Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 1: The Theoretical Foundations of Nursing Neglectful
Uploaded by
Ruffy Casin FernandezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 1: The Theoretical Foundations of Nursing Neglectful
Uploaded by
Ruffy Casin FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS (NCMA 111) ⮚ Practiced since pre-historic times
< venice > among primitive tribes and lasted
through the early Christian era
LESSON 1: THE THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS ⮚ INTUITION: the ability to
OF NURSING NEGLECTFUL understand something
immediately, without the need of
THEORIES
conscious reasoning
⮚ A systematic explanation of an event in
⮚ Nursing was “untaught” and
which constructs and concepts are identified
instinctive
and relationships are proposed and
⮚ Women’s role: to take care of
predictions are made (Streubert and
their child, the sick, and aged
Capenter, 1999)
⮚ No training programs
⮚ System of interrelated propositions used to
⮚ Practice of nursing is based on
predict, explain, understand, and control a
observation and experience
part of empirical world. (Adam, 1985)
COURSE OF EVENTS FAMOUS PEOPLE
⮚ Comprised of concepts, propositions, laws,
AND PRACTICES THEIR
and set of propositions that can be FORMED CONTRIBUTIONS
verbalized and communicated. EARLY CIVILIZATION
⮚ Ex: Big Bang Theory, The Theory of ⮚ Music or singing
Evolution was often used
to chase away
CONCEPTS the evil spirits
⮚ Is a symbolic statement describing a ⮚ In some cases,
phenomenon or group of phenomena trephining was
⮚ Are formulated in words to be able to used wherein
communicate meanings about realities in the they cut a hole
world or give meaning to phenomena that in the head of
can be directly seen or indirectly seen, the afflicted to
heard, taste, smelled, or touched (Faucett, let out the evil
1999) spirit out.
⮚ TYPES OF CONCEPTS:
● A. ABSTRACT – hope, love, desire CODE OF
● B. CONCRETE – airplane, HAMMURABI
temperature, weight (BABYLONIA)
⮚ Concepts can be formulated: ⮚ 1st recording on
● A word – grief, empathy, pain the medical
● Two words – patient’s satisfaction, practice
caring nurse ⮚ Established the
● Phrase – health promoting practices, medical fees
core competency standards ⮚ Discouraged
experimentation
HISTORICAL PERPECTIVE ⮚ Specific doctor
I. INTUITIVE NURSING (MEDIEVAL for each disease
PERIOD) ⮚ Right of patients
to use of
charms,
medicine, or,
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 1
surgical drug used for
procedure treatment
⮚ Prohibited the
ART OF EMBALMING
dissection of
(EGYPT)
dead human
⮚ Mummification,
body as a
removing the
worship to
internal organs
ancestors
of the dead,
⮚ Use of wax to
instillation of
preserve the
herbs and salt to
body of the dead
the dead
⮚ Believed that in
⮚ Used to
using girl’s
enhanced their
clothes for male
knowledge of
babies keep
the human
evils away from
anatomy
them
⮚ Documentation
of about 250 SUHSHURUTU
diseases and (INDIA)
treatments ⮚ 1st recording on
⮚ Slaves and the nursing
patient’s families practice
nursed the sick ⮚ Medicine
men-built
TEACHINGS OF Moses is the “Father
hospitals
MOSES of
⮚ They use
(ISRAEL) Sanitation” and he
⮚ Laws of control wrote intuitive form of
of spread of five books in the Old. asepsis
communicable He ⮚ There was
disease and emphasized the proficient
the ritual of practice practice of
circumcision of of hospitality and Medicine and
charity Surgery
male child was
wherein anyone who is
also established CADUCEUS HIPPOCRATES also
sick is catered and
⮚ Nurses are helped. (ANCIENT redefined the concept
referred as GREECE) of
midwives, wet ⮚ INSIGNIA OF medicine. He is called
nurse, or child’s MEDICINE as
nurse. the father of
Scientific/Modern
MATERICA MEDICA Medicine.
(CHINA) He was the 1st to
⮚ Book that reject the idea that
indicated the diseases are caused
pharmacologic by evil spirits and to
apply assessment. He
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 2
also practiced A. BEGININNING THE CRUSADERS
medical OF RELIGIOUS ⮚ KNIGHTS OF
ethics. WAR SAINT JOHN
ROME FABIOLA is a wealthy ⮚ From the 12th OF
⮚ A Roman made matron of the Roman Century-Crusa JERUSALEM
her home the Empire converted to des (Knights
first hospital in Christianity and used ⮚ This is war Hospitallers)
the Christian wealth to provide ⮚ TEUTONIC
between the
World houses of care and
Christian KNIGHTS
healing.
soldiers and –Established
IMPORTANT
NURSING EVENT the Muslim tent hospitals
⮚ Happened in Turks brought for the
this period: by prohibiting wounded
⮚ GROWTH OF Christians to ⮚ KNIGHTS OF
RELIGION visit the Holy SAINT
⮚ GROWTH OF Land. LAZARUS –
EARLIEST ⮚ In order to cared for
CIVILIZATION propagate people with
(Near East, Far Catholicism, leprosy,
East, Ancient the different syphilis, and
Greece, and religious skin
Ancient Rome) orders conditions
⮚ Illness is still established
believed to be Churches,
caused by evil schools,
spirits and orphanages,
nursing remains hospitals,
to be the and other
responsibility institutions in
of women in the
society. community
⮚ Through these
institutions,
II. APPRENTICE PERIOD (MIDDLE they intend to
AGES) bring the
⮚ Start of the training program for people to
Nurses Catholic faith.
⮚ Nuns and priests were considered ⮚ Priests and
to be the first trained. Thus, during nuns were
this era, nursing was thought to trained to
be a religious calling work in these
⮚ Care was done by Crusaders, institutions
Prisoners, and Religious Orders including
COURSE OF EVENTS FAMOUS PEOPLE hospitals
AND PRACTICES AND THEIR
FORMED CONTRIBUTIONS
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 3
THE RISE OF Many saints were led to the priest
SECULAR recognized for taking and nuns to go
ORDER care of sick during hiding for fear of
⮚ There was the this persecution
rise of Religious era, Hiding of the
Nursing Orders A. ST. CLARE priests and nuns
for Women. B. ST. result to a great
Although ELIZABET shortage of
Christianity H OF nurses during
promoted equality HUNGARY the 17th century.
to all men, women C. ST.
were still CATHERIN C. DARK PERIOD OF CHARLES DICKENS
concentrated in E OF NURSING (17TH – his
their roles as SIENA – CENTURY TO 19TH writings reflected the
known as CENTURY) attitude towards
wives and
the 1st ⮚ Because of nurses
mothers.
shortage of through his
⮚ Religious taboos Lady with
nurses, hospitals, character,
and social a Lamp
started to get Sairy Gamp, who
restrictions D. ST. cared
VINCENT women prisoners,
influenced nursing the sick by
DE PAUL thieves, drunks,
at the time of the neglecting
and prostitutes to
religious nursing them, stealing from
serve as nurses.
orders. them, and physically
⮚ This started the abusing them.
B. RISE OF Martin Luther is a bad image and
PROTESTANISM (1520 member of the reputation for
– 1562) Franciscan order, nurse. As a form
⮚ Because of denounced the of punishment for
abusers and practice these women,
corruption of of the Church to get nurses worked for
some popes, money from the a long period of
bishops, and people
time was not
cardinals, in the forgiveness of
given decent
their sins
peasants started living quarters and
to revolt against were constantly
the Catholic abused.
religion. They are ⮚ There was no
inspired by Martin formal education
Luther. for nurses
⮚ Protestants
started to destroy D. ESTABLISHMENT PASTOR
everything the OF THEODORE
THE 1ST TRAINING FLIEDNER and his
Church owned
SCHOOL OF NURSING wife
including
⮚ KAISSERSWERT FEDERIKA
hospitals, schools, established
H INSTITUTE OF
orphanages
DEACONESSES
churches, which
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 4
(were Nightingale the first training improved the
received her school standards for
three-month for nurses in the care of
course in Nursing) Kaisserswerth, war
⮚ Deaconess Germany casualties in
School of Crimea
Nursing ⮚ “Angel of
recognized as Crimea”
the first nursing ⮚ POLITICAL
school in the NURSE:
world founded by Reforms in
Theodore Fleidner hospital and
in 1836 at production and
Kaisers Werth, implementation
Germany of public health
⮚ To change the policies
bad reputation of ⮚ Nursing’s
nurses, Fliedner First
carefully chose Scientist-
the students Theorist
admitted at ⮚ Notes on
Deaconess Nursing: What
School it is, and what
it is not?
E. NIGHTINGALE ERA FLORENCE
⮚ She
⮚ The effects of the NIGHTINGALE
disapproved
previous period (1820-
1910) restriction on
marked the
⮚ Born in May admission of
beginning of a
12, 1820 patient and
formal education
(Coincides with considered this
system for
International Unchristian
Nursing when
Nurses’ Day) and contrary
Florence
⮚ Mother of the to health care
Nightingale
Modern ⮚ Upgraded the
School of Nursing
Nursing She practice of
opened at St.
believed she Nursing and
Thomas Hospital
was “Called made Nursing
in London
by God to an honorable
help others profession
and to ⮚ Led other
improve the nurses in
wellbeing of taking care of
the mankind” the wounded
⮚ “Lady with and sick
the Lamp” – soldiers during
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 5
the Crimean TRAINING ⮚ First graduate
War SCHOOL FOR nurse in the
⮚ She was NURSES (ST. US; graduated
designated as THOMAS in September 1,
Superintende HOSPITAL) 1872 from the
nt of the ⮚ Served as New England
Female model for Hospital for
Establishmen other Women in
t of English training Boston
General schools 2. DR. WILLIAM
Hospital in ⮚ Nightingale HALSTEAD
Turkey during system was ⮚ Designed the
the Crimean more on first rubber
War developing gloves
profession 3. CAROLINE
within the HAMPTON ROBB
DEFINITION OF NURSING ACCORDING TO hospital ⮚ First nurse to
FLORENCE NIGHTINGALE ⮚ Curriculum wear rubber
⮚ “Act of utilizing the environment of the includes gloves while
patient to assist him in his recovery.” theory and working as an
III. PERIOD OF EDUCATED NURSING practice operating room
(NIGHTINGALE ERA 19 TH TO 20 TH ⮚ 1st school nurse
CENTURY) of nursing 4. ESTABLISHMENT
⮚ Florence Nightingale was one of the to provide OF NURSING
pioneers in establishing the idea of theory-base ORGANIZATIONS;
nursing schools from her base at St. d knowledge the American
Thomas’ Hospital in London in 1860, and clinical Nurses
when she opened the Nightingale skill Association and
Training School for Nurses’, now part building the National
of King’s College London ⮚ Nursing League for
⮚ Development of Nursing is greatly evolved as Nursing Education
influenced by: an art and –contributed to the
● A. The aftermath of science uplift of nursing
Crimean War and Civil ⮚ Formal profession
War education 5. ISABEL HAMPTON
● B. Arousal of social and service ROBB
consciousness began ⮚ The first
● C. Increased in
principal of the
educational
John Hopkins
opportunities for women
Hospital
School of
COURSE OF FAMOUS PEOPLE AND Nursing; the
EVENTS AND THEIR CONTRIBUTIONS
most influential
PRACTICES
in directing the
FORMED
1860 – 1. LINDA RICHARDS development of
NIGHTINGALE
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 6
nursing during ⮚ Nursing students should be provided
this period with residence near their training
6. CLARA LOUISE hospitals
MAAS ⮚ Written orders of doctors were
⮚ Engaged in insisted Nurses should go with their
doctors during their rounds
medical
⮚ Training was required for administrative
research on
positions
yellow fever ⮚ Probationers kept diaries and case
during the notes of their work, examined by the
Spanish-Americ matron and home sister, and often by
an War Nightingale
7. DEVELOPMENT ⮚ A major component of training was
OF PRIVATE DUTY moral: ethical standards for the
NURSING patient
⮚ Settlement
house nursing IV. CONTEMPORARY NURSING (20TH
(PHN), NURSING)
government ⮚ This refers to the period after World
War I and the changes and
service of
development in the trends and
nurses, and
practices of Nursing occurring since
prenatal and 1945 after World War II.
maternal health ⮚ NURSING AFTER WORLD WAR I
nursing ⮚ Nursing is primarily hospital
8. PREPARATION OF sponsored program being trained by
STANDARD doctors and senior of nurses
CURRICULUM ⮚ Licensure of Nursing started
based on ⮚ Training of Nurses in diploma program
educational ⮚ Development of Baccalaureate and
objectives for Advanced Degree Program
schools of Nursing
9. EDITH CAVEL – VIRGINA HENDERSON
⮚ One of the FIRST MODERN NURSES TO
known as “Mata
DEFINE NURSING
Hari” served the ⮚ “The unique function of the nurse is to
wounded soldiers assist the individual, sick or well, in the
during World War I performance of those activities or its
recovery (or to peaceful death) that he
would perform unaided if he had the
CONCEPTS IN THE NIGHTINGALE SYSTEM OF
necessary strength, will, or knowledge,
EDUCATION and to do this in such a way as to help him
⮚ Government funds should be allotted gain independence as rapidly as possible.”
to nursing education (Henderson,1966)
⮚ First nurse political activist
⮚ Training schools of Nursing should be SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL
in close affiliation ADVANCEMENT
⮚ Professional nurses should train ⮚ Health is perceived as a human right. (law)
nurses ⮚ Community involvement of nurses
⮚ Disposable supplies and equipment
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 7
⮚ Expanded roles of nurses 5. LEADER - Influences others to work
⮚ WHO was established by United Nations together to accomplish a specific goal
⮚ Use of computer and sophisticated 6. MANAGER - Delegates nursing activities to
machines on hospitals ancillary workers and other nurses, and
⮚ NOTES: supervises and evaluates their performance
o “Nursing is caring” (womb to 7. CASE MANAGER - Works with the
tomb) multidisciplinary healthcare team to measure
o “Nursing is an Art” the effectiveness of the case management
plan and monitor outcomes
RECIPIENT OF NURSING 8. RESEARCH CONSUMER EXPANDED
1. CONSUMER – Individual, group of people, CAREER ROLES
or community that uses a service or ⮚ Nurse Practitioner
community ⮚ Clinical Nurse Specialist
2. PATIENT – person who is waiting for or ⮚ Nurse Anesthetist
undergoing medical treatment and care ⮚ Nurse Midwife
3. CLIENT – person who engages the ⮚ Nurse Researcher
advices or services of another who is ⮚ Nurse Administrator
qualified to provide this service ⮚ Nurse Educator
⮚ Nurse Entrepreneur
LESSON 02: HISTORY OF NURSING IN THE
SCOPE OF NURSING PHILIPPINES
1. PROMOTING HEALTH AND WELLNESS -
Means engaging in attitudes and EARLY BELIEFS
behavior that enhance the quality of life ⮚ Early Filipinos believes to superstitious
and maximize personal potential beliefs and practices in relation to health
2. PREVENTING ILLNESS - To maintain and sickness
optimal health by preventing disease ⮚ Evil spirits could be driven away by persons
3. RESTORING HEALTH - Focuses on the ill with powers to expel demons
client and extends from early detection of ⮚ Illnesses were believed to be caused by
disease through helping the client during “mangkukulam or manggagaway”
the recovery period ⮚ HERBULARIOS – herb doctors
4. CARE OF THE DYING - Involves ⮚ HERBICHEROS – practices witchcraft
comforting and caring for people of all ⮚ MABUTING HILOT – also known as good
ages who are dying midwife who attends during childbirths
⮚ “NONO” – cause of difficult child birth
ROLES AND FUNCTION OF THE NURSE ⮚ They use gunpowder exploded from a
1. CAREGIVER - Activities that assist the bamboo pole close to the head of the
client physically and psychologically while mother to drive the evil spirits away
preserving the client’s dignity
2. COMMUNICATOR - Nurses communicate HEALTHCARE DURING SPANISH REGIME
patient’s identified problems to other ⮚ “Babaylan” (priest physician) and
members of healthcare team “Albularyo” (Herb doctors) care for the
3. COUNSELOR - Process of helping the client sick individuals
recognize and with stressful psychologic or ⮚ 1578 – male nurses were acknowledged
social problems, to develop improved by Spanish friars referred as practicante or
interpersonal relationships, and to promote enfermero.
personal growth ⮚ Religious orders exerted their efforts to
4. CHANGE AGENT - Assisting clients to care for the sick by building hospitals in
make modifications in their behavior different parts of the Philippines
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 8
⮚ Provided
EARLY HOSPITAL nursing care to
1. HOSPITAL REAL DE MANILA (1577) the wounded
⮚ Established mainly for the care for night and day
the Spanish king’s soldiers, but
also admitted civilians 2. ROSA SEVILLA ⮚ Converted them
⮚ Founded by Gov. Francisco De DE ALVERO house into
Sande quarters for the
2. SAN LAZARO HOSPITAL (1578) Filipino
⮚ Founded by Brother Juan soldiers during
Clemente the Philippine-
⮚ Named after the Knights of St.
American War
Lazarus
that broke out
⮚ Administered for many years by
Hospitallers of San Juan De Dios during 1899
⮚ Built exclusively for patients with 3. DONA HILARIA ⮚ Wife of Emilio
leprosy DE Aguinaldo
3. HOSPITAL DE INDIOS (1586)
AGUINALDO ⮚ Organized the
⮚ Established by the Franciscan
Order Filipino Red
⮚ Hospital for the poor Filipino Cross under the
people inspiration of
⮚ Service was in general supported by Mabini
alms and contributions from
4. DONA MARIA ⮚ Second wife of
charitable persons
4. HOSPITAL DE AGUAS SANTAS (1590) AGONCILLO Emilio
⮚ Established in Laguna, near a DE Aguinaldo
medicinal spring because people AGUINALDO ⮚ Provided
believed that the spring has a nursing care to
healing power the Filipino
⮚ Founded by Brother J. Bautista of soldiers during
the Franciscan Order the revolution
5. SAN JUAN DE DIOS HOSPITAL (1596) ⮚ President of
⮚ Founded by the Brotherhood of the Filipino Red
Misericordia and administered by Cross branch
the Hospitallers of San Juan De in Batangas
Dios
⮚ Support was derived from alms 5. MELCHORA ⮚ Nursed the
and rents AQUINO wounded
⮚ Rendered general health service to A.K.A Filipino
the public “TANDANG soldiers
NURSING DURING PHILIPPINE REVOLUTION
SORA” (Katipuneros)
1. JOSEPHINE ⮚ Wife of Jose
and gave them
BRACKEN Rizal
shelter and food
⮚ Installed a field
hospital in an 6. CAPITAN ⮚ A revolutionary
estate house in SALOME leader in Nueva
Tejeros Ecija
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 9
⮚ Provided HOSPITAL SCHOOL NURSING’S FORMAL
nursing care to TRAINING (1901-1911)
the wounded
when not in ⮚ Formal training in hospital school of nursing
combat transpired. This began when American
missionary doctors and nurses that their
7. AGUEDA ⮚ Revolutionary manpower is insufficient.
KAHABAGAN leader in THIS RESULTS TO A DECISION TO TRAIN
Laguna FILIPINO NURSES THAT AMERICAN
⮚ Provided ESTABLISHED IN 1906.
nursing 1. ILOILO ⮚ Ran by the
services to her MISSION Baptists
troops HOSPITAL Foreign
SCHOOL OF Mission of
8. TRINIDAD ⮚ Stayed in the NURSING America
TECSON “INA hospital at Biak (Iloilo City, ⮚ There are no
NG BIAK NA na Bato to care 1906) strict
BATO” for her requirements
wounded for the
soldiers applicants as
long as they are
all willing to
HOSPITALS AND NURSING SCHOOLS
work.
⮚ 1907 – Training of Nursing Students by ⮚ APRIL 1944 –
the Americans Graduate
⮚ Filipino students studied the same nurses’ tool the
subject than that of the Americans but first Nurses
believed that the curriculum was never Board
the mirror image of the American Nursing Examination at
Curriculum the Iloilo
Mission
1ST TRAINING SCHOOL OF NURSING Hospital
⮚ ROSE
⮚ BELLEVUE HOSPITAL SCHOOL OF
NICOLET – a
NURSING
o Founded in 1873 in New York graduate of New
o It was the first school of nursing in England
the United States to be founded on Hospital for
the principles established by Women and
Florence Nightingale Children in
Boston was the
PENSIONADO ACT OF 1903 (ACT 854) first
superintendent
⮚ Allowing Filipino nursing students to study in for nurses
United States
⮚ Among of the first wave of nurses who went 2. SAINT PAUL’S ⮚ Established by
to the US HOSPITAL the Archbishop
SCHOOL OF of Manila,
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 10
NURSING Jeremiah Harty ⮚ Applicant must
(Manila, 1907) under the have
supervision of completed
St. Paul de elementary to
Chartres located seventh grade
in Intramuros education
⮚ Provided
general
MARY COLEMAN MASTERS
hospital
⮚ In 1906, Mary Coleman Masters, an
services educator advocated for the idea of the
⮚ 1908 – when it training of Filipino girls for the
opened its profession of Nursing with the approval of
training school the government officials
for nurses ⮚ Opened the first dormitory for girls
⮚ MOTHER enrolled at the Philippine Normal Hall and
MELANIE – University of the Philippines
superintendent
⮚ MISS 4. ST. LUKE’S ⮚ Opened with
CHAMBERS - HOSPITAL three girls
Principal SCHOOL OF admitted
NURSING ⮚ These girls had
3. PHILIPPINE ⮚ Began in 1901 (Quezon City, them first year in
GENERAL as a small 1907) combined
HOSPITAL dispensary for classes with the
SCHOOL OF Civil officers and PGH School of
NURSING Employees, Nursing and St.
(Manila, 1907) soon grew into a Paul’s Hospital
Civil Hospital School of
⮚ Opened nursing Nursing
classes with ⮚ HELEN HICKS
Admission – The first
based on principal
Entrance ⮚ VITALIANA
examinations BELTRA – First
⮚ JULIA Filipino
NICHOLS AND superintendent
CHARLOTTE ⮚ DR. JOSE
CLAYTON: FORES - first
taught the medical
students director of the
Nursing hospital
subjects;
American 5. MARY ⮚ Started as a
physicians also JOHNSTON small dispensary
served as HOSPITAL AND on Calle
lecturers. SCHOOL OF
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 11
NURSING Cervantes (now ⮚ First Executive Officers of the Board
(Manila, 1907) Avenida) Examiners for Nurses were physicians
⮚ Called the
Bethany MARY CHILES HOSPITAL SCHOOL OF
Dispensary NURSING (Manila, 1911)
⮚ Funded by the
⮚ MARY CHILES OF MONTANA – donated a
Methodist
large sum of money with which the present
Mission for the building the Gastambide was bought
relief of ⮚ Frank Dunn Memorial Hospital (Vigan,
suffering Ilocos Sur, 1912)
among women ⮚ San Juan De Dios Hospital School of
and children Nursing (Manila, 1913)
⮚ 1907 – Sister ⮚ Emmanuel Hospital School of Nursing
REBECCA (Capiz,1913)
PARRISH ⮚ Southern Islands Hospital School of Nursing
together with the (Cebu, 1918)
registered
nurses ROSE OTHER NURSING SCHOOLS
DUDLEY and
⮚ Zamboanga General Hospital School of
GERTUDE
Nursing (1921)
DREISBACH ⮚ Chinese General Hospital School of Nursing
organize the (1921)
Mary Johnston ⮚ Baguio General Hospital School of Nursing
School of (1923)
Nursing ⮚ Manila Sanitarium Hospital and School of
⮚ Nurse’s training Nursing (1930)
course began ⮚ St. Paul School of Nursing (1946)
with three ⮚ North General Hospital and School of
Filipino young Nursing (1946)
girls from ⮚ Siliman University School of Nursing (1947)
elementary as
ACCREDITED PROFESSIONAL ORGANIZATION
their first
(1921-1931)
students
⮚ The Filipino Nurses Association was
START OF NURSING PRACTICE (1911- 1921) established on October 15, and the
⮚ ACT 2943 – Amends Medical Law (Act. organization initiated the publication of
No. 310) allowing the regulation of nursing Filipino Nurse Journal which later changed
practice to The Philippine Journal of Nursing.
⮚ ACT 3025 – An act Regulating the
FIRST TRUE NURSING LAW (1919) Practice of Nursing Profession in the
Philippine Islands which necessitates that
⮚ Also known as Act 2808 all nurses who are practicing the
⮚ Board of Examiners for Nursing was profession to register yearly.
created ⮚ National League of Nurse
⮚ First Nursing Board Examinations was ⮚ Other organizations:
given on 1920 o A. ORNAP – for operating room
nurses
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 12
o B. ANSAP – ones who renders the Philippines
seminars for nurses (1946)
o C. MCNAP – for maternal and child ⮚ In 1947, the
nurses Bureau of
Private Schools
PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING DEVELOPMENT
permitted UST
(1931-1941)
to grant title
⮚ Nursing institution have increased them Graduate
requirement (1933) Nurse to the 21
⮚ Applicants must able to complete students who
secondary education were of
⮚ UNIVERSITY OF THE PHILIPPINES advanced
SCHOOL OF PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING standing from
– where the first collegiate nursing 1948 up to the
graduates of the Philippines graduated present
(1938) ⮚ SOR TACIANA
TRIANES – first
THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN directress
NURSING (1941-1951)
2. MCU COLLEGE ⮚ 1st College
⮚ JULITA V. SOTEJO, a graduate of the OF NURSING who offered
Philippine General hospital, presented her (June 1947) BSN as a
dissertation that tackles on the four-year
development of a nursing education program
within a university- based College of
⮚ The MCU
Nursing which become the basis of the
Nursing Curriculum in the Philippines Hospital first
⮚ Nursing became a Baccalaureate course offered BSN and
⮚ College of Nursing was created Doctor of
Medicine
RISE OF THE BSN CURRICULUM degrees in 1947
and served as
⮚ JAPANESE OCCUPATION (1942) – training the clinical field
and practice at the hospital schools of for practice
Nursing in Manila was “violently ⮚ CONSUELO
disrupted” GIMENO – first
⮚ 1945 - However, U.S. colonial patterns in principal
Philippine Nursing Education soon
returned after the U.S reclaimed the 3. UP COLLEGE ⮚ The idea of
country and even the Philippines gained OF NURSING opening the
independence from the U.S on July 4, 1946 (June 1948) college began in
a conference
THE FIRST COLLEGES OF NURSING IN THE between Miss
PHILIPPINES
Julita Sotejo and
UP president
1. UST COLLEGE ⮚ 1st College of
⮚ 1948 – the
OF NURSING Nursing in the
University
(1946)
Council
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 13
approved the implementation conducted by
curriculum and Specialty Certification Boards
the Board of ⮚ This improvement also prompted the
Regents start of Advanced Practiced Nursing
recognized the (APN) in the Philippines.
profession as
having and
THE PHILIPPINE NURSING ACT OF 2002
equal standing
⮚ The Philippine Nursing Act of 2002 was
as Medicine
enacted under the Republic Act No. 9173
⮚ JULITA
which entails changes in existing policies
SOTEJO – first
under Republic Act No. 7164.
dean
⮚ These changes underscore on the
4. FEU INSTITUTE requirements for faculty and Dean of the
OF NURSING Colleges of Nursing, as well as the
(June 1955) conduct for Nursing Licensure Exam.
5. UE COLLEGE NURSING LEADERS IN THE PHILIPPINES
OF NURSING
(October 1958) 1. ANASTACIA GIRON-TUPAS
HISTORY OF NURSING IN THE PHILIPPINES ⮚ First Filipino nurse to hold the
position of Chief Nurse
1. PROLIFERATION OR NURSES AS A Superintendent (PGH)
WORKFORCE: 1951-1971 ⮚ Founder of PNA (Philippine Nurses
⮚ The PHILIPPINE NURSING LAW Association)
was approved under the Republic
Act No. 877 on June 19, 1953 2. CESARIA TAN
⮚ 1966 – further amendment was ⮚ First Filipino nurse receive a
created which limits the practice of Master’s degree in Nursing abroad.
nurses among 21 years old and 3. SOCORRO SIRILAN
above
⮚ Pioneered in Hospital Social
⮚ PROCLAMATION NO. 539 –
Celebration of Nurses’ Week which Service in San Lorenzo Hospital
was proclaimed by President Carlos where she was the Chief Nurse
P. Garcia 4. ROSA MILITAR
2. NURSING PROFESSION DEVELOPMENT ⮚ A pioneer in school health
(1971-2001) education.
⮚ PRESIDENTIAL DECREE NO. 233 – 5. SOR RICARDA MENDOZA
Establishment of the agency, ⮚ A pioneer in Nursing Education
Professional Regulation 6. SOCORRO DIAZ
Commission ⮚ First editor of the PNA magazine
⮚ The Philippine Nursing Act of 1991 called “The Message”
was also amended under the 7. CONCHITA RUIZ
REPUBLIC ACT OF 7164
⮚ First full-time editor of the newly
⮚ NURSING CERTIFICATION
named magazine “The Filipino Nurse”
COUNCIL in 1999 under the Board of
8. LORETO TUPAZ
Nursing through Resolution No. 14 –
⮚ Dean of the Philippine Nursing
supervise the new programs’
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 14
⮚ Florence Nightingale of Iloilo ⮚ It also provided the holding of exam for the
9. MAGDALENA VALENZUELA practice of Nursing on the 2nd Monday of
⮚ First Filipino Industrial Nurse June and December of each year.
10. ANNIE SAND 1920
⮚ Founded the national league of ⮚ 1st Board examination for Nurses was
Philippines Government Nurses conducted by the Board of Examiners
11. CORNEL ELVEGIA MENDOZA ⮚ 93 candidates took the exam, 68 passed
⮚ First Female Military Nurse the exam with the highest rating of 93.5%
who was taken by Anna Dahlgren
FURTHER CHANGES IN NURSING LAW: 2001 ⮚ Theoretical Exam was held at the UP
TO PRESENT Amphitheater of the College of Medicine and
Surgery
⮚ PHILIPPINE NURSING ACT OF ⮚ Practical Exam at the Philippine General
1991: RA 7194 Hospital Library
o An act increasing the bed 1921
capacity of the Naval General ⮚ Philippine Nurses Association Building
Hospital in the municipality of ⮚ Filipino Nurses Association was
Naval in Biliran, Leyte from 25 established (now PNA) as the National
to 50 beds. Organization of Filipino Nurses
⮚ PHILIPPINE NURSING ACT OF ⮚ PNA: 1st President – ROSARIO
2002: RA 9173 DELGADO
⮚ COMPREHENSIVE NURSING LAW ⮚ FOUNDER: ANASTACIA GIRONTUPAS
OF 2015 1953
o Senate Bill 2720, adopted by ⮚ Republic Act 877, known as the “Nursing
both Senate and the House Practice Law” was approved.
o Declares that is the State
policy to uphold the dignity of INTRODUCTION TO NURSING THEORY
the nurses and assume ⮚ The history of professional nursing began
responsibility for the with Florence Nightingale
protection, respect, and ⮚ She envisioned nurses as a body of
improvement of the nursing educated women at a time when women
profession by instating neither educated nor employed in public
measures towards competent service
and relevant nursing practices. ⮚ Florence Nightingale vision and
establishment of a School of Nursing at
TIMELINE St. Thomas Hospital in London marked
the beginning of Modern Nursing
1909
⮚ 3 Females graduated as “qualified
medical-surgical nurses” THEORY ERA
1919 ⮚ Contemporary phase where the emphasis
⮚ The 1st Nurses Law (Act No. 2808) was is on theory-based nursing practice and
enacted regulating the practice of the theory development
nursing profession in the Philippine ⮚ Awareness that nursing is a profession
Islands ⮚ In mid-1800, Florence Nightingale
expressed firm conviction that nursing
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 15
knowledge was distinct from medical ⮚ SCIENCE
knowledge. Her concept of nursing function o Systematically organized body of
is putting the patient in best condition for knowledge
nature to act upon him and that nursing is o The intellectual and practical activity
based on person and environment encompassing the systematic
study of the structure and behavior
CURRICULUM ERA of the physical and natural world
⮚ Focuses on what must be studied and through observation and experiment.
learned to become a nurse from ⮚ PHILOSOPHY
hospital-based diploma program into college o Is the theorist viewpoint: what the
and university theorist assumes, believes, and
⮚ More and more nurses sought for higher values, or hold to be true
degree, from vocational heritage to an NOTE:
academic discipline (profession) ⮚ EPISTEMOLOGY – A branch of philosophy
concerned with the theory of knowledge in
RESEARCH ERA philosophical inquiry.
⮚ Nurses started to participate in scientific
works KNOWLEDGE
⮚ This course started to be introduced and ⮚ Information, skills, and expertise acquired by
integrated in the Nursing a person through various life experiences or
formal learning
GRADUATION EDUCATION ERA
⮚ From Bachelor of Science in Nursing HISTORICAL VIEWS OF THE NATURE OF
(BSN) to Master’s Program SCIENCE
⮚ Two competing philosophical foundations of
SIGNIFICANCE OF NURSING THEORY science is rationalism and empiricism, have
⮚ Through the accomplishment of the past 20th evolved in the era of modern science with
century that Nursing was recognized in several functions
the academic discipline
⮚ Discipline and profession are interrelated RATIONALISM
but they are not the same. ⮚ Rationalist epistemology (scope of
knowledge) emphasizes the importance of
DISCIPLINE a priori reasoning as the appropriate
⮚ Specific to academia method for advancing knowledge
⮚ Refers to a branch of knowledge, education, ⮚ Deductive Reasoning (Cause and effect)
a department of learning or domain of ⮚ Theory- then research Strategy
knowledge ⮚ Innate, Reason, and Deduction
⮚ Case/Application: Poor hand washing
PROFESSION technique will result in spreading diseases to
⮚ Refers to a specialized field of practice all patients
⮚ Profession is founded on the theoretical
structure of the science or knowledge of
EMPIRICISM
that discipline and accompanying abilities
⮚ The empiricist view is based on the central
idea that scientific knowledge can be
HISTORY OF PHILOSPHY AND SCIENCE
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 16
derived only from sensory experience conditions, better career prospects and
(i.e., seeing, feeling, hearing facts) dignified existence for nurses.
⮚ Inductive Reasoning – collection of facts ⮚ Inter alia: to provide for organization of
precedes attempts to formulate board of nursing, examination and
generalizations registration of nurses, nursing education,
⮚ Research-then theory strategy nursing practice, as well as several related
matters. Repeals Nursing Act, 1991.
⮚ Gathering facts through experience and
observation and then formulating theories
QUALIFICATIONS OF THE BOARD OF
⮚ Case/Application: Differential Diagnosis NURSING
Patient – 31 years old productive cough for ⮚ Creation of a Professional Regulatory Board
two weeks, low grade fever occurring every of Nursing referred to as a Board
afternoon, vital signs all in normal rage, composed of a Chairperson and six (6)
weight, clinical observation Diagnostics – members which shall represent the three
X-ray (clear) Sputum Test – Negative History areas of Nursing, which are nursing
– Smoker for 15 years, 1 pack of cigars education, nursing service, and
everyday community health of nursing
⮚ They are appointed by the President from
EARLY TWENTIETH CENTURY VIEWS OF among two recommendees of the
SCIENCE AND THEORY Professional Regulation Commission
⮚ During the first half of the century, ⮚ The Board shall hold the office for a term of
philosophers focused on the analysis of three years until their successors have been
theory structure, whereas scientists focused appointed and qualified
on empirical research ⮚ The qualifications are:
⮚ According to H. Brown (1997), theory o A. Be a natural born citizen and
determines what observations are worth resident of the Philippines
o B. Be a member of good standing
making and how they are to be understood,
of the accredited professional
and observation provides challenge to
organization of nurses
accepted theoretical structures. o C. Be a registered nurse and
⮚ The continuing attempt to produce a holder of a master’s degree in
coherently organized body of theory and nursing, education or other allied
observation is the driving force of the medical profession conferred by a
research, and the prolonged failure of college or university duly recognized
specific research projects to lead scientific by the Government
revolutions o D. Have at least ten (10) years of
continuous practice of the
RA 9173: PHILIPPINE NURSING ACT OF 2002 profession prior to appointment (last
⮚ Comprehensive legislation regulating five years shall be in the Philippines)
various aspects of nursing profession. o E. Not have been convicted of any
⮚ Begun and held: Metro Manila, 22nd of July offense involving moral turpitude
2002 approved on October 21, 2002
under the office of president Gloria EXAMINATION AND REGISTRATION
Macapagal Arroyo, along with the ⮚ LICENSURE EXAMINATIONS shall be
president senate, Franklin M, Drillon, given to the all applicants for license to
⮚ Main objective: to provide for protection practice nursing are required to pass a
and improvement of nursing profession written examination that are given by the
by instituting measures that shall result in Board in such places and dates
relevant nursing education, humane working designated by the Commission;
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 17
Provided, that it shall be in accordance ⮚ C. Be a member of a good standing in the
with Republic Act No. 8981, otherwise accredited professional organization of
known as the “PRC Modernization Act of nurses
2000.” ⮚ D. Should be a holder of Master’s Degree in
⮚ The qualifications for Admission to the Nursing or other allied medical health
Licensure Examination are the sciences conferred by a college or university
o A. following: Citizen of the
Philippines or a citizen of a The dean of a college must also have a master’s
country which permits Filipino degree and must at least have 5 years of
nurses to practice within its experience in Nursing.
territorial limits (the requirements
in that country are substantially NURSING PRACTICE
the same) ⮚ SCOPE OF NURSING
o B. He/she is of good moral o States that a person shall be deemed
character to be practicing nursing within the
o C. Should be a holder of a meaning of this Act when he/she
Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing from singly or in collaboration with
a college that complies with the another, initiates and performs
standards of nursing education nursing services to individuals,
⮚ In order to pass the examination, an families and communities in any
examinee must obtain a general average health care setting.
of at least seventy-five percent (75%) o Includes, but not limited to, nursing
with a rating of not below sixty percent care during conception, labor,
(60%) in any subject. If an examinee got a delivery, infancy, childhood, toddler,
rating below 60% in any subject, he/she preschool. School age, adolescence,
needs to take the examination again in adulthood, and old age
that subject. o NURSING CARE INCLUDES:
▪ I. traditional and innovative
NURSING EDUCATION PROGRAM approaches
⮚ States that it shall provide sound general ▪ II. therapeutic use of self,
and professional foundation for the executing health care
practice of Nursing techniques and procedures,
⮚ Adhere strictly to specific requirements essential primary health care,
embodied prescribed curriculum as comfort measures, health
promulgated by the Commission on teachings
Higher Education (CHED) policies and ▪ III. administration of written
standards of nursing education prescription for treatment,
⮚ NURSES WHO HAVE NOT ACTIVELY therapies, oral topical and
PRACTICED THE PROFESSION for 5 parenteral medications,
years shall undergo 1 month of didactic ▪ IV. internal examination during
training and 3 months practicum labor in the absence of
antenatal bleeding and
QUALIFICATIONS OF THE FACULTY delivery in case of suturing of
⮚ A. Be a registered nurse in the Philippine perineal laceration
⮚ B. Have at least 1 year of clinical practice in o The nurse is duty-bound to observe
a field of specialization the Code of Ethics for nurses and
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 18
uphold the standards of safe identification card or special
nursing practice. permit
o The nurse is required to maintain ▪ E. Any person who falsely
competence by continual learning poses or advertises as a
through continuing professional registered and licensed
education to be provided by the nurse or uses any other
accredited professional organization means that tend to convey the
or any recognized professional impression that he/she is a
nursing organization. registered and licensed
nurse
PENAL AND MISCELLANEOUS PROVISIONS ▪ F. Any person who appends
⮚ According to Section 35, Prohibitions in the B.S.N./R.N. or any similar
Practice of Nursing appendage to his/her name
o A fine of not less than P50,000 nor without having been
more than P100,000 or conferred said degree or
imprisonment of not less than 1 registration; G. Any person
year nor more than six 6 years, or who, as a registered and
both, upon the discretion of the court, licensed nurse, abets or
shall be imposed upon: assists the illegal practice of
▪ A. Any person practice a person who is not lawfully
Nursing in the Philippines qualified to practice nursing
without a professional
license and identification LESSON 03: STRUCTURE OF NURSING
card or special temporary
permit STRUCTURE OF NURSING KNOWLEDGE
▪ B. Any person who uses as 5 COMPONENTS
his/her own certificate of 1. Metaparadigm
registration/professional 2. Philosophies
license and professional 3. Conceptual Models
identification card or special 4. Theories
temporary permit of another 5. Empirical Indicators
▪ C. Any person who uses an o The components of the structural
invalid certificate of hierarchy are made up of concepts
registration/professional and propositions
license, a suspended or o CONCEPT – Is a word or phrase that
revoked certificate of summarizes the essential
registration/professional characteristics or properties of
license, or an expired or phenomenon.
cancelled special/temporary o PROPOSITION – Is a statement
permits about a concept or a statement of the
▪ D. Any person who gives any relation between two or more or
false evidence to the Board in different concepts.
order to obtain a certificate of
registration/professional METAPARADIGM
license, a professional ⮚ The first component of the structural
hierarchy of knowledge.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 19
⮚ It is the most abstract component of the time that nursing occurs, which can
structural hierarchy. range from high-level wellness to
⮚ The concepts and propositions of a terminal illness.
metaparadigm are admittedly extremely 4. The metaparadigm concept nursing
global and provide no definitive direction for refers to the definition of nursing, the
such activities is research and clinical actions taken by nurses on behalf of or in
practice. conjunction with the person, and the
⮚ “Meta” means with and “Paradigm” means goals or outcomes of nursing actions.
pattern of shared understanding and
assumption. PHILOSOPHY
⮚ The Metaparadigm of Nursing is made up
of four concepts, four non-relational ⮚ The second component of the structural
propositions, and four relational hierarchy of contemporary nursing
propositions. knowledge is the philosophy.
⮚ A statement encompassing ontological
⮚ 4 concepts of Metaparadigm of Nursing: claims about how those phenomena come
to be known, and ethical claims about what
o Person – Recipient(s) of care. Can the members of a discipline value.
be individual/community. Significant
as person. CONCEPTUAL MODELS
o Environment – Internal & External ⮚ The third component of the structural
Factors. Surrounding of patient that hierarchy of contemporary nursing
applied client. External beliefs and knowledge is the conceptual model.
practices. ⮚ A set of relatively abstract and general
o Health – Defined by person. Degree concepts that address the phenomena of
of well being central interest to a discipline, the
o Nursing – Nursing actions. propositions that broadly describe those
Attributes. Characterize of nurses concepts, and the propositions that state
toward patient. relatively abstract and general relations
between two or more of the concepts.
METAPARADIGM OF NURSING
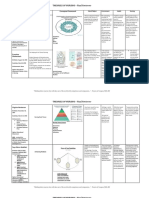
INPUT THROUGHPUT OUTPUT
⮚ 4 non-related propositions Demographic ⮚ Level of Can for
1. The metaparadigm concept person Profile awarenes Muslim
refers to the individuals, families, A. Age in s on the Women
communities, and other groups who are marriage implement and their
participants in nursing. B. Age ation of families
2. The metaparadigm concept C. Educatio family
nal Programs
environment refers to the person’s planning.
Attainme on
significant others and physical ⮚ Natural
planning
surroundings, as well as to setting in nt and focusing
which nursing occurs, which ranges from D. Employm Modern on
the person’s home to clinical agencies to ent family achieving.
society as a whole. Status planning
3. The metaparadigm concept health refers practices. Sustainabl
to the person’s state of well-being at the e
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 20
E. Socio ⮚ Level of developme ⮚ The fourth component of the Structural
Economi acceptanc nt goal 3 hierarchy of contemporary Nursing
c Status e on the “Ensure knowledge is the theory.
F. Number use of healthy ⮚ One or more relatively concrete and specific
of family lives and concepts that are derived from a conceptual
children planning. promote model, the propositions that narrowly
well being describe those concepts, and the
G. Source ⮚ Factors of
for all at all
of non-avail propositions that state relatively concrete
ages
informati ment on and specific relations between two or make
on on the the use of Sustainabl of the concepts.
use of family. e
contrace Developme GRAND THEORY
ption nt Goal 5 ⮚ Grand Theories are broad in scope. They
H. Preferred “Promote are made up of concepts and propositions
learning women that are less abstract and general than the
material empowerm concepts and propositions of a conceptual
on family ent and model but are not as concrete and specific
planning. gender as the concepts and propositions of a
equality”> middle-range theory
CONCEPTUAL MODELS
⮚ The term conceptual model is synonyms
with the terms: conceptual framework,
conceptual system, paradigm, and
disciplinary matrix.
⮚ Functions of a conceptual model
1. Provides distinctive frame of reference.
2. Tells how to observe and interpret the
phenomena of interest to the discipline.
3. Simplication of reality that includes only
those concepts that the model author
considers relevant and as aids to
understanding.
MIDDLE RANGE THEORY
⮚ Middle-range theories are narrower in scope
than grand theories. They are made up of a
limited number of concepts and propositions
that are written at a relatively concrete and
specific level.
⮚ Each middle-range theory addresses a more
or less relatively concrete and specific
phenomenon by describing what the
phenomenon is, explaining why it occurs, or
predicting how it occurs.
THEORY
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 21
FUNCTION OF A THEORY Ex. Prof. Rem did research on the reasons
⮚ One function of a theory is to narrow and why nurses stay in the hospital to work and
more fully specify the phenomena contained their reason for leaving she called it “Theory
in a conceptual model. of Tenure”.
⮚ Another function is to provide a relatively
concrete for the interpretation of initially THEORY DEVELOPMENT PROCESS’
puzzling behaviors, situations, and events. ⮚ Development of theory requires
understanding of selected scholarly terms,
EMPIRICAL INDICATORS definitions, and assumptions so that
⮚ The fifth and final component of the scholarly review and analysis may occur.
structural hierarchy of contemporary Attention is given to terms and defined
nursing knowledge is the empirical meanings to understand and theory
indicator development process that was used.
⮚ Nursing Empirical Indicators ⮚ Three categories of theory components are
⮚ Nurses have developed a plethora of presented as a basis for understanding the
empirical indicators in the form of research function of each element in the
instruments and district clinical tools. theory-building process.
⮚ The function of empirical indicators is to
provide the means by which middle-range THEORY COMPONENTS
theories are generated or tested. Empirical 1. CONCEPTS AND DEFINITION
indicators that are instruments yield data ⮚ Concept – The building blocks of
that can be sorted into qualitative categories theories, classify the phenomena of
or calculated as quantitative scores. interest. May be abstract or concrete.
⮚ Definition – Conveys general
METHODS OF THEORY DEVELOPMENT meaning and reduce vagueness in
1. Theory-Practice-Theory – Directs that understanding a set of concepts.
theory development in nursing is based on ⮚ Abstract – Concepts are mentally
and parallel to other theories used in other constructed independent of a specific
discipline/ time or place
Ex. Nurse Rodney wants to develop a new ⮚ Concrete – Directly experienced and
theory that is inspired from Abraham relate to a particular time or place.
Maslow’s of need. 2. RELATIONAL STATEMENTS
⮚ Propose relationship between and
among two or more concepts.
2. Practice-Theory – Directs that the theory Concepts are the building blocks of
development is based on the life/work theory, and theoretical statements are
experience and professional practice of the the chains that link blocks to build
theorist. theory. Concepts must be connected
Ex. Nurse Harry is assigned in the ICU for with one another in a series of
20 years, he developed a theory about theoretical statements to devise a
nurse’s coping mechanism in caring for nursing theory.
terminally ill patients called the “Theory of
attachment”
3. Research Theory – Directs that the theory
development is based on the extensive
research done by the theorist.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 22
o Defined nursing more than 100 years
ago as the “Act of utilizing the
environment of the patient to assist
him in his recovery”
o Linked health in 5 environmental
factors (pure/fresh air, pure water,
efficient drainage, cleanliness,
light)
o Stress the importance of keeping the
client warm, maintaining a noise-free
environment, and attending to the
client’s diet in terms of assessing
intake, timelines of the food, and its
CHARACTERISTICS OF THEORY effect on the person
1. A theory must be “falsifiable” ⮚ 10 Aspects of the Environmental Theory
2. A theory must be simple in terms of the 1. Environment - Patients should have
general principles involved. clean air and a
3. It must be workable temperature-controlled
4. It must be elegant or beautiful (Symmetry, 2. Patients - Should have access to
Simplicity, Accuracy) direct sunlight and not be subjected
5. The theory should be as general as to unnecessary noise, especially
possible. when sleeping
6. It should have few or no anomalies 3. Rooms - Should be kept clean
7. If possible, the theory ought not to be purely 4. Hospital facilities - Should be
statistical. well-constructed
8. The theory should bring out analogies and 5. Bedding - Should be changed and
use models. aired frequently
6. Patients - Should be kept clean
PURPOSE OF NURSING THEORY 7. Nurses - Should wash hands
⮚ Education frequently.
⮚ Research 8. Patients - Should be offered a variety
⮚ Clinical Practice of scenery, such as new books or
⮚ It guides nursing practice and flowers, to prevent boredom
generates 9. Nurses - Should be positive but not
offer false hope to patients or
PURPOSES OF NURSING THEORY 10. Patients - Should be kept clean and
⮚ It guides nursing practice and generates nurses should wash hands frequently
knowledge Offer a variety of small meals instead
⮚ It helps to describe and explain nursing of large ones, and do not do patient
⮚ It enables nurse to know what they are care while patient is eating as it is
doing and why they are doing distracting Consider not only the
LESSON 04: individual patient but the context of
FLORENCE NIGHTIMGALE where he or she lives
⮚ The Environmental Theory
o Florence Nightingale often WHAT ARE YOUR 2 CENTS?
considered the first nurse theorist.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 23
⮚ (1) PERSON
o In Florence Nightingale’s theory, the
Person, one of the elements in the
four metaparadigms, is the
individual receiving care
o Nightingale’s perception of the
Person is that the person is a
multidimensional being, that
includes biological, psychological,
social and spiritual components
o BIOLOGICAL
▪ Addressed by the use of
medicine and nursing to
address various diseases
o PSYCHOLOGICAL AND SOCIAL
COMPONENTS
▪ Consists of self-concept,
feelings, thought-processes
and social interactions
o SPIRITUALITY
▪ Intertwined with Nightingale’s
own spiritual beliefs; that the
person is valued
▪ Nightingale theory of the
Person is based on holism.
Holism is the concern of
integrating the biological,
social, psychological and
spiritual with its
environment
⮚ (2) HEALTH
o Health is viewed as the combined
result of environmental, psychological
and physical factors, not just the
THE HOSPITAL WINDOW absence of disease.
o Nightingale states that “health is not
only to be well, but to be able to use
well every power we have.”
o This is consistent with our perception
of health today, where one does not
have to be disease free to be healthy
but to maximize their potential to be
in a healthy state.
o Disease is portrayed as dys-ease,
THE 4 METAPARADIGMS OF ENVIRONMENTAL or the absent of comfort.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 24
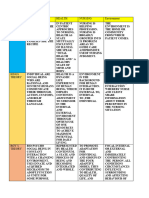
o Nightingale isolated 5 factors were not directly related to their
essential in securing an individual’s disease or ailment, but rather
health; these include pure air, pure consequences of poor environmental
water, efficient drainage, conditions
cleanliness and light o The duties of nursing include
o Nightingale’s 6 D’s of “Dys-ease” providing essentials such as fresh
air, warmth, light, cleanliness,
quiet and a proper diet. By helping
to control environmental
influences, nurses can aid in the
maintenance of health of their
patients.
MAJOR ASSUMPTIONS
1. NURSING – Every woman at one time in her
life would be a nurse in the sense that
nursing is being responsible for someone
else’s health.
2. PERSON – Patient. The nurse was in
control of and responsible for the patient’s
environmental surroundings.
⮚ (3) ENVIRONMENT 3. HEALTH – Being well and using every
o There exist five environmental power to the fullest extent. She envisioned
components which are all essential to the maintenance of health through
an individual’s health. These are prevention of disease by environmental
known collectively as the “health of control and social responsibility.
houses”, and outline factors of the
4. ENVIRONMENT – Nursing was to assist
physical environment which must nature in healing the patient. Create and
receive attention maintain a therapeutic environment. Her
o The underlying principle of assumptions and understanding about the
maintaining health of houses is to put environmental conditions were most relevant
the patient in a condition which is to her philosophy.
best for nature to act upon him or her.
An environment that promotes health
allows the patient to retain their JEAN WATSON
energy, or “vital powers” for use
⮚ "We are the light in institutional darkness,
towards self-healing
and in this model, we get to return to the
⮚ (4) NURSING light of our humanity." -Dr. Jean Watson
o Nightingale’s view on nursing is one
that is largely intertwined by factors ⮚ (June 10, 1940 – present) Watson was born
pertaining to the environment. Margaret Jean Harmon and grew up in the
o Nightingale believed that many of the
small town of Welch, West Virginia, in the
symptoms and sufferings of patients
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 25
Appalachian Mountains. She was the involved in the relationship as encompassed
youngest of eight children and was by nursing.
surrounded by an extended
family–community environment. Watson
attended high school in West Virginia and
then the Lewis Gale School of Nursing in
Roanoke, Virginia, where she graduated in
1961.
⮚ Educated: BSN, University of Colorado,
1964, MS, University of Colorado, 1966,
PhD, University of Colorado, 1973
⮚ Distinguished Professor of Nursing and
Chair in Caring Science at the University of
Colorado Health Sciences Center.
⮚ Fellow of the American Academy of Nursing.
⮚ Dean of Nursing at the University Health
Sciences Center and President of the
National League for Nursing
⮚ Undergraduate and graduate degrees in
nursing and psychiatric-mental health
nursing and PhD in educational psychology
and counseling.
⮚ Six (6) Honorary Doctoral Degrees.
⮚ Research has been in the area of human
THE TEN (10) CARITAS PROCESSES
caring and loss.
1. Cultivating the practice of loving- kindness
⮚ In 1988, her theory was published in
and equanimity toward self and other as
“nursing: human science and human care”. foundation to caritas consciousness
THE THEORY 2. Being Authentically Present- Enabling,
OF sustaining, and honoring faith, hope, and
TRANSPERSONAL deep belief system and the inner subjective
CARING world of self/other
⮚ Watson bases her theory for nursing 3. Cultivation of one’s own spiritual practices
practice on the following 10 curative factors. and transpersonal self, going beyond
Each has a dynamic phenomenological ego-self
component that is relative to the individuals
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 26
4. Development and sustaining a helping trust ⮚ PERSON
caring relationship o Watson uses interchangeably the
terms human being, person, life,
5. Being present to, and supportive of, the personhood, and self. She views the
expression of positive and negative feelings. person as “a unity of
mind/body/spirit/nature”
6. Creative use of self and all ways knowing as o Watson states, “I make the point to
part of the caring process; engage in the use mind, body, soul or unity within
artistry of caritas nursing an evolving emergent world
view-connectedness of all,
7. Engage in genuine teaching-learning sometimes referred to as Unitary
experience that attends to unity and being Transformative
and subjective meaning- Attempting to stay Paradigm-Holographic thinking.
within other’s frame of reference
⮚ HEALTH
8. Creating a healing environment at all levels
o She defined health as “unity and
9. Administering sacred nursing acts of caring harmony within the mind, body, and
healing by tending to basic human needs soul”; associated with the “degree of
congruence between the self as
10. Opening and attending to spiritual / perceived and the self as
mysterious and existential unknowns of experienced”
life-death. o Watson’s definition of health has
evolved. The positive state of
THE SEVEN (7) ASSUMPTIONS physical, mental and social well-being
with the inclusion of 3 elements;
1. Caring can be effectively demonstrated and 1. A high level of overall physical,
practiced only interpersonally. mental and social functioning
2. A general adaptive maintenance
2. Caring consists of curative factors that result
level of functioning
in the satisfaction of certain human needs.
3. Absence of illness
3. Effective caring promotes health and
individual or family growth. ⮚ ENVIRONMENT
o Watson speaks to the nurse’s role in
4. Caring responses accept person not only as the environment as “attending to
he or she is now but as what he or she may supportive, protective, and or
become. corrective mental, physical, societal,
and spiritual environments”
5. A caring environment is one that offers the o She emphasizes the person and the
development of potential while allowing the environment has a connection,
person to choose the best action for himself nurses are part of the patient’s
or herself at a given point in time. environment and once a nurse enters
the patient’s room an expectation is
6. Caring is more “health genic” than is curing. already present.
A science of caring is complementary to the
science of curing. ⮚ NURSING
o “Nursing is concerned with promoting
7. The practice of caring is central to nursing. health, preventing illness, caring for
the sick and restoring health”
TRANSPERSONAL CARING THEORY o According to Watson, the word nurse
METAPARADIGM is both a noun and a verb. To her,
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 27
nursing consists of “Knowledge, KATIE ERIKSSON
thought, values, philosophy, THEORY OF CARATIATIVE CARING
commitment and action with some
degree of passion” ⮚ Eriksson was born on November 18, 1943,
in Jakobstad, Finland.
THEORETICAL ASSERTIONS ⮚ 1965 graduated at the Helsinki Swedish
School of Nursing,
⮚ NURSING – Consist of knowledge, thought, ⮚ 1967 completed her Public Health Nursing
values, philosophy, commitment and action specialty education.
with some degree of passion. Using the 10
curative factors, the nurse provides care to
CARITATIVE CARING
various patients.
⮚ PERSONHOOD – Views person as a unity ⮚ Caritas refers when caring for the human
of mind/body/spirit/nature. The body is a being in health suffering.
living spirit that manifests one’s being in the ⮚ True caring, occurs when the one caring in a
world spirit of caritas alleviates the suffering of the
patient.
⮚ HEALTH – Unity and harmony within the
⮚ It is not equated to service with quality
mind, body and spirit, associated with the
degree of congruence between the self as and compensation.
perceived and the self as experienced. ⮚ Love- Charity-faith-hope
⮚ ENVIRONMENT – Healing spaces can be
used to help others transcend illness, pain PUBLISHED BOOKS
and suffering. The aim of the environment is
to create healing places. ⮚ The Idea of Caring
⮚ The Suffering Human Being
APPLICATION
THE BASICS IN CARITATIVE CARING ETHICS
ARE:
⮚ Human dignity
⮚ Caring communion
⮚ Invitation & responsibility
MAJOR ASSUMPTIONS
⮚ Nursing – Viewed as love and charity
⮚ Person – Human being is an entity of
body-soul and spirit
⮚ Environment - Ethos/home, human being’s
innermost space where it appears
nakedness.
⮚ Health - Soundness, freshness, & well being
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 28
• Consistency, predictability and time
PATRICIA BENNER management are important in
competent performance.
⮚ Patricia Benner was born in Hampton, › Recognize patterns
Virginia and spent her childhood in › Prioritize
California, where she received her early and › Devise new rules and plan
professional education. She obtained a › Less supervision
baccalaureate of arts degree in nursing from › High Anxiety
Pasadena College in 1964. In 1970 she
earned a master’s degree in nursing, with ⮚ PROFICIENT
major emphasis in medical surgical nursing • Nurses at this level demonstrate a
from University of California, San Francisco new ability to see changing relevance
School of Nursing in a situation, including recognition
⮚ Her PhD in stress, coping and health was and implementation of skilled
conferred in 1982 at the University of responses to the situation as it
California, Berkeley, and her dissertation evolves.
was published in 1984. Benner has a range • Nurses are more confident with their
of clinical experience, including acute knowledge and abilities
medical surgical, critical care and home
health care. ⮚ EXPERT
• Nurses have an intuitive grasp of the
NOVICE TO EXPERT THEORY situation, and as being able to identify
the region of the problem without
⮚ Benner adapted Hubert Dreyfus Model of losing time considering a range of
skill acquisition. Benner applied it to her alternative diagnoses and solutions.
work “From novice to Expert” Benner’s • Expert nurses “know the patient”
model is situational and describes five levels • Key aspect of expert nurse
of skill acquisition and development. › Demonstrating a clinical grasp
MAJOR CONCEPTS AND DEFINITION and resource-based practice
› Possessing embodied know
⮚ NOVICE how
• The person has no background › Seeing the big picture
experience of the situation in which › Seeing the unexpected
he or she is involved. Context free
rules and objectives attributes must METAPRADIGM
be given to guide performance.
⮚ NURSING
⮚ ADVANCED BEGINNER • Described nursing as a caring
• The person can demonstrate relationship, an enabling condition of
marginally acceptable performance, connection and concern
having coped with enough real • Caring is primary because caring sets
situations to note, or to have pointed up the possibility of giving help and
out by a mentor, the recurring receiving help.
meaningful components of the • Nursing is viewed as a caring practice
situation. Nurses functioning at this whose science is guided by the moral
level are guided by rules and are art and ethics of care and
oriented by task completion. responsibility
⮚ COMPETENT ⮚ PERSON
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 29
• The body of a person has 5 ⮚ ENVIRONMENT - She believes that the
dimensions, Benner pointed out that term situation is to be used rather than
nurses should attend to all these environment. Personal interpretation of the
dimensions of the body and seek to situation is bounded by the way the
understand the role of embodiment in individual is in it of past, present, & future.
particular situation of health illness Situation/ being situated conveys a social
and recovery environment with social definition &
meaningfulness.
⮚ HEALTH
• Is defined as what can be assessed,
whereas well-being is the human
experience of health or wholeness.
Health is described as not just the
absence of disease and illness. A
person may have the disease and not
experienced illness, because illness
is the human experience of loss or
dysfunction, whereas disease is what
can be assessed at the physical level
⮚ SITUATION
• Benner and Wrubel use the term
situation rather than environment,
because situation conveys a social
environment with social with social
definition and meaningfulness. The
person’s past, present, and future,
which include her or his own personal
meanings, habits, and perspectives,
influence the current situation.
MAJOR CONCEPTS
⮚ NURSING- Nursing is viewed as a caring
practice whose science is guided by the
moral art & ethics of care & responsibility’s
caring relationship, an enabling condition of
connection & concern. Nursing practice as
the care & study of the lived experience of
health, illness, & disease
⮚ PERSON - A person is a self- interpreting
being, that is, the person does not come into
the world predefined but gets defined in the
course of living a life.
⮚ HEALTH - Health is defined as what can be
assessed, whereas well-being is the human
experience of health or wholeness.
THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS 110 {VENICE} 30
You might also like
- Complications Associated With Intravenous TherapyDocument18 pagesComplications Associated With Intravenous TherapyIyah Jane Villahermosa50% (2)
- Mapeh 10 q2 P.E Active RecreationDocument23 pagesMapeh 10 q2 P.E Active RecreationJuliuselmerNo ratings yet
- TFN NotesDocument33 pagesTFN NotesMcnurseNo ratings yet
- 15 Health Benefits of GarlicDocument4 pages15 Health Benefits of GarlichiteshNo ratings yet
- Assignment of HypertensionDocument28 pagesAssignment of HypertensionjefferyNo ratings yet
- Good NotesDocument5 pagesGood NotesMikee BoomNo ratings yet
- Theorists Phil BarkerDocument12 pagesTheorists Phil BarkerAlleah Mendoza100% (1)
- Module 2 History of NursingDocument90 pagesModule 2 History of NursingPatricia Vea Malangis100% (1)
- Fundamentals of NursingDocument11 pagesFundamentals of Nursingdrummernico25No ratings yet
- Traditional Aboriginal Medicine PracticeDocument16 pagesTraditional Aboriginal Medicine PracticeAlike Camarillo Rabago100% (2)
- AbortionDocument66 pagesAbortionGunu SinghNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis Seamen's HospitalDocument17 pagesSwot Analysis Seamen's HospitalCris Cancio67% (3)
- How to Work with Your Chakras: The Missing Dimension in Well BeingFrom EverandHow to Work with Your Chakras: The Missing Dimension in Well BeingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Theoretical Foundations in Nursing: Nursing As An Art and ScienceDocument23 pagesTheoretical Foundations in Nursing: Nursing As An Art and ScienceRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- DEMONSTRATION ON Newborn ResuscitationDocument5 pagesDEMONSTRATION ON Newborn ResuscitationAnjali Das100% (1)
- Contoh Judul Jurnal Kesehatan InternasionalDocument3 pagesContoh Judul Jurnal Kesehatan Internasionalnadya100% (1)
- One Spirit Medicine Press KitDocument13 pagesOne Spirit Medicine Press Kitshybumi100% (1)
- TFN Reviewer PDFDocument4 pagesTFN Reviewer PDFViea Pacaco SivaNo ratings yet
- Test Results Clinical PartnersDocument3 pagesTest Results Clinical PartnersAbdurrahman SalehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Theoretical Foundations of NursingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Theoretical Foundations of NursingDenise CalderonNo ratings yet
- Tfn111 Reviewer Prelim - Docx 1Document21 pagesTfn111 Reviewer Prelim - Docx 1angelita aquinoNo ratings yet
- O Egypt: A. Period of Intuitive NursingDocument18 pagesO Egypt: A. Period of Intuitive NursingyanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For TFNDocument23 pagesReviewer For TFNSharmaine FernandezNo ratings yet
- FACT OR MYTH: Misconceptions On Ancient HumanityDocument11 pagesFACT OR MYTH: Misconceptions On Ancient HumanityNazylheinsGuevaraNo ratings yet
- TFN Notes BSN1Document3 pagesTFN Notes BSN1jewelNo ratings yet
- Theorist Nursing Theory Nursing Environment Health Person What Is TheoryDocument5 pagesTheorist Nursing Theory Nursing Environment Health Person What Is TheoryJam BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pain HistoricaloverviewDocument17 pagesPain HistoricaloverviewtruckerpunkNo ratings yet
- Hypnosis As The Substratum of Many Different Psychotherapies (American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis, Vol. 3, Issue 1) (1960)Document24 pagesHypnosis As The Substratum of Many Different Psychotherapies (American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis, Vol. 3, Issue 1) (1960)Hashem Al AttasNo ratings yet
- Florence Nightingale: The Environmental TheoryDocument27 pagesFlorence Nightingale: The Environmental TheoryPatricia Marie PalenciaNo ratings yet
- Ten Nursing TheoryDocument32 pagesTen Nursing TheoryleiNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of Science in NursingDocument1 pagePhilosophy of Science in NursingMary EvansNo ratings yet
- Health Care EthicsDocument5 pagesHealth Care EthicsClaire Julianne CapatiNo ratings yet
- (Trans) Unit 02 - Grand Nursing Theories Based On Human NeedsDocument7 pages(Trans) Unit 02 - Grand Nursing Theories Based On Human NeedsYlyza MarquezNo ratings yet
- Katharine KolcabaDocument3 pagesKatharine KolcabaPatrice Danielle LimNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lec. NCMA110. Evolution of NursingDocument4 pagesWeek 2 Lec. NCMA110. Evolution of NursingMai DeiNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations in NursingDocument3 pagesTheoretical Foundations in NursingIssaiah Nicolle CeciliaNo ratings yet
- (Pmls1) Lesson 3 - EthicsDocument2 pages(Pmls1) Lesson 3 - Ethicsteresa.catudayNo ratings yet
- African Medicine: Tradition and Beliefs: ArticlesDocument2 pagesAfrican Medicine: Tradition and Beliefs: Articlesmarvin kyerehNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHERSDocument6 pagesPHILOSOPHERSHanna BuadaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledLei Anne AguilorNo ratings yet
- TFN NotesDocument3 pagesTFN NotesJane BelvisNo ratings yet
- (Advanced NG.) History of Dev. Ng. ProfDocument27 pages(Advanced NG.) History of Dev. Ng. ProfRicha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Finish Falsafah & TheoryDocument37 pagesFinish Falsafah & Theoryfitri indahNo ratings yet
- TFN ReviewerDocument14 pagesTFN ReviewerJERILOU QUIZONo ratings yet
- Infographics3, Sanjose CherryjoyDocument4 pagesInfographics3, Sanjose CherryjoySanjose CherryjoyNo ratings yet
- Finals Notes UnfinishedDocument23 pagesFinals Notes UnfinishedNicholeGarcesCisnerosNo ratings yet
- 1 TFN Evolution of NursingssssssssssssssskDocument7 pages1 TFN Evolution of NursingssssssssssssssskJamie Lou PerezNo ratings yet
- Ncma113 LectureDocument34 pagesNcma113 LectureJULIANA NICOLE TUIBUENNo ratings yet
- TFN PrelimDocument20 pagesTFN PrelimANGELO MOGRONo ratings yet
- Definitions of Nursing NCMP100Document3 pagesDefinitions of Nursing NCMP100Elishah CaprichoNo ratings yet
- THEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS IN NURSING NotesDocument8 pagesTHEORETICAL FOUNDATIONS IN NURSING NotesDha Na RubellanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theories Final ReviewerDocument11 pagesNursing Theories Final ReviewerMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- TFN Transes - Evolution of Nursing TheoryDocument4 pagesTFN Transes - Evolution of Nursing TheoryYvi AshenaNo ratings yet
- Pestana J. 2015 - Shamanism IntoxicationDocument16 pagesPestana J. 2015 - Shamanism Intoxicationstefan marinNo ratings yet
- T1 Yerxa Ocupación Curriculum Centrado en La OcupaciónDocument8 pagesT1 Yerxa Ocupación Curriculum Centrado en La OcupaciónDulceNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Nursing Theories (Prelim)Document42 pagesIntroduction of Nursing Theories (Prelim)kimashleymandronNo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument2 pagesTheorybldewnaNo ratings yet
- NCM 100-Theoritical Foundation in Nursing: Module 1 Unit 1 - Evolution of NursingDocument2 pagesNCM 100-Theoritical Foundation in Nursing: Module 1 Unit 1 - Evolution of NursingAkirah Jewelle JaenNo ratings yet
- History of Nursing TheoryDocument53 pagesHistory of Nursing TheoryNileNo ratings yet
- Kelompok KDK - Paradigma KepDocument3 pagesKelompok KDK - Paradigma KepSilvia AnidaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of NursingDocument9 pagesEvolution of NursingJEREMY MAKALINTALNo ratings yet
- TFN NotessDocument14 pagesTFN NotessLYZZYTH ASENCINo ratings yet
- Pain NCPDocument2 pagesPain NCPJakes Katheriene AbadNo ratings yet
- TFN Notes BSNDocument6 pagesTFN Notes BSNErika MarieNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy in Context - GFPDocument21 pagesPsychotherapy in Context - GFPKarolina UchanNo ratings yet
- Theorist Person Health Nursing Environment Lydia Hall: "Three Aspects of Nursing: Care, Cure, Core."Document2 pagesTheorist Person Health Nursing Environment Lydia Hall: "Three Aspects of Nursing: Care, Cure, Core."LYZZYTH ASENCINo ratings yet
- Gonikman Emma Taoist SAMPLEDocument13 pagesGonikman Emma Taoist SAMPLEwhiteyasminNo ratings yet
- GhetrrrrrrrrrreffDocument7 pagesGhetrrrrrrrrrreffCharesse Angel SaberonNo ratings yet
- Sleep DisturbanceDocument2 pagesSleep DisturbanceKirα ChannelNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding Technique and Associated Factors Among Lactating Mothers Visiting Gondar Town Health FacilitiesDocument19 pagesBreastfeeding Technique and Associated Factors Among Lactating Mothers Visiting Gondar Town Health FacilitiesannisanabilaasNo ratings yet
- Practical Exercise Theme: Modern DeontologyDocument8 pagesPractical Exercise Theme: Modern DeontologyАкбота АлдиярNo ratings yet
- Patient Safety QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesPatient Safety QuestionnaireRuru JojoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Understanding The Essentials of Critical Care Nursing 2nd Edition Kathleen PerrinDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Understanding The Essentials of Critical Care Nursing 2nd Edition Kathleen PerrinRoger Enriquez100% (26)
- BPT 2018 2 Aug Bachelor of Physio Therapy Microbiology andDocument1 pageBPT 2018 2 Aug Bachelor of Physio Therapy Microbiology andViren ManiyarNo ratings yet
- Discrimination Its Effect Among The E.I.M Students of Tibag High SchoolDocument3 pagesDiscrimination Its Effect Among The E.I.M Students of Tibag High SchoolRM AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- CV Stratford Sydney IptecDocument7 pagesCV Stratford Sydney Iptecapi-611918048No ratings yet
- USAID Unsolicited ProposalDocument5 pagesUSAID Unsolicited Proposalthamiz nilaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Tool EpcbDocument5 pagesAssessment Tool EpcbJered MoratoNo ratings yet
- Format For Rle ObjectivesDocument2 pagesFormat For Rle ObjectivesNUR-HATHI SANAANINo ratings yet
- Gap AnalysisDocument9 pagesGap Analysisapi-706947027No ratings yet
- Autism Concept MapDocument2 pagesAutism Concept Mapapi-286043563100% (1)
- Pamphlet 2Document2 pagesPamphlet 2api-345915599100% (1)
- Story of Micro Organisms 2Document4 pagesStory of Micro Organisms 2monika gompaNo ratings yet
- Association Between Low Back Pain and Various Everyday PerformancesDocument9 pagesAssociation Between Low Back Pain and Various Everyday Performancesshaik chandiniNo ratings yet
- National Aids Control Programme Phase-Iv Current Status and Critical AppraisalDocument71 pagesNational Aids Control Programme Phase-Iv Current Status and Critical AppraisalNeethu Vincent100% (1)
- Al Amaal English High SchoolDocument18 pagesAl Amaal English High SchoolLaibaNo ratings yet
- FILGRASTIMDocument2 pagesFILGRASTIMErza GenatrikaNo ratings yet
- PST 06208 Pharmaceutical Public HealthDocument81 pagesPST 06208 Pharmaceutical Public HealthAthumaniNo ratings yet
- Brief of FDA CDER Warning Letters Feb 2023 Part I 1677260461Document6 pagesBrief of FDA CDER Warning Letters Feb 2023 Part I 1677260461kaushalesh vaishnavNo ratings yet
- Jeanne Lloraine R. Fiel Date&Time: November 23, 2020 at 5:00 P.M. Informant: Mother % Reliability: 95%Document6 pagesJeanne Lloraine R. Fiel Date&Time: November 23, 2020 at 5:00 P.M. Informant: Mother % Reliability: 95%Jeanne Lloraine FielNo ratings yet