,000 P37,500 P37,500 used?
Absorption costing P37,500 P30,000 P30,000 P37,500 a. P11.00 c. P7.50
b. P9.50 d. P5.00
Use the following information for the next three
questions. 30. What is the total throughput contribution?
The following information was extracted from the first a. P1,500,000 c. P720,000
year of absorption-based accounting records of b. P2,000,000 d. P1,200,000
Soconfused Co.
Total fixed costs incurred P100,000
Total variable costs incurred 50,000
Total period costs incurred 70,000
Total variable period costs incurred 30,000
"No one is going to give you a map; you have to walk your own path." - Anonymous
– end -
Page 5 of 5 www.teamprtc.com.ph MS.3405
You might also like
- Danshui Plant No. 2Document2 pagesDanshui Plant No. 2Sahil Kashyap83% (6)
- Cost Concept Exercises PDFDocument2 pagesCost Concept Exercises PDFAina OracionNo ratings yet
- Variable and Absorption CostingDocument38 pagesVariable and Absorption CostingstarlightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document36 pagesChapter 6Janine LerumNo ratings yet
- RFBT.10 - Lecture Notes (SSS Law)Document10 pagesRFBT.10 - Lecture Notes (SSS Law)Monica Garcia100% (1)
- Instruction: You Have 3 Hours To Complete This Examination Including Accomplishing The Google Answer SheetDocument16 pagesInstruction: You Have 3 Hours To Complete This Examination Including Accomplishing The Google Answer SheetasdfghjNo ratings yet
- Relevant Costs and Product Planning Decisions: Hapter EvenDocument6 pagesRelevant Costs and Product Planning Decisions: Hapter EvenEsther MpyisiNo ratings yet
- Paper Cup Manufacturing ProjectionsDocument17 pagesPaper Cup Manufacturing ProjectionsMOHAN MADANNo ratings yet
- The Synchronic Production SystemDocument260 pagesThe Synchronic Production Systempp2211mb2707No ratings yet
- 3MA 03 Absortion and Variable CostingDocument3 pages3MA 03 Absortion and Variable CostingAbigail Regondola BonitaNo ratings yet
- Direct Costing and CVP AnalysisDocument25 pagesDirect Costing and CVP AnalysisQueeny Mae Cantre ReutaNo ratings yet
- MAS 9204 Product Costing Activity-Based Costing (ABC)Document19 pagesMAS 9204 Product Costing Activity-Based Costing (ABC)Mila Casandra CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - FAR01 - Accounting For Equity InvestmentsDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word - FAR01 - Accounting For Equity InvestmentsDisguised owlNo ratings yet
- Mas 9403 Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisDocument21 pagesMas 9403 Standard Costs and Variance AnalysisBanna SplitNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Production Losses in A Job Order Costing SystemDocument7 pagesAccounting For Production Losses in A Job Order Costing Systemfirestorm riveraNo ratings yet
- ASR3 Materials - Auditing Equity and Debt InvestmentsDocument4 pagesASR3 Materials - Auditing Equity and Debt InvestmentsHannah Jane ToribioNo ratings yet
- ACCCOB3 CVP Analysis Case Problems Instructions:: Ryan - Roque@dlsu - Edu.phDocument2 pagesACCCOB3 CVP Analysis Case Problems Instructions:: Ryan - Roque@dlsu - Edu.phdanii yaahNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost Management Exercises 12369Document2 pagesStrategic Cost Management Exercises 12369Arlene Diane OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing Vs Variable CostingDocument20 pagesAbsorption Costing Vs Variable CostingMa. Alene MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Saint Paul School of Business and LawDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Saint Paul School of Business and LawKim FloresNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Joint Products and by ProductsDocument13 pagesAccounting For Joint Products and by ProductsSteffi CabalunaNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Variable Costing ReviewDocument13 pagesAbsorption and Variable Costing ReviewRodelLabor100% (1)
- Intacc Review Questions Micha 1Document3 pagesIntacc Review Questions Micha 1Christian ContadorNo ratings yet
- Allocation of Joint Costs and Accounting For By-Product/ScrapDocument31 pagesAllocation of Joint Costs and Accounting For By-Product/ScrapMichelle Rotairo100% (1)
- Ch19 (4) Cost Behavior and Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument43 pagesCh19 (4) Cost Behavior and Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysischuchuNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions ReviewDocument46 pagesMultiple Choice Questions ReviewMarylorieanne CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Cost Quiz 3Document5 pagesCost Quiz 3Jerric CristobalNo ratings yet
- BORROWING COSTS With AnswerDocument3 pagesBORROWING COSTS With AnswerMaeNo ratings yet
- ch11 Doc PDF - 2 PDFDocument39 pagesch11 Doc PDF - 2 PDFRenzo RamosNo ratings yet
- Practice Set - A3Document6 pagesPractice Set - A3Dayanara VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- University of Caloocan City Cost Accounting & Control Midterm ExaminationDocument8 pagesUniversity of Caloocan City Cost Accounting & Control Midterm ExaminationAlexandra Nicole IsaacNo ratings yet
- Cost Chap 6Document24 pagesCost Chap 6Peter Paul DeiparineNo ratings yet
- Strat Cost Drop or ContinueDocument1 pageStrat Cost Drop or ContinueStephannieArreolaNo ratings yet
- p2 Guerrero Ch15Document27 pagesp2 Guerrero Ch15Michael Brian TorresNo ratings yet
- Name: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - DateDocument13 pagesName: - Section: - Schedule: - Class Number: - Datechristine_pineda_2No ratings yet
- Job Order, Operation and Life Cycle Costing Job Order CostingDocument19 pagesJob Order, Operation and Life Cycle Costing Job Order Costingjessa mae zerdaNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Job Orderprocess Costing ActivityDocument8 pagesWeek 9 Job Orderprocess Costing ActivityfbaabgfgbfdNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1 Part 3 Multiple Choice Problems Attempt ReviewDocument1 pageQuiz No. 1 Part 3 Multiple Choice Problems Attempt ReviewEly RiveraNo ratings yet
- Quiz-3 Cost2 BSA4Document7 pagesQuiz-3 Cost2 BSA4Jessa HerreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AbcDocument5 pagesChapter 7 AbcAyu FaridYaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Process Costing and Hybrid Product-Costing SystemsDocument33 pagesChapter 4: Process Costing and Hybrid Product-Costing Systemsrandom17341No ratings yet
- Additional Data For The Period Were ProvidedDocument3 pagesAdditional Data For The Period Were Providedmoncarla lagon100% (1)
- Absorption and Variable CostingDocument11 pagesAbsorption and Variable CostingalliahnahNo ratings yet
- QUIZ3Document6 pagesQUIZ3Jillian Mae Sobrino BelegorioNo ratings yet
- Prelim Mas 1-TestDocument16 pagesPrelim Mas 1-TestChrisNo ratings yet
- Abc and Abm Quiz PracticeDocument8 pagesAbc and Abm Quiz PracticeJyNo ratings yet
- Melcher Mixalot Pricing and Profit AnalysisDocument7 pagesMelcher Mixalot Pricing and Profit Analysisnaura syahdaNo ratings yet
- MAS04-06 - Standard Costing - MF - EncryptedDocument9 pagesMAS04-06 - Standard Costing - MF - EncryptedRachel FuentesNo ratings yet
- 2019 Vol 2 CH 4 AnswersDocument8 pages2019 Vol 2 CH 4 AnswersElla LopezNo ratings yet
- Ch13 Relevant CostDocument142 pagesCh13 Relevant CostJames Crombez100% (1)
- Depletion Notes: Disclaimer: Not EntirelyDocument3 pagesDepletion Notes: Disclaimer: Not EntirelyRes GosanNo ratings yet
- ACC/349 Final Exam ReviewDocument15 pagesACC/349 Final Exam ReviewAnmol NadkarniNo ratings yet
- Handout - ManufacturingDocument17 pagesHandout - ManufacturingArjay OlivasNo ratings yet
- Wasting Assets Impairment of AssetsDocument14 pagesWasting Assets Impairment of AssetsJohn Ferd M. FerminNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing Reconciliation StatementDocument4 pagesAbsorption Costing Reconciliation Statementali_sattar15No ratings yet
- Job Order Costing System ExplainedDocument47 pagesJob Order Costing System Explainedslow dancerNo ratings yet
- 18 x12 ABC ADocument12 pages18 x12 ABC AKM MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Finals - GONZALESDocument21 pagesCost Accounting Finals - GONZALESAdolph Christian GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Golden Shower Company Journal EntriesDocument4 pagesGolden Shower Company Journal EntriesnicoleNo ratings yet
- MS_3605_Variable_and_Absorption_CostingDocument5 pagesMS_3605_Variable_and_Absorption_Costingrichshielanghag627No ratings yet
- Mas 2605Document6 pagesMas 2605John Philip CastroNo ratings yet
- MAS Absorption Costing/Variable Costing Study ObjectivesDocument6 pagesMAS Absorption Costing/Variable Costing Study ObjectivesMarjorie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Mas 9404 Product CostingDocument11 pagesMas 9404 Product CostingEpfie SanchesNo ratings yet
- MS103 SendingDocument3 pagesMS103 SendingEthel Joy Tolentino GamboaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Absorption and Variable CostingDocument5 pagesOverview of Absorption and Variable CostingJarrelaine SerranoNo ratings yet
- Marginal & Absorption CostingDocument12 pagesMarginal & Absorption CostingMayal Sheikh100% (1)
- FAR.3207 PPE-RevaluationDocument2 pagesFAR.3207 PPE-RevaluationMira Louise HernandezNo ratings yet
- FAR.3408 2017-10 PAS 40 - Separation of Property and Classification As Investment PropertyDocument5 pagesFAR.3408 2017-10 PAS 40 - Separation of Property and Classification As Investment PropertyMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- FAR.3408 2017-06 PAS 2 16 and 40 - Accounting For Collector S ItemsDocument4 pagesFAR.3408 2017-06 PAS 2 16 and 40 - Accounting For Collector S ItemsMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Interpretations Committee (Pic) Questions and Answers (Q&As)Document5 pagesPhilippine Interpretations Committee (Pic) Questions and Answers (Q&As)RicaNo ratings yet
- IFRS List Philippines 2023Document5 pagesIFRS List Philippines 2023Monica GarciaNo ratings yet
- MS 3411 Risks Returns and Capital StructureDocument4 pagesMS 3411 Risks Returns and Capital StructureMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- FAR.3402 2018-10 PAS 2 - Scope of Disclosure of Inventory Write-DownsDocument2 pagesFAR.3402 2018-10 PAS 2 - Scope of Disclosure of Inventory Write-DownsMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- FAR.3405 PPE-Acquisition and Subsequent ExpendituresDocument6 pagesFAR.3405 PPE-Acquisition and Subsequent ExpendituresMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis RatiosDocument6 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis RatiosMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Cebu Davao Inventory Discussion ProblemsDocument8 pagesCebu Davao Inventory Discussion ProblemsMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument5 pagesManila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.09 - Lecture Notes (Truth in Lending Act)Document3 pagesRFBT.09 - Lecture Notes (Truth in Lending Act)Monica GarciaNo ratings yet
- MS 3403 Costs Volume Profit AnalysisDocument6 pagesMS 3403 Costs Volume Profit AnalysisMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- MS 3413 Activity-Based Costing SystemDocument5 pagesMS 3413 Activity-Based Costing SystemMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- MS 3412 Capital BudgetingDocument6 pagesMS 3412 Capital BudgetingMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- MS 3402 Costs Behavior Determination and PredictionDocument5 pagesMS 3402 Costs Behavior Determination and PredictionMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- MS 3404 Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument6 pagesMS 3404 Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Roles and FunctionsDocument7 pagesManagement Accounting Roles and FunctionsANTONIA LORENA BITUINNo ratings yet
- Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument7 pagesManila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3408 Ipl Eca Dpa PDFDocument14 pagesRFBT.3408 Ipl Eca Dpa PDFMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3410 Insurance Labor SSS PDFDocument39 pagesRFBT.3410 Insurance Labor SSS PDFMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.10 - Lecture Notes (Labor Law)Document9 pagesRFBT.10 - Lecture Notes (Labor Law)Monica GarciaNo ratings yet
- MS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingDocument7 pagesMS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3409 Fria Tila PDFDocument12 pagesRFBT.3409 Fria Tila PDFMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3405 CorporationDocument22 pagesRFBT.3405 CorporationMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3406 AMLA and BP 22 PDFDocument10 pagesRFBT.3406 AMLA and BP 22 PDFMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3404 PartnershipDocument11 pagesRFBT.3404 PartnershipMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- RFBT.3407 Cooperatives PDIC and Bank Secrecy PDFDocument10 pagesRFBT.3407 Cooperatives PDIC and Bank Secrecy PDFMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document4 pagesChapter 21Rahila RafiqNo ratings yet
- IIPMSI Clinic ProfileDocument7 pagesIIPMSI Clinic ProfilePatricia ZamoraNo ratings yet
- JIPMAT 2022 PyqDocument31 pagesJIPMAT 2022 Pyqtanishkhetan874No ratings yet
- Insurance Claims For Loss of Stock and Loss of Profit 2 PDFDocument22 pagesInsurance Claims For Loss of Stock and Loss of Profit 2 PDFEswari Gk100% (1)
- Value Analysis or Value EngineeringDocument3 pagesValue Analysis or Value EngineeringJeff TapuNo ratings yet
- Question No.1 Is Compulsory. Answer Any Four Questions From The Remaining Five Questions. Working Notes Should Form Part of The AnswerDocument8 pagesQuestion No.1 Is Compulsory. Answer Any Four Questions From The Remaining Five Questions. Working Notes Should Form Part of The AnswerKv kNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management ScienceDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Management SciencebababababananaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Tutorial Questions 1Document6 pages4.1 Tutorial Questions 1Lee XingNo ratings yet
- POSTER Fico Flowchart 29092008 V0.2Document1 pagePOSTER Fico Flowchart 29092008 V0.2itmuesNo ratings yet
- Examples For Brids StudyDocument4 pagesExamples For Brids StudyMunir HussainNo ratings yet
- ECO 101 Assignment - Introduction To EconomicsDocument5 pagesECO 101 Assignment - Introduction To EconomicsTabitha WatsaiNo ratings yet
- CA6 Job Order CostingDocument15 pagesCA6 Job Order CostinghellokittysaranghaeNo ratings yet
- Accounting Voucher TypesDocument141 pagesAccounting Voucher TypesAshish Salunkhe100% (1)
- Corporate RestructuringDocument40 pagesCorporate RestructuringSarita ThakurNo ratings yet
- Accounting Charts - Quick Referencer by ICAIDocument22 pagesAccounting Charts - Quick Referencer by ICAIQuestion Bank100% (1)
- Job Order Costing HMDocument11 pagesJob Order Costing HMYamato De Jesus NakazawaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Assignment1Document28 pagesAccounting Assignment1Runaway ShujiNo ratings yet
- MA Mids Muneeb Ahmed 10180Document11 pagesMA Mids Muneeb Ahmed 10180zainNo ratings yet
- Full Operation PlanDocument14 pagesFull Operation PlanmarshaNo ratings yet
- F2Document17 pagesF2TRINH DUC DIEPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Cost Terminology and Cost Behaviors: LO1 LO2 LO3 LO4 LO5Document29 pagesChapter 2 - Cost Terminology and Cost Behaviors: LO1 LO2 LO3 LO4 LO5nikkaaa60% (5)
- Internationalization Theories & International Market SelectionDocument29 pagesInternationalization Theories & International Market Selectioniamrockrock7407No ratings yet
- Practice Exam 01 312S04Document12 pagesPractice Exam 01 312S04coolankit10No ratings yet
- Topic 3 Job Order Costing ExercisesDocument4 pagesTopic 3 Job Order Costing ExercisesThao Le TranNo ratings yet
- Combined Profit of Home Office and BranchDocument59 pagesCombined Profit of Home Office and BranchAllecks Juel LuchanaNo ratings yet