Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Site Calibration
Uploaded by
EngMustafe BashirCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Site Calibration
Uploaded by
EngMustafe BashirCopyright:
Available Formats
Site Calibration
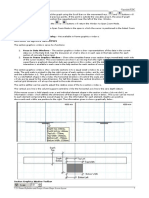
Cube-a offers the ability to localize, i.e., convert outbound coordinates from the GNSS receiver, into
an unconventional reference system. The screen for this feature is shown in Figure. At the top are the
points that will be used to calculate localization, the points can be added to the table by pressing
the "Add" command at the bottom. The screen to add is the one shown in Figure. Here you can enter
the known (local) coordinates, on which you want to locate, these can be entered by hand or by
selecting a point in memory with the selection commands. The conversion's target coordinates
are below and can be collected from the current GNSS location or selected from a point in
memory. The options below the coordinates provide the ability to enable planimetric and/or
planimetric localization.
The localization points you add can be changed with the "Edit" command, under Figure, at the
bottom.
Stonex Software Cube-a 5.1 – User Manual 112
Added the point (or points) for localization, you can perform the conversion. There are three methods
of converting coordinates: Inclined plane + Delta dimension (Rotostralation), 7 parameters +
Inclined plane + Delta dimension, 7 parameters, click the "Options" command in Figure, to access
the reference screen in Figure.
Stonex Software Cube-a 5.1 – User Manual 113
In the figure above, you can set one of the expected conversion methods. In case of 7-parameter
conversion calculation, you can set the Helmert or Bursa-Wolf model, for the management of the
sign of the rototranslations parameters. For the 4-parameter model, you can set up a barycentric or
non-barycentric rototranslation. And finally, you can set the quota control and a horizontal and
vertical accuracy limit. By clicking the "Save" command at the bottom, the options will be saved for
calculation.
Below is a brief description of the calculation methods 4 parameters and 7 parameters.
4 parameters: At least two cornerstones related to an arbitrary coordinate system must be known.
It is the coordinate transformation mode used to perform a conversion between different coordinate
systems within the same ellipsoid. Parameters include four values (north translation, east translation,
rotation, and scale), the scale must be infinitely close to 1.
In general, the distribution of control points directly determines the dimension difference and the
four parameters to be controlled. The use of four parameters for the RTK measurement method, can
be used in a reduced area (20-30 square kilometers).
Measure a point in flat coordinates and operate in the precision of a control network with dimensions
of known points. The more known points you will have, the higher the accuracy (2 or more than 2).
But in a very large point distribution (e.g. tens of kilometers), the 4 transformation parameters often
do not help, in this case to have an increase in precision both in the planimetric coordinates and on
the altitude should use the 7-parameter transformation.
First, you need to perform a static survey in the area where the cornerstones are present, and then
select a cornerstone A as a static reference station (in WGS84), which will be used to correct the point
network. Use a static receiver to measure a single fixed point for more than 24 hours (this step, in
test zones you can perform in less time and in case of low precision required this step can also be
omitted) and then import into the software, as a single point all the captured data, the average of
the readings will be the actual coordinates of point A in WGS84 coordinates. Absolute accuracy
should be below 2 meters, so regarding adjusting the three-dimensional control network, you need
to take point A WGS84 as the cornerstone to calculate the 3D coordinates of other points.
Stonex Software Cube-a 5.1 – User Manual 11
You might also like
- Histogram Equalization: Enhancing Image Contrast for Enhanced Visual PerceptionFrom EverandHistogram Equalization: Enhancing Image Contrast for Enhanced Visual PerceptionNo ratings yet
- Calibrate GNSS PointDocument2 pagesCalibrate GNSS PointEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- COGO+ v4 Chapter6Document13 pagesCOGO+ v4 Chapter6bedoed2140No ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document26 pagesChapter 14andi_ml_bdgNo ratings yet
- Projection and Transformation CalculationsDocument38 pagesProjection and Transformation Calculationsnevadamike_001No ratings yet
- Visual 2012 Help - Chapter08Document38 pagesVisual 2012 Help - Chapter08sasi taranNo ratings yet
- HEC-RAS Mapper User's Manual-Páginas-101-149Document49 pagesHEC-RAS Mapper User's Manual-Páginas-101-149David Flores ChoqueNo ratings yet
- Winalc: Plasser TheurerDocument35 pagesWinalc: Plasser TheurerSuciu Florin100% (5)
- Projection and Transformation CalculationsDocument37 pagesProjection and Transformation CalculationsMuhammad Junaid100% (1)
- Combined Height/Lining Laser: Operating ManualDocument16 pagesCombined Height/Lining Laser: Operating ManualAlanNo ratings yet
- Hi-RTK Road Operation ManualDocument134 pagesHi-RTK Road Operation ManualUna DouaNo ratings yet
- Kongsberg Simrad Transducer Alignment: A New Tool for "HPR CalibrationDocument4 pagesKongsberg Simrad Transducer Alignment: A New Tool for "HPR CalibrationAdi VNo ratings yet
- Filtered Image (Fir) : Vol 2, No 3 (July 2011) ©ijoat 408Document24 pagesFiltered Image (Fir) : Vol 2, No 3 (July 2011) ©ijoat 408Rõßhîñî GõßûNo ratings yet
- Lab9 Lcs 26052023 101701amDocument10 pagesLab9 Lcs 26052023 101701amMaryam anjumNo ratings yet
- Seismic Interpretation ParadigmDocument5 pagesSeismic Interpretation Paradigmsantosmonetta2No ratings yet
- Programa Dips RocscienceDocument40 pagesPrograma Dips RocscienceDanielLozada100% (1)
- Time Domain Back Projection Algorithms For SARDocument4 pagesTime Domain Back Projection Algorithms For SARnaivedya_mishraNo ratings yet
- Geo-referencing steps and importance of RMSEDocument7 pagesGeo-referencing steps and importance of RMSENIKHIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- $RJK9VX1Document10 pages$RJK9VX1Qaisar KhanNo ratings yet
- Combining Local Survey Data With Geodetic World: Presented by Andrej MocickaDocument33 pagesCombining Local Survey Data With Geodetic World: Presented by Andrej MocickaNT SpatialNo ratings yet
- Advanced Adjustment ConceptsDocument17 pagesAdvanced Adjustment ConceptsAntonio JelacicNo ratings yet
- TRIMBLE ACCESS SETTOP LEVEL MEDocument2 pagesTRIMBLE ACCESS SETTOP LEVEL MEツ ツNo ratings yet
- Topography and Geodesy Module: Digital Terrain Model - V7.5Document5 pagesTopography and Geodesy Module: Digital Terrain Model - V7.5GerardinNo ratings yet
- Rapt 14Document16 pagesRapt 14tailieuxaydung2019No ratings yet
- GIS GeoReferencingDocument29 pagesGIS GeoReferencingNawanjana Maheepala100% (1)
- RoadCalc PDFDocument13 pagesRoadCalc PDFMohsinKhanNo ratings yet
- Motor FlowDocument14 pagesMotor FlowAbenav SankarNo ratings yet
- Create A New Local Coordinate System With Affine TransformationDocument12 pagesCreate A New Local Coordinate System With Affine TransformationCatarina Baptista GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- KRONOS baseline processingDocument11 pagesKRONOS baseline processingFaris MusyaffaNo ratings yet
- Optimize 5-Axis Machining Function TitleDocument51 pagesOptimize 5-Axis Machining Function TitleAnonymous PJP78mSx33% (3)
- Experiment 3 Contracer - Contour Measureing Machine: Mechatronic Engineering Advanced ProgramDocument10 pagesExperiment 3 Contracer - Contour Measureing Machine: Mechatronic Engineering Advanced ProgramCao KhảiNo ratings yet
- SurveyNoteReduction05Feb14 PIADocument35 pagesSurveyNoteReduction05Feb14 PIALimuel Richa Paghubasan TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Adjustment ConceptsDocument18 pagesAdvanced Adjustment ConceptsAlihuertANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Control SurveyDocument33 pagesChapter 6 Control SurveyGemechis BachaNo ratings yet
- HPLC Peak Integration For ChromatographyDocument45 pagesHPLC Peak Integration For ChromatographyLiu HànNo ratings yet
- Pid Loop ShapingDocument7 pagesPid Loop ShapingCAFECHINONo ratings yet
- Rapt 12Document16 pagesRapt 12tailieuxaydung2019No ratings yet
- Calibration (Georeferencing) of Maps and OrthophotosDocument8 pagesCalibration (Georeferencing) of Maps and OrthophotosNadia reggamiNo ratings yet
- BLI ManualDocument7 pagesBLI ManualKURTNo ratings yet
- Campbell Diagram Chart ResultsDocument4 pagesCampbell Diagram Chart ResultsParag NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Superelevation: Superelevating The Roadway Using Rule-Based SuperelevationDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Superelevation: Superelevating The Roadway Using Rule-Based SuperelevationBalachanter RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Two Dimensional Viewing Viewing PipelineDocument8 pagesUnit - 4 Two Dimensional Viewing Viewing PipelineprincejiNo ratings yet
- Elevation Topographic Mapping RTK GPS SOPDocument3 pagesElevation Topographic Mapping RTK GPS SOPMero GraceNo ratings yet
- Azimuth Elevation PolarizationDocument31 pagesAzimuth Elevation PolarizationtunisianouNo ratings yet
- C !" !! !#$"%&'!$ (#) ( (C !" !!!#$"%+&+'!$ +!%PMDocument8 pagesC !" !! !#$"%&'!$ (#) ( (C !" !!!#$"%+&+'!$ +!%PMing_nistorNo ratings yet
- In CST To Choose A Point That Lies in The Center Between Two PointsDocument10 pagesIn CST To Choose A Point That Lies in The Center Between Two PointsAlfredo DezoNo ratings yet
- Training Materials - Adjustments Advanced Network AdjustmentDocument19 pagesTraining Materials - Adjustments Advanced Network AdjustmentLuis Fernando Jimenez RiojaNo ratings yet
- Tube and Pipe Inventor PDFDocument15 pagesTube and Pipe Inventor PDFLucky ChinnaNo ratings yet
- Steering Assist For An Agricultural Sprayer: MechatronicsDocument7 pagesSteering Assist For An Agricultural Sprayer: MechatronicsJarod RayNo ratings yet
- QRG 22 Coordinate TransformationsDocument7 pagesQRG 22 Coordinate TransformationsariyarathneNo ratings yet
- Application Note #3416: A Brief Overview of Coordinate TransformationDocument12 pagesApplication Note #3416: A Brief Overview of Coordinate TransformationKavya M BhatNo ratings yet
- Ground Control For Photogrammetric MappingDocument10 pagesGround Control For Photogrammetric MappingPambudiSusilaNo ratings yet
- Guide to realigning railway curves using a computer programDocument15 pagesGuide to realigning railway curves using a computer programvpmohammedNo ratings yet
- Geospatial Modeling Environment and Data AssemblyDocument31 pagesGeospatial Modeling Environment and Data AssemblyMas Inoenk Nurdin SulistiyonoNo ratings yet
- TPS1200 Quick SetupDocument50 pagesTPS1200 Quick SetupbrutalcutieNo ratings yet
- Total StationDocument12 pagesTotal StationLic Torres JimenezNo ratings yet
- Creating A Variogram From Porosity Well Log Data in SKUA-GOCADDocument2 pagesCreating A Variogram From Porosity Well Log Data in SKUA-GOCADBouregaNo ratings yet
- Setting Up Cruise Lines With The Basic Yellow Etrex 8-27-06Document1 pageSetting Up Cruise Lines With The Basic Yellow Etrex 8-27-06runnealsNo ratings yet
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Differential GPSDocument10 pagesDifferential GPSEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- DGPS Performance Analysis of Aircraft SystemsDocument2 pagesDGPS Performance Analysis of Aircraft SystemsEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- The Research and TechnologyDocument2 pagesThe Research and TechnologyEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument2 pagesExecutive SummaryEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- AGARDograph Series 160 and 300Document1 pageAGARDograph Series 160 and 300EngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- Point Stake OutDocument4 pagesPoint Stake OutEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- Enable GIS Mapping in Cube-a ProjectsDocument3 pagesEnable GIS Mapping in Cube-a ProjectsEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- Project ManagerDocument2 pagesProject ManagerEngMustafe BashirNo ratings yet
- Local and Global TechnopreneursDocument25 pagesLocal and Global TechnopreneursClaire FloresNo ratings yet
- Singapore ItineraryDocument4 pagesSingapore ItineraryAleah LS KimNo ratings yet
- Complex Analysis, Gamelin, II.5 Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesComplex Analysis, Gamelin, II.5 Problems and SolutionsC. Ephrem StuyvesantNo ratings yet
- Basic Control Valve and Sizing and SelectionDocument38 pagesBasic Control Valve and Sizing and SelectionNguyen Anh Tung50% (2)
- HPSC Haryana Civil Service Judicial ExamDocument6 pagesHPSC Haryana Civil Service Judicial ExamNDTV100% (1)
- My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic #14 PreviewDocument10 pagesMy Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic #14 PreviewGraphic Policy100% (3)
- E-Government in Developing Countries: Experiences From Sub-Saharan AfricaDocument11 pagesE-Government in Developing Countries: Experiences From Sub-Saharan AfricaMashael AzizNo ratings yet
- Home ImplementationDocument7 pagesHome ImplementationiceyrosesNo ratings yet
- IAM, How Asset Management Can Enable The Circular EconomyDocument18 pagesIAM, How Asset Management Can Enable The Circular EconomyCarlos Jose Sibaja CardozoNo ratings yet
- Quality Hospital Billing and Prioritizing ProjectsDocument7 pagesQuality Hospital Billing and Prioritizing ProjectsCamille Abraham70% (27)
- Working Capital ManagmentDocument7 pagesWorking Capital ManagmentMarie ElliottNo ratings yet
- 5 Schedule Timetable FLIFODocument8 pages5 Schedule Timetable FLIFOAlba FernándezNo ratings yet
- Harmonization and Standardization of The ASEAN Medical IndustryDocument75 pagesHarmonization and Standardization of The ASEAN Medical IndustryGanch AguasNo ratings yet
- Notes On Cash BudgetDocument26 pagesNotes On Cash BudgetJoshua P.No ratings yet
- STD 2 ComputerDocument12 pagesSTD 2 ComputertayyabaNo ratings yet
- Customer Guide Electrical Service Information FormDocument2 pagesCustomer Guide Electrical Service Information FormRyder BergerudNo ratings yet
- GEC 6 Lesson 12Document19 pagesGEC 6 Lesson 12Annie CabugNo ratings yet
- Tata-Aig General Insurance Company LTD: Policy No. 0238443404 / 0238443469 Claim No.Document3 pagesTata-Aig General Insurance Company LTD: Policy No. 0238443404 / 0238443469 Claim No.Mahendra SinghNo ratings yet
- How To Install Elastix On Cloud or VPS EnviornmentDocument4 pagesHow To Install Elastix On Cloud or VPS EnviornmentSammy DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Why Coolant Plays a Critical Role in Engine LongevityDocument57 pagesWhy Coolant Plays a Critical Role in Engine LongevityPETER ADAMNo ratings yet
- The Stock Market For Dummies PDFDocument2 pagesThe Stock Market For Dummies PDFJoe D100% (1)
- History of US Medical Device RegulationDocument7 pagesHistory of US Medical Device RegulationHector Tinoco GarciaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker GalilioDocument34 pagesCircuit Breaker GalilioMoaz KhursheedNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.3 Practice TestDocument16 pagesUnit 1.3 Practice TestYoann DanionNo ratings yet
- W.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueDocument2 pagesW.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueParth PatelNo ratings yet
- Elsie Kundai Mapeto Final DraftDocument74 pagesElsie Kundai Mapeto Final DraftAnonymous yEPScmhs2qNo ratings yet
- ml350p g8.Document57 pagesml350p g8.Aboubacar N'dji CoulibalyNo ratings yet
- Bibicoff Ic Resume 2022 09 For WebsiteDocument3 pagesBibicoff Ic Resume 2022 09 For Websiteapi-633250343No ratings yet
- Final E-Portfolio AssignmentDocument7 pagesFinal E-Portfolio Assignmentapi-302594281No ratings yet
- Sale of Goods .Document24 pagesSale of Goods .Goodman supremacyNo ratings yet