Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WHE-0542 Pediatric-Ref-Range PG EUROW MECH
Uploaded by
Pamela Carherine Barreda COriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WHE-0542 Pediatric-Ref-Range PG EUROW MECH
Uploaded by
Pamela Carherine Barreda CCopyright:
Available Formats
Hemostasis Innovation is Here.
Hemostasis test results, particularly
global assays such as prothrombin Optimizing
time (PT) or activated partial
thromboplastin time (aPTT), are
Pediatric
known to vary with the reagents and
analyzers used.7 The Perinatal and
Hemostasis
Pediatric Hemostasis Subcommittee References
1. Appel IM, Grimminck B, Geerts J, Stigter R, Cnossen MH, Beishuizen A.
Testing
of the SSC of the ISTH recommends Age dependency of coagulation parameters during childhood and
puberty. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10:2254–2263.
that each laboratory define
2. Andrew M. Developmental Hemostasis: Relevance to Hemostatic
Problems During Childhood. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1995;21:341–356.
3. Toulon P, Berruyer M, Brionne-François M, Grand F, Lasne D, Telion C,
age-dependent reference ranges et al. Age dependency for coagulation parameters in pediatric
populations: results of a multicenter study aimed at defining the
using their own methodologies.8 age-specific reference ranges. J Thromb Haemost. 2016 Mar 17;116(1)
[Epub ahead of print].
4. Appel IM, Grimminck B, Geerts J, Stigter R, Cnossen MH, Beishuizen A.
Age dependency of coagulation parameters during childhood. Poster
presented at 57th ASH Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL, December 2015.
To assist labs in this endeavor, Werfen 5. Timm A, Hillarp A, Philips M, Goetze JP. Comparison of automated von
Willebrand factor activity assays. Thrombosis Research. 2015;135:684–691.
collaborated with six hospital laboratories 6. Costa-Pinto J, Pérez-Rodríguez A, del C Goméz-del-Castillo M, Lourés E,
Rodríguez-Trillo A, Batlle J, et al. Diagnosis of inherited von Willebrand
to define reference ranges for the use of disease: comparison of two methodologies and analysis of the
discrepancies. Haemophilia. 2014;20(4):559–567.
About this guide
HemosIL assays in children. 3 The results 7. Lippi G, Franchini M, Montagnana M, Guidi GC. Coagulation testing in
pediatric patients: the young are not just miniature adults. Semin Thromb
Hemost. 2007;33:816–820.
from this collaboration3 confirmed that 8. Ignjatovic V, Kenet G, Monagle P. On behalf of the Perinatal and Paediatric
Diagnostic testing is critical to ensuring
Haemostasis Subcommittee of the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost.
most Hemostasis test results are highly 2012;10:298–300. optimal patient management of hemorrhagic
dependent on age, and that age-specific and thrombotic diseases in children.1, 2
reference ranges must be used to ensure This guide presents the reference ranges
werfen.com
proper evaluation. of diagnostic assays for pediatric patients
PEDREFPG EUROW Rev00 03/22
For more information, contact your local
Werfen sales representative or distributor. (ages 15 days to 17 years), as determined
ACL, ACL AcuStar, ACL Elite, ACL TOP, HemoCell, HemoHub, HemosIL,
ReadiPlasTin, RecombiPlasTin, SynthAFax and SynthASil are trademarks of by a multi-center study using ACL TOP®
Instrumentation Laboratory Company and/or one of its subsidiaries or parent
companies and may be registered in the United States Patent and Trademark
Office and in other jurisdictions. The Werfen logo is a trademark of Werfen Hemostasis testing systems.3
and may be registered in the Patent and Trademark Offices of jurisdictions
throughout the world. All other product names, company names, marks, logos
and symbols are trademarks of their respective owners.
©2022 Instrumentation Laboratory. All rights reserved.
Age dependency of Hemostasis parameters during childhood 3–6
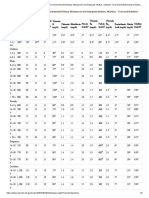
Pediatric reference ranges for HemosIL Assays on ACL TOP Hemostasis Testing Systems
Test HemosIL Assay 15 Days–4 Weeks 1–5 Months 6–11 Months 1–5 Years 6–10 Years 11–17 Years
PT (sec) RecombiPlasTin® 2G 11.2 [9.5–12.6] 11.0 [9.7–12.8] 11.0 [9.8–13.0] 11.3 [9.9–13.4] 11.7 [10.0–14.6] 11.8 [10.0–14.1]
aPTT (sec) SynthASil® 35.4 [27.6–45.6] 33.5 [24.8–40.7] 32.4 [25.1–40.7] 31.6 [24.0–39.2] 31.6 [26.9–38.7] 31.0 [24.6–38.4]
aPTT (sec) aPTT-SP 39.0 [33.2–45.6] 33.3 [25.0–43.3] 33.3 [25.0–43.3] 32.4 [25.7–38.4] 32.8 [25.5–42.4] 32.6 [26.1–47.4]
Fibrinogen (mg/dL) Fibrinogen-C 254 [143–402] 226 [150–376] 233 [157–360] 273 [188–413] 278 [189–475] 266 [177–420]
Fibrinogen (mg/dL) Q.F.A. Thrombin 240 [136–300] 210 [141–437] 230 [148–367] 260 [164–497] 276 [171–537] 248 [168–529]
FII (%)** Factor II Deficient Plasma 56.3 [44.8–74.3] 75.0 [46.7–110.6] 91.5 [73.9–117.2] 99.0 [49.4–130.0] 90.0 [68.4–132.0] 93.5 [47.6–119.2]
FV (%)** Factor V Deficient Plasma 100.0 [69.0–123.7] 99.5 [59.5–147.0] 102.0 [59.0–159.8] 110.5 [73.2–188.1] 101.0 [82.0–140.6] 97.0 [61.7–124.8]
FVII (%)** Factor VII Deficient Plasma 75.6 [55.0–108.0] 88.0 [43.0–141.1] 88.0 [55.2–128.0] 82.0 [47.8–124.2] 77.0 [55.0–135.4] 81.5 [55.4–133.1]
FVIII (%)* Factor VIII Deficient Plasma 95.5 [65.2–153.4] 84.5 [50.3–187.3] 75.0 [53.4–132.2] 95.0 [59.0–167.0] 86.5 [60.6–154.4] 93.0 [42.8–154.6]
FIX (%)* Factor IX Deficient Plasma 43.5 [30.0–77.0] 53.0 [29.0–105.1] 76.5 [50.5–106.8] 84.0 [52.6–128.9] 80.0 [55.3–156.0] 96.5 [60.2–138.4]
FX (%)** Factor X Deficient Plasma 85.0 [66.0–92.0] 89.0 [67.5–122.2] 100.0 [75.8–134.4] 99.0 [59.7–152.8] 99.0 [71.3–161.5] 93.0 [64.0–130.5]
FXI (%)* Factor XI Deficient Plasma 56.0 [32.9–75.0] 64.0 [27.6–126.4] 86.0 [60.9–125.6] 92.0 [58.0–154.0] 83.0 [31.8–154.0] 84.0 [55.4–139.4]
FXII (%)* Factor XII Deficient Plasma 69.2 [25.0–81.0] 76.0 [38.0–136.6] 109.2 [48.0–156.1] 107.0 [50.0–174.7] 83.7 [49.4–153.5] 91.7 [49.4–153.5]
FXIII (%) Factor XIII Antigen 86.0 [78.4–100.0] 82.9 [55.3–133.2] 92.0 [51.1–136.8] 97.4 [49.4–137.2] 96.5 [53.5–142.4] 106.0 [64.4–133.1]
von Willebrand Factor
vWF:GP1bR (%) 99.6 [87.8–121.5] 89.0 [33.2–154.1] 67.1 [37.1–118.6] 83.3 [40.8–131.8] 89.1 [42.1–162.6] 92.8 [45.0–139.1]
Ristocetin Cofactor Activity
vWF:Ab (%) von Willebrand Factor Activity 121.5 [73.7–188.9] 104.0 [40.9–191.0] 86.0 [42.7–176.0] 82.4 [43.6–155.8] 83.0 [41.2–128.9] 83.5 [54.0–136.9]
vWF:Ag (%) von Willebrand Factor Antigen 163.3 [46.0–219.5] 101.5 [35.5–217.0] 78.6 [48.4–199.4] 89.1 [41.0–185.7] 80.0 [44.8–141.1] 92.0 [55.6–123.4]
Antithrombin (%) Liquid Antithrombin 41.0 [32.8–62.8] 80.1 [29.0–120.0] 96.0 [63.0–121.8] 96.5 [60.5–128.3] 97.0 [64.2–136.4] 97.0 [69.1–135.9]
PC chromogenic (%) Protein C 39.1 [27.2–48.0] 51.2 [22.8–95.0] 79.9 [46.6–150.9] 92.6 [59.1–147.5] 100.5 [45.9–153.5] 99.0 [72.3–155.1]
PC clotting (%) ProClot 37.5 [29.7–114.6] 82.0 [28.1–127.8] 85.0 [43.7–151.3] 86.3 [61.0–143.5] 91.0 [39.3–170.3] 95.1 [65.8–126.6]
Free Protein S
PS Free Ag (%) 83.8 [61.0–108.0] 94.9 [48.0–126.5] 86.0 [63.0–138.9] 86.4 [53.0–134.9] 95.1 [61.5–141.7] 93.5 [61.4–130.7]
(antigenic immunoassay)
PS clotting (%) Protein S Activity 90.1 [29.0–115.2] 81.6 [33.3–153.9] 88.3 [51.8–138.4] 97.6 [60.2–148.8] 104.8 [66.5–161.5] 99.3 [52.5–147.1]
Plasminogen (%) Plasminogen 52.6 [41.0–82.7] 69.2 [37.6–109.6] 80.7 [49.3–126.4] 91.8 [59.6–178.0] 92.0 [52.4–158.1] 91.8 [58.1–130.6]
D-dimer (ng/mL FEU) D-Dimer HS 500 530 [445–1200] 515 [90–878] 270 [133–844] 280 [88–780] 275 [60–567] 245 [69–580]
Pediatric claims have not been reviewed by regulatory agencies. Listed products should be used per labeled claims. Units of measure from publication converted to those listed on Product Insert Sheets.
*Used with SynthASil. **Used with RecombiPlasTin 2G.
You might also like
- Bio 120 Exer 9-10Document4 pagesBio 120 Exer 9-10Asi JenNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Purity of Enzyme PreparationDocument24 pagesCriteria For Purity of Enzyme Preparationshabana75% (4)
- Shnitt and Jacobs AJCP 2000Document5 pagesShnitt and Jacobs AJCP 2000Vukosava Milic TorresNo ratings yet
- Ijlh 12531Document12 pagesIjlh 12531Yohana SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Nilai Rujukan Hematologi AnakDocument6 pagesNilai Rujukan Hematologi AnakirdinamarchsyaNo ratings yet
- Vascular Limb Occlusion in Twin To Twin Tranfusion SyndromeDocument10 pagesVascular Limb Occlusion in Twin To Twin Tranfusion Syndromejhon heriansyahNo ratings yet
- Hand RefractometerDocument5 pagesHand RefractometerAntigona2001No ratings yet
- Artigo Dra LucianaDocument5 pagesArtigo Dra LucianaIeda GuedesNo ratings yet
- 382-Article Text-1808-1-10-20210816Document8 pages382-Article Text-1808-1-10-20210816Dr. Asaad Mohammed Ahmed BabkerNo ratings yet
- Dermatology and Dermatologic DiseasesDocument4 pagesDermatology and Dermatologic DiseasesM TarmiziNo ratings yet
- Annals of Diagnostic Pathology: Gerard Nuovo, MDDocument6 pagesAnnals of Diagnostic Pathology: Gerard Nuovo, MDamelia zettaNo ratings yet
- PSTK 2Document6 pagesPSTK 2subhashbhukyaNo ratings yet
- Article G CTDocument9 pagesArticle G CTLaura Paola UrquizoNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Laboratory ResultsDocument3 pagesAbnormal Laboratory Resultstotty331117867No ratings yet
- RI, Hema&immnoDocument9 pagesRI, Hema&immnoHabtamu WondifrawNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diagnostic Methods For Inherited Eye DiseaDocument6 pagesGenetic Diagnostic Methods For Inherited Eye Diseaputri dwi nofrianiNo ratings yet
- ALTERNATE RAPID MAXILLARY EXPANSION AND CONSTRICTION (ALT-RAMEC) MAY BE MORE EFFECTIVE THAN RAPID MAXILLARY EXPANSION ALONE FOR PROTRACTION FACIAL MASK TREATMENTzhao2020Document3 pagesALTERNATE RAPID MAXILLARY EXPANSION AND CONSTRICTION (ALT-RAMEC) MAY BE MORE EFFECTIVE THAN RAPID MAXILLARY EXPANSION ALONE FOR PROTRACTION FACIAL MASK TREATMENTzhao2020محمد نبيل الدعيس100% (1)
- E6CBABB61857Document8 pagesE6CBABB61857RIVALDO JUNINHO ZINEDINE ADIKPETONo ratings yet
- Translating Best Evidence Into Best CareDocument4 pagesTranslating Best Evidence Into Best CareJorge Vivanco RiosNo ratings yet
- AC GuidelinesDocument5 pagesAC GuidelinesGayathiri GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Establishing Reference Ranges of Hematological Parameters From Malian Healthy AdultsDocument11 pagesEstablishing Reference Ranges of Hematological Parameters From Malian Healthy AdultsnurulNo ratings yet
- omnitropeDocument10 pagesomnitropedimi2207No ratings yet
- Current Issues in ER and HER2 Testing by IHC in Breast CancerDocument8 pagesCurrent Issues in ER and HER2 Testing by IHC in Breast CancerOncology FatmawatiNo ratings yet
- Artikel Asli: Volume 1, Nomor 3 September - Desember 2016Document8 pagesArtikel Asli: Volume 1, Nomor 3 September - Desember 2016Dinda ArmeliaNo ratings yet
- Gene-Expression Patterns in Drug-Resistant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells and Response To TreatmentDocument10 pagesGene-Expression Patterns in Drug-Resistant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells and Response To TreatmentAmairani MorenoNo ratings yet
- Brochure Euroclone JUIL12Document12 pagesBrochure Euroclone JUIL12czumoffenNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The Rheologic Properties of Neonatal and Adult BloodDocument4 pagesComparison of The Rheologic Properties of Neonatal and Adult BloodPrasad BorkarNo ratings yet
- 9424-Article Text-69428-1-10-20200725Document10 pages9424-Article Text-69428-1-10-20200725KELLY ALEJANDRA CAICEDO DIAZNo ratings yet
- Hemangioma Activity ScoreDocument6 pagesHemangioma Activity ScoreneonitesNo ratings yet
- Adiposity ReboundDocument9 pagesAdiposity ReboundImanuel Far-FarNo ratings yet
- Valores Referencia Neonatos Adlutos JovenesDocument12 pagesValores Referencia Neonatos Adlutos JovenesRandy HuyhuaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PropanololDocument11 pagesJurnal PropanololDina saniasihNo ratings yet
- Poster No.: Congress: Type: Authors:: Page 1 of 12Document12 pagesPoster No.: Congress: Type: Authors:: Page 1 of 12Dina MariniNo ratings yet
- 1-s2.0-S2305050014600099-mainDocument5 pages1-s2.0-S2305050014600099-mainMD LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Study of Spectrum of Hemoglobinopathies in Adult Age Group Diagnosed On High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Tertiary Care HospitalDocument9 pagesStudy of Spectrum of Hemoglobinopathies in Adult Age Group Diagnosed On High Performance Liquid Chromatography in Tertiary Care HospitalIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Investigation of de Novo Variation in Pediatric CardiomyopathyDocument8 pagesInvestigation of de Novo Variation in Pediatric CardiomyopathyIsabella-Diana ChelbanNo ratings yet
- Ijpo 5 (1) 6-11Document6 pagesIjpo 5 (1) 6-11Rajesh SahuNo ratings yet
- MTA1 Omar AhmedDocument5 pagesMTA1 Omar Ahmedlukman f0028No ratings yet
- Variant ClassificationDocument5 pagesVariant ClassificationPeter OlejuaNo ratings yet
- Honk R7Document10 pagesHonk R7fitri asymidaNo ratings yet
- Childhood ALL KET HOPDocument12 pagesChildhood ALL KET HOPDo Cam TunNo ratings yet
- A Study On Growth Profiles in Children With Thalassemia Major Between 2-10 Years of Age On Regular Transfusions and Oral Chelation TherapyDocument9 pagesA Study On Growth Profiles in Children With Thalassemia Major Between 2-10 Years of Age On Regular Transfusions and Oral Chelation TherapysagarNo ratings yet
- Or 32 6 2836 PDFDocument9 pagesOr 32 6 2836 PDFJose SirittNo ratings yet
- Treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia in children with romiplostimDocument2 pagesTreatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenia in children with romiplostimfitri asymidaNo ratings yet
- 2018Andrology-Colpi-European Academy of Andrology Guideline Management of Oligo Astheno TeratozoospermiaDocument12 pages2018Andrology-Colpi-European Academy of Andrology Guideline Management of Oligo Astheno Teratozoospermiakong_666064846No ratings yet
- Journal of Pediatric SurgeryDocument6 pagesJournal of Pediatric SurgeryMeta ParamitaNo ratings yet
- COMPLETEPAPER Ready To Pub - PYOGENIC GRANULOMADocument6 pagesCOMPLETEPAPER Ready To Pub - PYOGENIC GRANULOMAolanrewajuoduolaNo ratings yet
- Aqw 076Document9 pagesAqw 076Cesar E Sanchez AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Recommendations For Reporting Results of Diagnostic Genetic Testing (Biochemical, Cytogenetic and Molecular Genetic)Document11 pagesRecommendations For Reporting Results of Diagnostic Genetic Testing (Biochemical, Cytogenetic and Molecular Genetic)Fearless AngelNo ratings yet
- Nej M 199603213341203Document4 pagesNej M 199603213341203Krinta AlisaNo ratings yet
- Screening z2Document6 pagesScreening z2zahraa aliNo ratings yet
- s00431 022 04409 8Document12 pagess00431 022 04409 8Marcela SinisterraNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Effects of Levetiracetam and Topiramate MonotherapyDocument6 pages2.1 Effects of Levetiracetam and Topiramate MonotherapyRaluca ElenaNo ratings yet
- Alloimmunization and Red Cellautoimmunization in Multitransfused Thalassemic of Indian OriginDocument5 pagesAlloimmunization and Red Cellautoimmunization in Multitransfused Thalassemic of Indian OriginFatimatuzzahra ShahabNo ratings yet
- Prospectivo - Grunwell2017Document8 pagesProspectivo - Grunwell2017MecheVSNo ratings yet
- Emam2019 2 PDFDocument3 pagesEmam2019 2 PDFSama AsimNo ratings yet
- Epilepsia - 2010 - Locharernkul - HLA B 1502 Screening Time To Clinical PracticeDocument3 pagesEpilepsia - 2010 - Locharernkul - HLA B 1502 Screening Time To Clinical PracticeNaziBrola TsivadzeNo ratings yet
- BMC Endocrine DisordersDocument10 pagesBMC Endocrine Disordersiq_dianaNo ratings yet
- Fossella Pers Med ValuationDocument2 pagesFossella Pers Med Valuationjohn fossellaNo ratings yet
- Clinical ChemistryfulltextDocument15 pagesClinical Chemistryfulltextmiesoabdela57No ratings yet
- EGFR in MEningiomaDocument7 pagesEGFR in MEningiomaApriyanto LatiefNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways of GlucoseDocument31 pagesMetabolic Pathways of GlucoseLisandrea BrownNo ratings yet
- Haematinics, Coagulants and Anticoagulant - DR - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, LecturerDocument27 pagesHaematinics, Coagulants and Anticoagulant - DR - Jibachha Sah, M.V.SC, Lecturerjibachha sahNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Channel & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument55 pagesElectron Transport Channel & Oxidative PhosphorylationShahabNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Cellular Respiration CompleteDocument31 pagesCH 7 Cellular Respiration CompleteWilly WonkaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Questions and Answers - Overview of DNA RepairDocument4 pagesMolecular Biology Questions and Answers - Overview of DNA Repairmwesige ronaldNo ratings yet
- Vitamins A, D, E, KDocument28 pagesVitamins A, D, E, KDavid Jasher AbadNo ratings yet
- Provisional List of Firms Issued Form 7 ImportedDocument142 pagesProvisional List of Firms Issued Form 7 ImportedMuhammad Irfan100% (1)
- Biochemistry - WikipediaDocument1 pageBiochemistry - WikipediaBadhon Chandra SarkarNo ratings yet
- DNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonDocument6 pagesDNA vs. RNA 5 Key Differences and ComparisonRomalyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Functions: ImmunologyDocument40 pagesAntibody Structure and Functions: ImmunologyMoody Maxi KhanNo ratings yet
- DNA NotesDocument12 pagesDNA NotesSeekerNo ratings yet
- Primescript™ Reverse Transcriptase: Code No. 2680Q Size: 2,000 Units Shipping at 20 Store at 20Document2 pagesPrimescript™ Reverse Transcriptase: Code No. 2680Q Size: 2,000 Units Shipping at 20 Store at 20Isaac Nicholas NotorioNo ratings yet
- Lac Operon - Definition, Structure, Inducers, DiagramDocument14 pagesLac Operon - Definition, Structure, Inducers, DiagramGayathri deviNo ratings yet
- The Requirements of Mannose Binding LectinDocument2 pagesThe Requirements of Mannose Binding LectinNurul NadiaNo ratings yet
- PCR Lab ProtocolDocument5 pagesPCR Lab Protocolhk8atema1lNo ratings yet
- Dietary Reference Intakes For Vitamins - NCBI BookshelfDocument2 pagesDietary Reference Intakes For Vitamins - NCBI Bookshelfmuthu kumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Inorganic Chemistry Part 3 Bioinorganic ChemistryDocument44 pagesBasic Inorganic Chemistry Part 3 Bioinorganic ChemistryGuru P MNo ratings yet
- BIOC 315 - Lecture - 1Document28 pagesBIOC 315 - Lecture - 1Kevin KipropNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of LipidsDocument11 pagesNomenclature of LipidsJaella ANo ratings yet
- Code Item Code / Pack Intended Use: NX 500 Reagents CodesDocument2 pagesCode Item Code / Pack Intended Use: NX 500 Reagents CodesBrijeshNo ratings yet
- Understanding Enzymes and Their Role in Biological SystemsDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Enzymes and Their Role in Biological SystemsCassy Joy Rellama100% (1)
- Respiration in PlantsDocument34 pagesRespiration in PlantsPukazhvanthen ParamanandhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unsolved Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unsolved Important QuestionsDeep Kumar BasakNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument13 pagesCarbohydratesAustin LaurenNo ratings yet
- Enzymes used in Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument43 pagesEnzymes used in Recombinant DNA TechnologyYuppie RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Enzymes and VitaminsDocument65 pagesChapter 20 Enzymes and Vitaminsbevzie datuNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I (SGS 236)Document25 pagesBiochemistry I (SGS 236)Mustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- G S RajuDocument1 pageG S RajuAir DropNo ratings yet